LITHOFACIES CHARACTERISTICS OF GRAVITY FLOW DEPOSITS AND THEIR IMPACTS ON RESERVOIR QUALITY IN THE YANCHANG FORMATION, ORDOS BASIN
-
摘要:
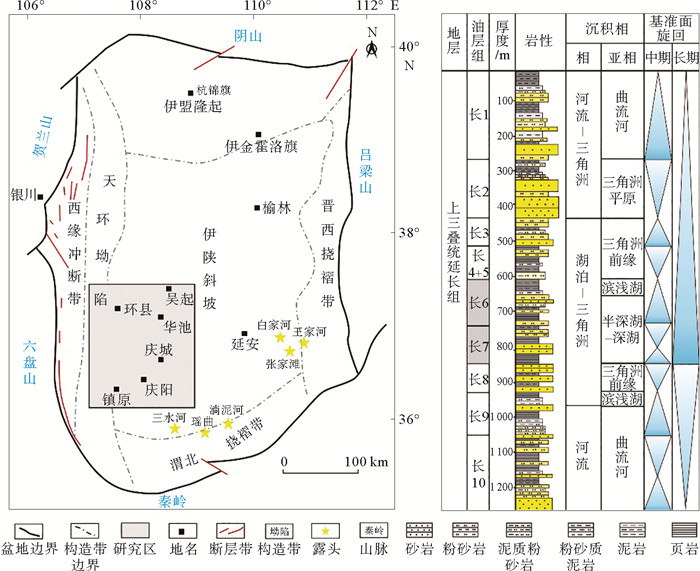
鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区长7、长6油层组广泛发育深水重力流,基于对长7-长6段共计852.7 m岩心的精细分析并结合测井、录井等数据,总结分析了湖盆重力流沉积岩相的类型、成因、特征和发育规律。综合岩石类型、沉积构造和发育规模,共识别出8种岩相类型,分别是:滑动砂岩相(Sl)、滑塌砂岩相(Ss)、滑塌泥岩相(Sm)、中-薄层块状含砾砂岩相(Sc)、中-薄层块状纯净砂岩相(Sp)、厚层块状含砾砂岩相(St)、块状含砾泥岩相(Mc)、中-薄层具层理砂岩夹泥岩相(Tb)。按照Shanmugam基于重力流沉积过程的分类方法,Sl是滑动成因,Ss、Sm是滑塌成因,St、Sp、Sc、Mc是碎屑流成因,Tb是浊流成因。不同岩相发育规模差别较大,从累计厚度和发育频次上看,St、Sp规模最大。砂岩岩相可构成良好储层,St储层质量最好,其次为Sp、Sc,但Sp、Sc的发育规模远大于St,综合认为在实际勘探中Sp、Sc是重力流储层最有利的勘探目标。
Abstract:During the periods of Chang 7 and Chang 6 Members in Late Triassic, gravity flows developed widely in the deep water of Longdong area of the Ordos Basin. Based on the detailed study of 852.7m cores in addition to loggings and testing data, this paper classified the types of lithofacies, then summarized the sedimentary characteristics, forming process, distribution scale and reservoir quality of each lithofacies. Eight types of lithofacies are recognized, i.e., sliding sandstone (Sl), slumping sandstone (Ss), slumping mudstone (Sm), thin- to medium-bedded massive conglomeratic sandstone (Sc), thin- to medium-bedded massive pure sandstone (Sp), thick-bedded massive conglomeratic sandstone (St), massive conglomeratic mudstone (Mc), and thin- to medium-bedded sandstone with beddings (Tb), belonging to slides-dominated lithofacies (Sl); slumps-dominated lithofacies (Ss, Sm); sandy debris flow-dominated lithofacies (Sc, Sp, St); muddy debris flow-dominated lithofacies (Mc); and turbidity current-dominated lithofacies(Tb) respectively according to Shanmugam's classification. The distribution scale of different lithofacies varies greatly, St and Sp are the largest in terms of accumulated thickness and depositional frequency. All the sandstone lithofacies can be good reservoir, and lithofacies St is the best, followed by Sp and Sc. However, the distribution scale of Sp and Sc is much larger than St. It is generally believed that Sp and Sc are the most favorable targets in exploration of gravity flow reservoirs.
-
Key words:
- gravity flow /
- lithofacies /
- reservoir /
- Yanchang Formation /
- Ordos Basin
-

-
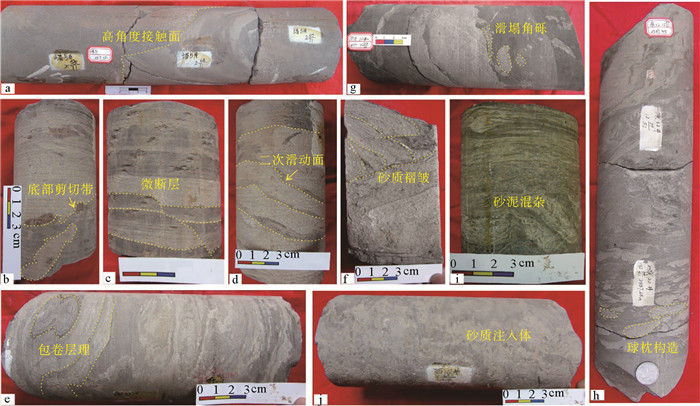
表 1 陇东地区延长组重力流岩相类型及其特征
Table 1. The characteristics of 8 lithofacies of Yanchang Formation in Longdong area
代号 岩相 粒度 单层厚度 沉积特征 成因类型 流体类型 Sl 滑动砂岩相 细砂、粉砂 0.15~1.3 m,
平均0.54 m顶底突变接触面、底部剪切带、内部二次滑动面、微断层 滑动沉积 块体搬运 Ss 滑塌砂岩相 细砂、粉砂 0.25~1.8 m,
平均0.75 m包卷层理、砂质褶皱、
滑塌角砾滑塌沉积 块体搬运 Sm 滑塌泥岩相 泥质、粉砂质泥 0.1~1.5 m,
平均0.64 m砂泥搅混、砂质注入体 滑塌沉积 块体搬运 Sc 中-薄层块状含砾
砂岩相含泥岩撕裂屑或砂质团块的中、细砂 0.12~4 m,
平均0.59 m块状构造、侵蚀底面、
变形砾屑砂质碎屑流 层流 Sp 中-薄层块状纯净
砂岩相纯净细砂 0.1~3.1 m,
平均0.78 m块状构造、侵蚀底面、
重荷模砂质碎屑流 层流 St 厚层块状含砾
砂岩相含砾或含撕裂屑的中粗砂 4.2~7.9 m,
平均5.84 m块状构造、侵蚀底面、
重荷模砂质碎屑流 层流 Mc 块状含砾泥岩相 含撕裂屑的粉砂质泥、泥质 0.05~1.3 m,
平均0.71 m块状构造、砂质团块 泥质碎屑流 层流 Tb 中-薄层具层理砂岩夹泥岩相 细砂、粉砂 0.05~0.85 m,
平均0.43 m正递变、平行层理、波状交错层理、水平层理、火焰构造 浊流 紊流 表 2 陇东地区重力流成因类型及发育规模
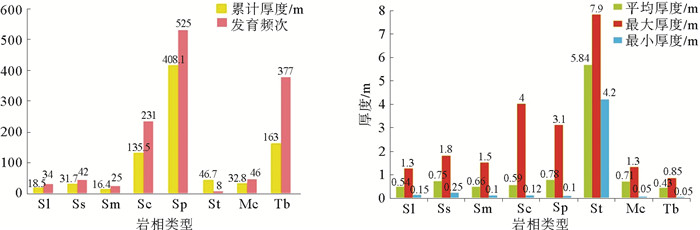
Table 2. Genetic types and distribution scales of gravity flow in Longdong area
重力流类型 累计厚度/m 发育频次 平均厚度/m 滑动沉积 18.5 34 0.54 滑塌沉积 48.1 67 0.72 砂质碎屑流 590.3 764 0.77 泥质碎屑流 32.8 46 0.71 浊流 163 377 0.43 表 3 陇东地区重力流不同岩相物性、产能参数特征
Table 3. Physical properties and productivity parameters of different lithofacies of gravity flows in Longdong area
重力流类型 岩相类型 孔隙度区间/
均值/%渗透率区间/
均值/×10-3μm2试油产量/
(t/d)工业油层
频次低产油层
频次非油层
频次滑动沉积 Sl 5.7~10/7.8 0.04~0.12/0.07 2.2 4 6 9 滑塌沉积 Ss 2.3~9.1/5.6 0.01~0.21/0.05 1.2 2 7 13 Sm 1.0~5.9/3.6 0.01~0.05/0.02 0 0 0 3 砂质碎屑流沉积 Sc 3.1~13.4/8.7 0.01~0.87/0.08 3.2 24 30 18 Sp 5.9~17.1/10.8 0.02~2.65/0.25 7.1 58 35 15 St 6.2~20.7/11.9 0.09~5.33/0.61 11 18 3 3 泥质碎屑流沉积 Mc 0.8~6.2/3.2 0.003~0.04/0.01 0 0 0 4 浊流沉积 Tb 1.5~11.9/7.3 0.01~0.12/0.05 1.4 6 16 30 -
[1] 杨华, 邓秀芹.构造事件对鄂尔多斯盆地延长组深水砂岩沉积的影响[J].石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(5):513-520. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syktykf201305001
[2] 王建民, 王佳媛.鄂尔多斯盆地西南部长7深水浊积特征与储层发育[J].岩性油气藏, 2017, 29(4):11-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2017.04.002
[3] 杨华, 付金华, 欧阳征健, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地西缘晚三叠世构造—沉积环境分析[J].沉积学报, 2011, 29(3):427-439. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb201103002
[4] 梁建设, 田兵, 王琪, 等.深水沉积理论研究现状、存在问题及发展趋势[J].天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(10):1488-1496. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trqdqkx201710003
[5] Shanmugam G. Ten turbidite myths [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2002, 58(3/4):311-341. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ028433134/
[6] Shanmugam G. High Density Turbidity Current:Are They Sandy Debris Flow [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1996, 66 (1):2-10. doi: 10.1306/D426828E-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D
[7] 李相博, 卫平生, 刘化清, 等.浅谈沉积物重力流分类与深水沉积模式[J].地质论评, 2013, 59(4):607-614. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2013.04.002
[8] 邹才能, 赵政璋, 杨华, 等.陆相湖盆深水砂质碎屑流成因机制与分布特征——以鄂尔多斯盆地为例[J].沉积学报, 2009, 27(6):1065-1075. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb200906006
[9] 刘芬, 朱筱敏, 李洋, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地西南部延长组重力流沉积特征及相模式[J].石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(5):577-588. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syktykf201505004
[10] 付金华, 罗顺社, 牛小兵, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区长7段沟道型重力流沉积特征研究[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2015, 34(1):29-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.01.003
[11] 刘芬, 朱筱敏, 李洋, 等.鄂尔多斯湖盆西南部晚三叠世深水坡折特征及其对砂体的控制[J].高校地质学报, 2015, 21(4):674-684. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxdzxb201504012
[12] 潘树新, 刘化清, Zavala C, 等.大型坳陷湖盆异重流成因的水道—湖底扇系统——以松辽盆地白垩系嫩江组一段为例[J].石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(6):860-870. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201706003
[13] Zakaria A A, Johnson H D, Jackson A L, et al. Sedimentary facies analysis and depositional model of the Palaeogene West Crocker submarine fan system, NW Borneo[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 76:283-300. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.05.002
[14] 周瑶琪, 张振凯, 许红, 等.灵山岛沉积物软变形构造特征[J].海洋地质前沿, 2015, 31(4):42-54. http://hydt.cbpt.cnki.net/WKA/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=15c83817-8d03-48d8-a3d7-4c0e396cd286
[15] 逄林安.西非下刚果盆地大型湖相浊积岩特征及勘探意义[J].海洋地质前沿, 2018, 34(4):41-48. http://hydt.cbpt.cnki.net/WKA/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=28f025ab-df4f-4128-bb62-ffa8b6b77f6c
-



 下载:
下载: