BEACH SAND-COASTAL DUNES-MODERN VEGETATION-SAND ISLAND GENETIC MODEL OF THE QILIANYU ISLAND
-
摘要:
海滩沙是砂岛形成的基础,成长初始状态原生态海滩沙是砂岛形成的标志;沿岸沙丘是植被成长屏障,二者都具有重要的研究意义。笔者以2019年科考航次现场海滩沙-沿岸沙丘、砂岛及植被调查与卫星遥感资料分析为基础,对七连屿海滩沙-沿岸沙丘-植被地质特征,形态、位置,它们与砂岛的关系进行讨论;揭示了海滩沙-沿岸沙丘形成不但决定于海浪、潮汐,风暴潮等动力作用,而且也与沉积物搬运过程、沉积作用关系密切;同时探讨了岛屿形成过程中现代植物的分布:从点状发育过渡到逐渐覆盖整个潮上带区域,即先是沿岸沙丘,再是海岛中心,最后呈面状覆盖全岛。其中,植物的定植起到了重要作用,不但能够起到固沙作用,而且参与了砂岛的型成。由此,提出建立七连屿海滩沙-海滩岩-植被-砂岛成因模式。
Abstract:The beach sand is the material base of a sand island. It is not only the home for sea animals, but also the evidence of the forming process of a sand island. Coastal dunes may act as barriers to protect vegetation from the damage by wave and surge. Both of them have important research significance for protection of a sand island. Based on the field survey on beach sands, coastal dunes and sand islands and vegetation on the Qilianyu Island in the scientific expedition 2019 in addition to the interpretation of satellite remote sensing data, this paper discussed the geological features, morphological characteristics, and geographic positions of the beach sands, coastal dunes and vegetation as well as their relationship to the development of the sand island. It is revealed that the formation of beach-coastal dunes is not only determined by the dynamic actions of waves, tides and storm surges, but also related to the process of sediment transportation and sedimentation. With regard to the formation of sand island, vegetation plays critical roles. It starts from a pattern of spots in the beginning and then gradually expands to the whole supratidal area, and moves from coastal dunes to the center of island, and finally occupies the whole island. In the process, plant colonization plays a key role in sand fixation and sand island formation. Upon the observations mentioned above, a genetic model of beach sand-beach rock-vegetation-sand island in Qilianyu Island is proposed.
-
Key words:
- Qilianyu Island /
- grain size analysis /
- beach sand /
- coastal dunes /
- modern vegetation
-

-
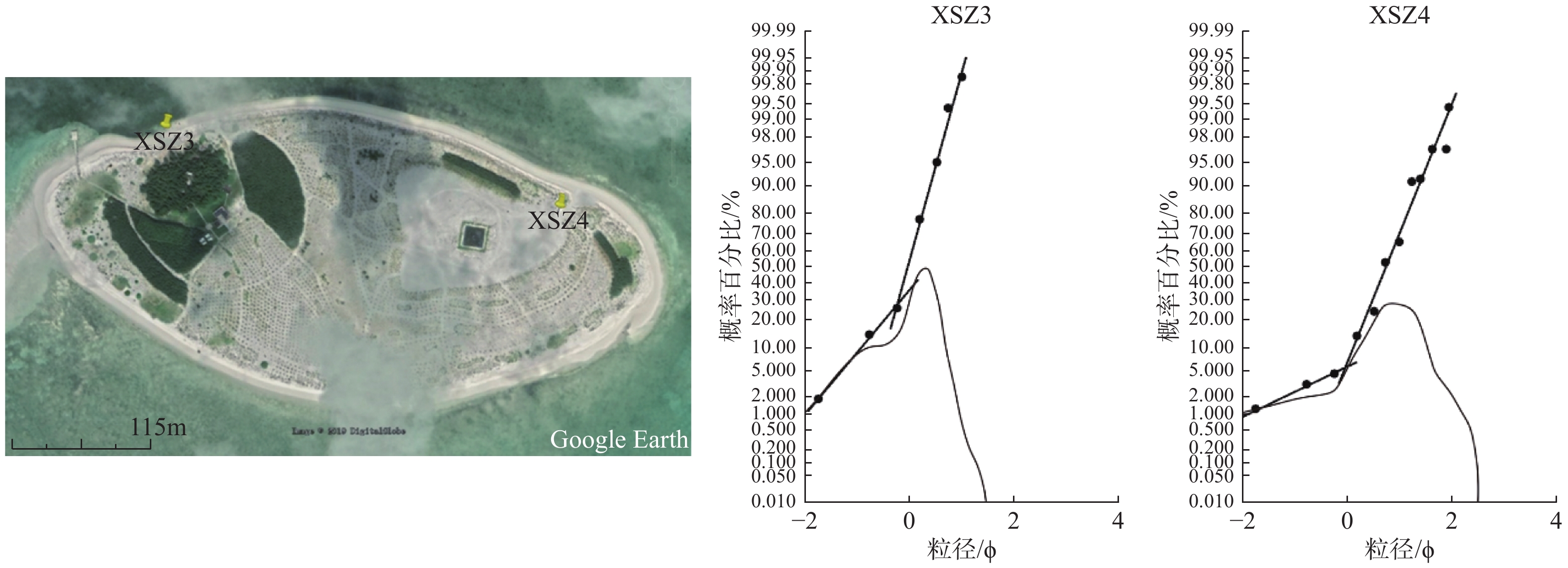
表 1 西沙群岛沿岸沙丘样品粒度参数
Table 1. Grain-size parameters of coastal dune samples from Xisha Islands
粒度参数 BD5 BD6 BD7 ZD7 ZD8 ZD9 XSZ3 XSZ4 LYJ2 JQD1 平均粒径/Ф 1.52 1.22 0.83 1.14 1.82 0.24 −0.14 0.70 −0.04 0.59 标准偏差/Ф 0.47 0.57 0.80 1.29 0.43 0.83 0.56 0.50 1.10 1.20 偏度 −0.17 0.00 −0.14 −0.28 −0.44 0.06 −0.39 −0.05 0.26 0.33 峰态 0.86 1.01 1.03 1.01 1.41 1.34 1.95 1.27 0.42 1.31 粒度中值 1.56 1.22 0.87 1.41 1.91 0.16 -0.03 0.71 0.23 0.21 分选系数 1.73 1.66 2.11 3.77 3.54 1.40 1.84 2.44 1.33 1.47 表 2 七连屿岛屿面积变化
Table 2. Changes in the area of Qilianyu Island
岛屿 日期 总面积/m2 植物面积/m2 海滩砂面积/m2 西沙洲 2002-07 254 217 0 254 217 2012-05 257 044 7 591 249 453 2019-05 233 683 194 952 38 731 北沙洲 2002-07 15 142 1 242 13 900 2012-10 17 455 3 108 14 347 2019-05 13 094 4 745 8 349 南沙洲 2002-07 51 983 31 379 20 604 2012-10 53 147 32 202 20 945 2019-05 57 970 33 139 24 831 中岛 2002-07 119 226 91 008 28 218 2012-05 116 506 92 340 24 166 2019-05 115 792 94 564 21 228 -
[1] SIGREN J M,FIGLUS J,ARMITAGE A R. Coastal sand dunes and dune vegetation:restoration,erosion,and storm protection[J]. Shore and Beach,2014,82(4):5-12.
[2] HESP P A. Geomorphology of desert dunes,N. LANCASTER,publisher routledge,london (1995) (290 pp) 55.00 (hardback) isbn 0509317.99 (paperback) isbn 05094[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science,1997:12.
[3] TSOAR H. Two-dimensional analysis of dune profile and the effect of grain size on sand dune morphology[M]. Springer Netherlands, 1986.
[4] SHI X,CHEN C,LIU Y,ET AL. Trend analysis of sediment grain size and sedimentary process in the central South Yellow Sea[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2002,47(14):1202-1206.
[5] CHENG P,GAO S,BOKUNIEWICZ H. Net sediment transport patterns over the Bohai Strait based on grain size trend analysis[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science,2004,60(2):203-212. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2003.12.009
[6] WASSON R,NANNINGA P. Estimating wind transport of sand on vegetated surfaces[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,1986,11(5):505-514. doi: 10.1002/esp.3290110505
[7] HESP P A. A review of biological and geomorphological processes involved in the initiation and development of incipient foredunes[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh,Section B:Biological Sciences,1989,96:181-201.
[8] HESP P. Foredunes and blowouts:initiation,geomorphology and dynamics[J]. Geomorphology,2002,48(1/3):245-268. doi: 10.1016/S0169-555X(02)00184-8
[9] NOVELLO V F,CRUZ F W,MCGLUE M M,et al. Vegetation and environmental changes in tropical South America from the last glacial to the Holocene documented by multiple cave sediment proxies[J]. Earth and Planetary Sciences Letters,2019,524:115717. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2019.115717
[10] DAYNES C N,FIELD D J,SALEEBA J A,et al. Development and stabilisation of soil structure via interactions between organic matter,arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and plant roots[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2013,57(C3):683-694.
[11] 魏喜,贾承造,孟卫工,等. 西琛1井碳酸盐岩的矿物成分,地化特征及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报,2007,23(11):3015-3025. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.11.031
[12] 业治铮,何起祥,张明书,等. 西沙群岛岛屿类型划分及其特征的研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,1985,5(1):1-13.
[13] 魏喜,贾承造,孟卫工,等. 西沙群岛石岛根管石特征,成因及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报,2008,24(10):2415-2422.
[14] 李亮,何其江,龙根元,等. 南海宣德海域表层沉积物粒度特征及其输运趋势[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2017,37(6):140-148.
[15] 张浪,刘振文,姜殿强. 西沙群岛植被生态调查[J]. 中国农学通报,2011,27(14):181-186.
[16] 赵晋军,徐利强,吴礼彬,等. 西沙赵述岛和北岛海鸟遗迹~(14)c年代模型及意义[J]. 地球环境学报,2018,9(1):28-37.
[17] 董玉祥,杜建会. 海岸风沙地貌台风响应研究的现状与趋势[J]. 中国沙漠,2014(3):634-638. doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2013.00366
[18] AAGAARD T,DAVIDSON-ARNOTT R,GREENWOOD B,et al. Sediment supply from shoreface to dunes:linking sediment transport measurements and long-term morphological evolution[J]. Geomorphology,2004,60(1/2):205-224.
[19] 马克伟. 土地大辞典[J]. 长春:长春出版社, 1991.
[20] 赵强. 西沙群岛海域生物礁碳酸盐岩沉积学研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2010.
[21] Davies J L, Clayton K M. Geographical variation in coastal development[M].London: Longman , 1980.
[22] HEHP P. Morphodynamics of incipient foredunes in New South Wales,Australia[J]. Developments in Sedimentology,1983,38:325-342.
[23] HESP P A. Foredune formation in southeast Australia[J]. Coastal geomorphology in Australia,1984:69-97.
[24] COWLES H C. The ecological relations of the vegetation on the sand dunes of Lake Michigan. Part i. -geographical relations of the dune floras[J]. Botanical gazette,1899,27(2):95-117. doi: 10.1086/327796
[25] Willis R B A J. Ecology of salt marshes and sand dunes[J]. Journal of Ecology,1972,62(2):665.
[26] 书贤. 植物的根系[J]. 农业科学实验,1982(9):47.
[27] 覃业曼. 西沙群岛琛航岛全新世珊瑚礁的发育过程及其记录的海平面变化[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2019.
-




 下载:
下载: