HYDROCARBON ACCUMULATION IN SOUTH LOKICHAR BASIN, EASTERN BRANCH OF EAST AFRICAN RIFT SYSTEM
-
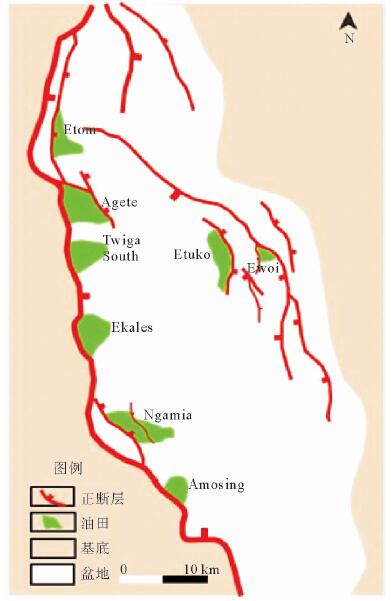
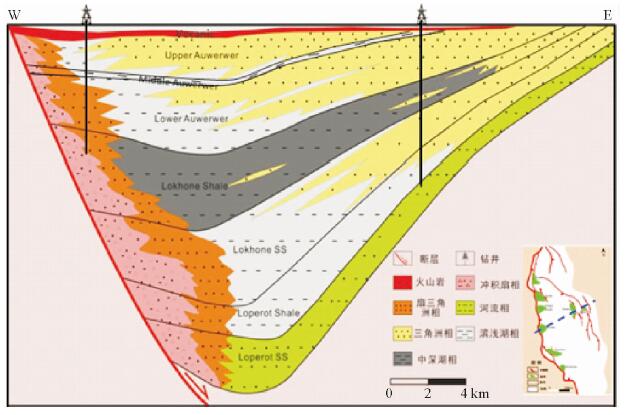
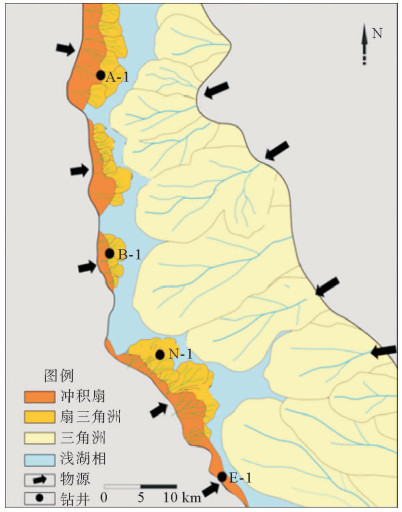
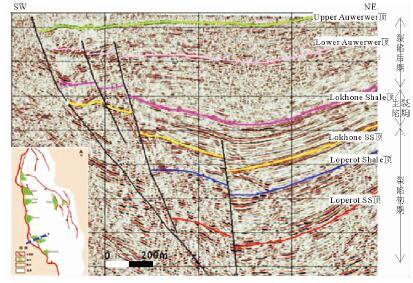
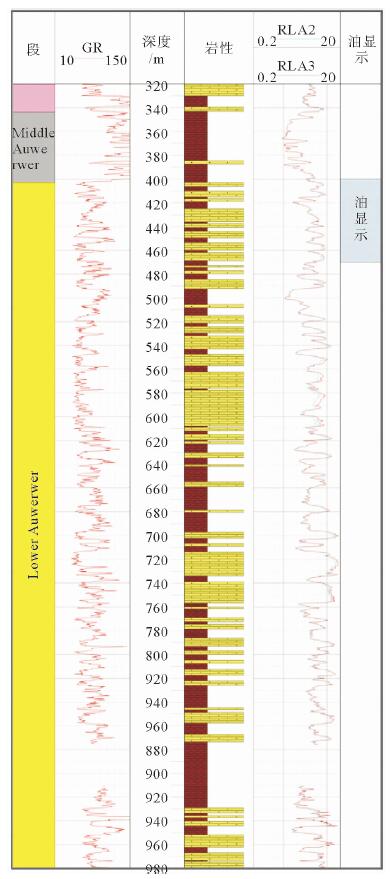
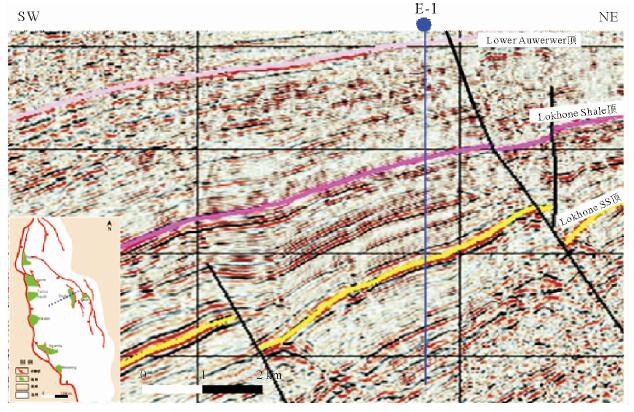
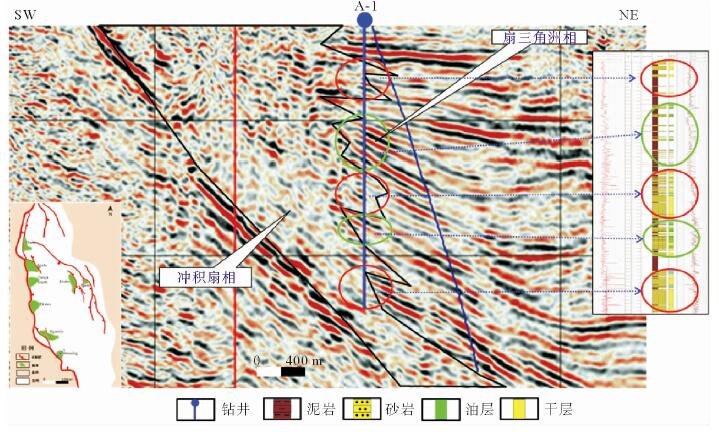
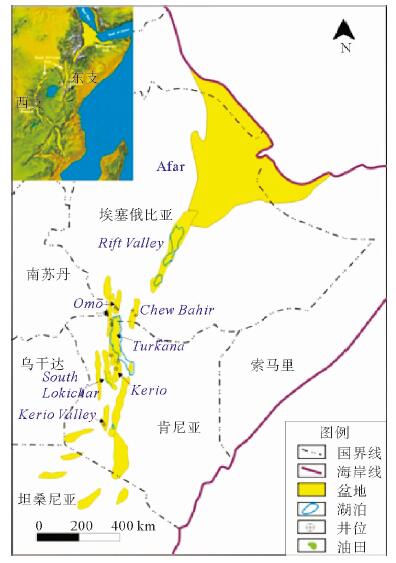
摘要: 东非裂谷东支由多个盆地组成,勘探程度低,目前仅South Lokichar盆地有油气发现。通过以钻井、地震及分析化验资料为基础,对South Lokichar盆地的油气地质条件及成藏规律进行详细分析认为:South Lokichar盆地成藏条件优越;油气发现集中于Lower Auwerwer组和Lokhone Shale组,Lower Auwerwer组为主要目的层;西部陡坡带为主要油气聚集带,储层是影响成藏及油层厚度的主控因素;东部缓坡带目前储量很小,主要目的层未成藏,侧封条件差是影响其成藏的主控因素。
-
关键词:
- South Lokichar盆地 /
- 油气地质 /
- 油气富集特征 /
- 成藏规律 /
- 东非裂谷
Abstract: The eastern branch of the East African Rift System is composed of several basins. It remains low in hydrocarbon exploration degree and only in the South Lokichar basin there are oil discoveries. The paper is to analyze the geological conditions for hydrocarbon accumulation in the South Lokichar basin with drilling, seismic and laboratory data. The study shows that the South Lokichar Basin has favorable conditions for oil and gas accumulation. Both of the Lower Auwerwer Formation and the Lokhone Shale Formation have oil accumulations being found and the former is the main exploration target. The western steep slope zone is the main hydrocarbon accumulation zone, in which both of the exploration targets have oil discoveries. Reservoir is the main factor affecting oil and gas accumulation and net pay thickness. The eastern gentle zone has little discovery until now, in which the main exploration target, the Lower Auwerwer Formation, has nothing discovered yet and poor lateral sealing is proposed as the main factor. -

-
[1] 温志新, 童晓光, 张光亚, 等.东非裂谷系盆地群石油地质特征及勘探潜力[J].中国石油勘探, 2012, 17(4):60-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2012.04.010
[2] Kreuser T. Rift to drift evolution in Permian-Jurassic basins of East Africa[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 1995, 80(1):297-315. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1995.080.01.14
[3] Chorowicz J. The East African rift system[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2005, 43(1):379-410. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2005.07.019
[4] 徐宁, 张杰, 史卜庆, 等.红海盆地石油地质特征及其油气勘探潜力[J].地学前缘, 2014, 21(3):155-165. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201403018
[5] 金宠, 陈安清, 楼章华, 等.东非构造演化与油气成藏规律初探[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2012, 42(2):121-130. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CCDZ2012S2015.htm
[6] Tatsumi Y, Kimura N. Secular variation of basalt chemistry in the Kenya Rift: Evidence for the pulsing of asthenospheric upwelling[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1991, 104(1):99-113. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012821X91902419
[7] Mechle J, Keller G R, Prodehlc C, et al. A model for the structure, composition and evolution of the Kenya rift[J]. Tectonophysics, 1997, 278(1/4):95-119. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195197000978
[8] Morley C K, Wescott W A, Stone D M, et al. Tectonic evolution of the northern Kenya Rift[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1992, 149(3):333-348. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.149.3.0333
[9] Smith M. Stratigraphic and structural constraints on mechanisms of active rifting in the Gregory Rift, Kenya[J]. Tectonophysics, 1994, 236(1/4):3-22. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/004019519490166X
[10] Macgregor D. History of the development of the East African Rift System: A series of interpreted maps through time[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2015, 101(1):232-252. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2014.09.016
[11] 姜在兴.沉积学[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2001:270-398.
-



 下载:
下载: