APPLICATION OF POST-STACK HYDROCARBON DETECTION TECHNOLOGY BASED ON MATCHING PURSUIT ALGORITHM TO QHD33/34 STRUCTURE, BOHAI BAY BASIN
-
摘要:
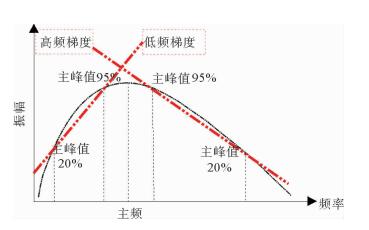
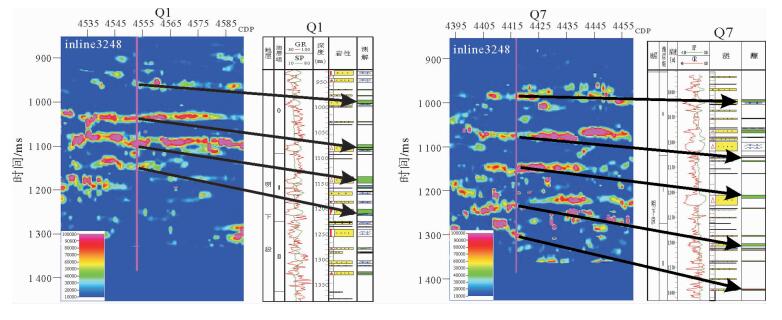
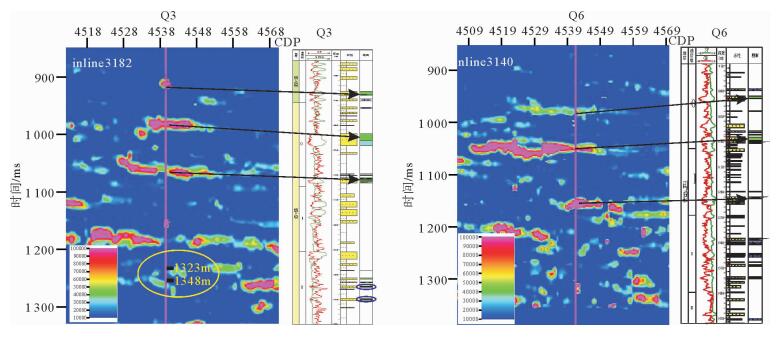
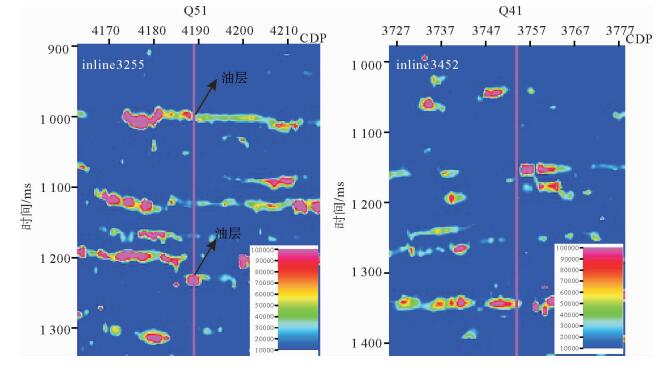
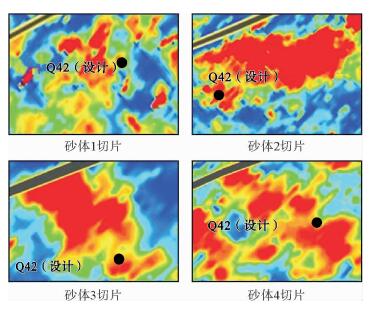
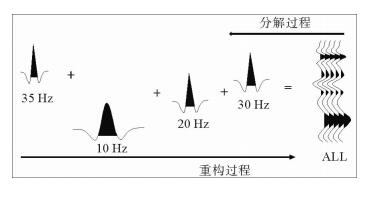
渤海中北部海域的QHD33/34构造位于石臼坨凸起中段及中段东南部斜坡带上。受新构造运动影响,石臼坨凸起浅层发育一系列NE向、近EW向晚期活动断层,在斜坡带浅层明化镇组形成了多个断鼻、断块型圈闭,但是构造圈闭面积总体较小、幅度低,并且受断层对油气疏导作用影响,油气成藏有一定的风险。为揭示QHD33/34构造浅层储层的含油气性,应用基于匹配追踪算法的低频增加梯度异常对该区进行烃类检测,取得了一定效果。最终烃检结果与已钻井揭示的构造浅层储层含油气性较匹配,吻合率达到79%,应用烃检结果可进一步指导该构造井位部署,尽最大可能规避风险。通过研究表明,在研究区浅层,基于匹配追踪算法的低频增加梯度异常能够最大程度上识别油层与水层。该方法能够识别大于3 m的油层,水层则没有明显响应特征,应用该方法进行烃类检测,效果明显。
Abstract:The structure of QHD33/34 is located on the middle and southeastern middle slope of the Shijiutuo Uplift. Affected by neo-tectonic movement, there are a series of NE and EW active faults in the shallow part of the Shijiutuo Uplift, and a number of fault-nose and fault-block traps have been found in the Minghuazhen Formation at the shallow zone of the slope belt. However, the structural traps are generally small in scale and low in amplitude. Migration and accumulation of oil and gas are easy to be affected by the faults. In order to reveal the oil-gas-bearing possibility of shallow reservoir in the structure QHD33/34, the method of low-frequency gradient anomaly based on the matching pursuit algorithm is used to detect the hydrocarbons in this area. The agreement rate between the final result of hydrocarbon detection and oil-gas-bearing possibility of shallow reservoir may be as high as 79%. The results suggest that the method is effective to the identification of both the oil reservoir and water layer to the greatest extent and useful for well location placement in the shallow part of the structure, and helpful to avoid risks as much as possible. Using this method we may identify the oil reservoir thicker than 3 meters, but response to water layer is not clear.
-
Key words:
- Shijiutuo Uplift /
- matching pursuit /
- hydrocarbon detection /
- frequency attenuation gradient /
- Bohai Bay
-

-
表 1 烃检结果吻合率统计
Table 1. The statistics of the agreement rate of hydrocarbon detection results
井名 实钻油层厚度≥3m的砂体 烃检含油气砂体 吻合率 平均吻合率 Q7 7 5 71% 79% Q1 5 4 80% Q3 4 3 75% Q6 4 3 75% Q51 3 4 75% Q41 0 0 100% -
[1] 苑书金, 高君.应用AVO和DHI技术检测安哥拉深水域油气[J].石油地球物理勘探, 2012(物探技术研讨会专刊):373-376. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8141646
[2] 韩强.塔里木盆地轮台地区低幅度构造圈闭落实技术及其应用[J].石油与天然气地质, 2010, 31(1):43-48. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz201001007
[3] 刘继承, 富爽.基于MP算法的快速地震信号谱分析[J].计算机技术与发展, 2010, 20(7):231-239. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-629X.2010.07.059
[4] 石战战, 庞溯, 唐湘蓉, 等.基于匹配追踪算法的碳酸盐岩储层低频伴影识别方法研究[J].岩性油气藏, 2014, 26(3):114-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2014.03.019
[5] 张固澜.地震波吸收特性及应用研究[D].成都: 成都理工大学, 2008.
[6] 张固澜.基于改进的广义S变换的低频吸收衰减梯度检测[J].地球物理学报, 2011, 54(9):2407-2411. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.09.024
[7] 滕团余, 潘建国, 谭开俊.频率衰减梯度属性在油气检测中的应用[J].石油地球物理勘探, 2012(物探技术研讨会专刊):126-128. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8141705
[8] 王德英, 于海波, 李龙, 等.渤海海域石臼坨凸起新近系岩性油气藏充满度特征及主控因素[J].油气地质与采收率, 2015, 22(5):21-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2015.05.004
[9] 杨璐, 贺振华, 文晓涛, 等.频率衰减属性在深层碳酸盐岩油气勘探中的应用[J].岩性油气藏, 2012, 24(5):98-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2012.05.020
[10] 必研斌, 龙胜祥, 郭彤楼, 等.应用频率衰减属性预测TNB地区储层含气性[J].石油与天然气地质, 2007, 28(1):116-120. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2007.01.017
[11] 张猛刚, 洪忠, 窦玉坛, 等.时频分析在苏里格地区含气性检测中的应用[J].岩性油气藏, 2013, 25(5):76-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2013.05.013
[12] 李才, 吕丁友, 马佳国, 等.叠后烃检方法在渤海海域PL稠油区块的应用[J].海洋石油, 2014, 34(2):37-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2014.02.037
[13] 李宏伟, 王九拴, 邵林海, 等.油气检测技术在三湖浅层生物气勘探中的应用[J].石油地球物理勘探, 2013, 48(5):770-775. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sydqwlkt201305015
-



 下载:
下载: