DENSIFICATION TIMING OF RESERVOIR AND ITS BEARINGON HYDROCARBON ACCUMULATION IN THE HUAGANG
-
摘要:
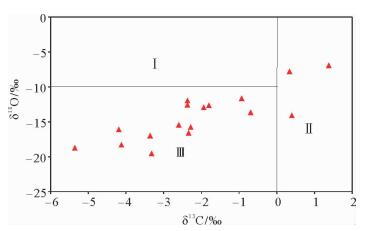
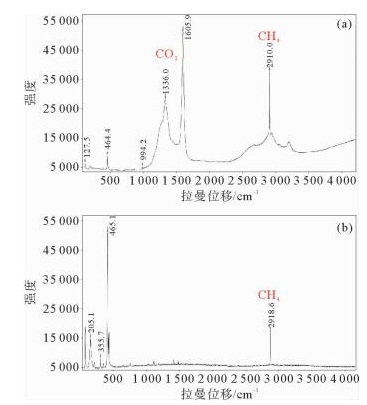
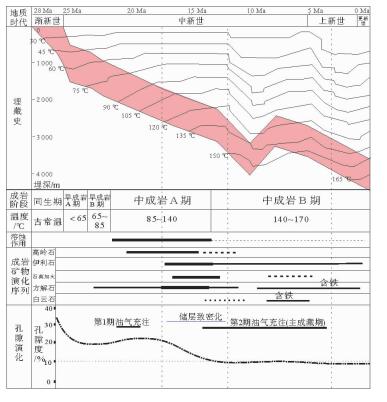
西湖凹陷花港组储层在埋深3 500 m以下的深层普遍致密化且含气饱和度低。利用铸体薄片、扫描电镜、碳氧同位素、激光拉曼和流体包裹体等资料,探讨储层致密化过程及其与油气成藏的关系。结果表明,强烈压实作用是原生孔隙大量损失的主要原因,自生石英、碳酸盐及伊利石胶结是储层致密的关键因素。根据胶结矿物形成时间推算储层致密化发生在中成岩阶段A期末,对应距今约17~13 Ma的中新世中后期。由储层致密化过程与成藏期次匹配关系分析认为,花港组初次成藏期发生在中成岩阶段A期早期,储层尚未致密,但油气充注时间短且强度弱,不能大面积成藏,主成藏期发生在中成岩阶段A期末至中成岩阶段B期,成藏时间对应大致距今15~5 Ma的中新世晚期,但由于储层普遍致密化,油气充注程度低。花港组深层储层“先致密后成藏”是造成含气饱和度普遍较低的重要原因。
Abstract:The deep-buried sandstone reservoirs of the Huagang Formation in the Xihu Sag, which usually occur 3 500 m below sea bottom, are quite dense and low in gas saturation. The process of reservoir densification and its bearing on hydrocarbon accumulation are discussed in this paper based on the data from cast sections, SEM, C-O isotopes, laser roman spectrum and fluid inclusions. The results indicate that strong compaction is the main reason for primary porosity loss and cementations by authigenic quartz, carbonates and illites are the key factors to reservoir densification. According to the time scale of cementation, reservoir densification occurred mainly in the stage A of the middle phase of digenesis in Middle and Late Miocene about 17~13 Ma. Study of timing of reservoir densification and hydrocarbon accumulation suggests that primary hydrocarbon accumulation mainly occurred before the early stage A of the middle digenesis phase, when the reservoir has not yet densified. Owing to the low hydrocarbon accumulation rate and short accumulation time; the reservoir could not fully infilled. The majority of hydrocarbon accumulation occurred in the late stage A of the middle digenesis phase up to the stage B of the middle digenesis phase, about 15~5 Ma before present in late Miocene, when reservoir became densified. As the result, the reservoir of Huagang Formation is low in gas saturation since hydrocarbon is difficult to charge the reservoir completely. Reservoir densification before hydrocarbon accumulation is the main reason for low gas saturation.
-

-
表 1 西湖凹陷花港组致密储层X衍射黏土矿物分析
Table 1. Clay mineralogy by X-ray analysis for tight sandstone reservoir of Huagang Formation in Xihu Sag
井号 深度/m 蒙脱石含量/% I/S/% I/% K/% C/% H2-1 3 932~3 983 ≤15 38.4 27.4 4.2 30 H1-3 3 958~3 968 ≤15 30.7 27.8 4.0 37.5 HY1-3 4 183~4 196 ≤15 41.7 43.2 1.6 13.5 N31-1 4 320~4 338 ≤15 31.9 33.5 3.7 30.9 N31-2 4 183~4 200 ≤15 43.5 41.3 1.7 13.5 表 2 花港组致密砂岩储层自生石英流体包裹体特征
Table 2. Characteristics of fluid inclusion in authigenic quartz of tight sandstone reservoir of Huagang Formation in Xihu Sag
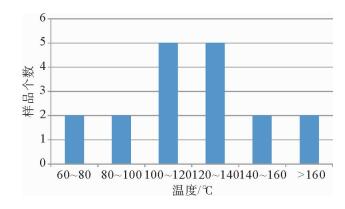
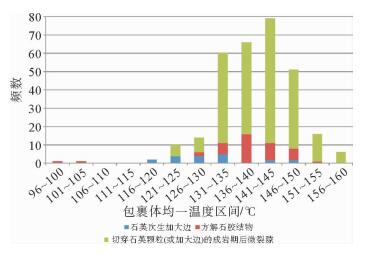
井号 深度/m 赋存矿物 气液比/% 大小/μm 均一温度/℃ H1-2 3 541 石英加大边 <10 4~10 133.5~142.5 H1-2 3 526.4 石英加大边 <10 4~13 128.7~140.3 H2-1 3 940 石英加大边 <10 4~10 128.8~140.2 H2-1 3 932.9 石英加大边 <10 4~8 125.2~137.1 N7-1 3 852 石英加大边 <10 4~9 120.4~140.5 N7-1 4 307 石英加大边 <10 5~18 125.4~144.6 -
[1] 谷江锐, 刘岩.国外致密砂岩气藏储层研究现状和发展趋势[J].国外油田工程, 2009, 25(7):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-641X.2009.07.001
[2] 关德师, 牛嘉玉.中国非常规油气地质[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 1995:60-85.
[3] 姜振学, 林世国, 庞雄奇, 等.两种类型致密砂岩气藏对比[J].石油实验地质, 2006, 28(3):210-219. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2006.03.003
[4] 张哨楠.致密天然气砂岩储层:成因和讨论[J].石油与天然气地质, 2008, 29(1):1-10. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2008.01.001
[5] 张建培, 徐发, 钟韬, 等.东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖组—花港组层序地层模式及沉积演化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(1):35-41.
[6] 张银国.东海西湖凹陷花港组油气地质条件与油气分布规律[J].石油实验地质, 2010, 32(3):223-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2010.03.004
[7] 刘金水, 曹冰, 徐志星, 等.西湖凹陷某构造花港组沉积相及致密砂岩储层特征[J].成都理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 39(2):130-136. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cdlgxyxb201202003
[8] 徐艳霞, 胡明毅, 梁建设, 等.东海盆地西湖凹陷渐新统花港组物源分析[J].石油天然气学报, 2010, 32(5):176-179. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=35692181
[9] 陈琳琳, 谢月芳.东海西湖凹陷花港组沉积模式初探[J].海洋石油, 1998, 98(4):15-21. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800271827
[10] 王果寿, 周卓明.西湖凹陷春晓区带下第三系平湖组、花港组沉积特征[J].石油与天然气地质, 2002, 23(3):257-265. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2002.03.012
[11] 胡明毅, 柯岭, 梁建设, 等.西湖凹陷花港组沉积相特征及相模式[J].石油天然气学报, 2010, 32(5):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2010.05.001
[12] Pittman E D, Larese R E.Compaction of lithic sand: experimental results and application[J]. AAPG, 1991, 75: 1279-1299. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/236542974_Compaction_of_lithic_sands_Experimental_results_and_applications
[13] 张哨楠.四川盆地西部须家河组砂岩储层成岩作用及致密时间讨论[J].矿物岩石, 2009, 29(4):33-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2009.04.005
[14] Irwin H, Curtis C, Coleman M L. Isotopic evidence for source of diagenetic carbonates for med during burial of organic-rich sediments[J]. Nature, 1977, 269(7) : 209-213. http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v269/n5625/abs/269209a0.html
[15] Hutcheon I, Abercrombie H J, Putnam P E, et al. Diagenesis and sedimentology of the Glearwater Formation at Tucker Lake[J]. Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, 1989, 37(1): 83-97. http://bcpg.geoscienceworld.org/content/37/1/83
[16] Keith M L, Weber J N.Carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of selected limestones and fossils[J].Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 1964, 28(10): 1786-1816.
[17] 陈丽华, 姜在兴.储层实验测试技术[M].东营:石油大学出版社, 1994:161-162.
[18] 梁建设, 王琪, 郝乐伟, 等.西湖凹陷渐新统花港组储层砂岩成岩环境演化探讨[J].天然气地质学, 2012, 23(4):673-680. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201204008
[19] Chuhan F A, Bjrlykke K, Lowrey C.The role of provenance in illitization of deeply buried reservoir sand stones from Haltenbanken and north Viking Graben, off shore Norway [J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2000, 17(6):673-689. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(00)00014-3
[20] 黄思静, 孙伟, 黄培培, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地东部太原组碎屑岩中自生伊利石形成机制及其对储层形成的影响[J].矿物岩石, 2009, 29(4):25-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2009.04.004
-



 下载:
下载: