KEY TECHNOLOGY FOR EXPLORATION OF COMPLEX PRESALT TRAPS IN THE DEEP WATERS OF GABON BASIN, WEST AFRICA
-
摘要:
近年来,以西非、墨西哥湾等为代表的全球深水盐下油气勘探日趋活跃,而构造落实一直是盐下勘探面临的主要难题,亟需形成一套有效的盐下圈闭落实技术方法。以加蓬某区为研究靶区,基于盐下地震成像特点,剖析盐下圈闭落实难点,再从盐岩形变机制分析入手,探索形成了一套复杂盐下圈闭落实关键技术组合,主要包括:①基于盐岩形变机制建立构造解释模型;②以脏盐体精细识别技术为核心的盐下层位解释技术;③利用重-磁-震资料联合,开展盐下断裂多尺度综合解释;④基于波动方程正演的构造假象识别技术。通过实践应用,在研究区内有效落实多个盐下圈闭,其中的M圈闭钻探证实为盐下大气田。形成的技术体系能够辅助解决盐下构造落实难题,可为西非及其他区域类似问题提供参考。
Abstract:In recent years, global deepwater oil and gas exploration, as demonstrated by West Africa and the Gulf of Mexico, has become increasingly active. Verification of structures is always the key problem in salt basin exploration. Therefore, it really is a great need to develop a set of technology for trap identification to support the exploration of oil and gas under salt cap in the deep water of Gabon Basin. Based on the studies of the mechanisms of salt rock deformation and its impacts on seismic imaging, a set of key technology is proposed in this paper. It includes: ①Establishment of interpretation models for structures based on the mechanism of salt rock deformation; ②Introducing the technique for pre-salt seismic horizon interpretation based on the fine recognition of dirty salt bodies; ③Integration of gravity, magnetic and seismic data for multiscale comprehensive interpretation of pre-salt faults; ④Adoption of the method for distinguishing false images from the real based on wave equation forward modeling. Using the method, a series of pre-salt traps are effectively identified in the research area, and drilling proves that the M trap is a large pre-salt gas field. It is concluded that the technical system proposed can help solve the problem of the verification of pre-salt structures, which can be used as a reference for similar oil fields in West Africa and other regions.
-

-
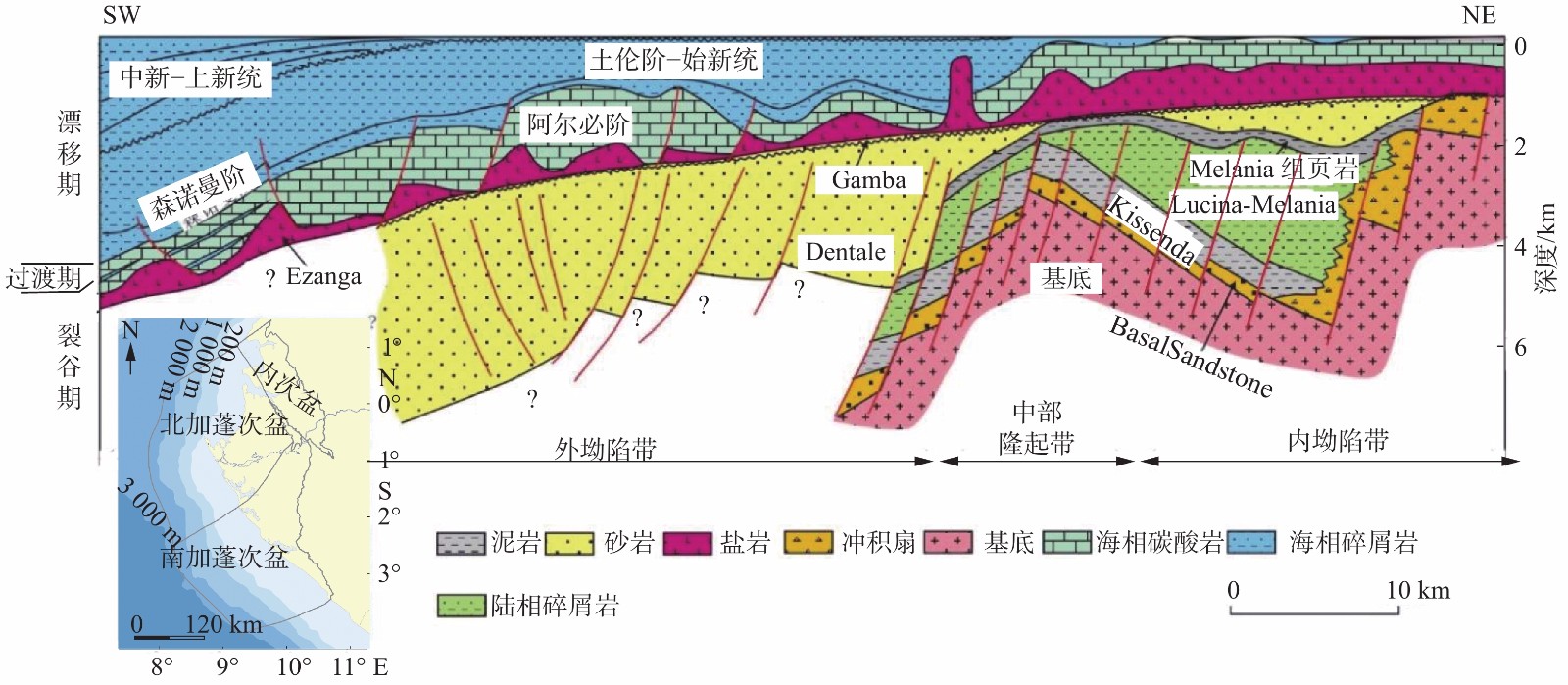
图 1 加蓬盆地地质剖面图[16]
Figure 1.
表 1 研究区主要盐构造解释模型
Table 1. Main salt-structural models of the study area
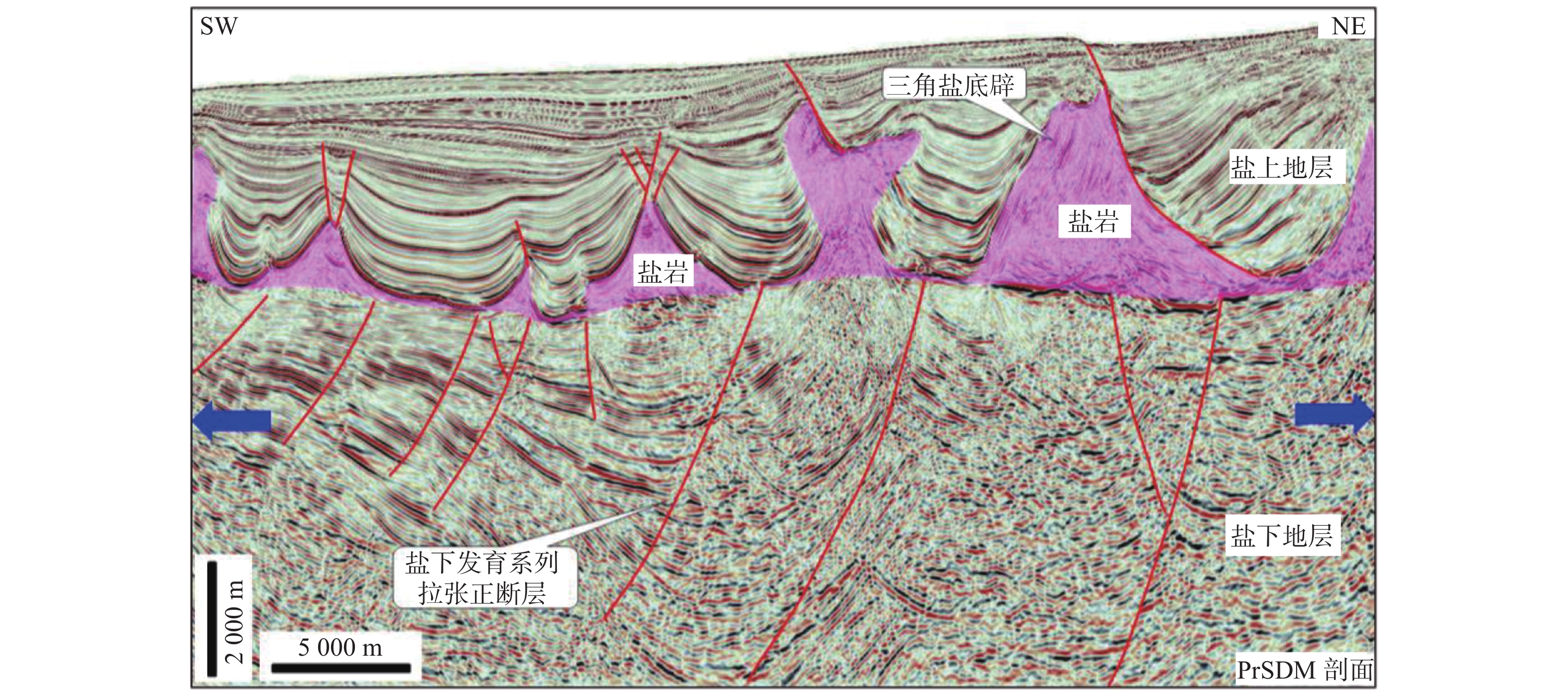
盐构造模型 构造解释实例 对盐下构造解释指导意义 三角底辟 
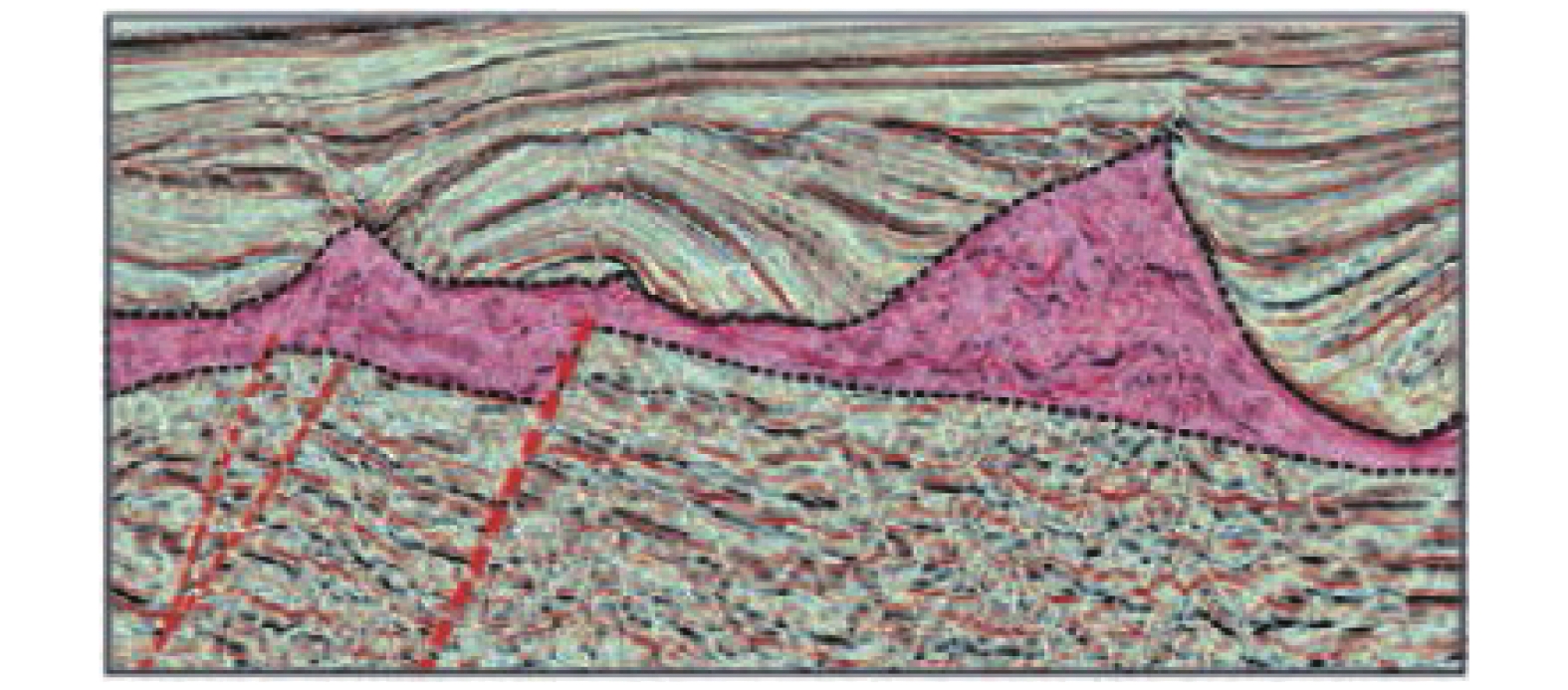
三角底辟通常指示盐下发育拉张作用,可以指导盐下正断层解释 盐焊、盐窗 

盐焊接、盐窗区盐上、盐下构造变形耦合性较好,可通过盐岩及盐上构造特征指导盐下构造解释 盐背斜 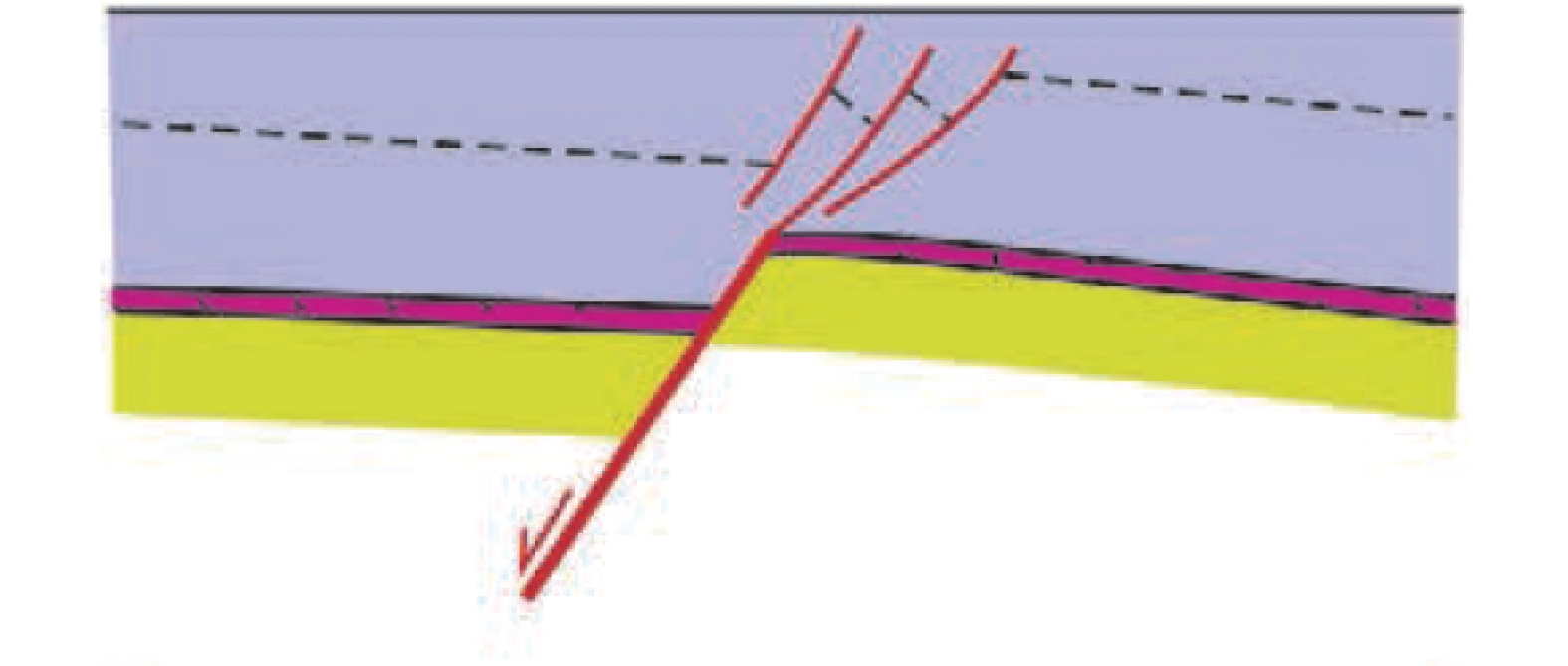

盐上、盐下构造变形耦合性较好,可以通过盐岩及盐上构造特征指导盐下构造解释 坡-坪式滑脱 

盐岩沿坡-坪式底板滑脱时,倾向于在断坡顶部发生底辟作用。该类盐构造可以指导盐下(断)坡-坪构造解释 推覆滑脱 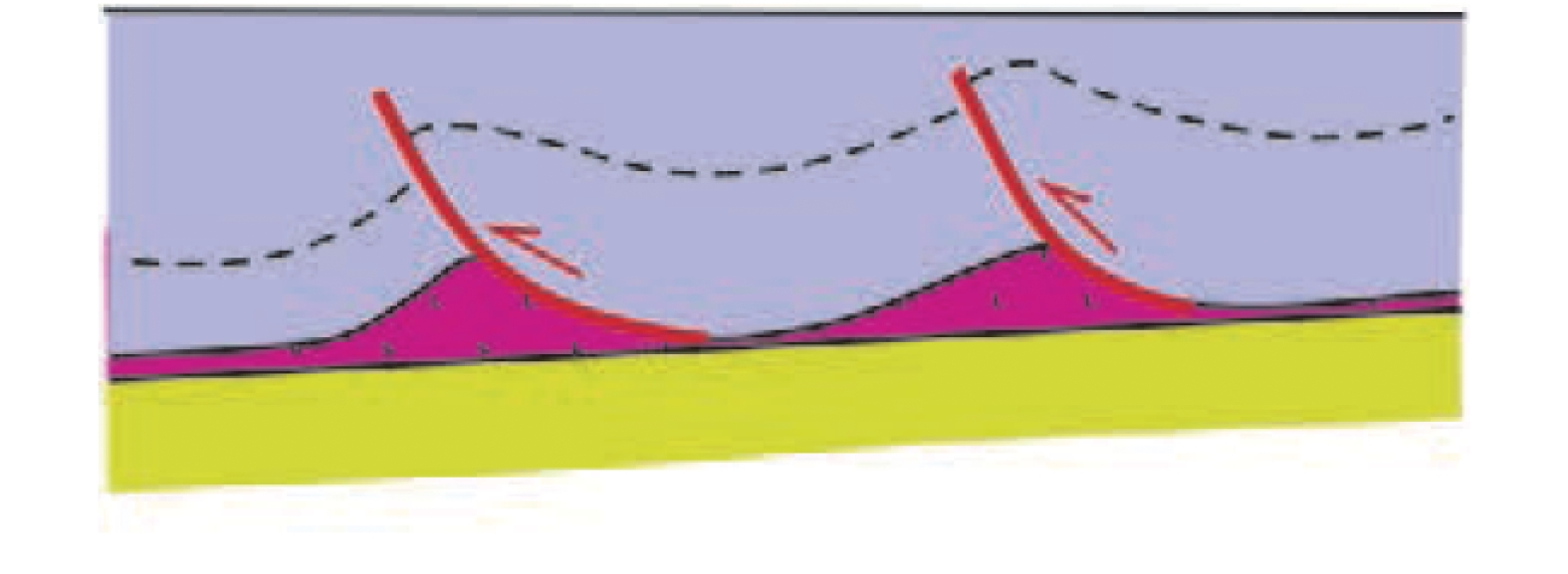

挤压作用形成沿盐岩滑脱的逆冲推覆构造,并在逆冲断层下盘形成盐底辟;可通过对盐上推覆构造的分析辅助构造复杂区盐岩识别及盐底解释 表 2 研究区Ezanga组内部主要岩性单元地震响应特征综合识别图版
Table 2. Seismic response characteristics of main lithologic units in Ezanga Formation
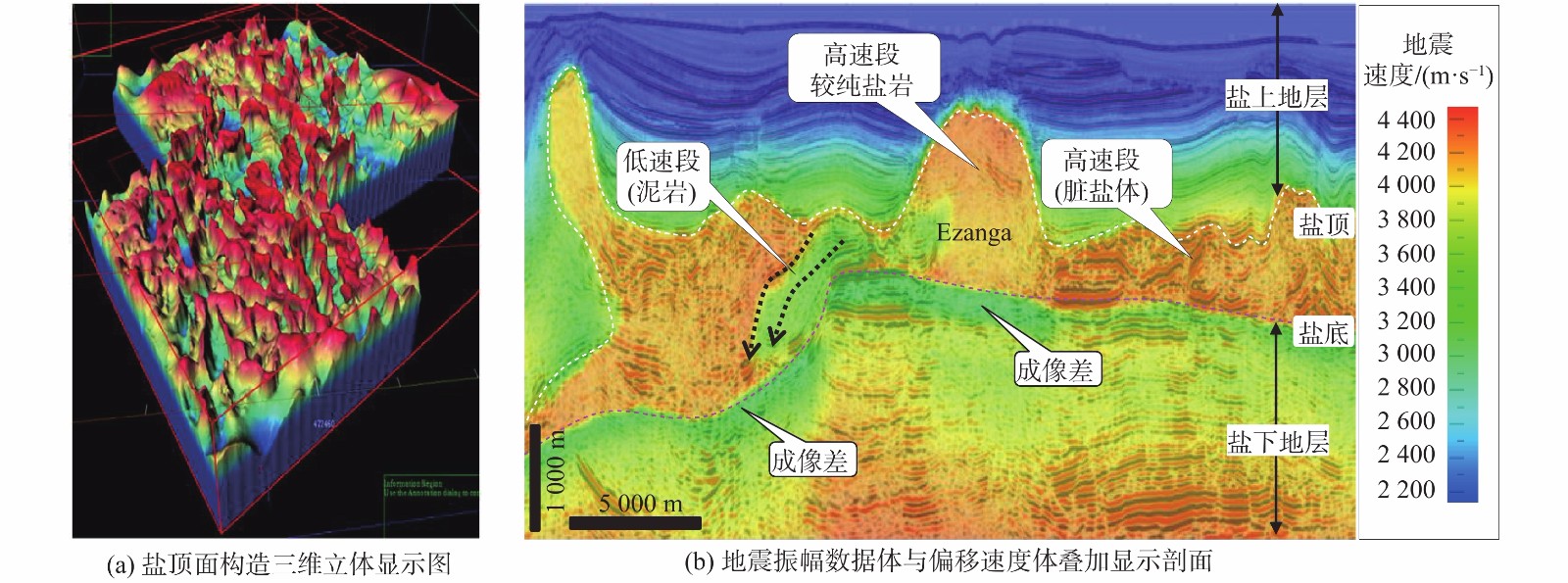
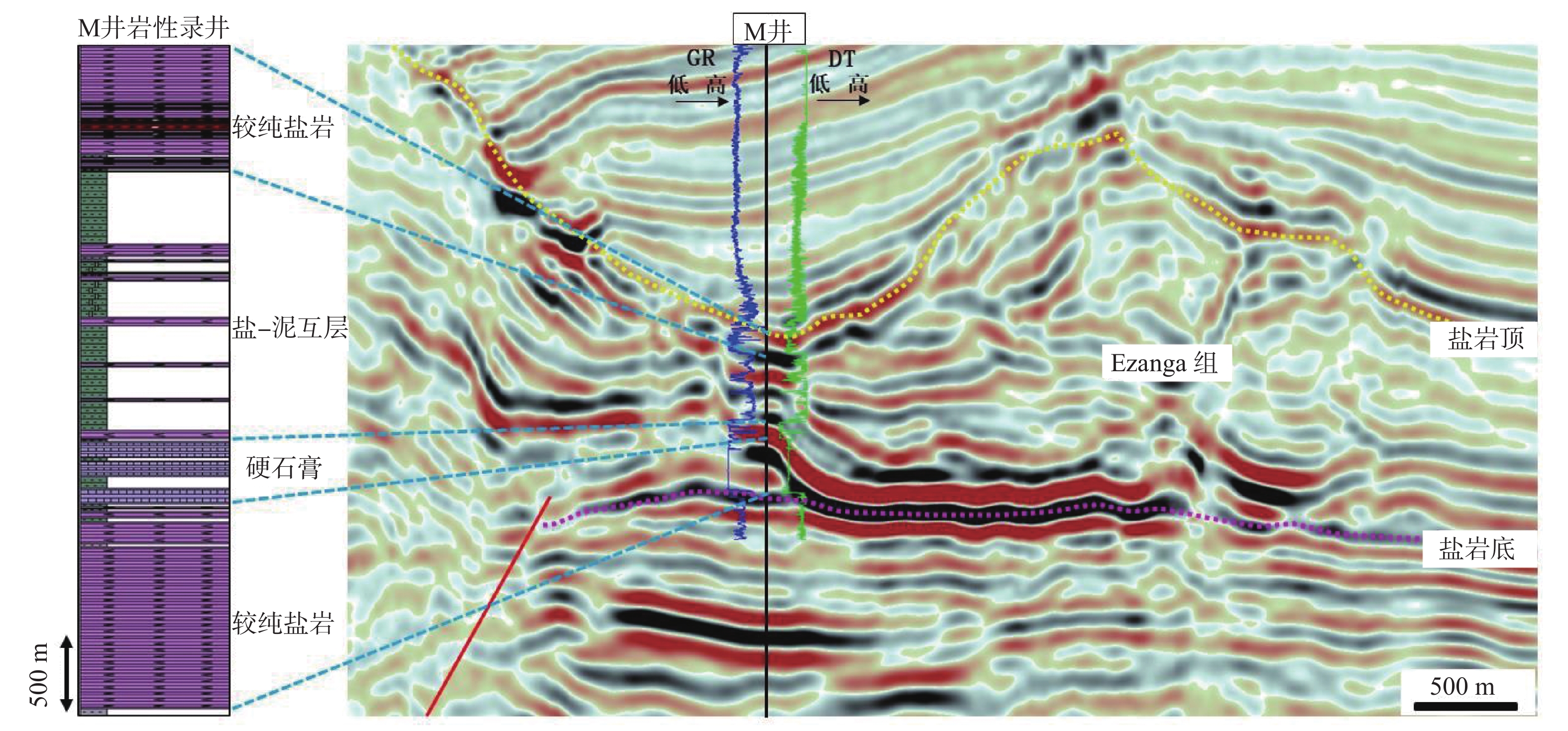
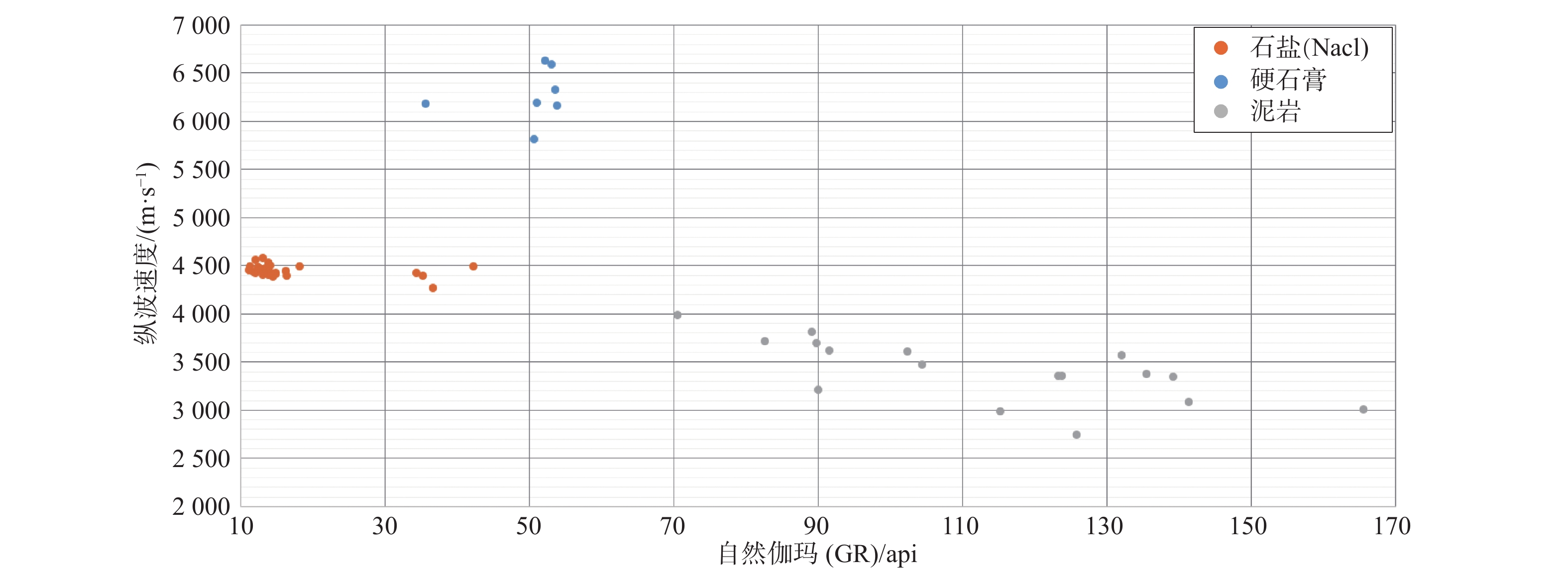
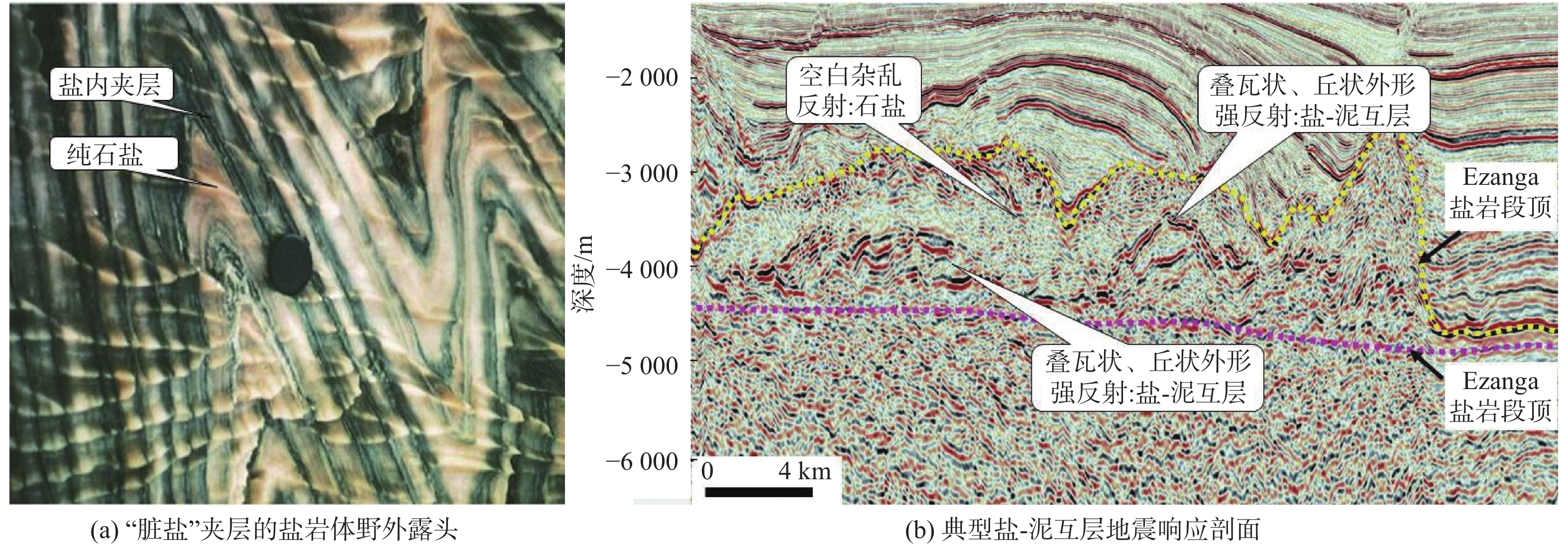
类别 岩性 地震速度/(m·s−1) 典型地震相 I 较纯盐岩 高速>4 000 空白—杂乱反射 II 盐-泥互层 中—低速2 600~3 800 成层状连续—断续中强反射,局部可见扭曲变形 Ⅲ 硬石膏 超高速5 800~6 800 成层状极强振幅反射 Ⅳ 脏盐 中—低速2 600~3 700 叠瓦状—丘状外形强反射 -
[1] 刘东周,窦立荣,郝银全,等. 滨里海盆地东部盐下成藏主控因素及勘探思路[J]. 海相油气地质,2004,19(1):53-58.
[2] 梁杰,杨艳秋,龚建明,等. 墨西哥湾深水油气勘探对我国的启示[J]. 海洋地质动态,2009,25(1):17-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2009.01.004
[3] 赵阳,卢景美,刘学考,等. 墨西哥湾深水油气勘探研究特点与发展趋势[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2014,30(6):27-32.
[4] 程涛,康洪全,白博,等. 巴西桑托斯盆地盐下湖相碳酸盐岩勘探关键技术及其应用[J]. 中国海上油气,2018,30(4):27-35.
[5] 梁顺军,梁霄,杨晓,等. 地震勘探技术发展在库车前陆盆地潜伏背斜气田群发现中的实践与意义[J]. 中国石油勘探,2016,21(6):98-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2016.06.0013
[6] 梁顺军,雷开强,王静,等. 库车坳陷大北—克深砾石区地震攻关与天然气勘探突破[J]. 中国石油勘探,2014,19(5):49-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2014.05.005
[7] 杨海军,李勇,唐雁刚,等. 塔里木盆地克拉苏盐下深层大气田的发现[J]. 新疆石油地质,2019,40(1):12-20.
[8] MUERDTER D,RATCLIFF D. Understanding subsalt illumination through ray-trace modeling,Part 1:Simple 2-D salt models[J]. The Leading Edge,2001,20(6):578-594. doi: 10.1190/1.1438998
[9] MUERDTER D,RATCLIFF D. Understanding subsalt illumination through ray-trace modeling,Part 2:Dipping salt bodies,salt peaks,and nonreciprocity of subsalt amplitude response[J]. The Leading Edge,2001,20(7):688-697. doi: 10.1190/1.1487279
[10] MUERDTER D,RATCLIFF D. Understanding subsalt illumination through ray-trace modeling,Part 3:Salt ridges and furrows,and the impact of acquisition orientation[J]. The Leading Edge,2001,20(8):803-816. doi: 10.1190/1.1487289
[11] 阳怀忠,邓运华,黄兴文,等. 西非加蓬盆地深水盐下油气勘探技术创新与实践[J]. 中国海上油气,2018,30(4):1-12.
[12] 梁瀚,马波,肖柏夷,等. 基于构造变形约束的川东寒武系膏盐层分布[J]. 古地理学报,2019,21(5):825-834. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2019.05.056
[13] 卞青,陈琰,张国卿,等. 柴达木盆地膏盐层岩石物理特征及其对构造变形的影响[J]. 石油学报,2020,41(2):197-204. doi: 10.7623/syxb202002005
[14] 代双河,高军,臧殿光,等. 滨里海盆地东缘巨厚盐岩区盐下构造的解释方法研究[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2006,41(3):303-307. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7210.2006.03.014
[15] 李明刚. 桑托斯盆地盐下裂谷系构造特征及圈闭发育模式[J]. 断块油气田,2017,24(5):608-612.
[16] TEISSERENC P, VILLEMIN J. Sedimentary Basin of Gabon-Geology and Oil Systems [M]// Edwards J D, Santogrossi P A. Divergent/Passive Margin Basins. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Memoir, 1989, 46: 117-199.
[17] 戈红星,JACKSON M P A. 盐构造与油气圈闭及其综合利用[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版),1996,32(4):640-647. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0469-5097.1996.04.001
[18] 余一欣,周心怀,彭文绪,等. 盐构造研究进展述评[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2011,35(2):169-182. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2011.02.001
[19] 赵鹏,王英民,周瑾,等. 西非被动大陆边缘盐构造样式与成因机制[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2013,29(10):14-22.
-



 下载:
下载: