SEDIMENTARY EVOLUTION OF RIFT BASINS IN SULAWESI ISLAND REGION, INDONESIA AND ITS CONTROLS ON HYDROCARBON GEOLOGICAL CONDITIONS
-
摘要:
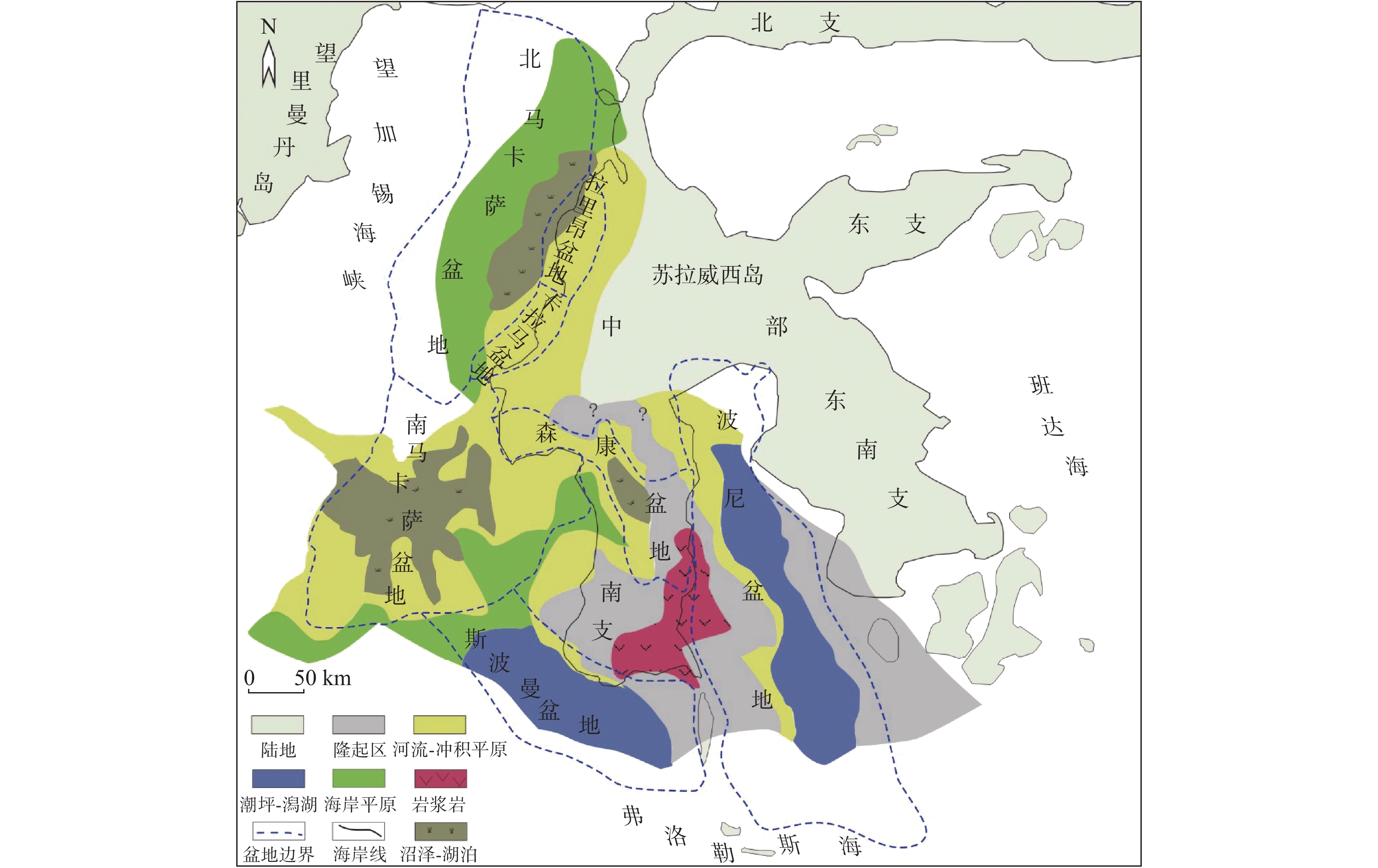
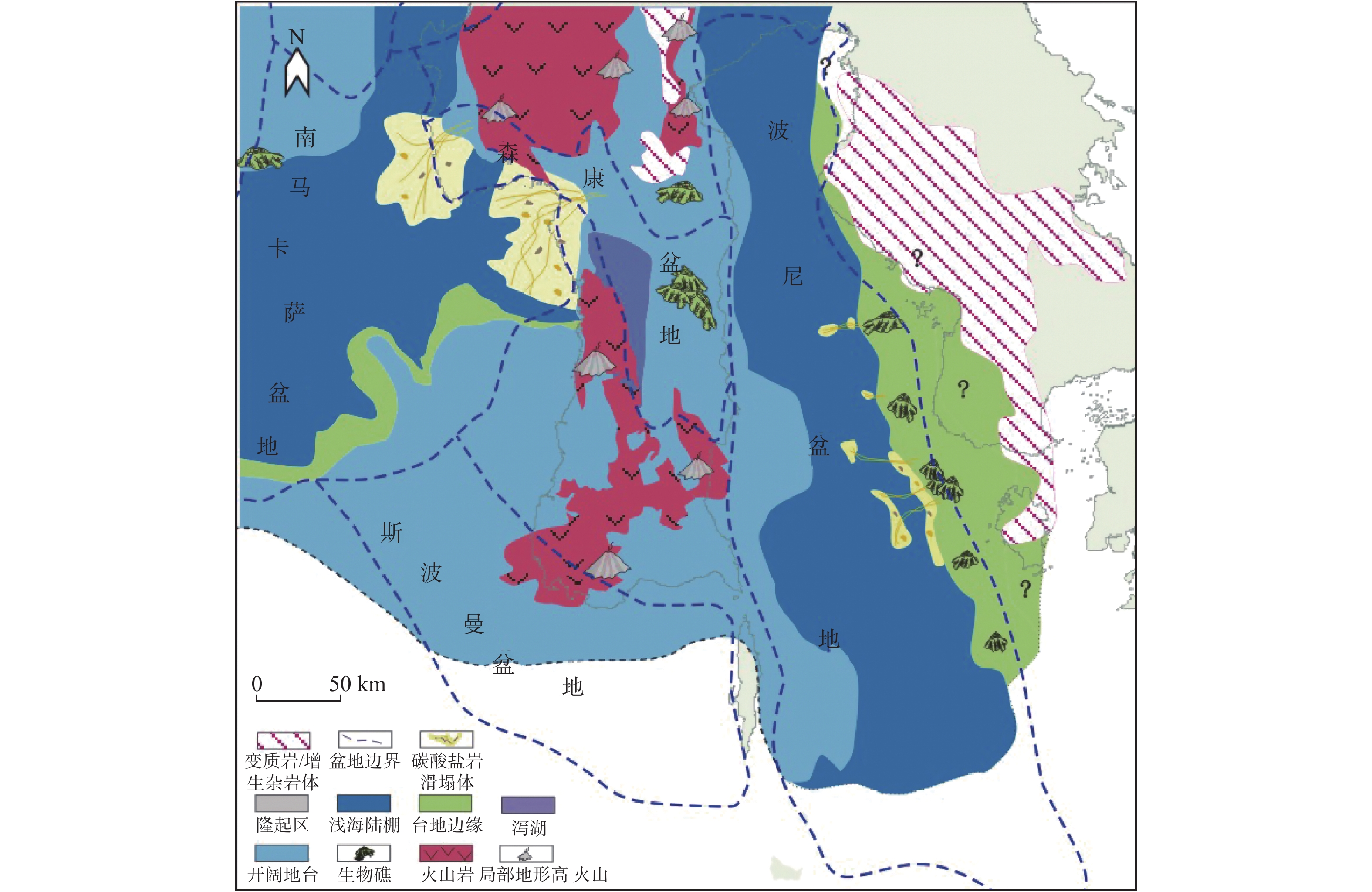
为了揭示印度尼西亚苏拉威西岛周缘裂谷盆地油气地质条件的差异性,有效指导该区的油气勘探,在综合现有勘探研究成果的基础上,从构造演化分析入手,系统分析了该区沉积演化特征及其对烃源岩和储盖组合的控制作用。结果表明,古新世—始新世的沉积相带控制了有效烃源岩的岩性和发育区,在断陷处形成了湖沼相、潮坪—潟湖相泥岩、煤系等类型的烃源岩;不同时期差异性的沉积充填形成2类储盖组合;苏拉威西地区西部河流—三角洲相控制形成了物性良好的碎屑岩储盖组合。晚中新世—上新世,台地—陆棚相控制形成了区域内最为重要的碳酸盐岩储盖组合,尤其台地和台地边缘的生物礁储层,物性优良,已获得重要发现,是今后该区油气勘探的重点关注目标。
Abstract:Sedimentary evolution characteristics of the rift basins in the Sulawesi Island Region and their effects on source rocks and reservoir-cap associations are studied comprehensively by this paper, in order to reveal the hydrocarbon accumulation conditions. The results suggest that the sedimentary facies of the Paleocene to Eocene controlled the lithology and distribution pattern of effective hydrocarbon source rocks. The source rocks are dominated by mudstone and coal of lacustrine to swamp facies with tidal flat and lagoon facies found in sags. There are two kinds of reservoir-cap associations. The Paleocene and Eocene river-delta facies in the west part of Sulawesi formed the clastic rock association with good petrophysical properties, while the Late Miocene to Pliocene shelf platform facies formed the most important carbonate rock association. Especially, the reef reservoirs with excellent properties occur on the platform or the border of platform. So far important discoveries have been made in the rift basins which has become the most important target for oil and gas exploration.
-
Key words:
- hydrocarbon geological conditions /
- sedimentary evolution /
- Cenozoic /
- rift basin /
- Sulawesi
-

-
图 3 苏拉威西地区裂谷盆地地质结构剖面(剖面位置见图1)
Figure 3.
-
[1] HALL R. Plate tectonic reconstruction of the Indonesian region[C]//Proceedings Indonesian Petroleum Association 24th Annual Convention, 1995(1): 71-84.
[2] SUDARMONO. Tectonic and stratigraphic evolution of the Bone Basin, Indonesia: insights to the Sulawesi collision complex[C]//Indonesia Petroleum Association 27th Annual Convention Proceedings, Jakarta, 1999: 713-725.
[3] CAMPLIN D J,HALL R. Neogene history of Bone Gulf,Sulawesi,Indonesia[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2014,57:88-108. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.04.014
[4] CALVERT S J,HALL R. Cenozoic evolution of the Lariang and Karama Regions,North Makassar Basin,Western Sulawesi,Indonesia[J]. Petroleum Geoscience,2007,13:353-368. doi: 10.1144/1354-079306-757
[5] WILSON M,MOSS S J. Cenozoic palaeogeographic evolution of Sulawesi and Borneo[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,1999,145:303-337.
[6] 杜宏宇,方勇,袭著纲,等. 印尼苏拉维西地区波尼盆地形成及其石油地质特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2019,35(10):49-55.
[7] COFFIELD D Q, BERGMAN S C, GARRARD R A, et al. Tectonic and stratigraphic evolution of the Kalosi PSC Area and associated development of a tertiary petroleum system, South Sulawesi, Indonesia[C]//Indonesia Petroleum Association 22nd Annual Convention Proceedings, Jakarta, 1993: 679-706.
[8] NEGRO R D, CASTELLANO P, KUHFUSS A, et al. Structural styles and petroleum system modeling of the North Makassar Straits, Indonesia[C]//Indonesia Petroleum Association 37th Annual Convention Proceedings, Jakarta, 2013: 799-818.
[9] GADJAH E P, DARDJI N D, Petroleum system overview of the Sebuku Block and the Surrounding Area: potential as a new oil and gas province in South Makassar Basin, Makassar Straits[C]// Indonesia Petroleum Association 34th Annual Convention Proceedings, Jakarta, 2010: 1099-1114.
[10] ARIYONO D, KUPECZ J, SAYERS I, et al, Generation and expulsion from Middle Eocene source in the South Makassar Basin, Indonesia[C]//Indonesian Petroleum Association. Proceedings of 37th Annual Convention. Jakarta: Indonesian Petroleum Asociation, 2013: 1343-1362.
[11] HALL R,CLOKE I R,NURAINI S,et al. The North Makassar Straits:what lies beneath?[J]. Petroleum Geoscience,2009,15:147-158. doi: 10.1144/1354-079309-829
[12] NUR’AINI S, HALL R, ELDERS C F. Basement architecture and sedimentary fill of the North Makassar Straits Basin[C]//Indonesia Petroleum Association 30th Annual Convention Proceedings, Jakarta, 2005: 483-497.
[13] 袭著纲,胡孝林,方勇,等. 印度尼西亚苏拉威西地区新生代盆地烃源岩特征[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2017,39(2):267-274. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2017.02.011
[14] GRAINGE A M, DAVIES K G. Reef exploration in the East Sengkang Basin, Sulawesi[C]//Indonesia Petroleum Association 12th Annual Convention Proceedings, Jakarta, 1983.
[15] 张强,吕福亮,毛超林,等. 印度尼西亚库泰盆地油气地质特征及勘探方向[J]. 海相油气地质,2012,17(4):8-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2012.04.002
[16] 李冬,胡孝林,郭刚,等. 印度尼西亚库泰盆地沉积演化与油气勘探潜力分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2015,35(6):127-131.
-




 下载:
下载: