DISCUSSION ON MAIN CONTROL FACTORS OF GAS HYDRATE IN INDIAN EXCLUSIVE ECONOMIC ZONES
-
摘要:
印度国家天然气水合物计划(NGHP-01)于2006年在克里希纳—戈达瓦里河(KG)盆地、曼哈纳迪盆地、安德曼海盆地、喀拉拉—康坎(KK)盆地实施,除KK盆地外均获得了水合物样品。为了探讨上述4个盆地天然气水合物的主控因素,较全面地收集、整理、比较了各个盆地的沉积背景、沉积速率、沉积物厚度、总有机碳(TOC)含量以及水合物钻探情况,发现KG盆地沉积物厚度最大,有机质含量最高,同时水合物饱和度较大,而KK盆地沉积物厚度最小、有机质含量最低,未钻获水合物样品,曼哈纳迪盆地和安德曼海盆地的沉积物厚度、有机质含量及水合物饱和度介于中间。结合我国南海水合物的钻探实际,可以认为沉积物厚度和有机质含量对印度专属经济区天然气水合物具有重要的控制作用。
Abstract:The Indian National Gas Hydrate Program Expedition 01 (NGHP-01) was executed in 2006 in the Krishna-Godavari(KG) Basin, Mahanadi Basin, Andaman Sea and Kerala-Konkan (KK) Basin. Hydrate samples were obtained from all these basins except for the KK Basin. In order to study the main controlling factors on gas hydrate in the four basins mentioned above, data of sedimentary background, including sedimentation rate, sediment thickness, total organic carbon (TOC) content in addition to the information on hydrate drilling are collected and compared. The KG Basin is the basin with largest sediment thickness and highest organic matter, and the hydrate saturation is relatively high; while the KK Basin is the basin with smallest sediment thickness and lowest organic matter, and no hydrate samples have been collected so far. Comparing with what we learnt from the South China Sea, it is concluded that sediment thickness and organic matter content have important control over gas hydrates occurrence in the Indian Exclusive Economic Zones.
-

-
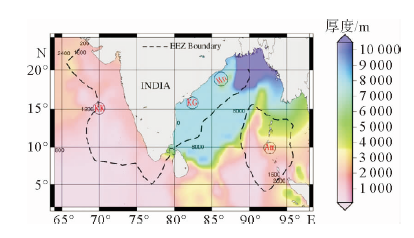
图 1 印度专属经济区沉积物厚度(EEZ Boundary:印度专属经济区边界; 据文献[7])
Figure 1.
表 1 KG盆地、曼哈纳迪盆地、安德曼海、KK盆地沉积速率和厚度对比表(据文献[7, 11, 15, 18, 20])
Table 1. Comparison of sedimentation rate and sediment thickness among KG、Mahanadi、Andaman Sea and KK Basin (from references[7, 11, 15, 18, 20])
盆地 盆地性质 沉积速率/(m/Ma) 沉积厚度/km KG盆地 被动陆缘 125~480 4~7 曼哈纳迪盆地 被动陆缘 10~130 4 安德曼海 弧后盆地 80 3 KK盆地 被动陆缘 4~25 2~3 表 2 KG、曼哈纳迪、安德曼海、KK盆地平均TOC含量和水合物饱和度(据文献[13, 22])
Table 2. Average TOC content and hydrate saturation among KG、Mahanadi、Andaman Sea and KK Basin (from references [13, 22])
盆地 TOC均值/% 水合物饱和度/% KG盆地 1.58 31 曼哈纳迪盆地 1.12 15 安德曼海 0.73 20 KK盆地 0.27 0 表 3 神狐海域和东沙海域沉积物沉积速率、有机碳含量及水合物饱和度对比表(据文献[26-29])
Table 3. Comparison of sedimentation rate, organic carbon content and hydrate saturation among KG、Mahanadi、Andaman Sea and KK Basin (from references [26-29])
海域 沉积速率/(m/Ma) 平均有机碳含量/% 水合物饱和度/% 神狐海域 更新世:40~80
上新世:20~600.7 SH2:25~48
SH3:20~25
SH7:20~42东沙海域 469~730 0.81 45~100 -
[1] Makogon Y F, Holditch S A, Makogon T Y. Natural gas hydrate—A potential energy source for the 21st century[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and engineering, 2007, 56:14-31. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2005.10.009
[2] Chopra N N. Gas hydrate-an unconventional trap in forearc regions of the Andaman offshore[J]. Bull. Oil Nat. Gas Corp., 1985, 22 (1):41-54. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912013005609
[3] Collett T S, Boswell R, Cochran J R, et al. Geologic implications of gas hydrates in the offshore of India:Results of the National Gas Hydrate Program Expedition 01[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 58:3-28. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.07.021
[4] Collett T, Riedel M, Cochran J, et al. The NGHP expedition 01 scientific party, Indian national gas hydrate program expedition 01 initial reports[R]. Prepared by the U.S. geological survey and published by the directional general of hydrocarbons ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas, India, 1 DVD.2008.
[5] Sain K, Gupta H K. Gas hydrates:Indian scenario [J]. Journal of Geological Society of India, 2008, 72:299-311. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=eefec0a3d63d8ebd7275277441d68e15&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[6] Sain K, Ojha M. Identification and quantification of gas hydrates:a viable source of energy in the 21st century[M]. Memoir, Geological Society of India, 2008, 68:273-288.
[7] Saina K, Rajesh V, Satyavani N, et al. Gas-hydrate stability thickness map along the Indian continental margin [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(10):1779-1786. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.03.008
[8] Milkov A V, Sassen R, Defreitas D. Gas Hydrate in the Gulf of Mexico[R]. Applied Gas Hydrate Research Program, Year Ⅲ, Final Report, 2002: 2-5.
[9] Davie M K, Buffet B A. A numerical model for the formation of gas hydrates below the seafloor [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2001, 106:497-514. doi: 10.1029/2000JB900363
[10] Bastia R. An overview of Indian sedimentary basins with special focus on emerging east coast deepwater frontiers [J]. The Leading Edge, 2006, 25 (7):818-829. doi: 10.1190/1.2221359
[11] Flores J A, Johnson J E, Mejía-Molina A E, et al. Sedimentation rates from calcareous nannofossil and planktonic foraminifera biostratigraphy in the Andaman Sea, northern Bay of Bengal, and Eastern Arabian Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 58:425-437. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.08.011
[12] Bastia R, Nayak P K. Tectonostratigraphy and depositional patterns in Krishna offshore basin, Bay of Bengal [J]. The Leading Edge, 2006, 25 (7):839-845. doi: 10.1190/1.2221361
[13] Kumar P, Collett T S, Boswell R, et al. Geologic implications of gas hydrates in the offshore of India:Krishnae Godavari Basin, Mahanadi Basin, Andaman Sea, Keralae Konkan Basin [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 58:29-98. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.07.031
[14] Max M D. Gas hydrate potential of the Indian sector of the NE Arabian Sea and Northern Indian Ocean[M]// Max M D. Natural Gas Hydrate in Oceanic and Permafrost Environments. Dordrecht, The Netherlands:Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2000:213-224.
[15] Nyak G K, Rao Ch R. Structural configuration of Mahanadi Offshore Basin, India:an Aeromagnetic study[J]. Marine Geophysical Researches, 2002, 23:471-479. doi: 10.1023/B:MARI.0000018244.65222.9a
[16] Sastri V V, Venkatachala B S, Narayanan V. The evolution of the east coast of India[J]. Paleogeogr. Paleoclimatol. Paleoecol., 1981, 36:23-54. doi: 10.1016/0031-0182(81)90047-X
[17] Biksham G, Subrahmanyam V. Sediment transport of the Godavari River Basin and its controlling factors [J]. Hydrol, 1988, 101:275-290. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(88)90040-6
[18] Sethi A K, Sathe A V, Ramana M V. Potential natural gas hydrate resources in Indian offshore areas[C]// Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol., Hedberg conference 'Gas hydrate: Energy resource potential and associated geologic hazards', Vancouver, BC, Canada, Proc. Aapg, 2004, 1-6.
[19] Kelvin S, Rodolfo. Sediments of the Andaman Basin, northeastern Indian Ocean [J]. Marine Geology, 1969, 7(5):371-402. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(69)90014-0
[20] Biswas S K, Singh N K. Western continental margin of India and hydrocarbon potential of deep sea basins[C]// 7th Offshore South Asia Conference, Singapore, 1988, 170-181.
[21] Clift P D, Shimizu N, Layne G, et al. Development of the Indus Fan and its significance for the erosional history of the western Himalaya and Karakoram[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2001, 113(8):1039-1051. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2001)113<1039:DOTIFA>2.0.CO;2
[22] Joel E J, Stephen C P, Marta E T, et al. Influence of total organic carbon deposition on the inventory of gas hydrate in the Indian continental margins[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 58:406-424. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.08.021
[23] Zhang G X, Yang S X, Zhang M, et al. GMGS2 expedition investigates rich and complex gas hydrate environment in the South China Sea [J]. Fire in the Ice, 2014, 14(1):1-5. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1875510015301347
[24] 王宏斌, 张光学, 杨木壮, 等.南海陆坡天然气水合物成藏的构造环境[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23(1):81-86. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200301013
[25] 杨涛, 蒋少涌, 葛璐, 等.南海北部神狐海域浅表层沉积物中孔隙水的地球化学特征及其对天然气水合物的指示意义[J].科学通报, 2009, 54(20):3231-3240. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb200920037
[26] 陈芳, 苏新, 周洋.南海神狐海域天然气水合物钻探区钙质超微化石生物地层与沉积速率[J].地球科学, 2013, 38(1):1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2013.01.001
[27] 付少英, 陆敬安.神狐海域天然气水合物特征及其气源[J].海洋地质动态, 2010, 26(9):6-10. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqgy201010025
[28] 陈芳, 庄畅, 周洋, 等.南海东北部陆坡天然气水合物钻探区生物地层与沉积速率[J].地球科学, 2016, 41(3):416-424. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201603008
[29] 张光学, 梁金强, 陆敬安, 等.南海东北部陆坡天然气水合物藏特征[J].天然气工业, 2014, 34(11):1-10. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.11.001
-



 下载:
下载: