HISTORICAL EVOLUTION OF THE HIGH VELOCITY SYSTEM OF THE YELLOW RIVER ESTUARY IN THE PAST 50 YEARS
-
摘要:
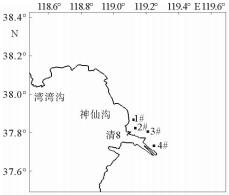
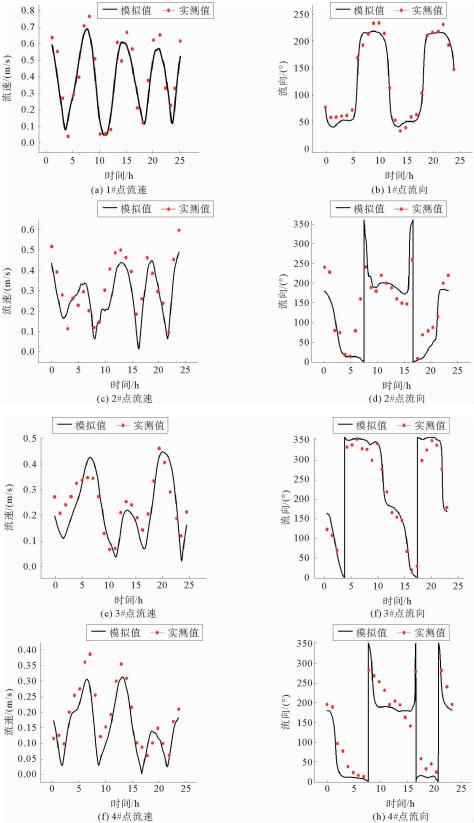
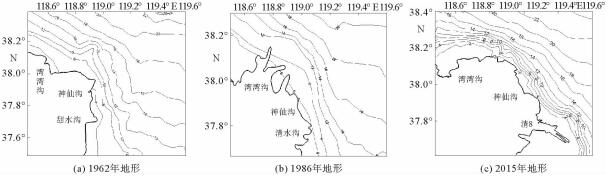
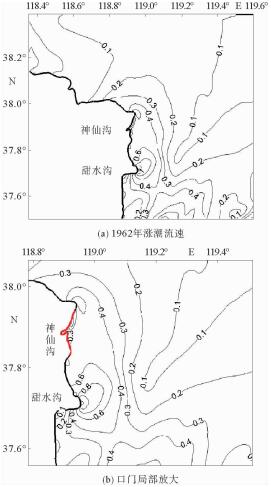
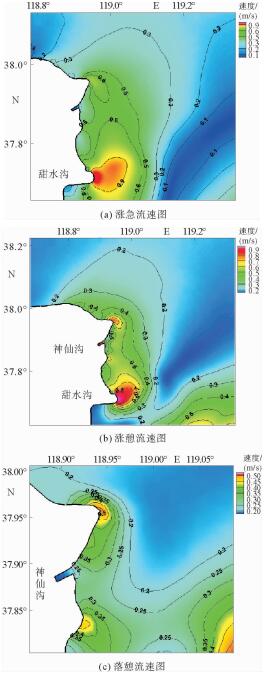
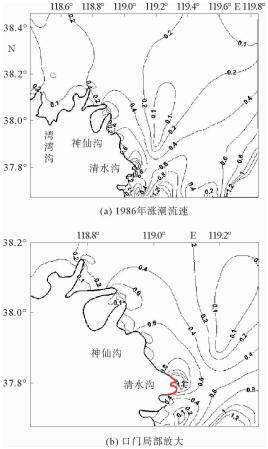
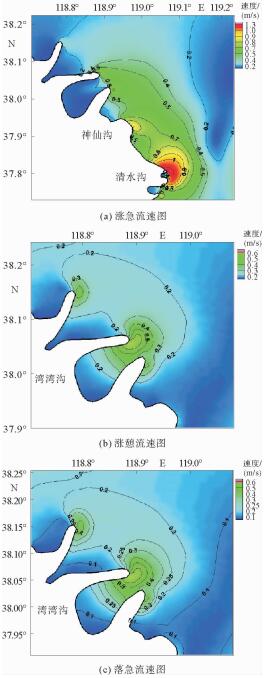
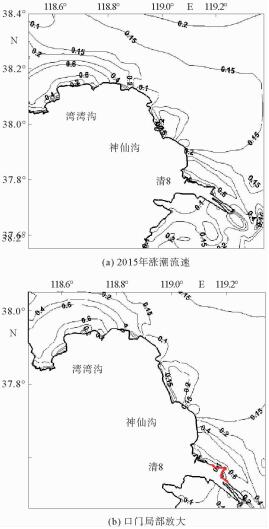
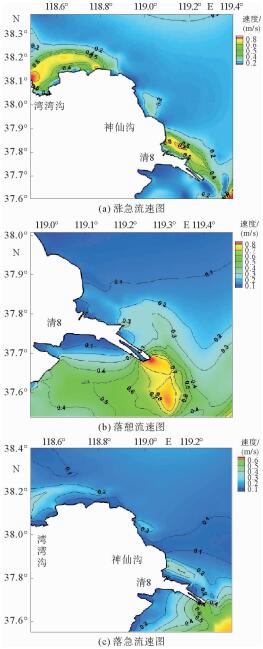
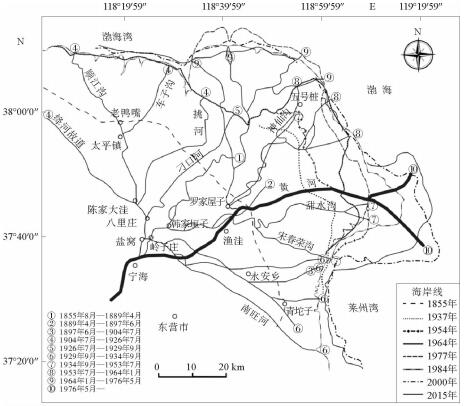
根据黄河口外大量的现场历史观测资料分析发现,其附近海域流场存在着明显的高流速区。这些高流速区在大时间尺度上随着入海流路的改变以及黄河三角洲的演变也发生着此消彼长的变化。利用ChinaTide潮汐预报软件模拟海域潮汐,并利用不同历史年代的海图资料构建海域地形,通过建立黄河口数学模型分析了黄河口流场特性;利用2015年营口港的潮位资料以及实测流速值对数学模型进行了率定和验证;然后分别利用数学模型,对不同代表年的流场进行模拟复演。计算结果表明:①自1962年,黄河口沿岸就已经存在高流速区,分别位于甜水沟和神仙沟口外;②1976年,从神仙沟到清水沟一线沿岸存在着多个小型的高流速区群;③1996年至今,该阶段内存在3个高流速区,分别位于湾湾沟、神仙沟以及清8口门3个沙嘴处;④高流速区的演变与海岸形态的变化存在着密不可分的联系,岸线凸出的沙嘴处往往容易形成平面高流速区。
Abstract:Historical observation data suggests that high velocity systems occurred outside the Yellow River estuary, and on a large time scale, these high velocity systems change with the alteration of the sea channels and the delta itself. This research aims to establish a mathematical model for the Yellow River estuary by using 3 different nautical charts.The tidal prediction software of "China Tide" is adopted to simulate the tide coming offshore. The calculation results show that: ①since 1962, there have been some high velocity systems outside the estuary, for examples the systems located at the Tianshuigou and Shenxiangou; ②in 1976, there were a number of small groups of high velocity systems along the coastline; ③sine 1996, there have been 3 high velocity systems located at the Wanwangou, Shenxiangou and the Qing 8 channel respectively; ④the change of high velocity system is closely related to the evolution of the coast, and the high velocity regions are always located at the place where protrude spits occur.
-

-
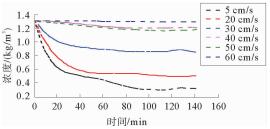
表 1 断面流速和对应淤积量
Table 1. Section flow rate and corresponding siltation
断面流速/(cm/s) 5 20 30 40 50 60 初始含沙量/(kg/m3) 1.31 1.30 1.32 1.31 1.29 1.31 平衡含沙量/(kg/m3) 0.24 0.45 0.81 1.19 1.16 1.30 淤积量/g 181 144 85 19 22 1 淤积百分比/% 81.5 65.4 38.2 8.85 0.10 0.92 -
[1] 程义吉, 程建刚.黄河口新口门海域流场分析[J].海岸工程, 2000(4):5-11. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=11432958
[2] Gao J, Chen X E, Yu H M, et al. Numerical simulation of tides, tidal currents and residual currents in the Yellow River estuary[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2016, 18(1):1-8. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hytb-e201601001
[3] 白玉川, 李大鸣, 王尚毅.流速和潮位变化对波浪在近岸区传播的影响[J].海洋学报:中文版, 1996, 18(3):92-99. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600455000
[4] 白玉川, 顾元棪, 蒋昌波.潮流波浪联合输沙及海床冲淤演变的理论体系与其数学模拟[J].海洋与湖沼, 2000, 31(2):186-196. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2000.02.011
[5] 王尚毅, 顾元棪.二维泥沙数学模型的理论基础及其应用[J].海洋学报:中文版, 1987, 9(1):104-114. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SEAC198701012.htm
[6] 寿玮玮, 宗海波, 丁平兴.夏季黄河入海径流对黄河口及附近海域环流影响的数值研究[J].海洋学报, 2016, 38(7):1-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2016.07.001
[7] 张占海, 吴辉碇.渤海潮汐和潮流数值计算[J].海洋预报, 1994, (1):48-54. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=1362846
[8] 常方强, 贾永刚.黄河口不同强度粉土液化特性的试验研究[J].岩土力学, 2011, 32(9):2692-2696. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.09.022
[9] 白玉川.河口泥沙运动力学[M].天津:天津大学出版社, 2011.
[10] 冯曦.黄河口细颗粒泥沙基本特性实验研究[C]//中国海洋学会海洋工程分会.第十四届中国海洋(岸)工程学术讨论会论文集(下册).中国海洋学会海洋工程分会, 2009: 5.
[11] 李秉天, 王永刚, 魏泽勋, 等.渤海主要分潮的模拟及地形演变对潮波影响的数值研究[J].海洋与湖沼, 2015, 46(1):9-16. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hyyhz201501002
[12] 刘锋, 陈沈良, 彭俊, 等.近60年黄河入海水沙多尺度变化及其对河口的影响[J].地理学报, 2011, 66(3):313-323. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlxb201103003
[13] 贾永刚, 张颖, 刘辉, 等.黄河三角洲海底土波致再悬浮研究[J].海洋学报:中文版, 2012, 34(5):100-110. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hyxb201205012
[14] 彭俊, 陈沈良, 李谷祺, 等.黄河三角洲岸线及现行河口区水下地形演变[J].地理学报, 2012, 67(3):368-376. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlxb201203008
[15] 李泽刚.黄河近代河口演变基本规律与稳定入海流路治理[M].山东:黄河水利出版社.
[16] 刘玲, 李广雪, 李季.黄河三角洲钓口叶瓣河道与岸线演化分析[J].海洋地质前沿, 2013, 29(6):1-6. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt201306001
[17] 乐肯堂, 刘兴泉, 史久新.黄河口的变迁对邻近海区潮波运动影响的数值研究[J].海洋科学集刊, 1995:33-46. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/70799X/19951/672757475199500002.html
-



 下载:
下载: