ANTI-ERODIBILITY OF CORAL REEF LIMESTONES ON THE XISHA-NANSHA ISLANDS
-
摘要:
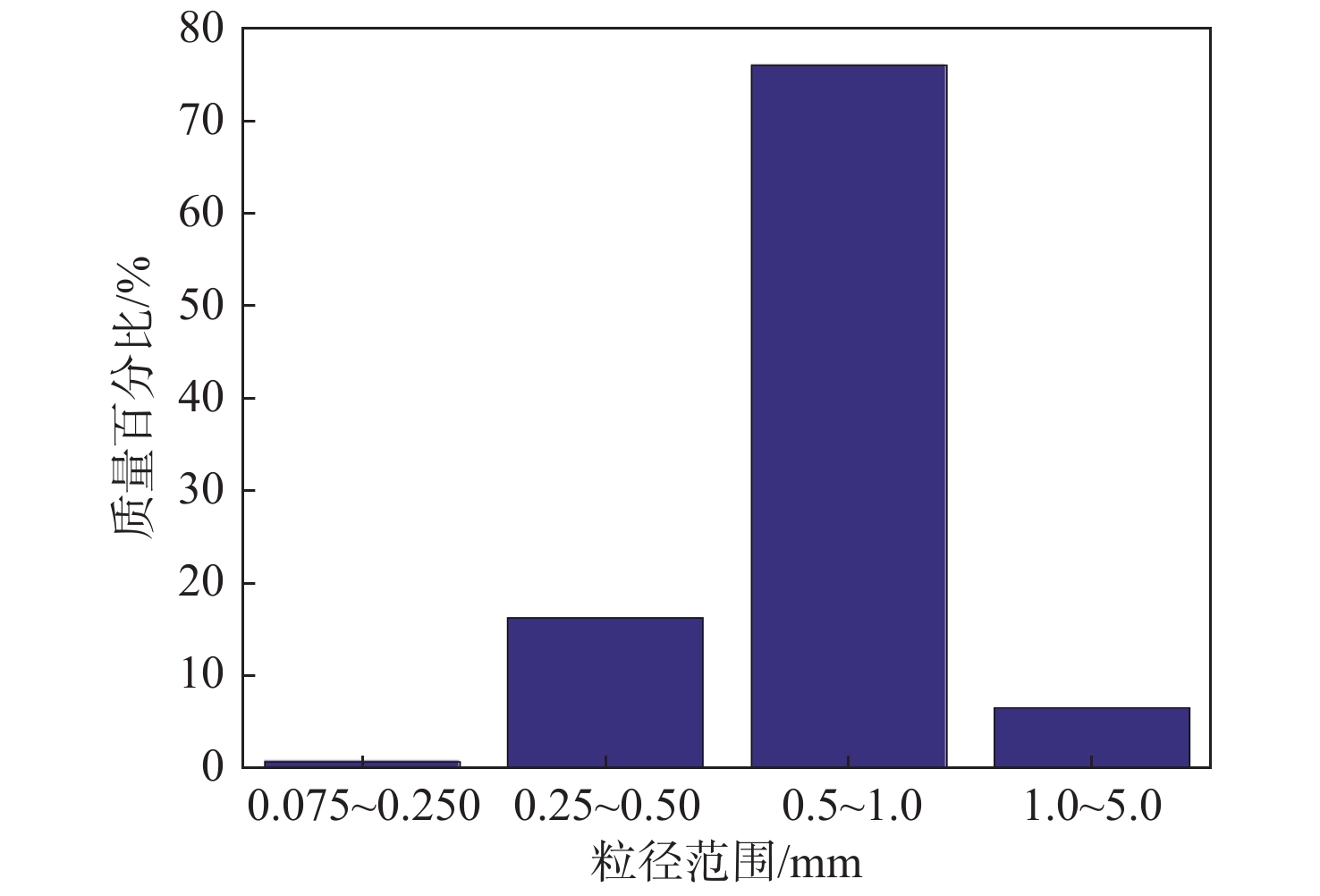
台风、风浪、涌浪、风暴潮、天文潮等现象中的气流和水流往往携带大量固体碎屑物,对南海岛礁礁灰岩体产生强烈的侵蚀作用。笔者首先通过珊瑚的磨蚀与压缩实验验证了磨蚀理论的可靠性;其次,由抗压强度和弹性模量定义了具有压强量纲的抗蚀因子,以定量描述岩石抵抗风水侵蚀的能力;最后,对石岛西南端地表风成灰岩进行了初步研究,发现其抗蚀能力较弱。礁灰岩抗蚀性研究将为南海岛礁防护提供一定的科学依据。
Abstract:In the South China Sea, carbonate debris and fragments are commonly transported by air and waterflow in forms of typhoon, wind wave, swell, storm surges and astronomic tide etc. accompanied by strongly erosion of the reef limestones. The research work presented in this paper confirmed the reliability of the abrasion theoretical model we developed via abrasion and compression experiments firstly. And then, the anti-erodibility factor with the dimension of pressure is defined using compressive strength and elastic modulus to quantificationally describe the anti-erodibility of rocks against wind and water. Finally, the preliminary investigation reveals that the aeolianites on the southwest of Shidao island have relative low anti-erodibility. The study of the anti-erodibility of reef limestones will provide certain scientific support for protection of the islands and reefs in the South China Sea.
-
Key words:
- coral reef limestone /
- anti-erodibility /
- abrasion /
- compression /
- Shidao island
-

-
表 1 珊瑚与石岛灰岩的力学参数
Table 1. Mechanical parameters of coral and carbonate rocks
样品形状 编号 抗压强度 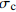 /MPa
/MPa弹性模量E/GPa 编号 抗压强度 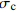 /MPa
/MPa弹性模量E/GPa 片状珊瑚 A1 4.549 0.102 A2 3.533 0.052 A3 3.535 0.204 A4 3.383 0.103 A5 2.416 0.135 A6 5.762 0.113 A7 1.629 0.215 A8 3.318 0.199 平均值 3.516 0.140 块状珊瑚 B1 19.657 1.818 B2 20.738 1.743 B3 3.176 0.151 B4 4.820 0.122 B5 6.888 0.168 B6 10.060 0.356 B7 3.722 0.402 B8 4.897 0.135 B9 4.648 0.113 B10 7.438 0.323 B11 8.905 0.248 B12 5.172 0.298 平均值 8.343 0.490 树枝状珊瑚 C1 15.441 0.948 C2 11.251 1.166 C3 26.080 1.194 C4 30.244 4.156 C5 36.329 1.034 C6 18.633 0.639 C7 22.562 4.084 C8 16.263 0.950 C9 22.769 1.563 C10 14.736 1.142 平均值 21.431 1.688 石岛灰岩 S1 6.139 0.575 S2 6.686 0.751 S3 5.513 0.252 S4 4.599 0.188 S5 4.560 0.318 S6 3.379 0.461 S7 4.259 0.461 S8 3.883 0.245 S9 9.095 0.303 S10 2.970 0.089 S11 3.431 0.218 S12 7.095 0.725 平均值 5.134 0.355 表 2 南海岛礁礁灰岩抗蚀性的定量比较
Table 2. Comparison of anti-erodibility factors among rocks collected on the islands and reefs in the South China Sea
-
[1] 钟晋樑, 陈欣树, 张乔民, 等. 南沙群岛珊瑚礁地貌研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996.
[2] 曾昭璇, 梁景芬, 丘世钧. 中国珊瑚礁地貌研究[M]. 广州: 广东人民出版社, 1997.
[3] 叶海民,周辉,钟小帅. 中国南海某珊瑚砂岛动力环境分析[J]. 土工基础,2013,27(5):50-51.
[4] 赵焕庭,王丽荣. 南海诸岛珊瑚礁人工岛建造研究[J]. 热带地理,2017,37(5):681-693.
[5] 梁海萍,梁海燕,陈海南,等. 1991—2013年发生在西沙永兴岛的台风风暴潮统计特征分析[J]. 应 用 海 洋 学 学 报,2017,36(2):243-248.
[6] 周乐序,赵利平. 波浪作用下珊瑚砂起动特性研究[J]. 中国水运,2015,15(3):170-171,175.
[7] 李建生. 西沙群岛的现代沉积成岩作用[J]. 华南师范学院学报(自然科学版),1982,14(1):29-33.
[8] SUNAMURA T. A fundamental equation for describing the rate of bedrock erosion by sediment-laden fluid flows in fluvial,coastal,and aeolian environments[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2018,43(15):3022-3041. doi: 10.1002/esp.4467
[9] 曾昭璇, 黄少敏, 曾迪鸣. 西沙群岛石岛地貌学上诸问题[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1984, 5(4): 335-341.
[10] 赵焕庭. 西沙群岛考察史[J]. 地理研究,1996,15(4):55-65.
[11] 孙宗勋. 南沙群岛珊瑚砂工程性质研究[J]. 热带海洋,2000,19(2):1-8.
[12] 王步雪岩,孟庆山,韦昌富,等. 多投影面下珊瑚砂砾颗粒形貌量化试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(10):3871-3878.
[13] 崔翔,胡明鉴,朱长歧,等. 珊瑚砂三维孔隙微观特性研究[J]. 岩土力学,2000,41(11):1-9.
[14] WANG Z T,WANG H T,NIU Q H,et al. Abrasion of Yardangs[J]. Physical Review E,2011,84(3):031304. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.84.031304
[15] WANG Z T. Erosion model for brittle materials under low speed impacts[J]. Journal of Tribology-Transactions of the ASME,2020,142:074501. doi: 10.1115/1.4046019
[16] 王新志,汪稔,孟庆山,等. 南沙群岛珊瑚礁礁灰岩力学特性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2008,27(11):2221-2226. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.11.007
[17] 刘志伟,李灿,胡昕. 珊瑚礁礁灰岩工程特性测试研究[J]. 工程勘察,2012,40(9):17-21.
[18] 金昱昕,陈天然,孟庆山,等. 单轴抗压强度揭示南海珊瑚骨骼结构的差异[J]. 热带海洋学报,2017,36(2):33-39.
[19] GHADIRI M,ZHANG Z. Impact attrition of particulate solids. Part 1:A theoretical model of chipping[J]. Chemical Engineering Science,2002,57(17):3659-3669. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2509(02)00240-3
[20] KIMBERLY L M,DOUGLAS J. Controls on the rates and products of particle attrition by bed-load collisions[J]. Earth Surface Dynamic Discussions,2020. doi: 10.5194/esurf-2020-86
[21] 业治铮,张明书,韩春瑞,等. 西沙石岛风成石灰岩和化石土壤层的发现及其意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,1984,4(1):1-10.
[22] 朱袁智,钟晋樑. 西沙石岛和海南岛沙丘岩初探[J]. 热带海洋,1984,3(3):64-71.
[23] ZHAO Q,WU S G,XU H,et al. Sedimentary facies and evolution of aeolianites on Shidao Island,Xisha Islands[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology,2011,29(2):398-413. doi: 10.1007/s00343-011-0018-6
[24] 朱长歧,周斌,刘海峰. 南海海滩岩的细观结构及其基本物理力学性质研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2015,34(4):683-693.
[25] YE Z Z,HE Q X,ZHANG M S,et al. Sedimentary structure and the facies model of the late Pleistocene eolian biocalcarenites in Shidao Island of Xisha Archipelago[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,1985,4(4):603-614.
-



 下载:
下载:




