Variable velocity mapping based on structure-fluid coupling constraints and its successful application in A Gas Field in the East China Sea
-
摘要:
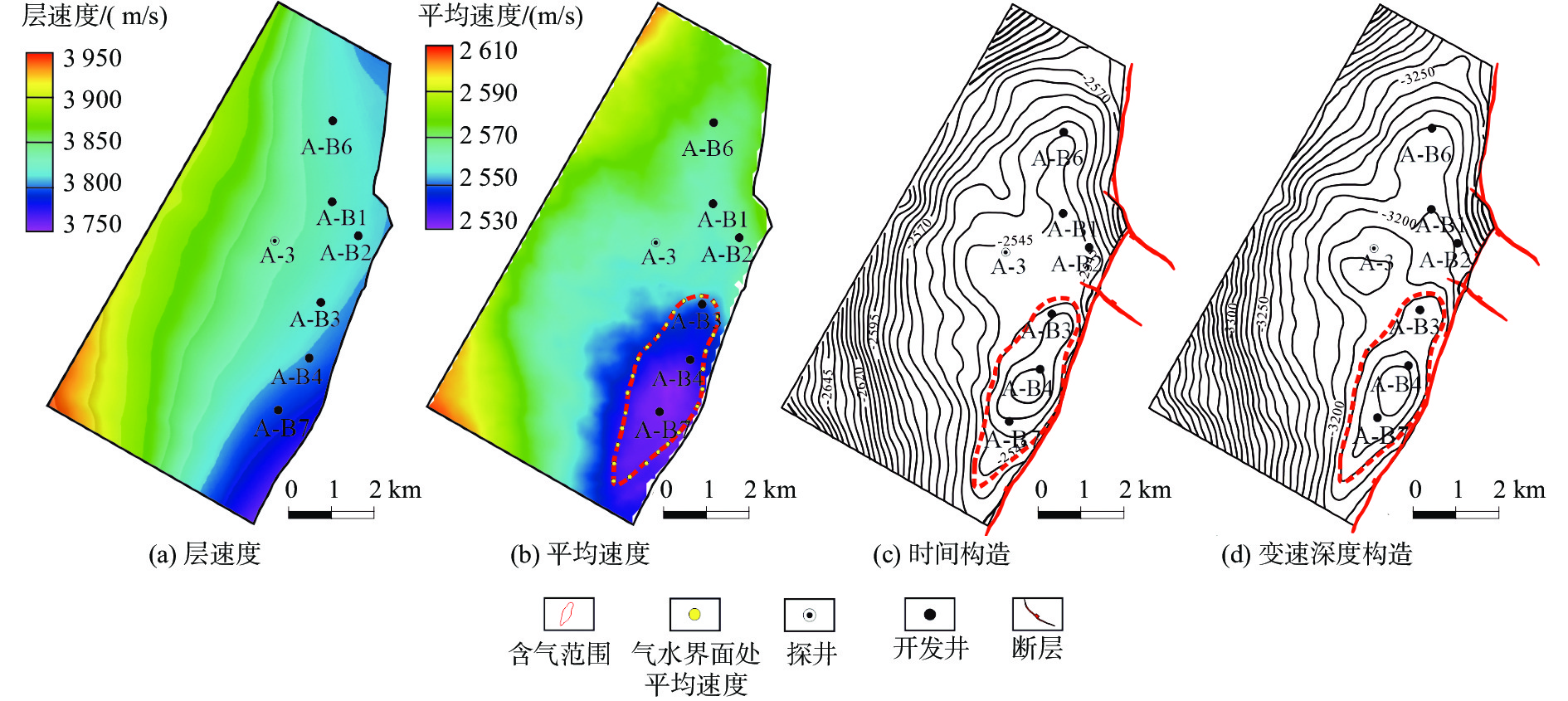
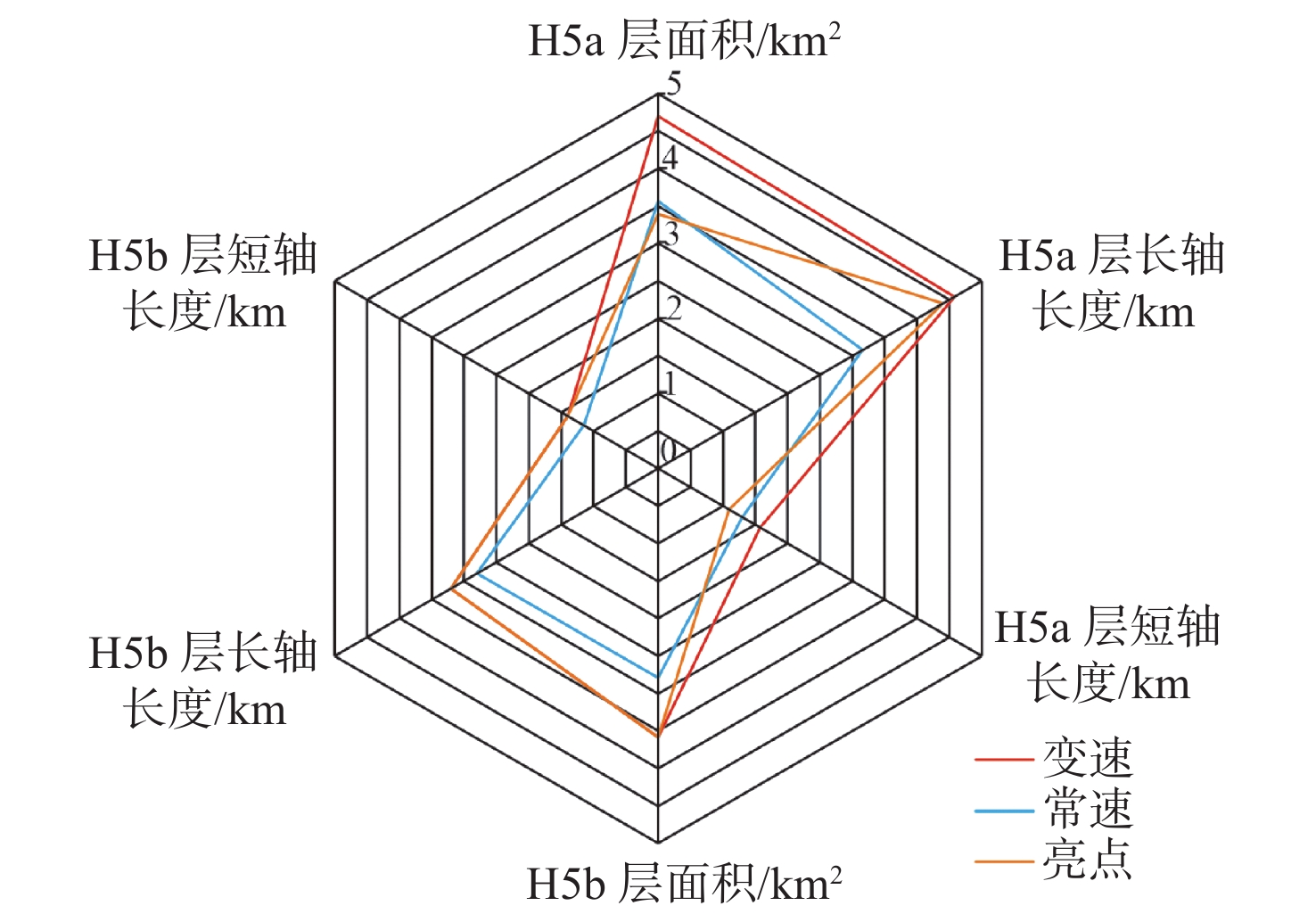
时深转换是构造解释关键步骤之一,时深转换方法主要包括常速成图与变速成图两大类。常速成图操作简单,应用普遍,但不适合速度场横向变化剧烈的工区。建立一种适应速度场横向变化且符合工区地质及油气藏特征的时深转换方法,是本研究探讨的重点。迭代变速成图技术基于叠加速度反演,综合了流体检测成果,通过不断优化速度场开展变速成图,能较准确地预测地下复杂构造的深度,该方法刻画的构造油气藏含气范围与流体检测分布一致,实现了同一油气藏的分布在不同地震信息维度下的耦合。利用迭代变速成图技术,较好解决了A气田钻前构造气藏面积与“亮点”展布范围之间的矛盾,统一了地质油藏认识,扩大了地质储量,有效推动了A气田的挖潜与调整,实现了增储上产。
Abstract:Time-depth conversion is one of the key steps in structural interpretation. It includes mainly two categories: constant-velocity mapping and variable-velocity mapping. The constant-velocity mapping is not suitable for a work area whose lateral velocity field changes intensely. The key point of this paper is to establish a time-depth conversion method that is suitable for the field with variation of lateral velocity and in accordance to the geological characteristics, for which an iterative variable velocity mapping technique was developed based on the inversion of superposition velocity, and the results of hydrocarbon detection were integrated. The iterative mapping technique was applied to the mapping of various complex underground structures, and the results are consistent with the distribution of hydrocarbon and geological implications. In addition, by using the iterative mapping technique, the controversy between structural gas reservoir area, "bright spot" area in the A Gas Field was well solved, and the geological reserves were expanded, and the construction and development of A Gas Field was effectively promoted.
-

-
[1] 王树华,刘怀山,张云银,等. 变速成图方法及应用研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报,2004,34(1):139-146.
[2] 马海珍,雍学善,杨午阳,等. 地震速度场建立与变速构造成图的一种方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2002,37(1):53-59. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7210.2002.01.011
[3] RESHEF M. The use of 3D prestack depth imaging to estimate layer velocities and reflector positions [J]. Geophysics, 1997, 62(1): 206-210.
[4] 彭军,周家雄,马光克,等. 构造成图时深转换方法[J]. 地质与勘探,2020,56(2):411-417.
[5] 白晓寅,黄玉,陈永波,等. 低幅度构造—岩性油气藏识别技术[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2012,47(2):1-8. doi: 10.13810/j.cnki.issn.1000-7210.2012.02.004
[6] 徐立恒,鲜波,薛玉英,等. 高精度地震时深转换方法研究及应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2014,44(5):1712-1719.
[7] JONES I F, IBBOTSON K, GRIMSHAW M, et al. 3-D prestack depth migration and velocity model building [J]. The Leading Edge, 1998, 19(7): 897-906.
[8] RUSSELL B. A simple seismic imaging exercise [J]. The Leading Edge, 1998, 19(7): 885-889.
[9] 李贺,秦童,张笑桀,等. 基于精细迭代建模的速度异常识别方法与应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2019,35(12):74-80. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2019.12010
[10] 樊奇,田继军,成赛男,等. 南沙东北部海域地震速度岩性分析应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2015,31(12):42-51. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2015.12006
[11] 黄兆林,王兴芝,李添才,等. 变速成图技术在南海西部地区的应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2011,27(11):55-59. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2011.11.011
[12] 陈广军,宋国奇. 低幅度构造地震解释探讨平[J]. 石油物探,2003,2(3):395-398. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2003.03.024
[13] 周蒂,胡登科,何敏,等. 深部地层时深转换中的拟合式选择问题[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报),2008,33(4):531-537.
[14] 左中航,姜利群,张海义,等. 渤海油田新近系地层速度异常研究[J]. 地球物理学进展,2019,34(5):2128-2132. doi: 10.6038/pg2019CC0184
[15] 蔡华,张建培,唐贤君. 西湖凹陷断裂系统特征及其控藏机制[J]. 天然气工业,2014,34(10):18-26.
[16] 徐发,张建培,张田,等. 西湖凹陷输导体系特征及其对油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2012,28(7):24-29. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2012.07.001
[17] 李文俊,段冬平,何贤科,等. 西湖凹陷HY气田低渗储层分类描述及流体检测[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2021,37(12):17-26. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2021.125
[18] 张建培,徐发,钟韬,等. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖组-花港组层序地层模式及沉积演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2012,32(1):35-41.
[19] 娄敏,刘江,涂齐催,等. 河流—三角洲相不同厚度储层的地震沉积学研究[J]. 地球物理学进展,2021,36(5):2191-2203. doi: 10.6038/pg2021EE0449
[20] 毛云新,娄敏. 河流相储层刻画与垂向非均质性分析—以西湖凹陷C油田柳浪组为例[J]. 东北石油大学学报,2021,45(5):51-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2021.05.006
[21] 涂齐催,刘江,崔树果,霍凤斌. 基于流体替换进行AVO分析检测深层Ⅰ类气藏[J]. 工程地球物理学报,2011,8(3):279-283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2011.03.005
[22] 涂齐催,张雷,蔡华,等. 砂岩孔隙度对地震反射影响的模型研究[J]. 中国海上油气,2013,25(4):22-25.
[23] 周晶,李久娣,江东辉,等. 海上X构造浅层“亮点”油气藏识别技术及应用[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2019,39(6):207-215. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2019070407
-




 下载:
下载: