GENESIS OF THE DOLOMITE IN THE SHAHEJIE FORMATION OF JZ OILFIELD, BOHAI BASIN
-
摘要:
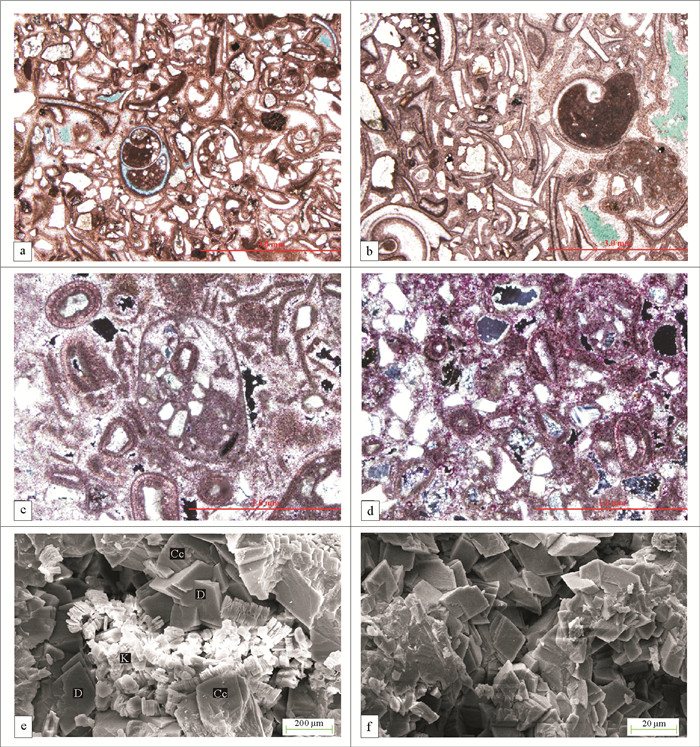
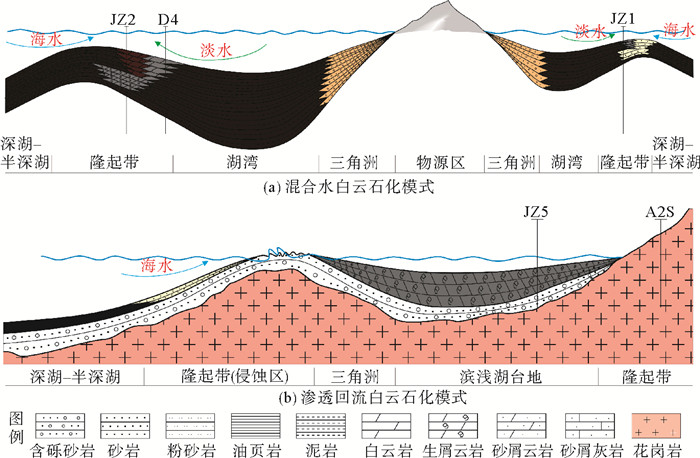
研究区以生屑白云岩及含砂屑的鲕粒白云岩为主,相邻井区白云岩类型及厚度变化大。为确定各类白云岩的成因,通过孢粉及微体古生物化石、碳氧同位素、微量元素B含量等分析手段,对本区的古气候、古环境、古沉积介质的物理化学性质进行系统地分析,自沙三段以来,由温暖的亚热带气候变得逐渐干燥,水体逐渐咸化,为白云岩的形成提供了必要条件。具有硬的基底的滨浅湖台地,水体能长期保持清澈,有利于底栖生物生长繁殖,适宜碳酸盐岩的形成、沉积了巨厚的生屑白云岩,其生屑含量高、孔隙较发育、方解石也被交代的更加彻底,建立了该类白云岩滨浅湖台地渗透回流成因模式。滨浅湖隆起带区域,淡水与咸水在此交汇,易形成具雾心亮边的粉晶白云岩和具有同心圆结构的鲕粒云岩或生物碎屑云岩,但常常白云石化不彻底,方解石含量高,个别井段甚至发育云质鲕粒灰岩,建立了该类白云岩滨浅湖隆起带混合水成因模式。此研究丰富了湖相白云岩成因模式,对渤海湾盆地碳酸盐岩的勘探具有重要的指导意义。
Abstract:Bioclastic dolomite and sand-bearing oolitic dolomite are widely distributed in the study area. Drilling shows that the lithology and thickness of dolomite vary greatly from well to well. In order to reveal the genesis of the dolomite, the physical and chemical properties of the depositional media, paleoclimate and paleoenvironment of the area are systematically studied by means of sporopollen and micro paleontology, carbon and oxygen isotopes and trace element B. It is found that since the 3rd Member of the Shahejie Formation, warm subtropical climate had gradually turned to dry, and the water body become salty, which provided basic conditions for the dolomite to form. On the nearshore and shallow lake platform with hard basement, however, water was clean, which was in favor of the growth and reproduction of benthic organisms and the formation of limestone and bioclastic dolomite with huge thickness. As the bioclastic content is high, pores are well developed, and the calcite is also more thoroughly replaced by dolomite. Upon the basis, a seepage reflux model for such kind of dolomite platform is established by the authors. In the uplifting zone of the nearshore and shallow parts of the lake, where fresh and saline water mixed, it is easy to form the silty dolomite with sparry edge and cloudy nucleus and the oolitic dolomite or bioclastic dolomite with concentric structure. However, dolomitization is often incomplete, calcite content is high sometimes, and therefore dolomitic oolitic limestone is common in some wells. For these dolomitic deposits, a genetic model of mixed water is proposed specially for nearshore-shallow lake uplift zones. The genetic models of lacustrine dolomite are of important significance for hydrocarbon exploration in carbonate rocks in Bohai Bay Basin.
-
Key words:
- bioclastic dolomite /
- genesis of dolomite /
- sedimentary model /
- Shahejie Formation
-

-
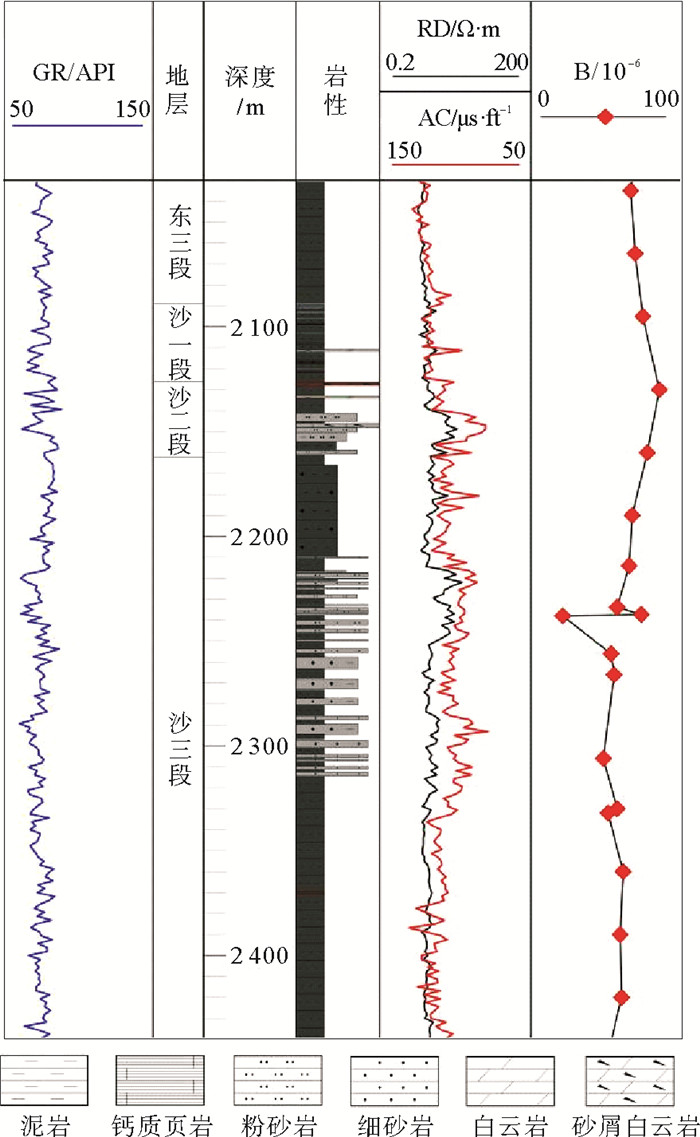
表 1 辽东湾坳陷辽西低凸起地区沙河街组碳酸盐岩碳、氧同位素分析数据
Table 1. Carbon and oxygen isotopic data of the Shahejie Formation carbonate rocks in Liaoxi low uplift area of Liaodongwan Depression
样品号 岩性 井深/
m层位 δ13CPDB/
‰δ18OPDB/
‰古盐度
指数Z古温度
T/℃古盐度
S/‰1 陆屑白云岩 2 234.3 E2s3 12.26 -12.66 146.10 93.83 14.00 2 生屑白云岩 1 877.35 E2s1 3.86 -15.58 127.45 116.24 9.21 3 生屑白云岩 1 639.68 E3s1 6.1 -14.5 132.57 107.77 10.98 4 生屑白云岩 2 047.2 E3s1 2.37 -13.1 125.63 97.17 13.28 5 生屑白云岩 2 341.0 E3s2 1.02 -4.89 126.95 43.25 26.74 6 陆屑灰岩 2 224.7 E3s2 8.35 -10.53 139.16 78.70 17.49 注:古盐度指数Z=2.048×(δ13CPDB+50)+0.498×(δ18OPDB+50);古盐度S=(δ18OPDB+21.2)/0.61;古温度T=16.9-4.38×(δC-δw)+0.10×(δC-δw)2,其中δC=41.2,δw=40.93+1.04093×δ18OPDB。 -
[1] 姚益民, 梁鸿德, 蔡治国, 等.中国油气区第三系(Ⅳ)渤海湾盆地油气区分册[M].北京:石油工业出版社. 1994: 1-240.
[2] 彭世福, 许红, 温珍河.试论渤海湾盆地沙河街组海侵作用与油气[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1989, 9(1):17-28.
[3] 袁文芳, 陈世悦, 曾昌民, 等.渤海湾盆地东营凹陷古近纪Paleodictyon遗迹化石的发现及其意义[J].地质科学, 2007, 42(4):779-786. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2007.04.012
[4] 孙钰, 钟建华, 袁向春.惠民凹陷沙河街组一段白云岩特征及其成因分析[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 2007, 27(3):78-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2007.03.011
[5] 南山, 韩雪芳, 潘玲黎, 等.辽东湾海域锦州20-2气田沙河街组沉积相研究[J].岩性油气藏, 2013, 25(3):36-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2013.03.006
[6] 赵俊青, 夏斌, 纪友亮, 等.湖相碳酸盐岩高精度层序地层学探析[J].沉积学报, 2005, 23(4):646-656. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.04.013
[7] 戴朝成, 郑荣才, 文华国, 等.辽东湾盆地沙河街组湖相白云岩成因研究[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 35(2):187-193. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2008.02.014
[8] 曲长伟, 林春明, 蔡明俊, 等.渤海湾盆地北塘凹陷古近系沙河街组三段白云岩储层特征[J].地质学报, 2014, 88(8):1588-1602. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201408019
[9] 潘文静, 王清斌, 刘士磊, 等.渤海海域石臼坨地区古近系沙河街组湖相生屑白云岩成因[J].古地理学报, 2017, 19(5):835-848. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gdlxb201705006
[10] 徐长贵, 于水, 林畅松, 等.渤海海域古近系湖盆边缘构造样式及其对沉积层序的控制作用[J].古地理学报, 2008, 10(6):627-635. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gdlxb200806008
[11] 徐长贵, 许效松, 丘东洲, 等.辽东湾地区辽西凹陷中南部古近系构造格架与层序地层格架及古地理分析[J].古地理学报, 2005, 7(4):449-459. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2005.04.003
[12] 常艳艳, 林畅松, 周心怀, 等.辽西凹陷北洼沙河街组沉积层序结构与有利砂体分布[J].地球科学, 2014, 39(10):1371-1380. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201410009
[13] 朱筱敏, 董艳蕾, 杨俊生, 等, 于水.辽东湾地区古近系层序地层格架与沉积体系分布[J].中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 2008, 38(S1):1-10. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd2008z1001
[14] 冯增昭, 王英华, 刘焕杰, 等.中国沉积学[M].北京: 石油工业出版社, 1994: 105-127, 623-631, 662-685.
[15] 刘士磊, 王启飞, 龚莹杰, 等.渤海海域古近纪微体化石组合特征及油气勘探意义[J].地层学杂志, 2012, 36(4):700-709. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DCXZ201204004.htm
[16] 项华, 周心怀, 任志勇, 等.渤海湾盆地锦州JZ25-1南地区古近纪生物组合及地层特征[J].微体古生物学报, 2005, 22(3):322-328. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0674.2005.03.012
[17] 张葳, 李智武, 冯逢, 等.川中东北部中—下侏罗统湖相碳酸盐岩碳氧同位素特征及其古环境意义[J].古地理学报, 2013, 15(2):247-259. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/gdlxb201302008
[18] 曹姝璐, 朱志军, 刘腾, 等.信江盆地白垩纪周田组碳、氧同位素特征及意义[J].四川地质学报, 2016, 36(3):506-509. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2016.03.035
[19] 贾鹏, 李伟, 李明, 等.四川盆地东部地区寒武系洗象池群碳酸盐岩碳、氧同位素特征及其意义[J].古地理学报, 2017, 19(3):503-512. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gdlxb201703010
[20] Urey H C.Oxygen iIsotopes in nature and in the laboratory [J]. Science, 1948, 108(2810):489-496. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2810.489
[21] Epstein S, Mayeda T. Variation of O18 content of waters from natural sources [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1953, 4(5):213-224. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(53)90051-9
[22] Shackleton N J. Attainment of isotopic equilibrium between ocean water and the benthonic foraminifera genus Uvigerina: isotopic changes in the ocean during the last glacial [J]. Colloques Internationaux du Centre National de Recherche Scientifique, 1974, 219: 203-209. https://epic.awi.de/32862/
[23] Keith M L, Weber J N. Carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of selected limestones and fossils [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1964, 28(10/11):1787-1816. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0016703764900225
[24] Weber J N, Williams E G, Keith M L. Paleoenvironmental significance of carbon isotopic composition of siderite nodules in some shales of Pennsylvanian age [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1964, 34(4):814-818. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/sepm/jsedres/article-abstract/34/4/814/95786/Paleoenvironmental-significance-of-carbon-isotopic
[25] 张秀莲.碳酸盐岩中氧、碳稳定同位素与古盐度、古水温的关系[J].沉积学报, 1985, 3(4):17-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1985-CJXB198504001.htm
[26] 刘策, 曹颖辉, 周波, 等.古城地区中下奥陶统白云岩碳氧同位素特征及成因[J].特种油气藏, 2017, 24(2):30-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2017.02.006
[27] 任影, 钟大康, 高崇龙, 等.四川盆地东部下寒武统龙王庙组碳、氧同位素组成及古环境意义[J].海相油气地质, 2016, 21(4):11-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2016.04.002
[28] 王永炜, 李荣西, 高胜利, 等.渤海湾盆地黄骅坳陷湖相碳酸盐岩微量元素特征及沉积环境[J].石油实验地质, 2017, 39(6):849-857. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sysydz201706017
[29] 赫云兰, 刘波, 秦善.白云石化机理与白云岩成因问题研究[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 46(6):1010-1020. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bjdxxb201006021
[30] 江青春, 胡素云, 汪泽成, 等.四川盆地中二叠统中-粗晶白云岩成因[J].石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(4):503-510. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syytrqdz201404009
[31] 胡作维, 黄思静, 张超, 等.碳酸盐白云化作用模式研究进展[J].海洋地质前沿, 2010, 27(10):1-13. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt201110001
[32] Eugster H P. Geochemistry of evaporitic lacustrine deposits [J]. Annual Review of Earth & Planetary Sciences, 1980, 8(1):35-63. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1146-annurev.ea.08.050180.000343/
[33] Badiozamani K. The dorag dolomitization modelapplication to the Middle Ordovician of Wisconsin[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1973, 43(4):965-984. https://www.crossref.org/iPage?doi=10.1306%2F74D728C9-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
[34] Adams J F, Rhodes M L. Dolomitization by seepage refluxion [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1960, 44:1912-1920. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1109-TIFS.2011.2162585/
-




 下载:
下载: