Application of offshore 3D dual-azimuth seismic data processing to the Panyu 4 Sag
-
摘要:
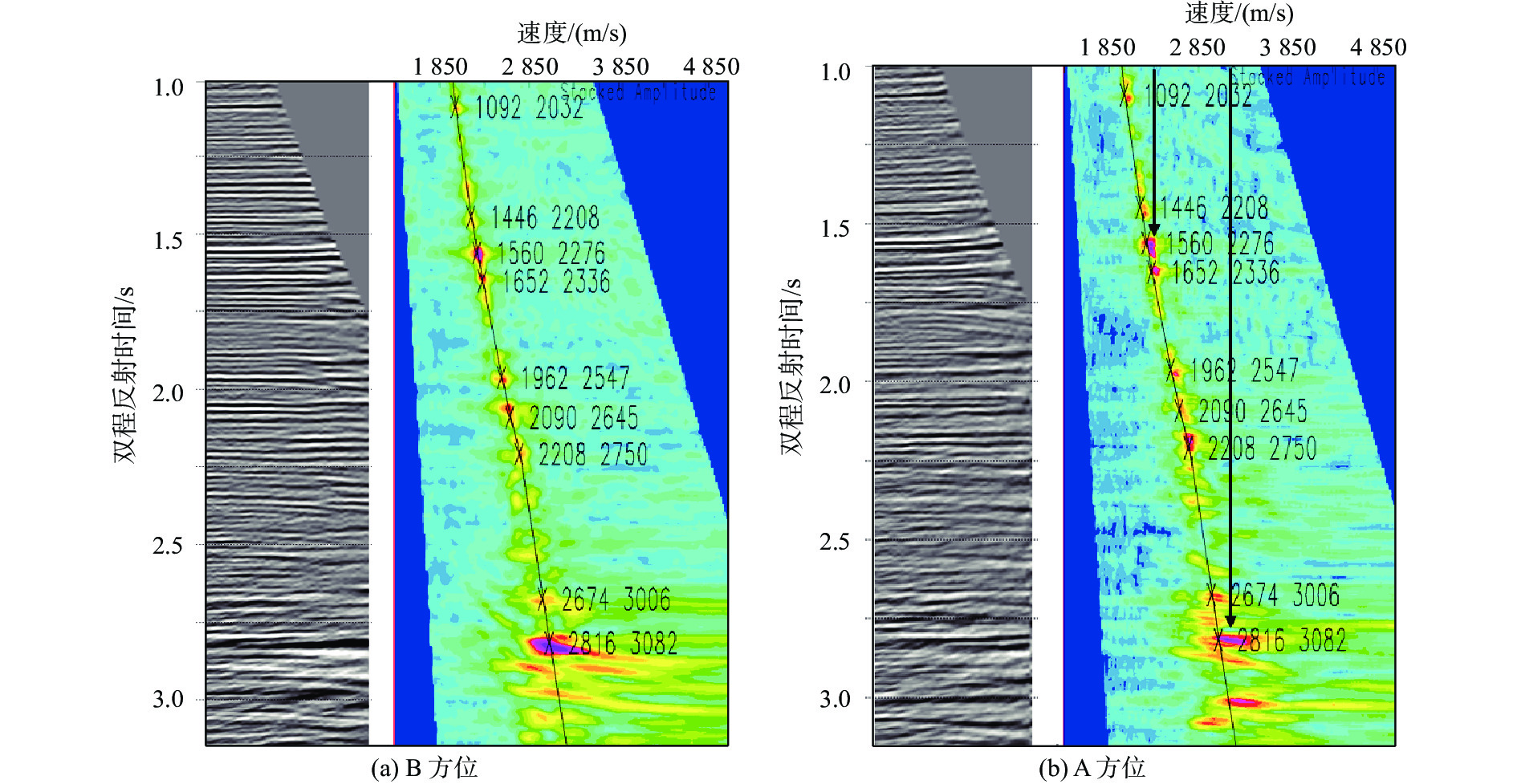
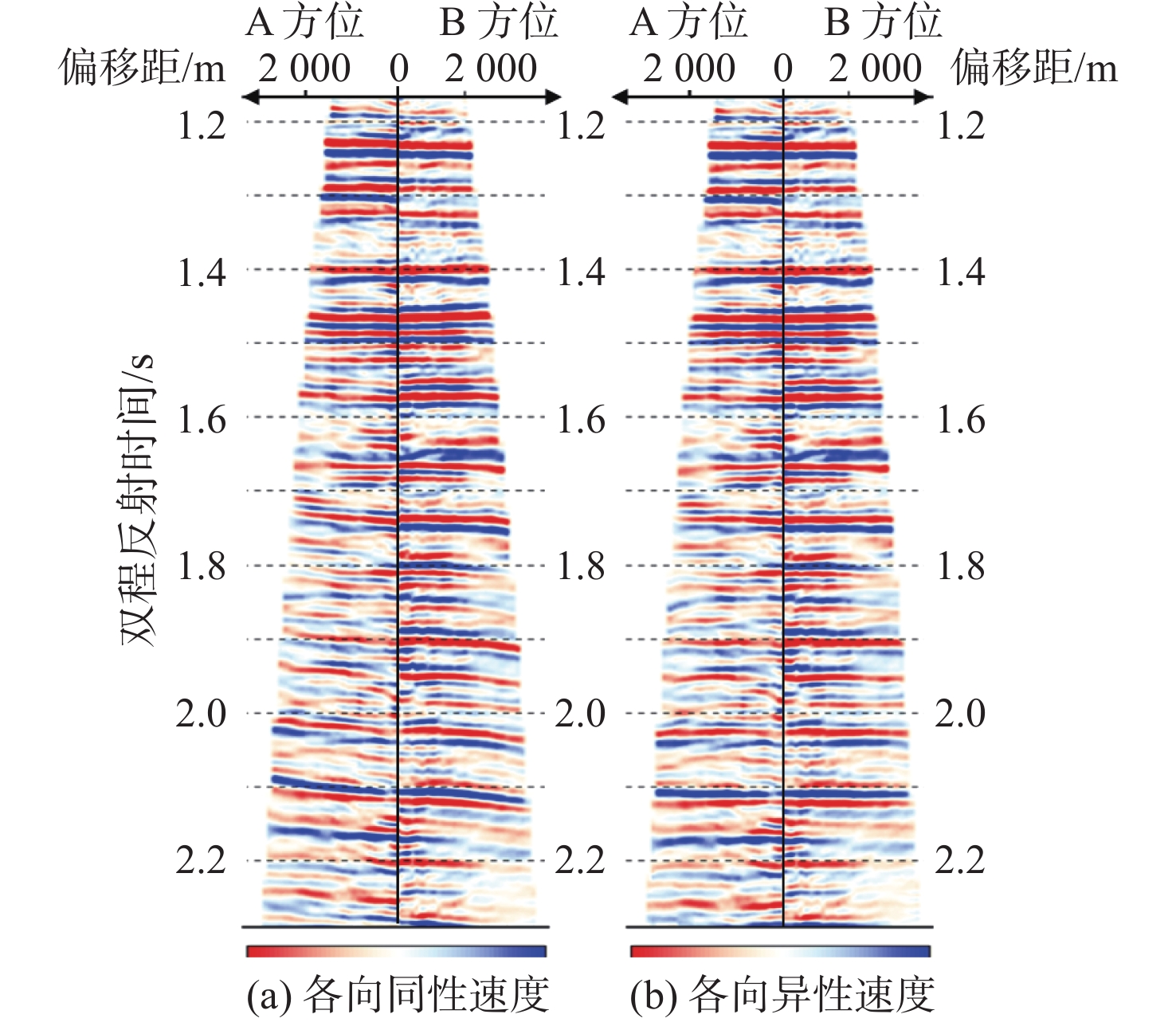
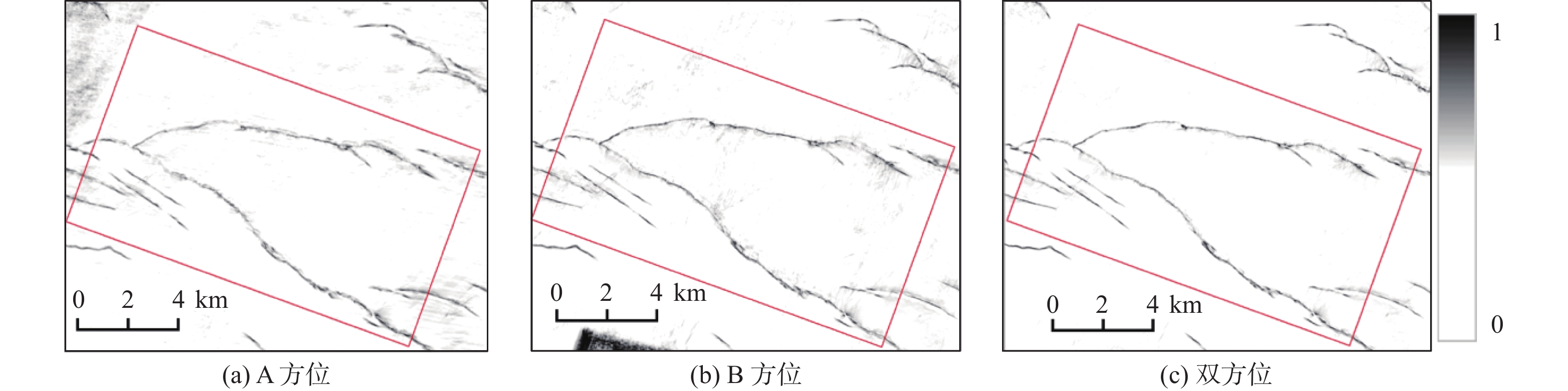
番禺4洼新近系NWW—SEE向正断层非常发育,这些断层上升盘的构造圈闭是重要的勘探目标。但由于一次三维地震资料采集方向与断层平行,断层附近阴影现象非常严重,表现为信噪比低、同相轴不合理的“下拉”和扭曲畸变的“假象”,严重影响断层上升盘的精细构造落实。为此,实施了垂直于断层方向的二次三维地震采集,使得断层阴影带成像比一次三维有较大改善。为了更好地解决断层阴影带成像难题,针对方位各向异性,对2次采集的三维资料进行了以双方位各向异性叠前深度偏移(PSDM)为核心的双方位融合处理。2个方位各自处理成果和双方位融合处理结果对比表明:对于断层阴影带成像,垂直断层方向采集的三维明显优于平行断层方向采集的三维;而结合2次采集的双方位融合处理资料效果最好:既能有效的消除断层阴影带成像畸变,又能提高信噪比。经研究区油田评价井在断层阴影带的钻探结果证实了双方位融合处理结果的可靠性,同时,可为类似地区解决断层阴影带成像难题提供采集设计和处理技术等方面的借鉴。
-
关键词:
- 番禺4洼 /
- 二次三维地震采集 /
- 方位各向异性 /
- 双方位融合处理 /
- 各向异性叠前深度偏移
Abstract:The study area, Panyu 4 Sag, occurs in the northern part of the Pearl River Mouth Basin where Neogene NWW-strike normal faults are well developed. The traps on the upside of those faults are important targets for hydrocarbon exploration. However, the first round of 3D seismic data of this area, which is parallel to the direction of fault strike, provides poor images in fault shadow zones, with low signal-to-noise ratio, abnormal event dropping down and strong structural distortion. Thus traps on the upside of normal faults always bear structural uncertainties in data interpretation. For this reason, a second round of 3D seismic is performed vertical to fault strike and fault shadow imaging is improved compared to the first round of 3D seismic. In order to further improve the fault shadow imaging, the dual-azimuth processing considering azimuthally anisotropic is employed using both of the 3D seismic datasets. The core of the dual-azimuth processing is the dual-azimuth anisotropic PSDM. By comparison of the dual-azimuth anisotropic PSDM results and the PSDM results using either of the single azimuth, it is found that the seismic data which is acquired vertical to the fault strike is more suitable for fault shadow imaging. What’s more, the dual-azimuth data shows the best illumination in fault shadow, as well as the highest signal-to-noise ratio. The reliability of the dual-azimuth data is demonstrated by the drilling results of the evaluation wells in the fault shadow zone. At the same time, some references on seismic acquisition design and data processing flow can be provided for solving the imaging problem of fault shadow zone in similar areas.
-

-
表 1 2次三维地震的主要采集参数
Table 1. Main parameters of 3D seismic data acquisition for two times
三维地震 电缆长度/m 采集方位 枪深/m 缆深/m 气枪容量/(cu.in) A方位 4 000 30°/210° 5 6 3 063 B方位 6 000 120°/300° 7 7 4 040 -
[1] 刘从印,周平兵,曾驿,等. 番禺4洼地区新近系油气成藏主控因素分析[J]. 中国海上油气,2009,21(2):91-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2009.02.004
[2] FAGIN S. The fault shadow problem:its nature and eli-mination[J]. The Leading Edge,1996,15(9):1005-1013. doi: 10.1190/1.1437403
[3] BRIDUS S. Removing fault shadow distortions by fault-constrained tomography[C]. Expanded Abstracts of 77th SEG Ann. Mtg. , 2007: 3039-3043.
[4] 徐敏,杨晓,王静,等. 叠前深度偏移技术在复杂断块井位目标优化中的应用[J]. 中国石油勘探,2015,20(3):73-78.
[5] 潘兴祥,秦宁,曲志鹏,等. 叠前深度偏移层析速度建模及应用[J]. 地球物理学进展,2013,28(6):3080-3085.
[6] 彭海龙,邓勇,郝建伟,等. 基于断层与层位约束的3D速度建模方法在消除断层阴影中的应用研究[J]. 地球物理学进展,2017,32(6):2520-2526. doi: 10.6038/pg20170632
[7] ARNTSEN B, THOMPSON M. The importance of wide azimuth in imaging[C]. Expanded Abstracts of 65th EAGE Ann. Mtg., 2003: A-40.
[8] HARDWICK A, RAJESH L. A 3D illumination study to investigate fault shadow effects over the Hoop Fault Complex[C]. Expanded Abstracts of 75th EAGE Ann. Mtg., 2013: 3315-3318.
[9] 刘依谋,印兴耀,张三元,等. 宽方位地震勘探技术新进展[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2014,49(3):596-603.
[10] 杜向东. 中国海上地震勘探技术新进展[J]. 石油物探,2018,57(3):321-331.
[11] 朱江梅,李列,杨薇,等. 多方位角地震资料在文昌凹陷勘探开发中的应用分析[J]. 地球物理学进展,2013,28(5):2587-2596.
[12] 朱明,何敏,张振波,等. 海上二次三维双方位地震资料联合成像[J]. 中国海上油气,2016,28(6):15-20.
[13] KEGGIN J, MANNING T, RIETVELD W, et al. Key aspects of Multi-Azimuth acquisition and processing[C]. Expanded Abstracts of 76th SEG Ann. Mtg., 2006: 2886-2890.
[14] 谢涛,邱铁成. 双方位地震资料处理技术及在M区块的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报,2019,16(3):329-333. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2019.03.010
[15] 李列, 盖永浩, 欧阳敏, 等. 南海西部双方位地震资料处理关键技术实践: 以珠三凹陷为例[J], 地球科学, 2019, 44(8): 2590-2596.
[16] TSVANKIN L. Anisotropic parameters and P-wave velocity for orthorhombic media[J]. Geophysics,1997,62(4):1292-1309. doi: 10.1190/1.1444231
[17] GRECHKA V,TSVANKIN L. 3-D moveout velocity analysis and parameter estimation for orthorhombic media[J]. Geophysics,1999,64(3):820-837. doi: 10.1190/1.1444593
[18] GRECHKA V,TSVANKIN L. Seismology of azimuthally anisotropic media and seismic fracture characterization[J]. The Leading Edge,2011,10(3):154-155.
[19] BALL G. Estimation of anisotropy and anisotropic 3-D prestack migration,offshore Zaire[J]. Geophysics,1995,60(5):1495-1513. doi: 10.1190/1.1443883
[20] VESTRUM R W,LAWTON D C,SCHMID R. Imaging structures below dipping TI media[J]. Geophysics,1999,64(4):1239-1246. doi: 10.1190/1.1444630
[21] 凌云,郭向宇,孙祥娥,等. 地震勘探中的各向异性影响问题研究[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2010,45(4):606-623.
[22] 白海军,孙赞东,李彦鹏,等. 3D VSP共检波点道集各向异性分析及参数提取[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2011,46(S1):53-59.
[23] 李振伟,全心怡,张天炬,等. TTI各向异性速度建模在涠西南探区的应用研究[J]. 海洋石油,2019,39(3):21-26.
-




 下载:
下载: