RESERVOIR HETEROGENEITY OF THE LIUSHAGANG FORMATION AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE IN THE W AREA OF SOUTHWEST WEIZHOU DEPRESSION OF BEIBU GULF BASIN
-
摘要:
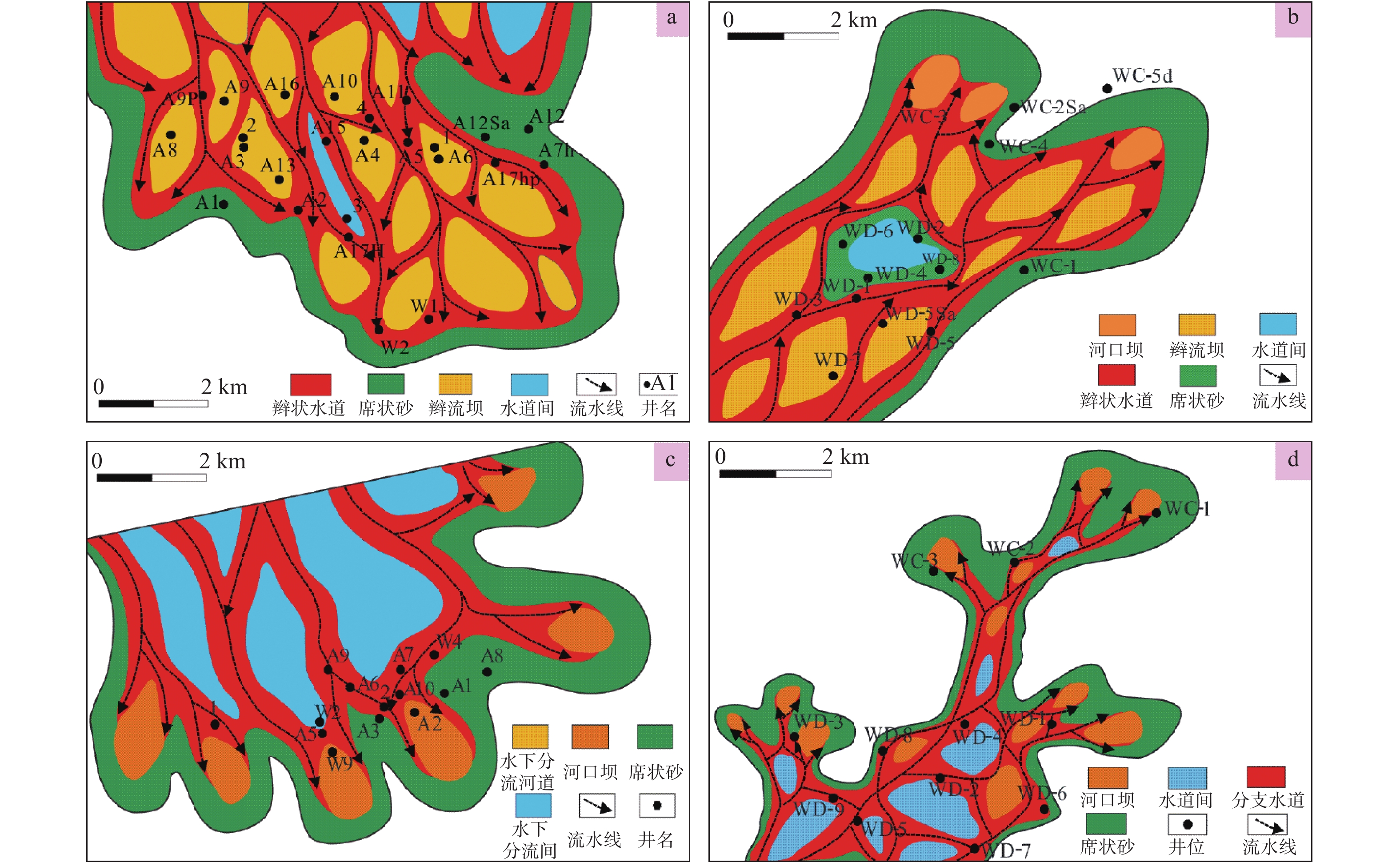
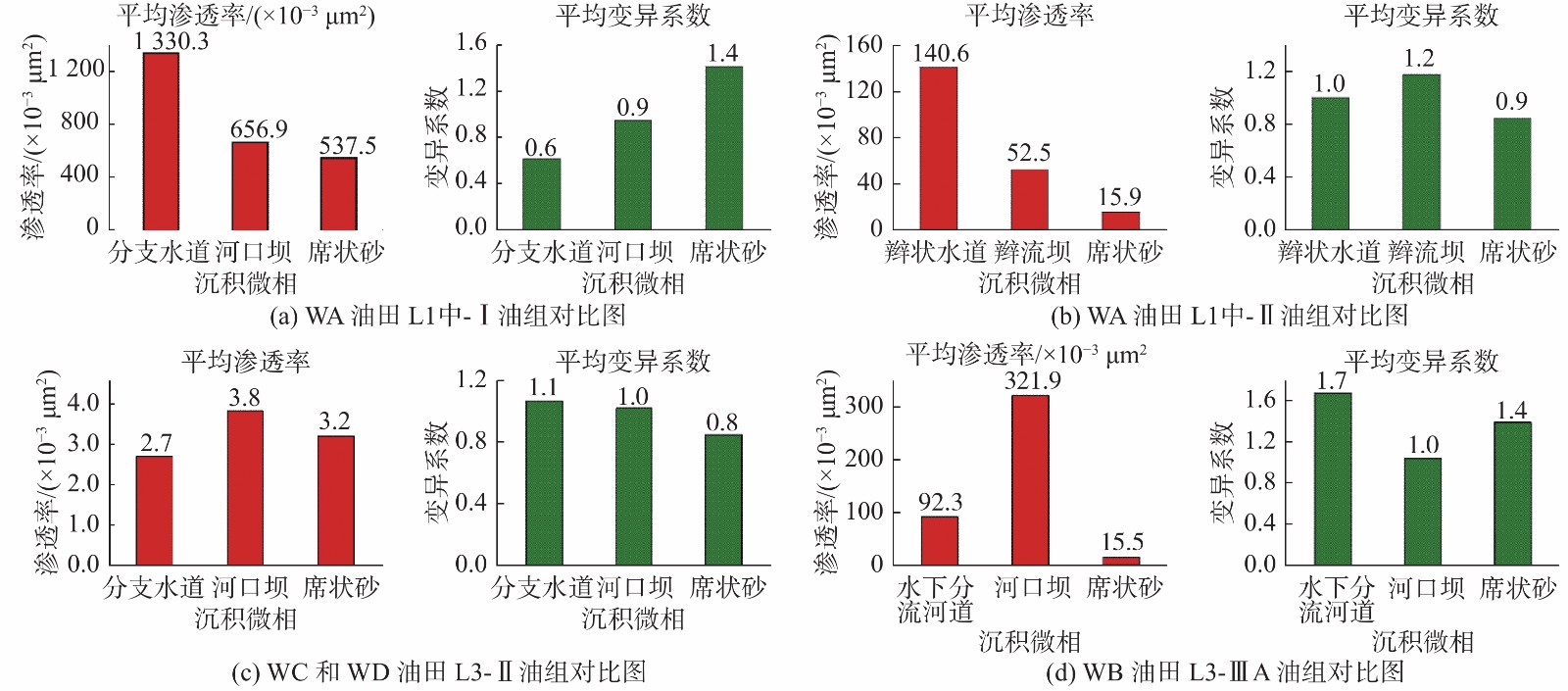
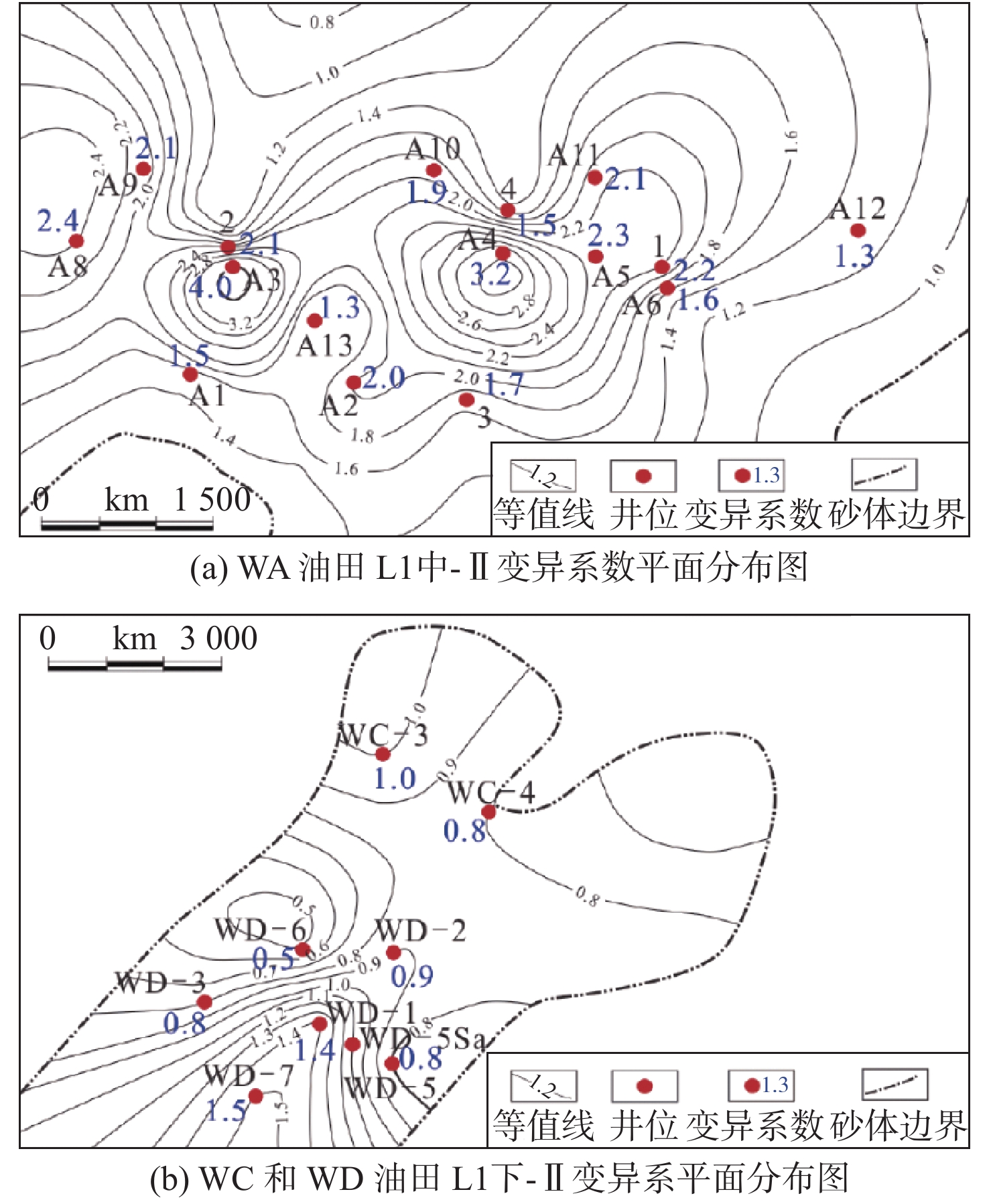
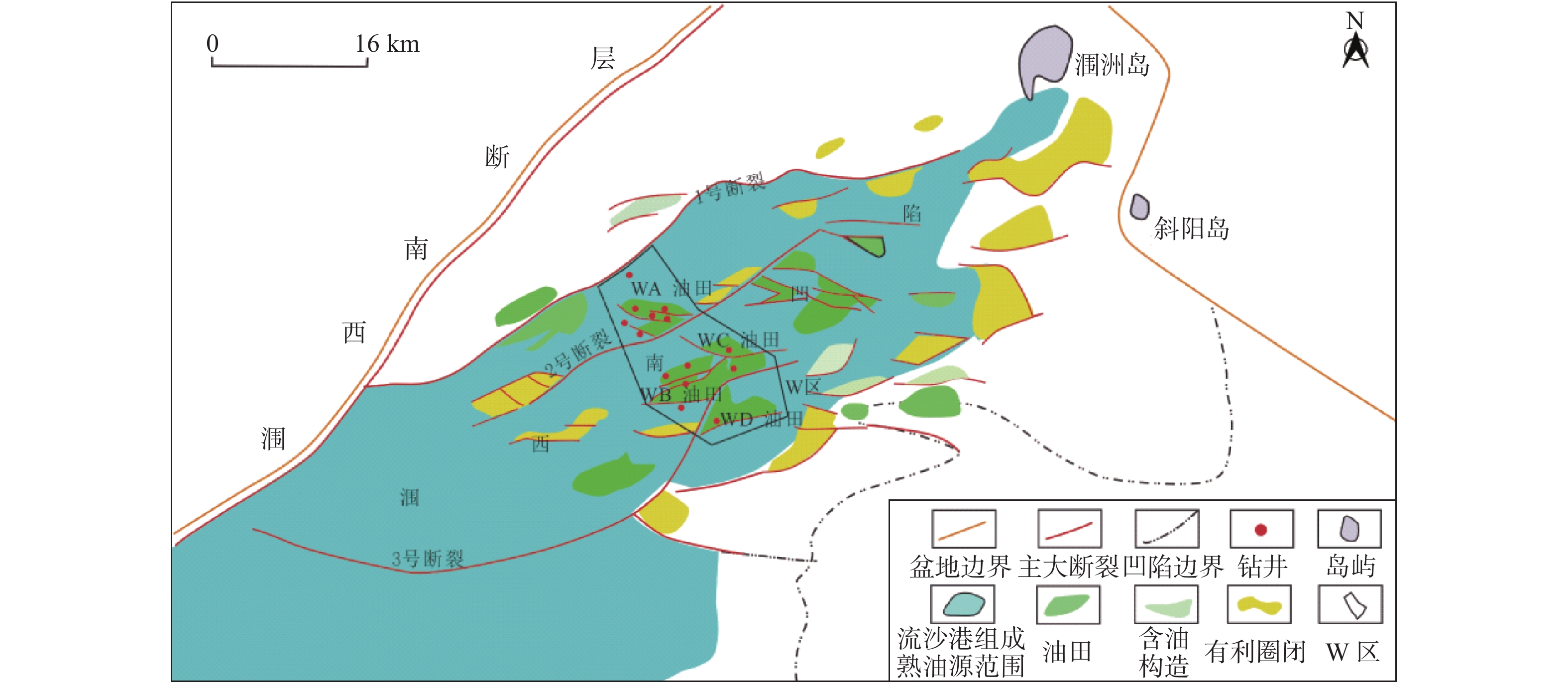
基于沉积微相研究和测井精细解释数据统计分析,开展了涠西南凹陷W区古近系始新统流沙港组储层非均质性研究。W区储层为流一段和流三段,沉积微相研究表明,流沙港组主要为正常三角洲相和扇三角洲相沉积。储层夹层岩性主要为泥岩、粉砂质泥岩,主要成因为分流水道间、水下分流河道与砂坝、砂坝与砂坝、辫流坝与辫状水道、辫状水道间的泥质沉积物。非均质性研究以沉积微相为基础进行,通过比较不同沉积微相的非均质性差别,分析储层的空间物性变化。非均质性研究表明,WA油田流一段夹层厚度>5 m的占51.4%,单层夹层层数>5个的占27.4%,变异系数平均值>1.2,整体上非均质性很强;WB油田流三段夹层分布均匀,东南部平面非均质性弱,西北部平面非均质强;WC和WD油田流三段整体上夹层多,但平面非均质性弱。依据非均质研究成果,对密井网的WA油田主力层进行了剩余油分布预测,并部署了2口调整井挖潜,实施后累增油4.2×104 t,采收率提高了2.3%。表明储层夹层分布和平面非均质性研究可以为油田剩余油挖潜提供依据,对油田高效开发具有重要意义。
Abstract:Detailed microfacies study and statistical analysis of fine well logging data are carried out for reservoir heterogeneity of the Liushagang Formation in the W area of the Southwest Weizhou Depression of the Beibu Gulf Basin. So far there have found four oilfields in the W area namely WA, WB, WC and WD respectively. Reservoirs mainly occur in the Member 1 and 3 of the Liushagang Formation. Sedimentary microfacies of the interlayers of the reservoir suggests that the Liushagang Formation is composed of normal delta front and fan delta front deposits including distributary channel depositss, sand bar deposits, barrier depositss and braided channel sandstones and mudstones. Sedimentology of the fan deltas is studied upon the basis of fine stratigraphic division and correlation. It shows that the interlayers in the Member 1 are dominated by mudstone, silty mudstone with argillaceous silty sandstone and some thin tight layers of sandstone. The interlayer is mainly formed in argillaceous depositional environments between the fluvial deltaic channels or between underwater distributary channels, and/or between sandy bars. Through the comparative study of reservoir heterogeneity based on microfacies, the spatial change in physical properties of reservoirs is revealed. From the statistical results of the fine-interpreted data, it is observed that the reservoirs in the Member 1 of Liushagang Formation in the WA Oilfield has more and thicker interlayers and higher heterogeneity in general; the WB Oilfield has uniformly distributed interlayers, heterogeneity is low in the southeast and high in the northwest. The Member 3 of Liushagang Formation in the oilfields WC and WD have abundant interlayers, but heterogeneity is low in general. Based on the study results of reservoir heterogeneity, prediction is made for the remaining oil of the main reservoir layers in the WA Oilfield. Then two adjustment wells were deployed to tap the remaining oil. The cumulative production is increased for 4.2×104 t, about 2.3% of enhanced oil recovery. This successful application shows that interlayer and plane heterogeneity study has provided solid scientific foundation for tapping the remaining oil out. It is of great significance for efficient oilfield development.
-
Key words:
- reservoir heterogeneity /
- normal delta deposit /
- fan delta deposit /
- interlayer /
- plane heterogeneity
-

-
表 1 WA和WC油田L1上夹层数据统计表
Table 1. Statistical table of interlayer data of WA and WC oilfields on upper Member L1
夹层厚度 夹层个数 夹层分布频率 夹层分布密度 范围/m 个数 占比/% 个数 层数 占比/% 范围 个数 占比/% 范围 个数 占比/% 0 24 16.6 0 24 16.6 0 24 16.6 0 47 32.4 0~1 1 0.7 1 33 22.8 0~0.1 67 46.2 0~1 27 18.6 1~2 2 1.4 2 27 18.6 0.1~0.2 36 24.8 1~2 12 8.3 2~3 3 2.1 3 10 6.9 0.2~0.3 12 8.3 2~3 9 6.2 3~4 3 2.1 4 14 9.7 0.3~0.4 4 2.8 3~4 6 4.1 4~5 2 1.4 5 8 5.5 0.4~0.5 1 0.7 4~5 7 4.8 >5 110 75.9 >5 29 20 >0.5 1 0.7 >5 37 25.5 表 2 WA油田L1中夹层数据统计表
Table 2. Statistical table of interlayer data of WA Oilfield on middle of Member L1
夹层厚度 夹层层数 夹层分布频率 夹层分布密度 范围/m 层数 占比/% 层数 层数 占比/% 范围 层数 占比/% 范围 层数 占比/% 0 0 42.5 0 90 42.5 0 90 42.5 0 102 48.1 0~1 1 0.5 1 15 7.1 0~0.1 22 10.4 0~1 46 21.7 1~2 2 0.9 2 9 4.3 0.1~0.2 61 28.8 1~2 31 14.6 2~3 5 2.4 3 11 5.2 0.2~0.3 26 12.3 2~3 15 7.1 3~4 1 0.5 4 10 4.7 0.3~0.4 10 4.7 3~4 8 3.8 4~5 4 1.9 5 19 9 0.4~0.5 3 1.4 4~5 2 0.9 >5 109 51.4 >5 58 27.4 >0.5 0 0 >5 8 3.8 表 3 WC和WD油田L1下夹层数据统计表
Table 3. Statistical table of interlayer data of WC and WD oilfields on lower Member L1
夹层厚度 夹层层数 夹层分布频率 夹层分布密度 范围/m 层数 占比/% 层数 层数 占比/% 范围 层数 占比/% 范围 层数 占比/% 0 22 17.2 0 22 17.2 0 22 17.2 0 58 45.3 0~1 1 0.8 1 43 33.6 0~0.1 32 25 0~1 20 15.6 1~2 4 3.1 2 24 18.8 0.1~0.2 41 32 1~2 19 14.8 2~3 6 4.7 3 18 14.1 0.2~0.3 15 11.7 2~3 9 7 3~4 15 11.7 4 12 9.4 0.3~0.4 10 7.8 3~4 6 4.7 4~5 2 1.6 5 6 4.7 0.4~0.5 6 4.7 4~5 2 1.6 >5 78 60.9 >5 3 2.3 >0.5 2 1.6 >5 14 10.9 表 4 WB油田 L3段夹层基础数据统计表
Table 4. Statistical table of interlayer data of WB Oilfield on Member L3
夹层厚度 夹层层数 夹层分布频率 夹层分布密度 范围/m 层数 占比/% 层数 层数 占比/% 范围 层数 占比/% 范围 层数 占比/% 0 139 49.5 0 139 49.5 0 139 49.5 0 143 50.9 0~1 3 1.1 1 16 5.7 0~0.1 44 15.7 0~1 43 15.3 1~2 9 3.2 2 28 10 0.1~0.2 63 22.4 1~2 33 11.7 2~3 8 2.9 3 22 7.8 0.2~0.3 31 11 2~3 14 5 3~4 3 1.1 4 18 6.4 0.3~0.4 4 1.4 3~4 10 3.6 4~5 2 0.7 5 16 5.7 0.4~0.5 0 0 4~5 8 2.9 >5 117 41.6 >5 42 15 >0.5 0 0 >5 30 10.7 表 5 WC和WD油田L3段夹层基础数据统计表
Table 5. Statistical table of interlayer data of WC and WD oilfields on Member L3
夹层厚度 夹层层数 夹层分布频率 夹层分布密度 范围/m 层数 占比% 层数 层数 占比% 范围 层数 占比% 范围 层数 占比% 0 19 16.1 0 19 16.1 0 19 16.1 0 21 17.8 0~1 2 1.7 1 7 5.9 0~0.1 14 11.9 0~1 41 34.8 1~2 3 2.5 2 22 18.6 0.1~0.2 33 28 1~2 25 21.2 2~3 5 4.2 3 19 16.1 0.2~0.3 35 29.7 2~3 10 8.5 3~4 1 0.9 4 16 13.6 0.3~0.4 13 11 3~4 9 7.6 4~5 8 6.8 5 11 9.3 0.4~0.5 3 2.5 4~5 7 5.9 >5 80 67.8 >5 24 20.4 >0.5 1 0.9 >5 5 4.2 -
[1] 张辉,李茂,蒋利平,等. 储层非均质性评价技术研究及应用:以涠洲A油田流一段为例[J]. 中国海上油气,2011,23(3):175-178. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2011.03.008
[2] 姚光庆,张建光,姜平,等. 涠西南凹陷11-7构造区流沙港组中深层有效储层下限厘定[J]. 地学前缘,2012,19(2):102-109.
[3] 张辉,姜平,蔡军,等. 涠西南凹陷流沙港组一段储层物性影响因素研究[J]. 海洋石油,2013,33(2):8-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2013.02.008
[4] 张辉,周伟,孙乐,等. 北部湾盆地W 油田流一下亚段储层特征及主控因素[J]. 资源与产业,2017,19(2):66-75.
[5] 彭志春,杨丽,汪新光,等. 北部湾盆地乌石17-X 油田流沙港组三段砂砾岩储层物性主控因素研究[J]. 科学技术与工程,2017,17(10):6-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.10.002
[6] 刘超,马奎前,陈剑,等. 旅大油田非均质性定量表征及开发调整[J]. 油气地质与采收率,2012,19(5):88-90,103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2012.05.024
[7] 刘文超. 码头庄油田储层非均质性及其与剩余油分布的关系[J]. 岩性油气藏,2012,24(2):111-116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2012.02.025
[8] 田景春,刘伟伟,王峰,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地高桥地区上古生界致密砂岩储层非均质性特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2014,35(2):183-189.
[9] 王越,陈世悦,李天宝,等. 扒楼沟剖面二叠系辫状河砂体构型与非均质性特征[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2016,40(6):1-8.
[10] 陈欢庆,王珏,杜宜静. 储层非均质性研究方法进展[J]. 高校地质学报,2017,23(1):104-116.
[11] 许建红,钱俪丹,库尔班. 储层非均质对油田开发效果的影响[J]. 断块油气田,2007,14(5):29-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8907.2007.05.010
[12] 汪立君,陈新军. 储层非均质对剩余油分布的影响[J]. 地质科技情报,2003,22(2):71-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2003.02.015
[13] 严科,杨少春,任怀强. 储层非均质对油田开发效果的影响[J]. 石油学报,2008,29(6):870-874. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2008.06.015
[14] 张满郎, 李熙喆, 谷江锐, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中东部山2段储层精细评价[J]岩性油气藏, 2010, 22(3): 71-77.
[15] 张铭,樊孝峰,方勇. 濮城油田东区沙二段下亚段沉积微相与储层非均质性及剩余油分布的关系[J]. 中国海上油气,2003,17(3):176-180.
[16] ALIZAD B, RASHID E, ZARASVANDI I, et al. Hydrocarbon vertical continuity evaluation in the Cretaceous reservoirs of Azadegan Oilfield, Southwest of Iran: implications for reservoir geochemistry[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020: 94(3): 847-860.
[17] PANG Z L, TAO S Z, ZHANG Q, et al. Evaluation methods of profitable tight oil reservoir of lacustrine coquina: a case study of Da'anzhai Member of Jurassic in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020: 94(2): 418-429.
[18] 龚再升, 李思田. 南海北部湾大陆边缘盆地分析与油气聚集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997: 66-68.
[19] 杨玉卿,崔维平,蔡军,等. 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷WZ油田古近系流沙港组一段沉积相[J]. 古地理学报,2012,14(5):607-616. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2012.05.006
[20] 姚光庆, 蔡忠贤. 油气储层地质学原理与方法[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2005: 123-126.
-



 下载:
下载: