Structural characteristics and physical simulation of X-shaped normal faults
-
摘要:
X型正断层是常见的伸展构造样式,其几何学特征、形成过程及成因机制缺乏系统研究。基于地震资料精细解释和构造物理模式实验,明确几何学特征,重构其形成过程,明确形成机制,并探讨控藏作用。研究结果表明,X型正断层分为新生型和继承型2大类。继承型X型正断层是基底断裂复活形成的,包括差异伸展和双向均匀伸展2种模式;新生型X正断层形成于张应力和剪应力配比关系为1:2~2:1范围内的应力背景;继承型X型正断层具有较好油气运移、储层改造等优势并且形成多类型圈闭,具有“多层楼”式的成藏模式。X型正断层的研究丰富了构造样式研究的理论认识,建立了合理的地质模型,为构造精细解释提供依据。
Abstract:The X-shaped normal fault is a common extensional tectonic fracture. However, its geometric characteristics, formation process, and genetic mechanism are lack of systematic research. Based on fine interpretation of seismic data and physical modelling, the geometric characteristics are clarified, the formation process is reconstructed, the formation mechanism is confirmed, and the reservoir control effect is discussed. The research result indicates that the X-shaped normal fault can be divided into two types: incipient X-shaped normal faults and the inherited X-shaped normal faults. The inherited X-shaped normal faults are formed by the reactivation of basement faults, including two modes of differential extension and bidirectional uniform extension. The incipient X-shaped normal faults are formed under the stress background whose tensile stress vs shear stress ratio is 1:2 ~ 2:1. In addition, the inherited X-shaped normal faults have advantages of good oil and gas migration and reservoir reconstruction. Meanwhile, they form various traps and feature “multi-storey”-styled oil-gas accumulation. This research provided a reference for hydrocarbon exploration in Bohai Bay basin, enriched the theoretical understanding of the structural patterns with a geological cue for fine structural interpretation of similar cases.
-

-
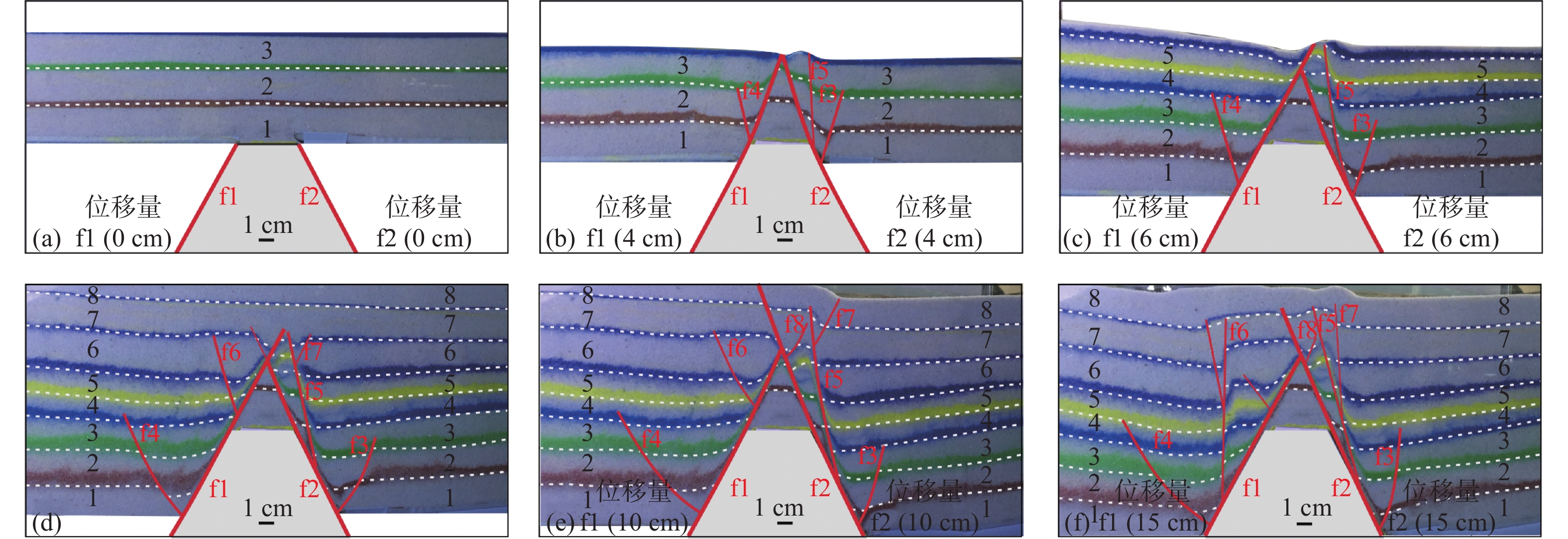
图 5 继承型X型正断层物理模拟装置[10]
Figure 5.
表 1 石臼坨地区X型正断层几何学参数(测线位置见图1)
Table 1. The geometric parameters of X-shaped normal faults (see Fig.1 for location of typical profiles)
类型 参数 α1 /(°) α2 /(°) β1 /(°) β2 /(°) β3 /(°) Η/m W/m L/m 测线号 新生型 74.5 78 25.5 22 47.5 1 567 2 700 0 I-5000 74.6 76 25.4 14 39.4 1 550 2 025 0 I-4900 69.6 73.5 21.4 16.5 37.9 1 612 1 750 0 I-4800 继承型 66.4 62.8 23.6 27.2 53 2 593 7 875 3 150 I-4300 63.3 74 26.7 16 50 2 419 8 000 2 550 I-4200 60.1 63 29.9 27 45 2 494 4 905 1 000 I-4100 65.6 68 24.4 22 46 2 281 5 400 1 800 I-3900 61.6 70 28.4 20 48 2 333 6 075 1 912 T-3100 66.4 69.3 23.6 20.7 54 2 400 4 575 1 875 T-3300 70.7 66 19.3 24 45 2 000 3 225 525 T-3500 61.7 71 28.3 19 46 2 619 4 350 750 T-3700 表 2 继承型X型断层构造物理模拟模型参数
Table 2. Geometric parameters of analogue modeling of the inherited X-shaped normal faults
模型 位移量 模型参数 模型 位移量 模型参数 序号 f1/cm f2/cm α1 /(°) α2 /(°) H/cm L1/cm) L2/cm 序号 f1/cm f2/cm α1 / (°) α2 / (°) H/cm L1/cm L2/cm 模型一 双向均匀伸展 1 4 4 60 60 12 13.5 4.5 模型二 双向均匀伸展 1 4 4 60 60 15 9 2 2 6 6 60 60 12 13.5 4.5 2 6 6 60 60 15 9 2 3 8 8 60 60 12 13.5 4.5 3 8 8 60 60 15 9 2 4 10 10 60 60 12 13.5 4.5 4 10 10 60 60 15 9 2 5 15 15 60 60 12 13.5 4.5 差异伸展 1 0 4 60 60 15 9 2 差异伸展 1 0 4 60 60 12 13.5 4.5 2 2 6 60 60 15 9 2 2 2 6 60 60 12 13.5 4.5 3 4 8 60 60 15 9 2 3 4 8 60 60 12 13.5 4.5 4 6 10 60 60 15 9 2 表 3 伸展走滑配比实验参数
Table 3. Geometric parameters at different ratios of extension vs strike-slip
实验序号 张应力作用 剪应力作用 配比关系 速率/(mm/s) 最终位移量/mm 速率/(mm/s) 最终位移量/mm 1 0.40 80 0.10 20 4:1 2 0.20 80 0.10 40 2:1 3 0.10 40 0.10 40 1:1 4 0.10 40 0.20 80 1:2 5 0.10 20 0.40 80 1:4 -
[1] ANDERSON E M. The dynamics of faulting and dyke formation[M]. London:Oliver and Boyd, 1951.
[2] FERRILL D A,MORRIS A P,STAMATAKOS J A,et al. Crossing conjugate normal faults[J]. AAPG Bulletin,2000,10(84):1543-1559.
[3] FERRILL D A,MORRIS A P,MCGINNIS R N. Crossing conjugate normal faults in field exposures and seismic date[J]. AAPG Bulletin,2009,93(11):1471-1488. doi: 10.1306/06250909039
[4] SCHWARZ H U,KILFITT F W. Confluence and intersection of interacting conjugate faults:a new concept based on analogue experiments[J]. Journal of Structural Geology,2008,30(9):1126-1137. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2008.05.005
[5] BRETAN P G,NICOL A,WALSH J J,et al. Origin of some conjugate or “X” fault structures[J]. the Leading Edge,2012,15(7):812,814,816.
[6] ÇIFTÇI N B,LANGHI L. Evolution of the hourglass structures in the Laminaria High,Timor Sea:implications for hydrocarbon traps[J]. Journal of Structural Geology,2012,36(36):55-70.
[7] 周天伟,周建勋. 南堡凹陷晚新生代X型断层形成机制及其对油气运聚的控制[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2008,32(1):20-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2008.01.003
[8] 余一欣,周心怀,汤良杰,等. 渤海湾地区X型正断层及油气意义[J]. 地质学报,2009,8(83):1083-1088.
[9] 包项,季建清,陶涛,等. 渤海湾盆地沉积层中X型正断层的发育特征与油气意义[J]. 地质科学,2010,45(2):395-410. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2010.02.004
[10] YU F S,KOYI H. Theoretical and experimental estimation of geometric relationship of non-parallel conjugate normal faults[J]. Tectonophysics,2017,703/704:85-97. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2017.03.009
[11] 何永垚,王英民,卿元华,等. 琼东南盆地X形共轭正断裂及其油气勘探意义[J]. 新疆石油地质,2012,33(5):527-530.
[12] YU F S,KOYI H,ZHANG X T. Intersection patterns of normal faults in the Lufeng Sag of Pearl River Mouth Basin,China:insights from 4D physical simulations[J]. Journal of Structural Geology,2016,93:67-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2016.10.007
[13] 李理,赵利,刘海剑,等. 渤海湾盆地晚古生代—新生代伸展和走滑构造及深部背景[J]. 地质科学,2015,50(2):446-472. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2015.02.007
[14] 漆家福. 渤海湾新生代盆地的两种构造系统及其成因解释[J]. 中国地质,2004,33(1):15-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2004.01.002
[15] 万桂梅,汤良杰,周心怀,等. 渤海海域新近纪—第四纪断裂特征及形成机制[J]. 石油学报,2010,31(4):591-595. doi: 10.7623/syxb201004012
[16] CAINE J S,EVANS J P,FORSTER C B. Fault zone architecture and permeability structure[J]. Geology,1996,24(11):1025-1028. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1996)024<1025:FZAAPS>2.3.CO;2
[17] WOODS E P. Vulcan Subbasin fault styles:implications for hydrocarbon migration and entrapment[J]. Australian Petroleum Production and Exploration Association Journal,1992,32(1):138-158.
[18] MORRIS A,FERRILL D A,HENDERSON D B. Slip tendency analysis and fault reactivation[J]. Geology,1996,24(3):275-278. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1996)024<0275:STAAFR>2.3.CO;2
-




 下载:
下载: