Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of Late Mesozoic Volcanic Rocks at DayushanIslands of Northern Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of Late Mesozoic Volcanic Rocks at DayushanIslands of Northern Fujian
-
摘要:
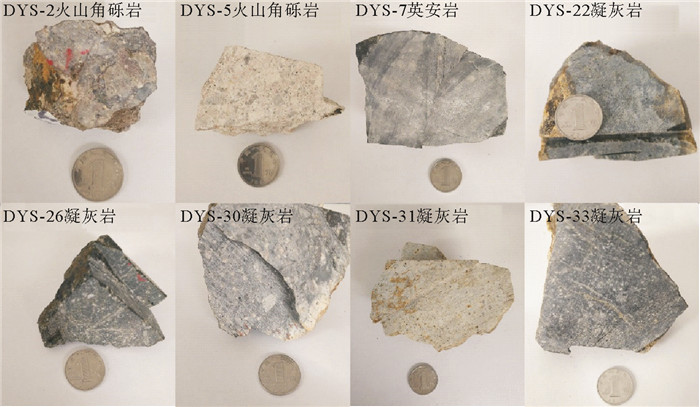
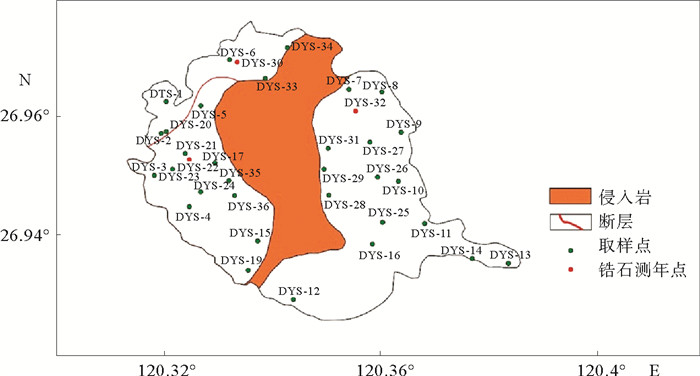
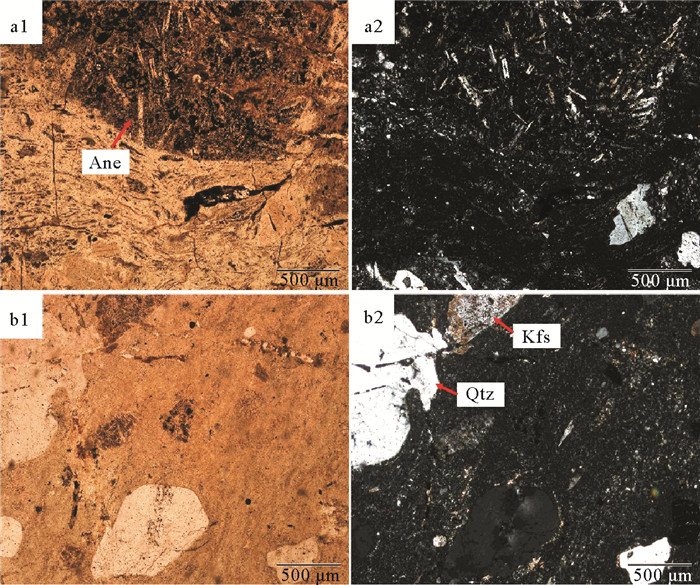
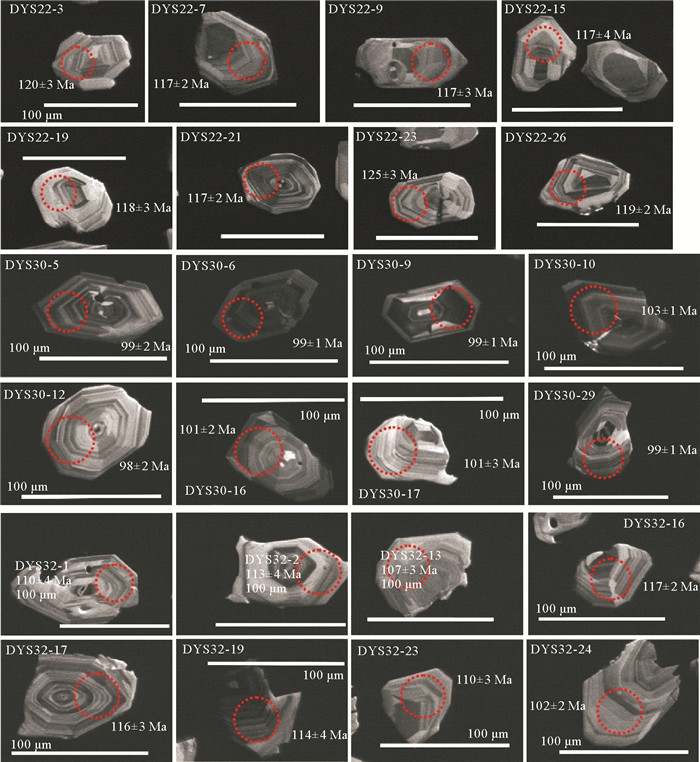
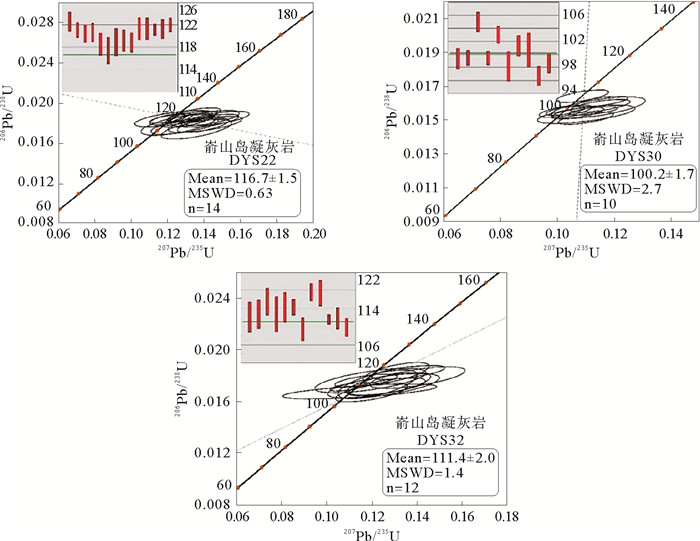
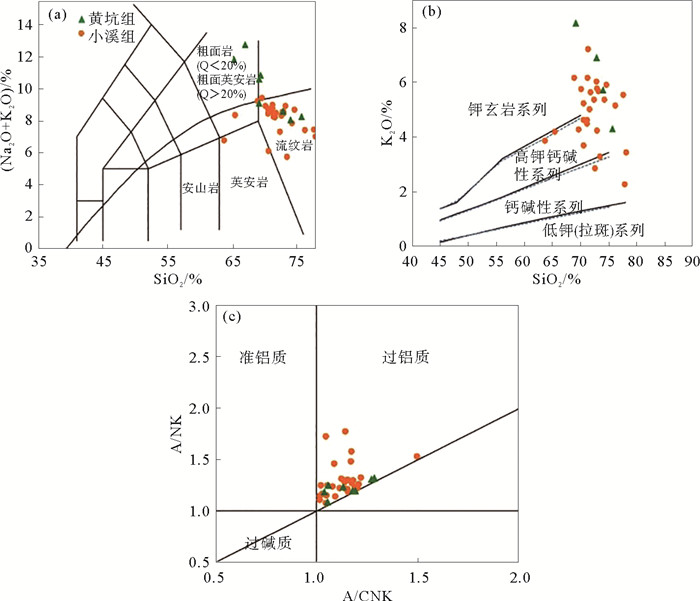
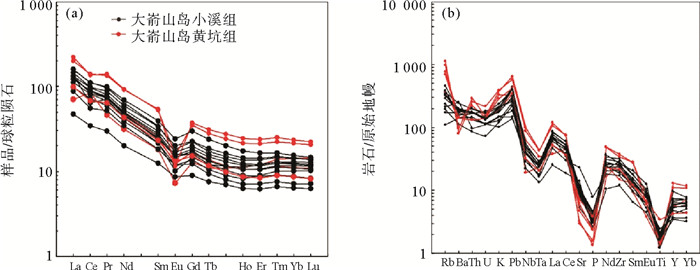
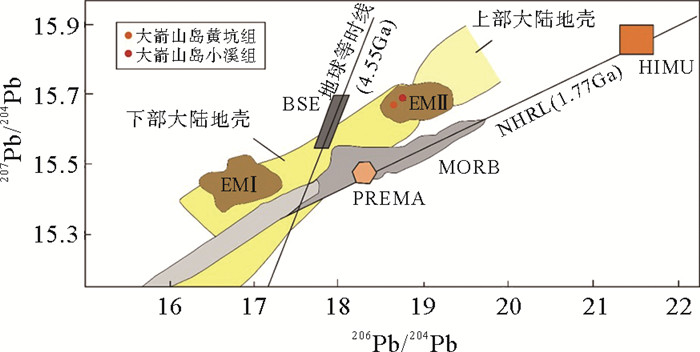
闽北近岸岛屿(大嵛山岛、浮鹰岛及东台山岛)晚中生代火山岩以凝灰岩、流纹岩类为主,偶见中基性安山岩类。大嵛山岛西北部火山岩定年结果为(100.2±1.7) Ma,可对应闽东上火山岩系石帽山群黄坑组,西部及东部火山岩定年结果为(116.7±1.5) Ma和(111.4±2.0) Ma,可对应闽东下火山岩系小溪组。主量元素结果显示该岛屿以酸性(SiO2含量>65%)火山岩为主,钾含量较高,主要为高钾钙碱性-钾玄岩。稀土元素配分图表现为轻稀土富集的右倾型特征,微量元素蛛网图表现出富集Rb、K、Pb等大离子亲石元素(LILE),亏损Ta、Nb、Ti等高场强元素(HFS),Eu负异常,具有明显的壳源特征。两阶段Nd模式年龄(T2DM)为1 401~1 327 Ma,表明岩浆可能主要来源于中元古界陆壳物质。Pb同位素特征显示与富集地幔EMⅡ存在亲缘关系,表明研究区火山岩岩浆可能主要来源于与俯冲作用有关的大陆地壳物质。小溪组和黄坑组火山岩Sr同位素初始比值(87Sr/86Sr)i分别为0.710 13~0.711 10和0.722 82,143Nd/144Nd值分别为0.512 208~0.512 214和0.512 267,ξNd(t)值分别为-6.1~-6.0和-5.2,表明两组火山岩岩浆来源存在差异,可能存在不同程度的幔源物质混合作用。结合区域构造背景认为,研究区晚中生代火山岩的形成与太平洋板块俯冲作用密切相关,具有板内及火山弧特征。
Abstract:The Late Mesozoic volcanic rocks on the offshore islands of northern Fujian are dominated by tuff and rhyolite, occasionally with mid-basic igneous rocks. The dating results of zircon suggest that the volcanic rocks in the northwest of the Dayushan Island are (100.2±1.7) Ma in age, corresponding to the upper volcanic rock series of Huangkeng Formation in east Fujian, and the western and eastern volcanic rocks are (116.7±1.5) Ma and (111.4±2.0) Ma respectively, which can be correlated to the Xiaoxi Formation of the lower volcanic series in eastern Fujian. The geochemical characteristics of the major elements show that the volcanic rocks of the area are mostly intermediate-acid (SiO2 > 65%), belonging to high potassium calcium alkaline-potassium rock series. The normalized pattern diagram of REE suggests a right-leaning pattern or light rare earth enrichment, whereas the diagram of trace elements shows the enrichment of LILE such as Rb, K, Pb, loss of HFS such as Ta, Nb, Ti, and the negative anomaly of Eu, with obvious shell source characteristics. T2DM=1 401~1 327 Ma, suggesting that the magma may have originated from the crustal material of the Mesoproterozoic.Pb isotope shows that they are related with EM Ⅱ, which indicates that the volcanic magma in the study area may be mainly originated from the continental crustal material related to subduction.The (87Sr/86Sr) of the Xiaoxi Formation and Huangkeng Formation are 0.710 13~0.711 10 and 0.722 82, 143Nd/144Nd are 0.512 208~0.512 214 and 0.512 267, ξNd(t) are -6.1~-6.0 and -5.2, suggesting that there may be mantle-derived mixing of the two groups. According to the regional tectonic setting, the Late Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the study area were formed in a plate extension environment of an active continental margin, with the characteristics of intraplate and volcanic arc.
-
Key words:
- Mesozoic volcanic rocks /
- petrogenesis /
- Dayushan Island /
- magmatic activity
-

-
图 10 207Pb/204Pb-206Pb/204Pb相关性图解(据文献[29]修改)
Figure 10.
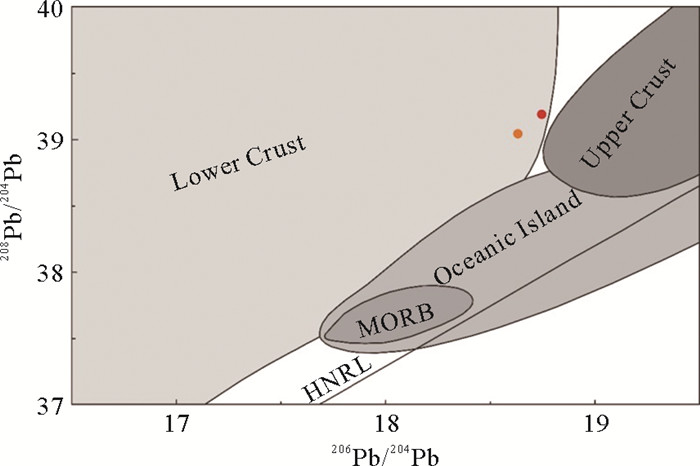
图 11 208Pb/204Pb-206Pb/204Pb相关性图解(据文献[30]修改)
Figure 11.
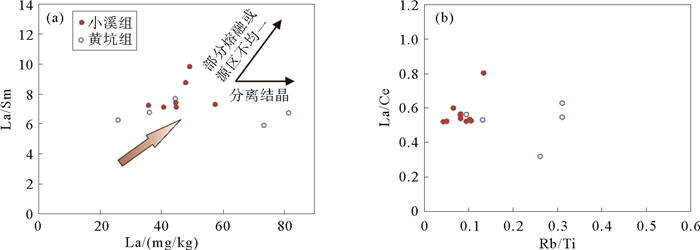
图 12 岩浆不均一性相关图解(据文献[16]修改)
Figure 12.
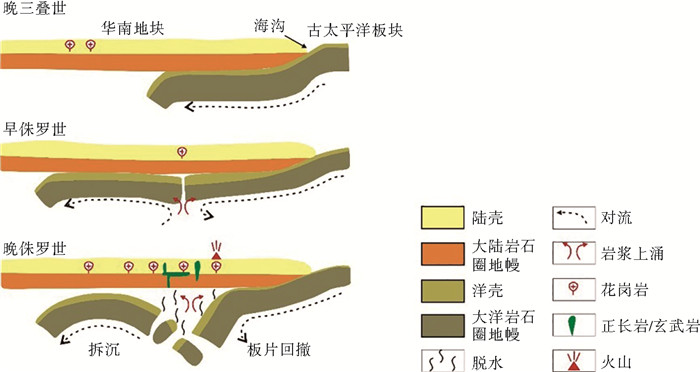
图 13 华南地区板块俯冲模式简图(据文献[34]修改)
Figure 13.
图 14 构造环境判别图(据文献[35]修改)
Figure 14.
-
[1] Wang D, Shu L. Late Mesozoic basin and range tectonics and related magmatism in Southeast China[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2012, 3(2):109-124. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2011.11.007
[2] 福建省地质矿产局.福建省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1985.
[3] 舒良树.华南构造演化的基本特征[J].地质通报, 2012, 31(7):1035-1053. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.07.003
[4] Mao J R, Li Z L, Ye H M. Mesozoic tectono-magmatic activities in South China: Retrospect and prospect[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2014, 57(12):2853-2877. doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-5006-1
[5] 宋传中, Lin S F, 周涛发, 等.长江中下游及其邻区中生代构造体制转换[J].岩石学报, 2011, 26(9):2835-2849. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201009024
[6] Yang C Q, Han B F, Yang C S. Mesozoic basin evolution of the East China Sea Shelf and tectonic system transition in Southeast China[J].Geological Journal, 2020, 55(1):239-252. doi: 10.1002/gj.3409
[7] 李三忠, 臧艺博, 王鹏程, 等.华南中生代构造转换和古太平洋俯冲启动[J].地学前缘, 2017, 24(4):213-225. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201704020
[8] 周建, 徐善法, 迟清华, 等.东南沿海中生代火山岩带地球化学特征[J].地学前缘, 2012, 19(3):93-100. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7857551
[9] Xing G F, Yang Z L, Tao K Y. Sources of Cretaceous Bimodal Volcanic Rocks in the Coastal Region of Southeastern China: Constrains of the Sr content and its isotopes [J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 1999, 73(1):84-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.1999.tb00814.x
[10] Lapierre H, Jahn B M, Charvet J, et al. Mesozoic felsic arc magmastism and continental olivine tholeiites in Zhejing province and their relationship with the tectonic activity in southeastern China[J]. Tectonophysics, 1997, 274(4):321-338. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(97)00009-7
[11] 卢清地.福建中生代火山岩岩石化学、地球化学特征及岩石成因探讨[J].福建地质, 1997(1):10-20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-FJDZ199701001.htm
[12] 高万里.浙东南中生代岩浆活动及其构造背景研究[J].北京: 中国地质科学院, 2014.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82501-1014269104.htm [13] 张岳桥.华南中生代大地构造研究新进展[J].地球学报, 2012, 33(3):257-279. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201203001
[14] 陈润生, 林东燕.福建早中生代火山作用研究进展[J].福建地质, 2006, 25(4):169-179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3970.2006.04.001
[15] Yang Z Y, Jiang S Y. Detrital zircons in metasedimentary rocks of Mayuan and Mamianshan Group from Cathaysia Block in northwestern Fujian Province, South China: New constraints on their formation ages and paleogeographic implication [J]. Precambrian Research, 2019, 320:13-30. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2018.10.004
[16] 邢光福, 陶奎元, 杨祝良, 等.中国东南沿海中生代火山岩成因研究现状与展望[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 1999, 18(3):189-193. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199900418983
[17] Medlin C C, Jowitt S M, Cas R A F, et al.Petrogenesis of the A-type, Mesoproterozoic intra-caldera rheomorphic kathleen ignimbrite and comagmatic rowland suite intrusions, West Musgrave Province, Central Australia: products of extreme fractional crystallization in a failed rift setting [J]. Journal of Petrology, 2014, 56(3):493-525. https://academic.oup.com/petrology/article/56/3/493/1602015
[18] 段政.浙闽相邻区晚中生代火山活动时序与成因研究[D].北京: 中国地质科学院, 2013.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82501-1013233504.htm [19] 邢新龙.浙闽交界地区侏罗纪—白垩纪火山活动年代学与岩石成因研究[D].成都: 成都理工大学, 2016.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10616-1016224588.htm [20] 刘磊.中国东南部晚中生代幕式火山岩浆作用及古太平洋板块俯冲机制[D].南京: 南京大学, 2015.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10284-1016003530.htm [21] Middlemost E A K.Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Annual Review of Earth & Planetary Sciences, 1994, 37(3/4):215-224. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/0012825294900299
[22] Peccerillo A, Taylor S R.Geochemistry of eocenecalc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey [J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 1976, 58(1):63-81. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00384745
[23] Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids [M]. GSA Bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643.
[24] Rollison H R.岩石地球化学[M].合肥:中国科学技术大学出版社, 2000.
[25] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[26] Chen C H, Lee C Y, Shinjo R. The epilog of the western paleo-Pacific subduction: Inferred from spatial and temporal variations and geochemistry of the Late Cretaceous to Early Cenozoic silicic magmatism in coastal South China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 115(5):520-546. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1367912015301085
[27] 颜丽丽.浙闽沿海白垩纪破火山杂岩中火山岩与侵入岩的成因联系[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1018017547.htm [28] 陈荣, 周金城.浙东早白垩世复合岩流和岩墙中蕴含的壳幔作用信息[J].地质论评, 1999, 45(S1):784-795. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199900984082
[29] 李敏.EPR和SWIR玄武岩岩石地球化学特征对比及其对岩浆过程的指示意义[D].青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10423-1014368511.htm [30] Zhao R, Wang Q F, Deng J, et al. Late Mesozoic magmatism and sedimentation in the Jiaodong Peninsula: New constraints on lithospheric thinning of the North China Craton [J].Lithos, 2018, 322: 312-324. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2018.10.020
[31] 刘凯.福建华安地区晚侏罗世南园组火山岩成因及其构造环境探讨[J].福建地质, 2017, 36(3):170-182. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3970.2017.03.002
[32] Li Z X, Li X H. Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinentalorogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China: A flat-slab subduction model[J]. Geology, 2007, 35: 179-182. doi: 10.1130/G23193A.1
[33] 李三忠, 索艳慧, 李玺瑶, 等.西太平洋中生代板块俯冲过程与东亚洋陆过渡带构造-岩浆响应[J].科学通报, 2018, 63(16):1550-1593. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201816006
[34] Li S Z, Suo Y H, Li X Y, et al. Mesozoic tectono-magmatic response in the East Asian ocean-continent connection zone to subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Plate [J].Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 192: 91-137. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.03.003
[35] Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace Element Discrimination Diagrams for the Tectonic Interpretation of Granitic Rocks [J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4):956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
[36] 秦社彩.浙闽白垩纪镁铁质火山岩地球化学特征及其深部动力学意义[D].广州: 中国科学院研究生院(广州地球化学研究所), 2007.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-80165-2007101599.htm -



 下载:
下载: