NEOGENE HYDROCARBON MIGRATION AND INSPIRATION IN THE GENTLE SLOPE BELT, SOUTHERN BOHAI SEA: A CASE FROM KENLI 9 OILFIELD GROUP
-
摘要:
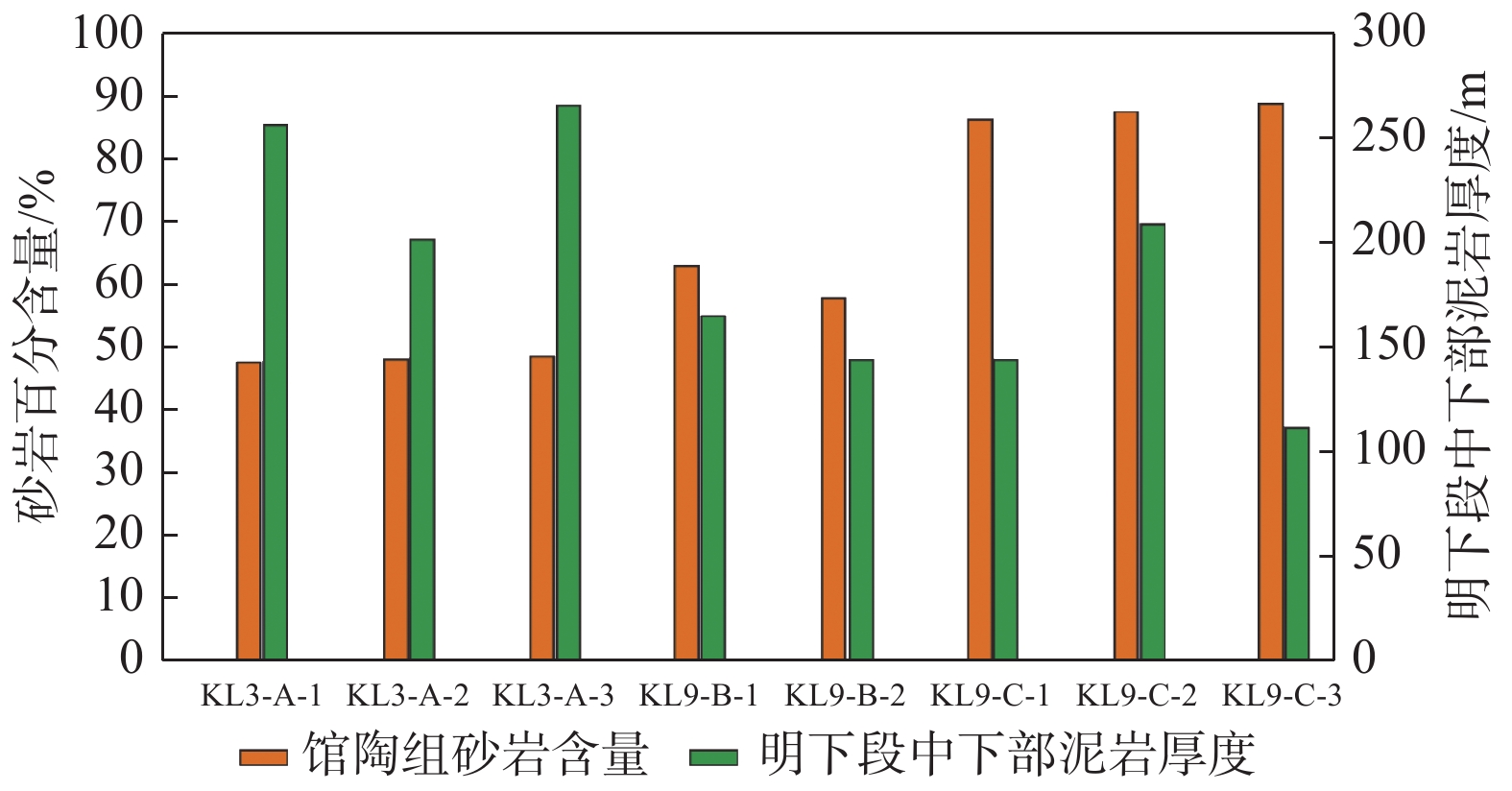
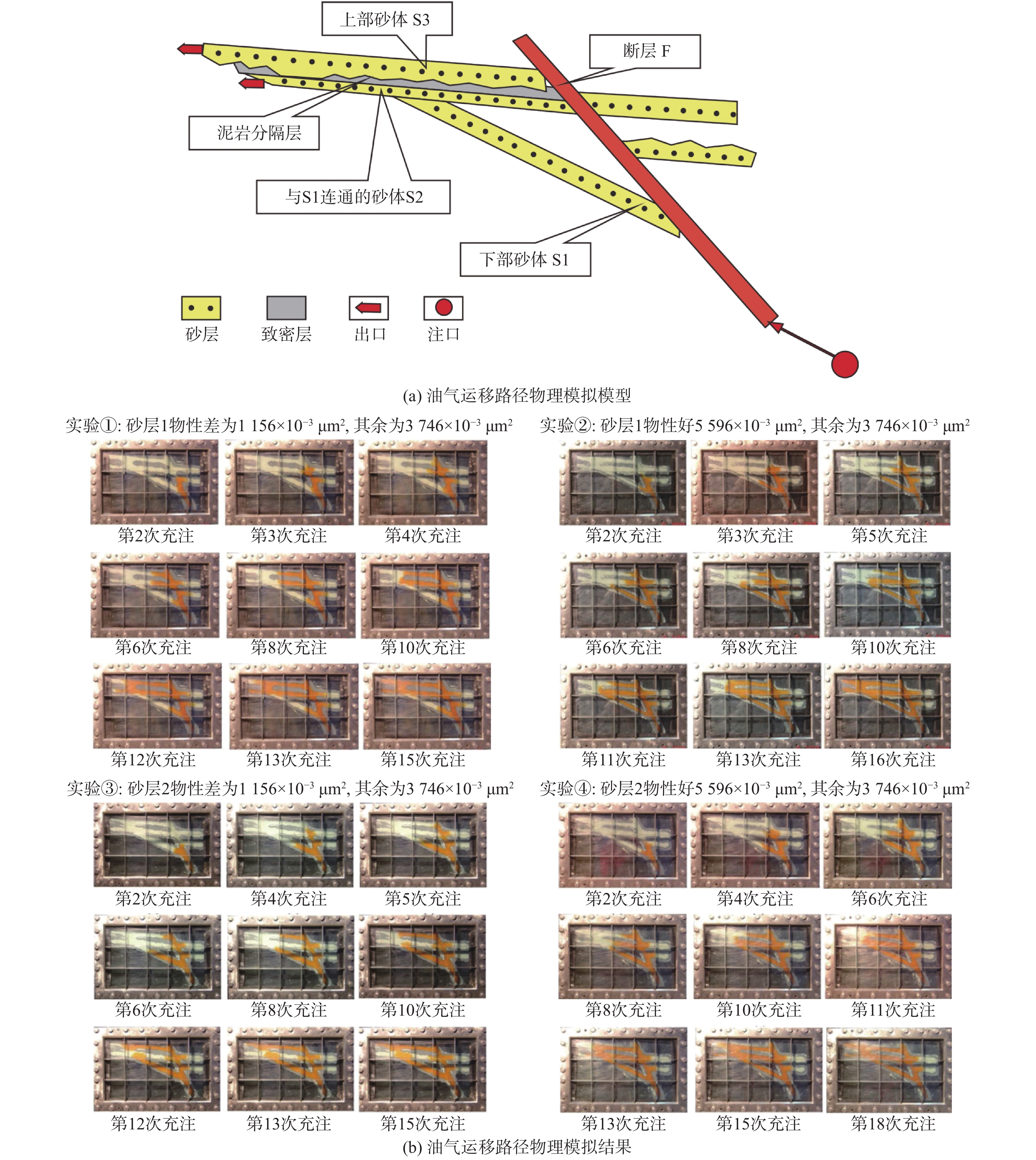
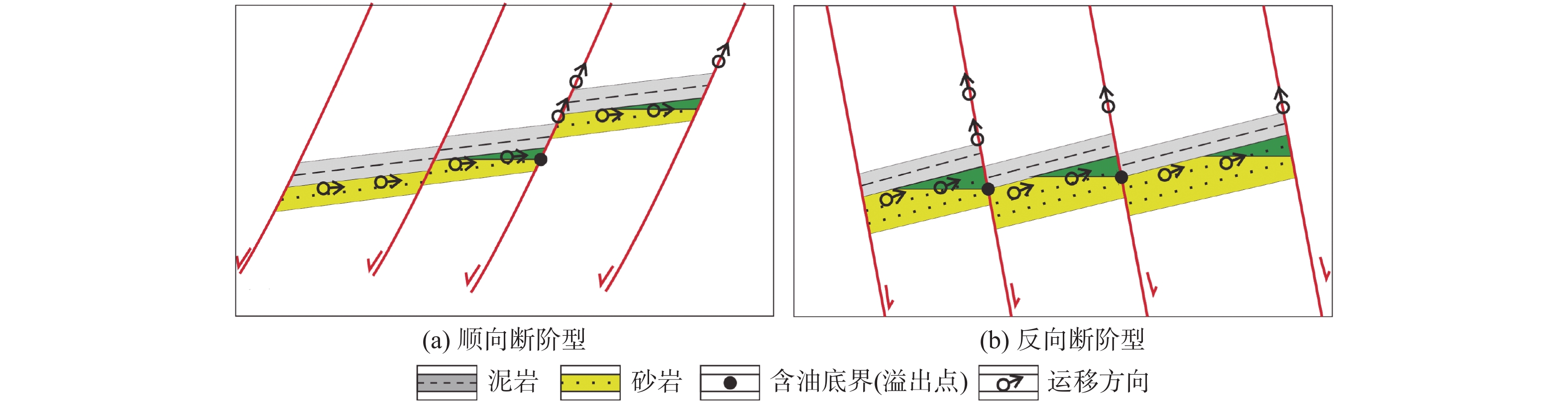
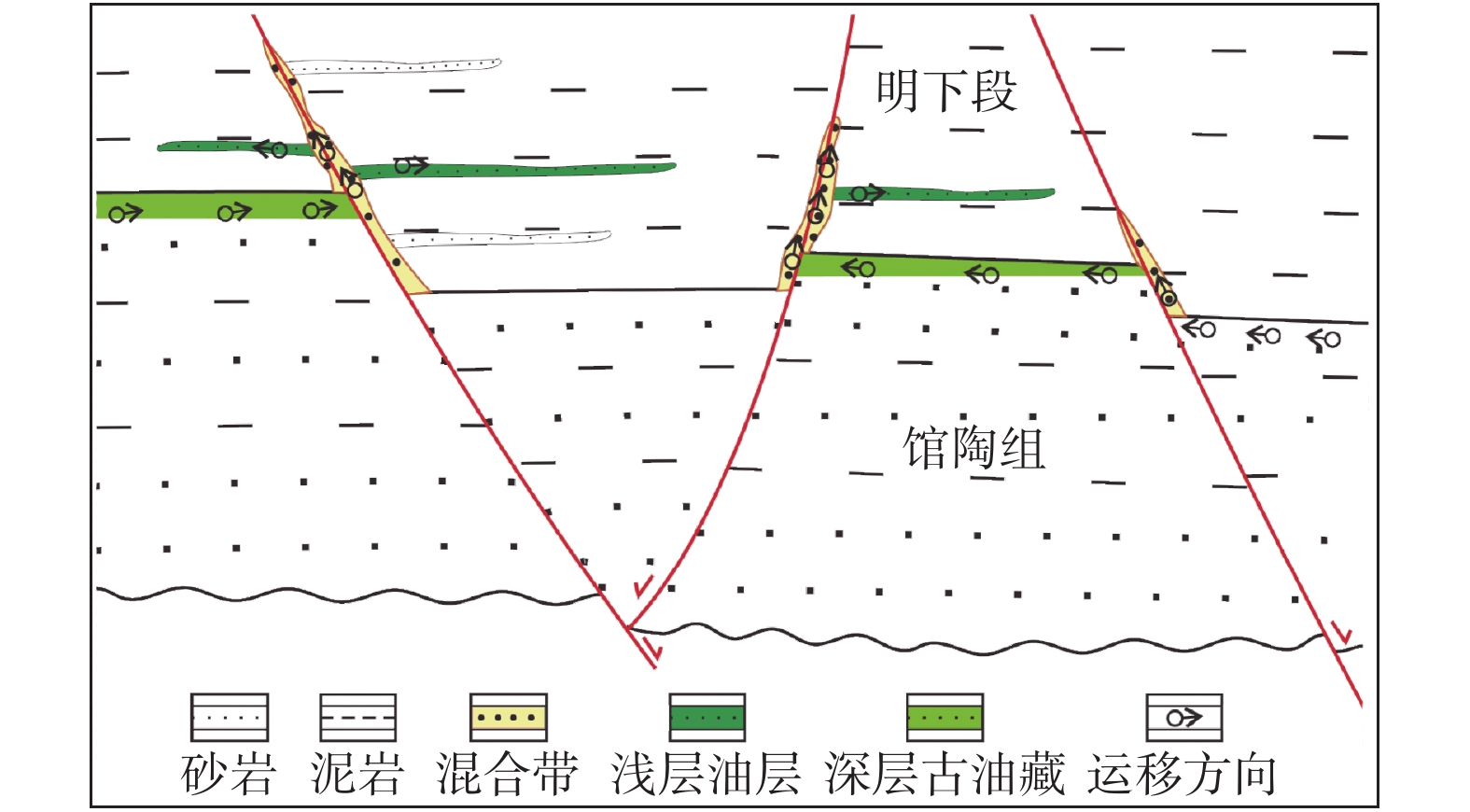
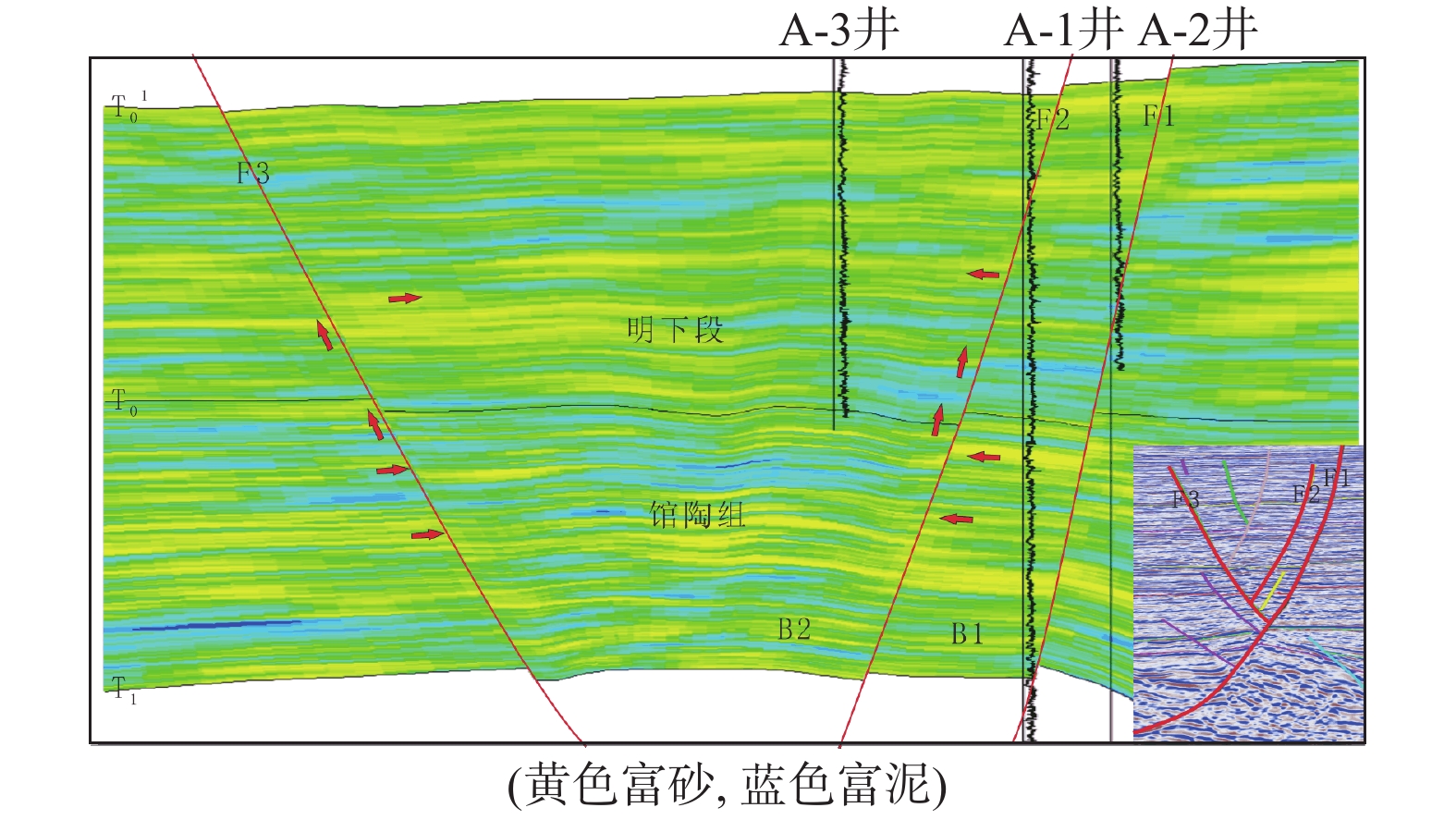
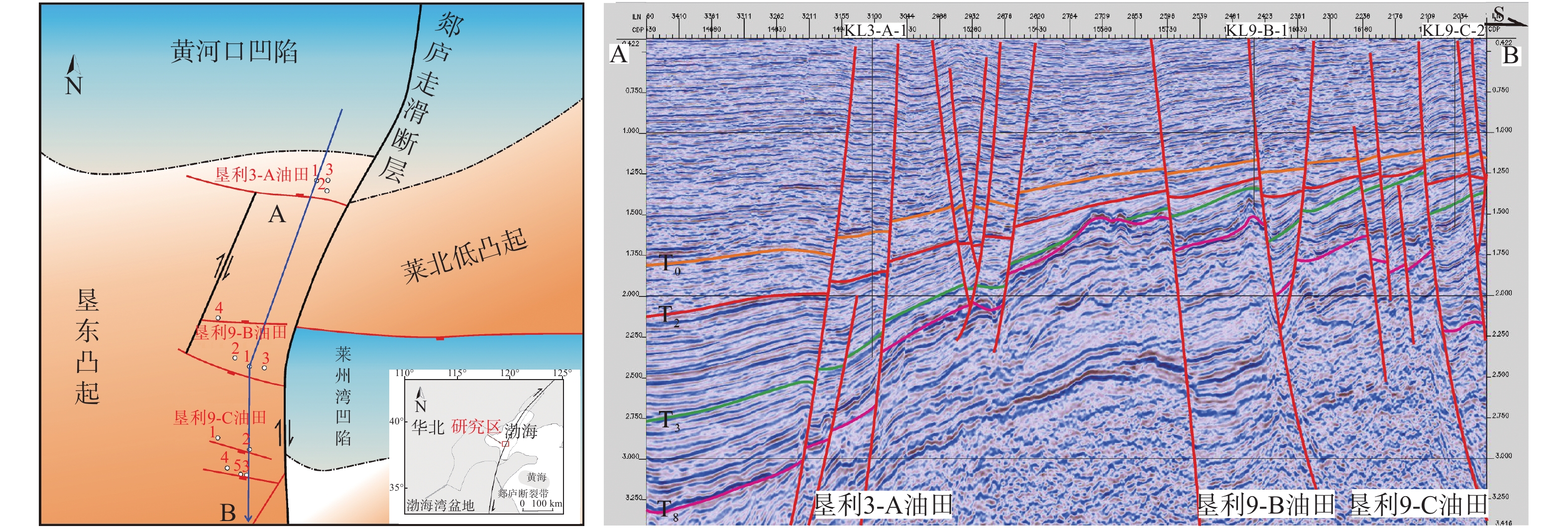
渤海南部缓坡带新近系属于远源成藏,运移路径复杂限制了勘探成效。利用垦利9油田群丰富的钻井资料,结合物理模拟实验、地球化学等手段,明确了渤海南部缓坡带明下段油气运移路径及其控藏作用。研究表明,馆陶组顶部富砂段与明下段底部富泥段组合形成横向输导体系;馆陶组输导层顶面圈闭充当明下段油气中转站,圈闭保存能力控制了明下段的油气富集特征;新近系属于未固结—弱固结地层,断裂带基本不发育裂缝,油气垂向运移能力主要受到卷入断裂带中砂岩含量的控制;明下段成藏是油气经历横向输导与垂向运移相互配合的结果。蓬莱A构造明下段钻遇高丰度油藏,证明了该模式的正确性。
Abstract:Oil and gas accumulation in gentle slope belt is under the control of remote source model in which migration conditions play key roles. Based on the abundant data from the Kenli 9 oilfield, using physical simulation and geochemical approaches, study on the hydrocarbon migration model on gentle slope is carried out and the accumulation-controlling factors are studied in this paper. It is concluded that the sandy member on the top of Guantao Formation and the muddy member on the bottom of Minghuazhen Formation made up the lateral migration passage; regional accumulation on the slope was determined by the traps on the top of passage and the hydrocarbon transfer stations; fractures were not developed in poorly consolidated- unconsolidated rocks, and vertical migration capability was related to the sandstone near the fault zone rather than the activity intensity; reservoirs in the Minghuazhen Formation were controlled by lateral and vertical migrations. Under the guidance of the new results, great success has been achieved in the shallow hydrocarbon exploration on Penglai A structure, which proved the accuracy of the new model.
-

-
表 1 KL9-C-1井潜山风化壳孔隙度和渗透率统计表
Table 1. porosity and permeability of the weathering crust of the buried hill of Well KL9-C-1
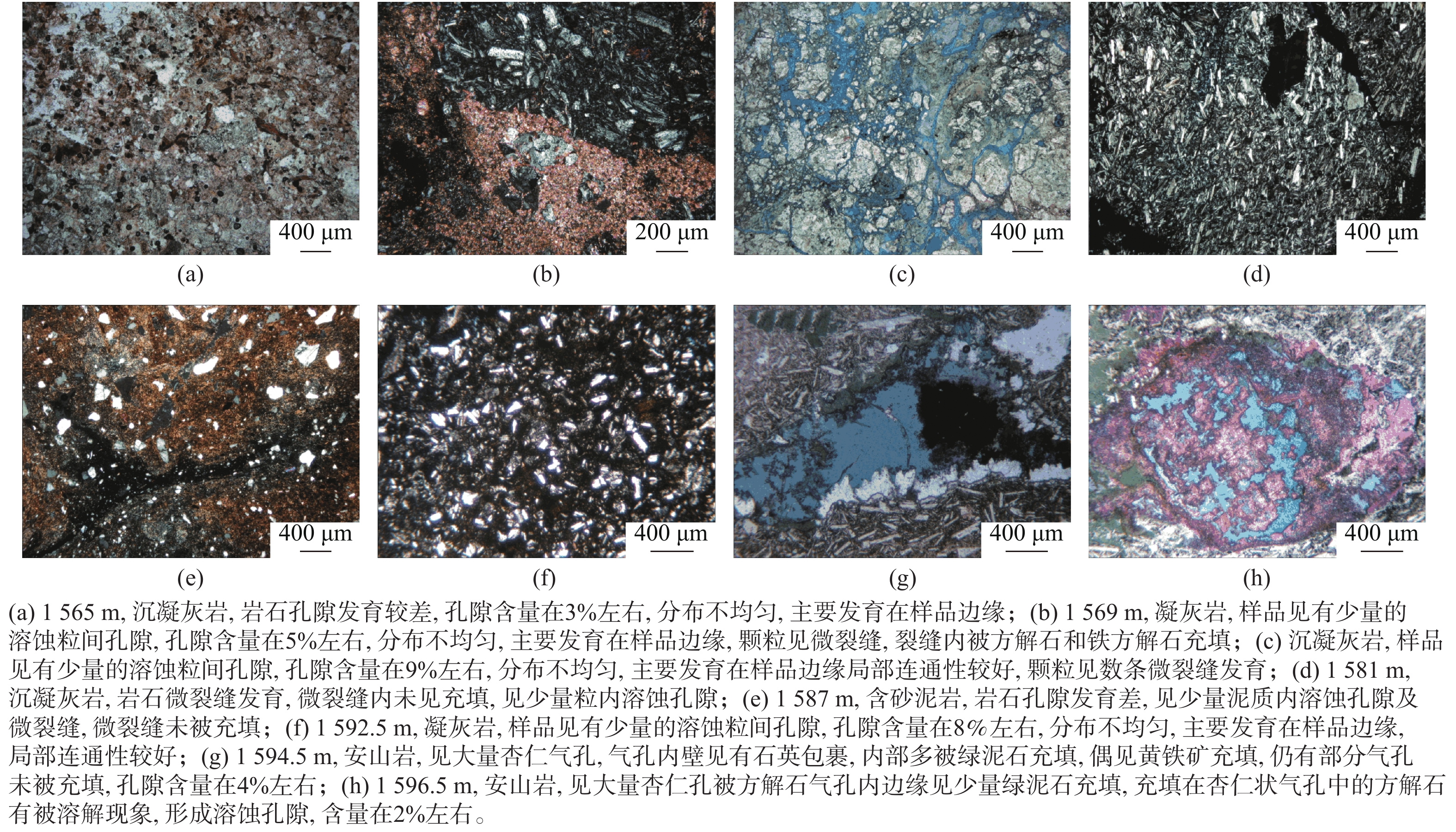
埋深/m 1563 1569 1581 1587 1592.5 1594.5 1596 1600 1602.5 1605 1609 1614.5 1616.5 1620.5 1623.5 1626 1627.5 孔隙度/% 26.0 24.4 34.5 37.6 35.5 18.4 13.0 2.1 16.4 1.1 1.7 1.1 9.2 2.8 8.9 3.5 12.8 渗透率/10−3 µm2 极小值 极小值 极小值 极小值 10.000 0.093 0.023 0.007 0.030 极小值 0.008 0.008 0.011 0.012 0.197 0.007 0.107 -
[1] 薛永安,杨海风,徐长贵. 渤海海域黄河口凹陷斜坡带差异控藏作用及油气富集规律[J]. 中国石油勘探,2016,21(4):65-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2016.04.007
[2] 周立宏,肖敦清,蒲秀刚,等. 陆相断陷湖盆复式叠合油气成藏与优势相富集新模式:以渤海湾盆地歧口凹陷为例[J]. 岩性油气藏,2010,22(1):7-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2010.01.002
[3] 吕丁友,张宏国,麻旭刚,等. 渤海东部凸起区与斜坡区油气勘探实践与认识[J]. 地质科技情报,2018,37(5):84-89.
[4] 张宏国,徐长贵,官大勇,等. 输导脊中转能力定量表征及在渤海东部油气勘探中的应用[J]. 中国石油大学学报:自然科学版,2018,42(3):41-49.
[5] 付晓飞,方德庆,吕延防,等. 从断裂带内部结构出发评价断层垂向封闭性的方法[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报),2005,30(3):328-336.
[6] 吴智平,陈伟,薛雁,等. 断裂带的结构特征及其对油气的输导和封堵性[J]. 地质学报,2010,84(4):570-578.
[7] 房茂军,曾祥林,梁丹. 疏松砂岩油藏出砂机理微观可视化实验研究[J]. 特种油气藏,2012,90(1):98-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2012.01.024
[8] LOVELESS S,BENSE V,TURNER J. Fault architecture and deformation processes within poorly lithified rift sediments,Central Greece[J]. Journal of Structural Geology,2011,33:1554-1568. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2011.09.008
[9] 方旭庆,林会喜,王智帮. 垦东凸起“陀螺式”演化与油气成藏[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版),2007,22(4):13-16.
[10] 周心怀,张新涛,牛成民,等. 渤海湾盆地南部走滑构造带发育特征及其控油气作用[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2019,40(2):215-222. doi: 10.11743/ogg20190201
[11] 武强,王应斌,杨在发,等. 莱州湾地区垦东凸起东斜坡输导体系与油气成藏模式[J]. 中国石油勘探,2010,69(4):31-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2010.04.005
[12] KING P R. The connectivity and conductivity of overlapping sand bodies[C]//Buller A T. North Sea Oil and Gas Reservoirs Ⅱ.London: Graham & Trotman, 1990: 353-358.
[13] RINGROSE P S, SKJETNE E, Elfenbein C. Permeability estimation functions based on forward modelling of sedimentary heterogeneity[C]//SPE. Denver Colorado: Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, 2003: 1-6.
[14] 薛永安. 渤海海域油气运移“汇聚脊”模式及其对新近系油气成藏的控制[J]. 石油学报,2018,39(9):963-970. doi: 10.7623/syxb201809001
[15] 陈伟,吴智平,侯峰,等. 断裂带内部结构特征及其与油气运聚关系[J]. 石油学报,2010,31(5):774-780. doi: 10.7623/syxb201005012
[16] 姜振学,庞雄奇,曾溅辉,等. 油气优势运移通道的类型及其物理模拟实验研究[J]. 地学前缘,2005,12(4):507-515. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.04.020
[17] 邓运华. 试论汇油面积对油田规模的控制作用[J]. 中国海上油气,2014,26(6):1-6.
[18] 刘德汉,肖贤明,田辉,等. 含油气盆地中流体包裹体类型及其地质意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2008,29(4):491-501. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2008.04.012
[19] 欧光习,李林强,孙玉梅. 沉积盆地流体包裹体研究的理论与实践[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2006,25(l):1-8.
[20] 王飞宇,师玉雷,曾花森,等. 利用油包裹体丰度识别古油藏和限定成藏方式[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2006,25(1):12-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2006.01.002
[21] 张宏国,官大勇,刘朋波,等. 渤东低凸起南段油气横向输导能力的定量评价[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2017,39(3):57-65.
[22] 陈斌,邓运华,郝芳,等. 黄河口凹陷BZ34断裂带油气晚期快速成藏模式[J]. 石油学报,2006(1):37-41. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2006.01.008
[23] HEYNEKAMP M R,GOODWIN L B,MOZLEY P S,et al. Controls on fault-zone architecture in poorly lithified sediments,Rio Grande Rift,New Mexico:Implications for fault zone permeability and fluid flow[J]. Faults and Subsurface Fluid Flow in the Shallow Crust,1999,113:27-49.
-



 下载:
下载: