ASSESSMENT OF HEAVY METAL POLLUTION OF THE SURFACIAL SEDIMENT IN NORTHWESTERN BOHAI SEA
-
摘要:
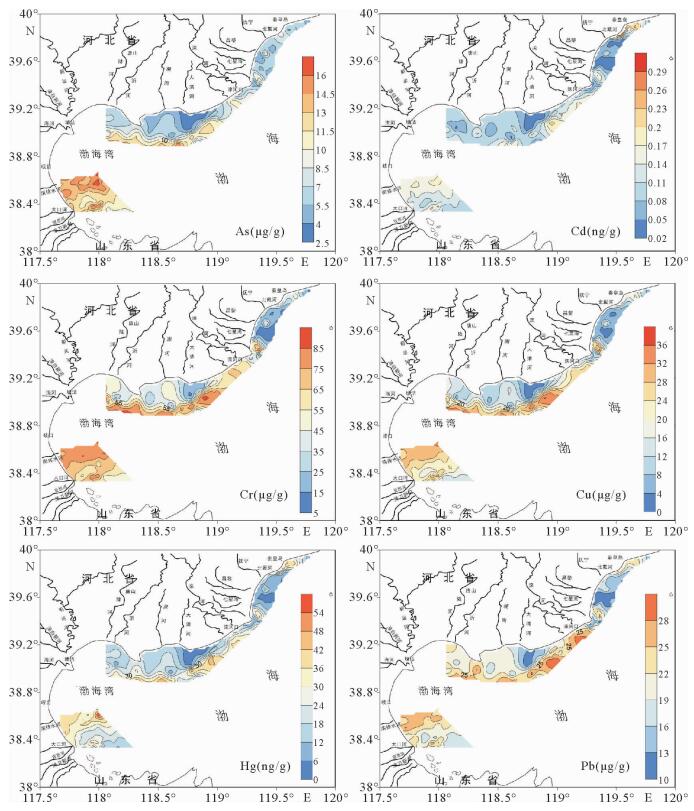
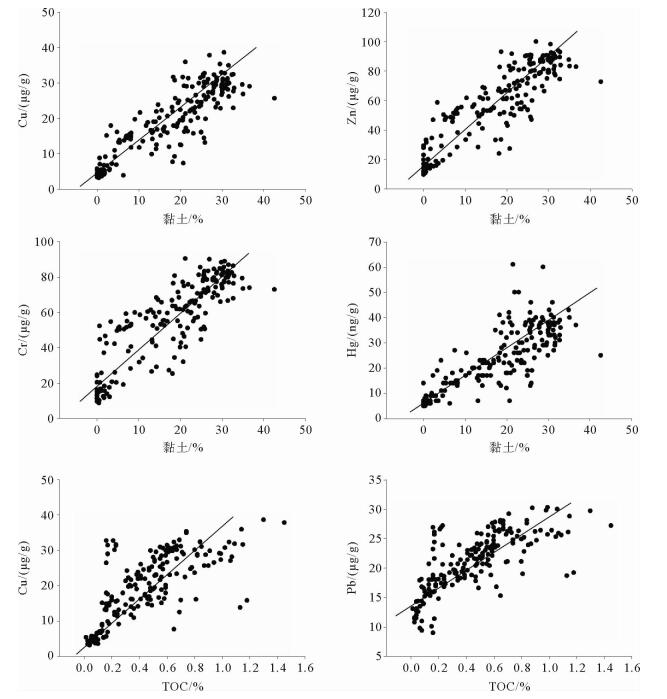
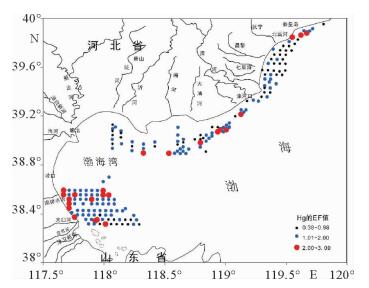
对取自渤海西北近岸海域的189个表层沉积物进行了重金属元素、粒度和有机碳(TOC)分析,查明了研究区重金属的分布特征和潜在污染水平。结果表明,As、Cr、Pb、Zn的空间分布比较均衡,Cd、Cu、Hg的空间变异系数较大,低值区都集中在昌黎沿海海域,高值区基本都集中在沿岸河口位置,总体上呈现出由西北部沿岸海区向东南降低的趋势。Cu、Cr、Pb、Hg与黏土含量、TOC之间表现出较强相关性。Pearson相关分析表明,黏土是重金属元素的主要载体,TOC是控制重金属元素的次要因素。根据地质累积指数法(Igeo)评价得出,渤海西北近岸海域仅在个别区域受到轻微污染,大部分区域沉积物底质环境良好。重金属富集因子(EF)显示研究区沉积物污染程度明显高于Igeo计算结果,多数重金属元素均处于中度污染水平,这可能与计算EF值时所取的区域背景值存在偏差有关。两种重金属元素评价方法同时表明Hg元素在沿岸河口位置存在一定程度污染,这与陆上人类经济活动向河口排放的污染物质经河流排入海有直接关系,说明人类经济活动给沿岸水域造成了一定程度的污染。
Abstract:189 surfacial samples collected from the offshore area of north-eastern Bohai sea are analyzed for heavy metal elements, grain size and organic carbon (TOC) in this paper. The distribution pattern of the heavy metals and potential pollution levels are studied. Results show that the spatial distribution of As, Cr, Pb, Zn is more or less balanced, whereas the Cd, Cu, Hg are rather high. Low values of the spatial variation coefficients appear in the coastal waters of Changli, and high values occur in the coastal estuaries. In general, the coefficient decreases from northwest to southeast.Cu, Cr, Pb and Hg show a strong correlation with clay and TOC content of the sediment. Pearson correlation analysis suggests that clay is the main carrier of heavy metal elements, and the TOC is the second factor which plays significant roles in heavy metal pollution. Geological accumulation index (Igeo) evaluation shows that the nearshore areas of northwest Bohai sea are not polluted by heavy metals except a few places where slight pollution may occur. The heavy metal enrichment factor (EF), however, tells us another picture that the pollution of sediments in the study area is on a moderate level, significantly higher than that Igeo says, probably owing to the higher regional background used for calculation of the EF values.All the two methods used for evaluation of heavy metal element pollution confirm that Hg element pollution does exist in the coast estuaries to certain extent, and it is directly related to human activities. The pollutants are discharged into the rivers by human being, and then carried by rivers to the sea.
-

-
表 1 研究区内表层沉积物中的重金属含量
Table 1. Heavy metals concentrations of surface sediments in the study area
元素 均值/(μg/g) 标准偏差 偏度 峰度 变异系数 最小值 最大值 As 8.33 3.68 0.59 -0.54 0.44 2.51 19.70 Cd 0.1 0.06 1.94 8.73 0.57 0.03 0.540 Cr 50.45 22.90 -0.01 -0.17 0.45 7.80 175.00 Cu 16.85 10.10 0.92 2.80 0.60 2.60 82.60 Hg 0.02031 13.22 1.46 4.63 0.65 0.005 0.112 Pb 19.55 5.08 0.15 -0.41 0.26 6.20 36.30 Zn 51.45 25.42 0.10 -0.95 0.49 8.70 121.90 TOC 0.45% 0.3 0.64 -0.22 0.30 0.01 1.45 黏土含量 17.91% 11.0 -0.30 -1.15 11.0 0.00 42.61 表 2 渤海西北部近岸海域重金属元素、有机碳和黏土的Pearson相关系数
Table 2. The Pearson correlation coefficient of heavy metal elements, organic carbon and clay contents in coastal area of the northwest Bohai sea
重金属 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Pb Zn TOC 黏土含量 As 1.00 Cd 0.62 1.00 Cr 0.83 0.70 1.00 Cu 0.83 0.76 0.96 1.00 Hg 0.74 0.85 0.83 0.89 1.00 Pb 0.67 0.79 0.85 0.88 0.86 1.00 Zn 0.82 0.78 0.93 0.92 0.84 0.91 1.00 TOC 0.45 0.56 0.66 0.72 0.61 0.73 0.70 1.00 黏土含量 0.76 0.66 0.85 0.87 0.80 0.79 0.88 0.62 1.00 表 3 渤海西北近岸海域重金属元素潜在危害程度分析统计
Table 3. Statistics of potential contamination analysis of heavy metals in the northwest Bohai Sea
Cfi Cu Pb Zn Cr As Hg Cd Cd 最大值 0.77 0.43 0.57 1.00 1.17 0.24 0.42 4.03 最小值 0.06 0.13 0.06 0.10 0.20 0.02 0.03 0.71 平均值 0.39 0.30 0.34 0.62 0.66 0.10 0.12 2.52 Eri Cu Pb Zn Cr As Hg Cd ERI 最大值 3.86 2.16 0.57 2.01 11.67 9.76 12.60 35.57 最小值 0.31 0.64 0.06 0.19 1.95 0.80 0.84 5.51 平均值 1.97 1.50 0.34 1.25 6.58 3.84 3.55 19.02 表 4 渤海西北近岸海域重金属元素背景值和EF值
Table 4. Background values and enrichment factors (EFs) of heavy metals in the northwest Bohai
Sea/(μg/g) Cu Pb Zn Cr As Hg Cd 背景值 13.28 19.55 51.45 50.45 7.31 15.71 0.09 EF 最大值 2.09 1.44 1.47 1.43 2.17 3.09 3.63 最小值 0.40 0.67 0.41 0.22 0.42 0.38 0.51 平均值 1.33 1.04 1.03 1.01 1.29 1.38 1.22 -
[1] Irabien M J, Velasco F. Heavy metals in Oka Rive sediments (Urdaibai National Biosphere Reserve, Northern Spain): Lithogenic and anthropogenic effects[J]. Environmental Geology, 1999, 37:54-63. doi: 10.1007/s002540050360
[2] Dou Y G, Li J, Zhao J T, et al. Distribution, enrichment and source of heavy metals in surface sediments of the eastern Beibu Bay, South China Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2013, 67:137-145. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.11.022
[3] Yu R L, Yuan X, Zhao Y H, et al. Heavy metal pollution in intertidal sediments from Quanzhou Bay, China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2008, 20: 664-669. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62110-5
[4] 杜俊涛, 陈洪涛, 田琳.北黄海表层沉积物中重金属含量及其污染评价[J].中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 40(增刊):167-172. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-QDHY2010S1028.htm
[5] 刘伟, 陈振楼, 许世远.上海市小城镇河流沉积物重金属污染特征研究[J].环境科学, 2006, 27(3):538-543. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2006.03.027
[6] Chapman P M, Wang F Y. Appropriate applications of sediment quality values for metals and metalloids[J]. Environmental Science Technology, 1999, 33:3937-3941. doi: 10.1021/es990083n
[7] Dassenakis M, Scoullos M, Gaitis A. Trace metals transport and behavior in the Mediterranean estuary of Acheloos River[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 1997, 34:103-111. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(96)00062-8
[8] Bettinetti R, Giarei C, Provini A. Chemical analysis and sediment toxicity bioassays to assess the contamination of the River Lambro (Northern Italy)[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology, 2003, 45: 72-78. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f395799a8792a0f248996efc75330bbb
[9] Singh K P, Malik A, Sinha S. Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources of Gomti River (India) using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study [J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2005, 538: 355-374. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2005.02.006
[10] 田琳, 陈洪涛, 杜俊涛, 等.北黄海表层海水溶解态重金属的分布特征及其影响因素[J].中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 2009, 39(4):617-621. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qdhydxxb200904010
[11] Radha R R M, Tripathi K A, VinodAP, et al. Assessment of Pb, Cd, Cu, and Zn exposures of 6- to 10-year-old children in Mumbai[J]. Environmental Research, 1997, 80:215-221. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=b3df6c63d90f675cfca972b9598743ab
[12] Li X D, Lee S L, Wong S C, et al.The study of metal contamination in urban soils of Hong Kong using a GIS-based approach[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2004, 129:113-124. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2003.09.030
[13] Carmen C M, Li D X, Zhang G, et al.Trace metal distribution in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary and the surrounding coastal area, South China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2007, 147:311-323. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2006.06.028
[14] 李淑媛, 刘国贤, 苗丰民.渤海沉积物中重金属分布及环境背景值[J].中国环境科学, 1994, 14(5):370-376. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.1994.05.006
[15] 申旭红, 肖飞鹏, 肖进中.中国三大海域沉积物中重金属的分布特征及其生态危害[J].安徽农业科学, 2012, 40(24):12199-12201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2012.24.097
[16] 刘成, 王兆印, 何耘, 等.环渤海湾诸河口底质现状的调查研究[J].环境科学学报, 2003, 23(1):58-63. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2003.01.012
[17] 盛菊江, 范德江, 杨东方, 等.长江口及其邻近海域沉积物重金属分布特征和环境质量评价[J].环境科学, 2008, 29(9):2405-2412. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.09.004
[18] 秦延文, 孟伟, 郑丙辉, 等.渤海湾天津段潮间带沉积物柱状样重金属污染特征[J].环境科学, 2006, 27(2):268-273. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hjkx200602014
[19] 张远辉, 杜俊民.南海表层沉积物中主要污染物的环境背景值[J].海洋学报, 2005, 27(4):161-166. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2005.04.022
[20] 王贵, 张丽洁.海湾河口沉积物重金属分布特征及形态研究[J].海洋地质动态, 2002, 18(12):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2002.12.001
[21] 胡宁静, 石学法, 黄朋, 等.渤海辽东湾表层沉积物中金属元素分布特征[J].中国环境科学, 2010;30(3):380-388. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghjkx201003016
[22] Goldberg E D, Gamble E, Grifin J J.Pollution history of Narragansett Bay as recorded in its sediments[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 1997, 5:549-561. doi: 10.1016/0302-3524(77)90101-3
[23] Attrill M J, Thomes R M.Heavy metal concentrations in sediment from the Thames estuary UK [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 1995, 30(11):742-744. doi: 10.1016/0025-326X(95)98339-X
[24] 蓝先洪.中国主要河口沉积物的重金属地球化学研究[J].海洋地质动态, 2004, 20(12):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2004.12.001
[25] 刘明, 张爱滨, 范德江, 等.渤海中部底质沉积物重金属环境质量[J].中国环境科学, 2012, 32(2):279-290. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2012.02.015
[26] 陈江麟, 刘文新, 刘书臻, 等.渤海表层沉积物重金属污染评价[J].海洋科学, 2004, 28(12):16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2004.12.005
[27] 刘建国, 李安春, 徐兆凯.全新世以来渤海湾沉积物的粒度特征[J].海洋科学, 2006, 30(3):60-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2006.03.013
[28] 李桂海.厦门海域现代沉积环境及重金属元素的环境地球化学研究[M].青岛:中国海洋大学, 2007:1-118.
[29] Qi L, Gregoire D C. Determination of trace elements in twenty six Chinese geochemistry reference materials by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry Geostandards Newsletter[J].The Journal of Geostandards and Geoanalysis, 2000, 24(1):51-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2000.tb00586.x
[30] 孙伟.原子荧光光谱法快速测定化探样品中的微量砷、锑、铋、汞[J].光谱实验室, 2001, 18(4):513-516. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8138.2001.04.028
[31] Hakanson L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sedimentological approach[J].Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
[32] Ansari A A, Singh I B, Tobschall H J. Importance of geomorphology and sedimentation processes for metal dispersion in sediments and soils of the Ganga Plain: identification of geochemical domains[J]. Chemical Geology, 2000, 162:245-266. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00073-X
[33] LI Y C. Geochemical cycles of elements and human perturbation. Geochim Cosmochim Acta[J]. 1981, 4(2):2073-2084. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(81)90061-2
[34] 霍文毅, 黄风茹, 陈静生, 等.河流颗粒物重金属污染评价方法比较研究[J].地理科学, 1997, 17(1):51-86. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700043892
[35] 丁喜桂, 叶思源, 高宗军.近海沉积物重金属污染评价方法[J].海洋地质动态, 2005, 21(8):31-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2005.08.009
-




 下载:
下载: