COASTAL ENGINEERING GEOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF LAIZHOU BAY AND SOME SPECIAL PROBLEMS
-
摘要:
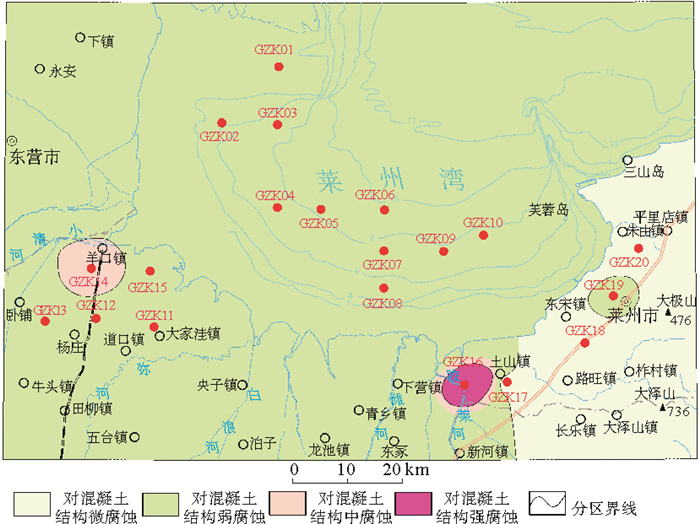
依据本次工程地质调查和钻探工作取得的大量数据,结合以往研究资料,对研究区土体工程地质层进行了系统研究,依据①沉积时代、成因类型和形成环境;②物质成分和结构特征;③工程特性指标等3个方面,对研究区地表以下50 m深度范围内的土层进行分层排序,将研究区土体划分为9个工程地质层,并对各层工程地质特征进行了分析;分析了研究区软土、盐渍土的分布范围、物理力学性质等;对研究区地基土液化等级、地下水和土的腐蚀性进行了综合评价。研究区7度地震作用下饱和砂土液化严重区和中等区主要分布在潍坊港北部莱州湾海域及东营市东部一带;轻微区和不液化区主要分布在莱州湾南岸、东岸一带。盐渍土主要分布在黄河三角洲、莱州湾滨海平原区。研究区地下水土对混凝土结构的腐蚀性以弱腐蚀和微腐蚀为主;对钢筋混凝土结构中钢筋的腐蚀性强腐蚀和中等腐蚀主要分布在莱州湾海域及其西岸、南岸一带,弱腐蚀和微腐蚀主要分布在莱州湾东岸。
Abstract:Based on the recent engineering geological investigation and the drilling data from previous studies, further research is devoted to the classification of engineering geological layers for the coastal sediments of Laizhou Bay according to the following criteria: (1) age, genetic types and forming environment of the sediments; (2) composition and texture of the sediments; (3) engineering characteristics. The first 50m of the soil layers below the ground of the study area can be subdivided into 9 layers. Engineering geological characteristics are analyzed for each layer. Attention is specifically paid to the distribution of the sediments and the physical and mechanical properties of soft soil and saline soil. Soil liquefaction grade, groundwater fluctuation and soil corrosion are evaluated. The severe and moderate areas, which may be damaged by saturated sandy soil liquefaction under a 7-grade earthquake in the study area are mainly distributed in Laizhou Bay to the north of Weifang port and the east of Dongying city. The areas with weak liquefaction or without liquefaction are mainly distributed along the south and east coast of Laizhou Bay. The saline soil is mainly distributed in the Yellow River delta and the coastal plain of Laizhou Bay. The corrosion of concrete structures by soil and water is weak in the study area in general. Strong and medium corrosion of reinforcement in the reinforced concrete structures mainly occur in the west and south of Laizhou Bay, while weak and very weak corrosion and corrosion occur in the east.
-
Key words:
- coastal zone /
- engineering geological characteristics /
- Laizhou Bay
-

-
表 1 土(岩)体工程地质层划分简表
Table 1. Engineering geological stratigraphic division of soils (or rocks)
时代 层号 亚层 名称 平均厚度/m 顶板埋深/m 特征简述 分布特征 沉积环境 全新统 0 填土 2.55 0 素填土为主,局部为杂填土,主要成分为粉土,局部为建筑垃圾 陆域普遍分布 人工回填 1 粉土、粉砂 7.48 0~4.30 灰色,湿润,松散 普遍分布 海陆交互 2 2-1 淤泥质土 2.76 0~12.68 黄灰色,饱和,软塑—流塑,切面光滑,有臭味 莱州湾北部、东营市一带 2-2 粉质黏土 5.63 3.00~24.30 灰黑—浅灰色,可塑,湿,干强度中等,韧性中等,切面光滑 莱州湾南部、潍坊市北部一带 3 粉土、粉砂 6.02 0~27.00 灰—青灰色,湿润,松散,贝壳碎屑较多,干强度弱,韧性差 莱州湾、南岸、西岸普遍分布 河流、潮间带沉积 更新统 4 粉质黏土 6.15 6.30~29.50 黄灰色,稍湿,可塑—硬塑,干强度中等,韧性中等,有大量锈痕 莱州湾、南岸、西岸 5 粉土、粉砂 5.41 14.80~38.65 黄灰—灰黄色,湿润—饱和,稍密—密实,干强度弱,韧性差 莱州湾、南岸、西岸 6 粉质黏土 5.76 19.00~42.00 深灰色,稍湿,可塑—硬塑,干强度中等—强,韧性中等—强 莱州湾、南岸、西岸 海相沉积 7 粉土、粉砂 5.04 26.00~56.00 黄灰色,饱和,密实 莱州湾、南岸、西岸 8 粉质黏土 7.27 28.60~58.00 灰色,湿润,可塑—硬塑,锈斑较多,干强度强,韧性强 莱州湾、南岸、西岸 河流、潮间带沉积 9 粉土、粉砂 6.40 34.80~68.50 黄灰—灰色,饱和,密实 莱州湾、南岸、西岸 J 二长花岗岩 0~24.30 灰黑色,中细粒结构,弱片麻状构造;主要成分为长石、石英、黑云母等 莱州湾东岸 侵入岩 -
[1] 李志强.雷州半岛海岸带生态环境脆弱性初探[J].资源开发与市场, 2008, 24(10):905-907. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8141.2008.10.015
[2] 宋晓帅, 王松涛, 吴振, 等.莱州湾海岸带工程地质分区及其特征[J].海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(1):43-52. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt201701006
[3] 郑继民.中国海洋工程地质研究[J].工程地质学报, 1994, 2(1):90-96. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GCDZ401.010.htm
[4] 唐大雄.关于我国细粒土分类的探讨[J].长春地质学院学报, 1981(3):69-77. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CCDZ198103006.htm
[5] 常银生.粘性土应力路径的试验研究与分析[D].南京: 南京工业大学, 2005.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10291-2005129290.htm [6] 李晓昭, 罗国煜, 龚洪祥, 等.土体工程地质层组的划分[J].岩体力学, 2004, 25(5):759-763. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ytlx200405018
[7] 杨辉, 刘红樱, 许乃政, 等.江苏省洋口港地区工程地质特征及分区评价[C]//2016年全国工程地质学术年会论文集.2016.
http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-GCDZ201610001012.htm [8] 李兵.淤泥质土大规模施工技术初探[J].中国水利, 2013(16):39-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2013.16.017
[9] 张宏亮, 杨贵永.复合土钉墙支护在超深基坑中应用[J].福建建筑, 2008(4):29-31. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fjjz200804010
[10] 齐波, 张一飞.天津市中心城区地下空间资源开发利用适宜性评价探讨[J].城市地质, 2010, 5(2):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2010.02.001
[11] 魏臣.钻机成孔人工扩底灌注桩施工技术的应用[J].煤炭工程, 2007(7):38-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0959.2007.07.016
[12] 李琰.28 ka以来莱州湾南岸的沉积学记录及环境意义[D].北京: 中国地质大学, 2014.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1014233630.htm [13] 张月东.横穿机场跑道捷运通道施工沉降控制研究[D].石家庄: 石家庄铁道大学, 2012.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10107-1013310981.htm [14] 阳生全, 周健, 陈秋南, 等.爆破震动作用下的地下结构及围岩幅频特性[J].地下空间与工程学报, 2006, 2(1):104-107. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxkj200601023
[15] 中华人民共和国国家标准GB 50011—2010建筑抗震设计规范(2016年版)[S].北京: 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部等, 2016.
[16] 凌红杰.宿迁某建筑地基液化评价与处理措施研究[J].江苏建筑, 2011(增刊2):58-61. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jsjz2011z1019
[17] 武卫星, 陈超敏.公路软土地基处理方法及施工特性[J].交通科技, 2001(4):27-29. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sykjxx200104009
[18] 俞跃平, 唐柏安.绍兴中心城区工程地质特征及场地工程建设适宜性评价[J].水文地质工程地质, 2011, 38(2):84-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2011.02.015
[19] 卢春华, 李艳松.浅谈软土路基处理[J].科技信息, 2012(9):347-347. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9960.2012.09.272
[20] 李念春.基于PSR模型的土壤环境承载力综合评价——以黄河三角洲高效生态经济区为例[J].国土资源科技管理, 2016, 33(5):117-125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4210.2016.05.017
[21] 张志超, 李萍, 许金良.基于ArcGIS的山东省公路岩土区划研究[J].公路工程, 2014(1):263-268. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=znglgc201401061
[22] 中华人民共和国国家标准GB 50021-2001岩土工程勘察规范[S].北京: 中华人民共和国建设部, 2001.
[23] 程祖锋.建筑基础腐蚀性试验与评价研究[D].长春: 吉林大学, 2006.
-




 下载:
下载: