DISTRIBUTION, MORPHOLOGY AND CHRONOLOGY OF THE AEOLIAN CALCARENITES IN SOUTHWESTERN AUSTRALIA
-
摘要:
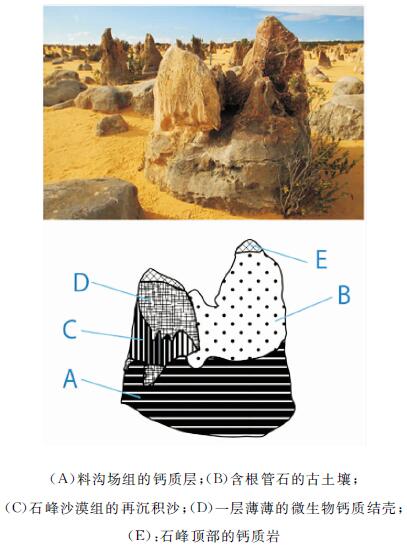
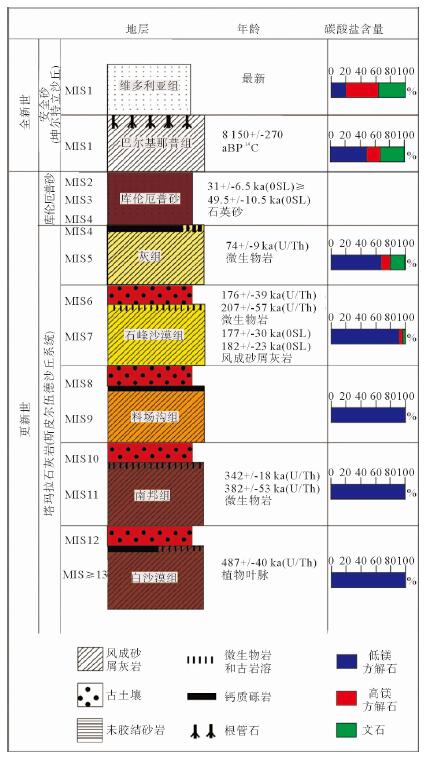
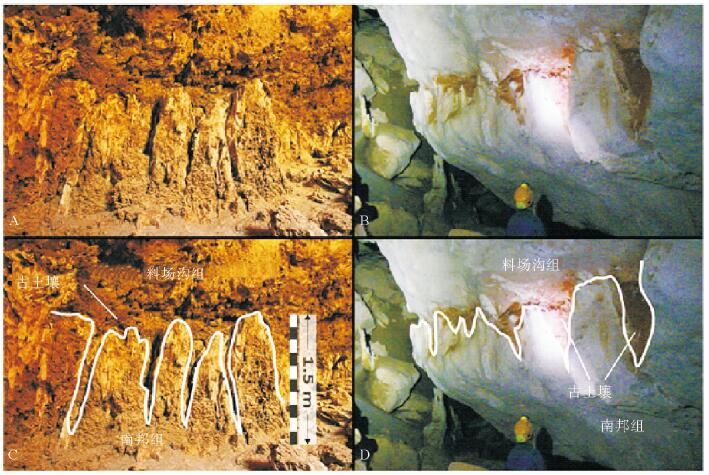
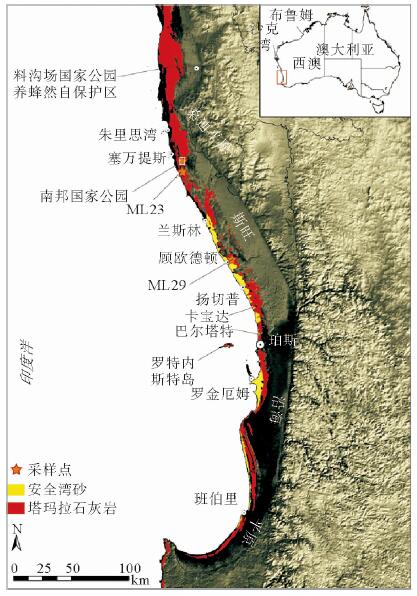
在澳大利亚西南沿海,特别是在南邦(Nambung)国家公园,成千上万个高达5 m、宽2 m、相距0.5 m的锥形风成砂屑灰岩组成壮观的喀斯特地貌,为形成于更新世含钙质/微生物的古土壤沉积物。锥形风成砂屑灰岩的形态多种多样,可以随岩性不同而变化,构成锥形风成沉积岩和圆柱形微生物岩。在南邦,锥形风成砂屑灰岩大量溶解,最后形成大量石英碎屑,石英碎屑经再沉积掩埋再形成这些锥状风成砂屑灰岩,属于风成岩溶作用,发生在70 ka前;340~380 ka间风成砂屑灰岩发育要弱。
Abstract:A spectacular landform of pinnacle karst occurs in the southwestern coast of Western Australia. It consists of thousands of pinnacles up to 5 m high, and 2 m wide and only 0.5-5 m apart, particularly well exposed in the Nambung National Park. The pinnacles are formed in the Pleistocene Tamala Limestone, which comprises of cyclic sequences of aeolian calcarenite, calcrete, microbialite and palaeosol. The morphology of the pinnacles varies with the lithology in which they are formed, for examples, typically conical in aeolianite and cylindrical in microbialite. However, the Nambung pinnacles is mainly influenced by joints and fractures. The extensive dissolution associated with pinnacle formation at Nambung resulted in a large amount of insoluble quartz residues, which are redeposited and even bury the pinnacles sometimes. This period of karstification occurred at around 70, 000 years before present, and there was an earlier but weaker stage of pinnacle development during the period 34-38 million years ago.
-
Key words:
- aeoliancalcarenites /
- dune /
- pinnacle /
- aeolian kanstification /
- Southwestern Australia
-

-
[1] Playford P E, Cockbain A E, Low G H, et al. Geology of the Perth Basin Western Australia[J]. Geology Survey Western Austria Bulletin, 1976, 124:311-336. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=cdec7c56f2280e3e5033cfa2e5c0671d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[2] Mory A. Geology of the Wedge Island 1: 100.000 sheet[R]. Perth, Geological Survey of Western Australia, 1995: 19-31.
[3] Gozzard J R. Geology and landforms of the Perth region[J]. Western Australia Geological Survey, 2007: 126-139. https://trove.nla.gov.au/work/26982314?selectedversion=NBD41360043
[4] Jennings J N, Mabbutt J A, et al. Physiographic outlines and regions[C]//Jeans D M. Australia A Geography. University of Sydney Press, Sydney, 1977, 38-52.
[5] Pain C, Gregory L, Wilson P, et al. The Physiographic Regions of Australia: Explanatory Notes[R]. Australian Collaborative Land Evaluation Program and National Committee on Soil and Terrain, 2011: 1-30.
[6] Jenkin J J, et al. Evolution of the Australian coast and continental margin[C]//Coastal Geomorphology in Australia Academic Press, 1984: 23-42.
[7] CadmanS J, Pain L, Vuclovic V, et al. Perth Basin, WA. Australian Petroleum Accumulations Report 10[R]. Bureau of Resources Sciences, Canberra, 1994: 103-132.
[8] Playford P E, Low G H, et al. Definitions of some new and revised rock units in the Perth Basin[R]. Western Australia Geological Survey, Annual Report, 1971: 44-46.
[9] Johnstone D, Playford P E, et al. Geology of the Shark Bay-Murchison River-Geraldton area, Carnarvon Basin[R]. Private report to West Australian Petroleum Pty Ltd, unpublished, 1955.
[10] Playford P E, Cockbain A E, et al. The geology of Shark Bay[J]. Geology Survey Western Austria Bulletin, 2013: 146-281. http://museum.wa.gov.au/whats-on/geology-shark-bay
[11] Passmore J R, et al. Shallow coastal aquifers in the Rockingham District, Western Australia[J]. Water Research Found Austria Bulletin, 1970, 18: 83-96. https://trove.nla.gov.au/work/17346085
[12] Semeniuk V, Cresswell I, Wurm P. The Quindalup Dunes: the regional system, physical framework and vegetation habitats[J]. Journal of the Royal Society of Western Australia, 1989, 71(2):23-47. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=09612f6104c8a5bc3b1284c8110d6ecd&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[13] Lipar M, Webb J A. Middlealate Pleistocene and Holocene chronostratigraphy and climate history of the Tamala Limestone, Cooloongup and Safety Bay Sands, Nambung National Park, southwestern Western Australia[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of Australia, 2014, 61(8):1023-1039. doi: 10.1080/08120099.2014.966322
-



 下载:
下载: