Sedimentary characteristics and potential of channel-type lithologic traps in Miocene in Enping Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin
-
摘要:
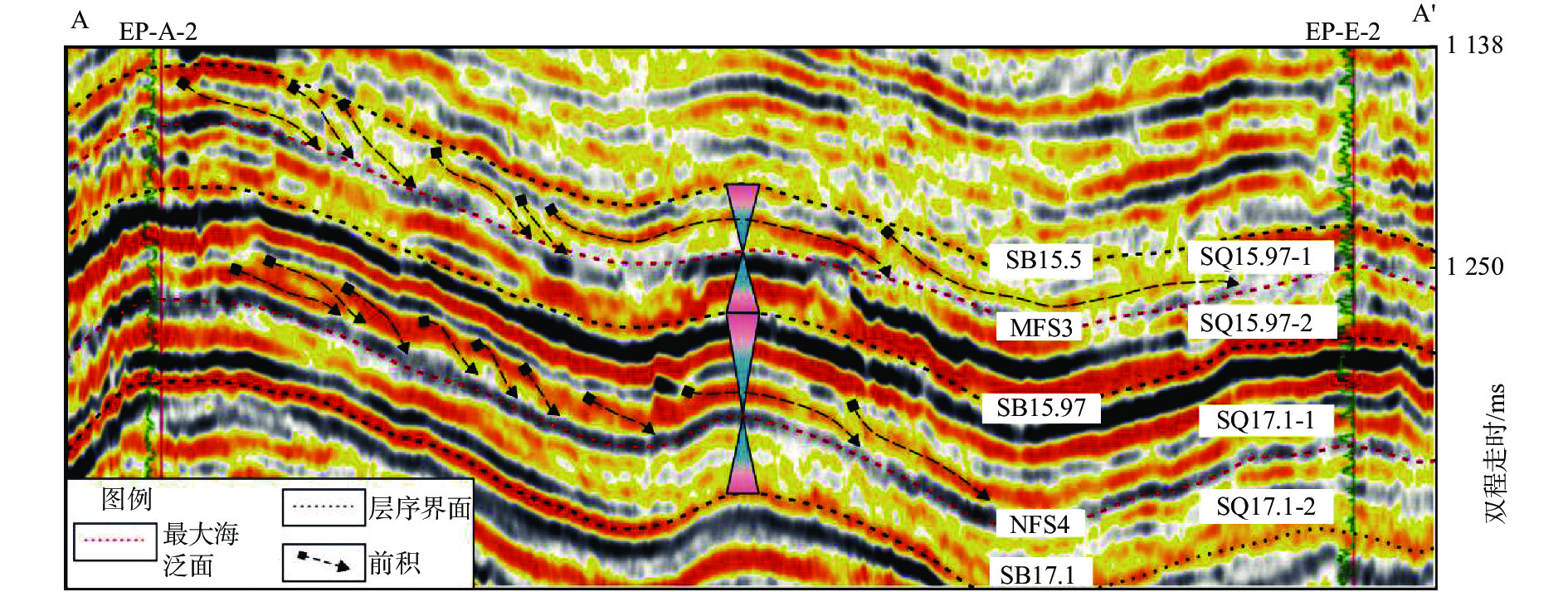
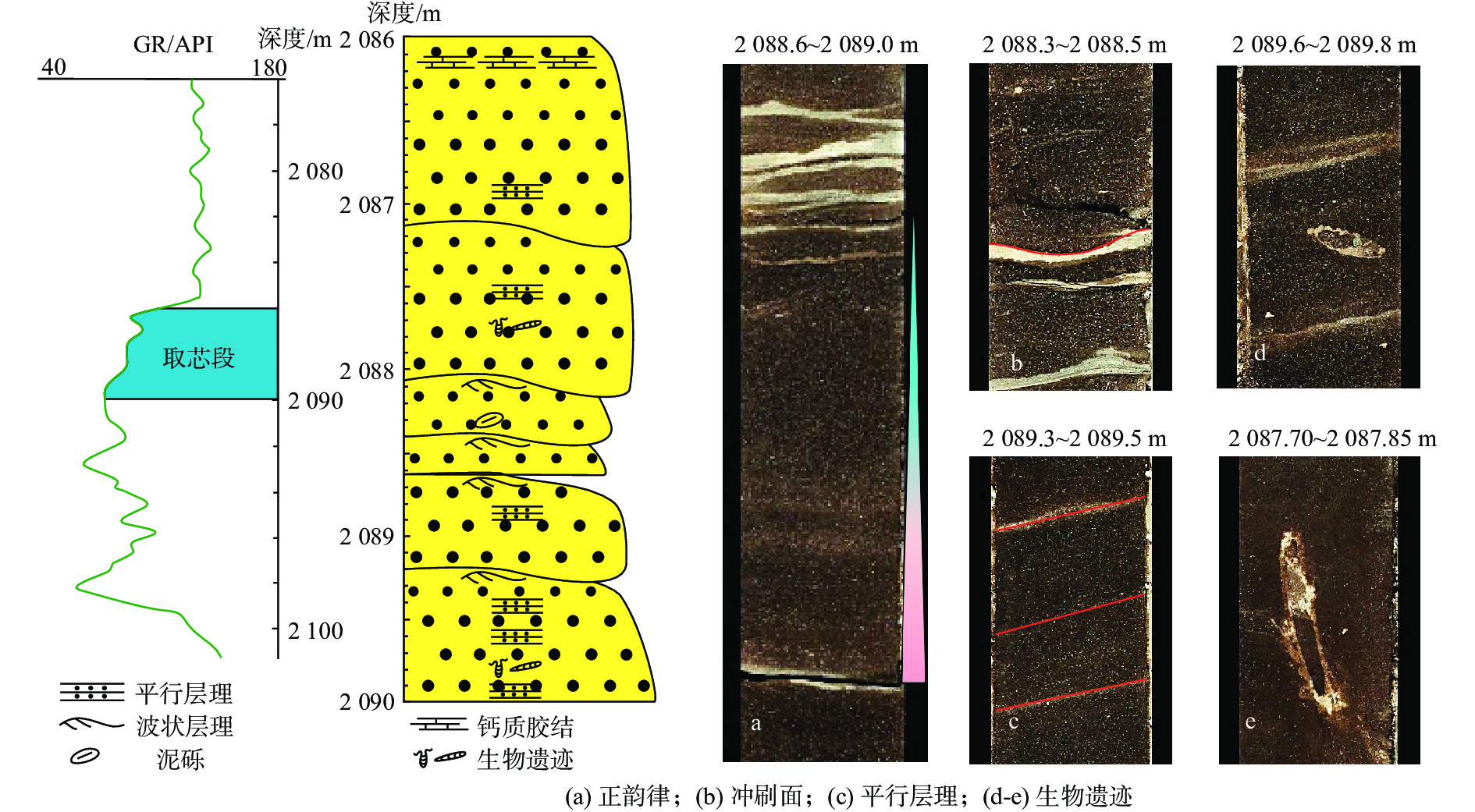
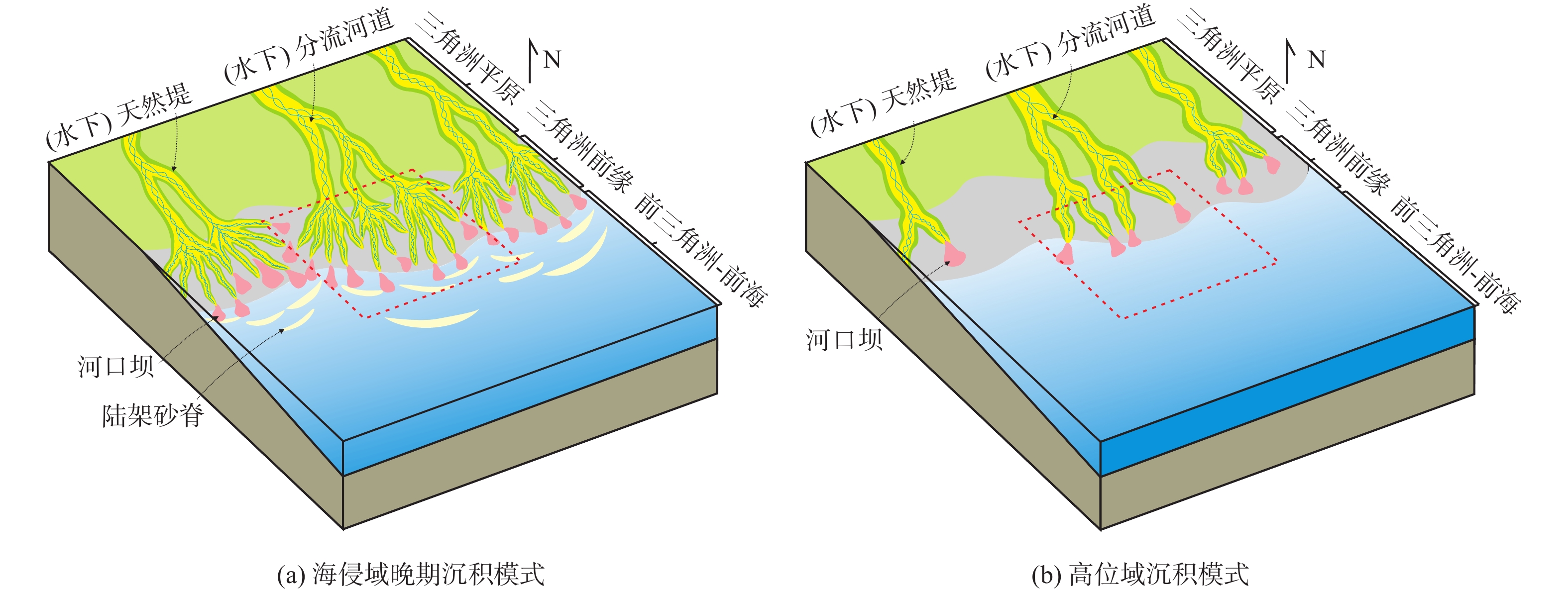
珠江口盆地恩平凹陷中浅层近年来相继有商业油气发现,虽目前仍然以构造圈闭为主,但古珠江三角洲相关岩性目标的评价亟待展开。基于高品质井、震资料,本次研究以恩平凹陷中新统珠江组上段—韩江组下段(T50—T35)为主要目的层,以三级层序界面和最大海泛面为界,建立了恩平凹陷T50—T35间的四级层序格架。在高精度层序地层格架的约束下,进一步采用地震沉积学手段揭示了恩平凹陷以分流河道为主的沉积特征,并建立了不同海平面背景下的河道沉积模式:海侵早期和高位末期河道规模较大,延伸距离较远,平面上常连片发育;海侵晚期和高位早期的河道规模适中,平面上孤立性较强,且前缘常被波浪改造。研究发现,不同类型的河道砂体与特定的构造背景结合可发育“河道切割型”岩性圈闭,并且最大海泛面上下更适合于相关圈闭的发育。据此,研究锁定了恩平A油田西侧斜坡带、E油田东侧斜坡带和G油田西侧披覆构造带等3个岩性圈闭有利区及2个有利勘探目标,为盆地岩性油气藏勘探提供了新思路。
Abstract:Commercial petrol resources have been discovered in the middle and shallow layers of Zhuyi Depression in the Pearl River Mouth Basin in recent years. Although structural traps are still the main ones, the evaluation of related lithologic targets in the paleo Pearl River delta needs to be carried out urgently. Based on high-quality well and seismic data, a fourth-order sequence framework between T50-T35 in Enping Sag is established with the upper member of Zhujiang Formation and the lower member of Hanjiang Formation (T50-T35) in Enping Sag as the main target layer, using a set of third-order sequence boundary and the maximum flooding surface as the boundary. With the constraint of high-resolution sequence stratigraphic framework, the sedimentary characteristics of distributary channel in Enping Sag are further revealed by seismic sedimentology method, and the channel sedimentary models under different sea-level backgrounds are established: the channel scale is larger in the early stage of transgression and the end of highstand, the extension distance is longer, and often developed continuously on the plane; in the late transgression and early highstand, the scale of the river channel moderate, the plane isolation is stronger, and the front edge is often transformed by waves. It is found that different types of channel sand bodies combined with specific structural background can develop "channel cutting" lithologic traps, and about the maximum flooding surface are more suitable for the development of related traps. Therefore, three favorable areas for lithologic trap: east slope of Enping A Oilfield , east slope of Enping E Oilfield and west slop of Enping G Oilfield. Two favorable exploration targets are proposed, which provided new ideas for lithologic reservoir exploration in the basin.
-

-
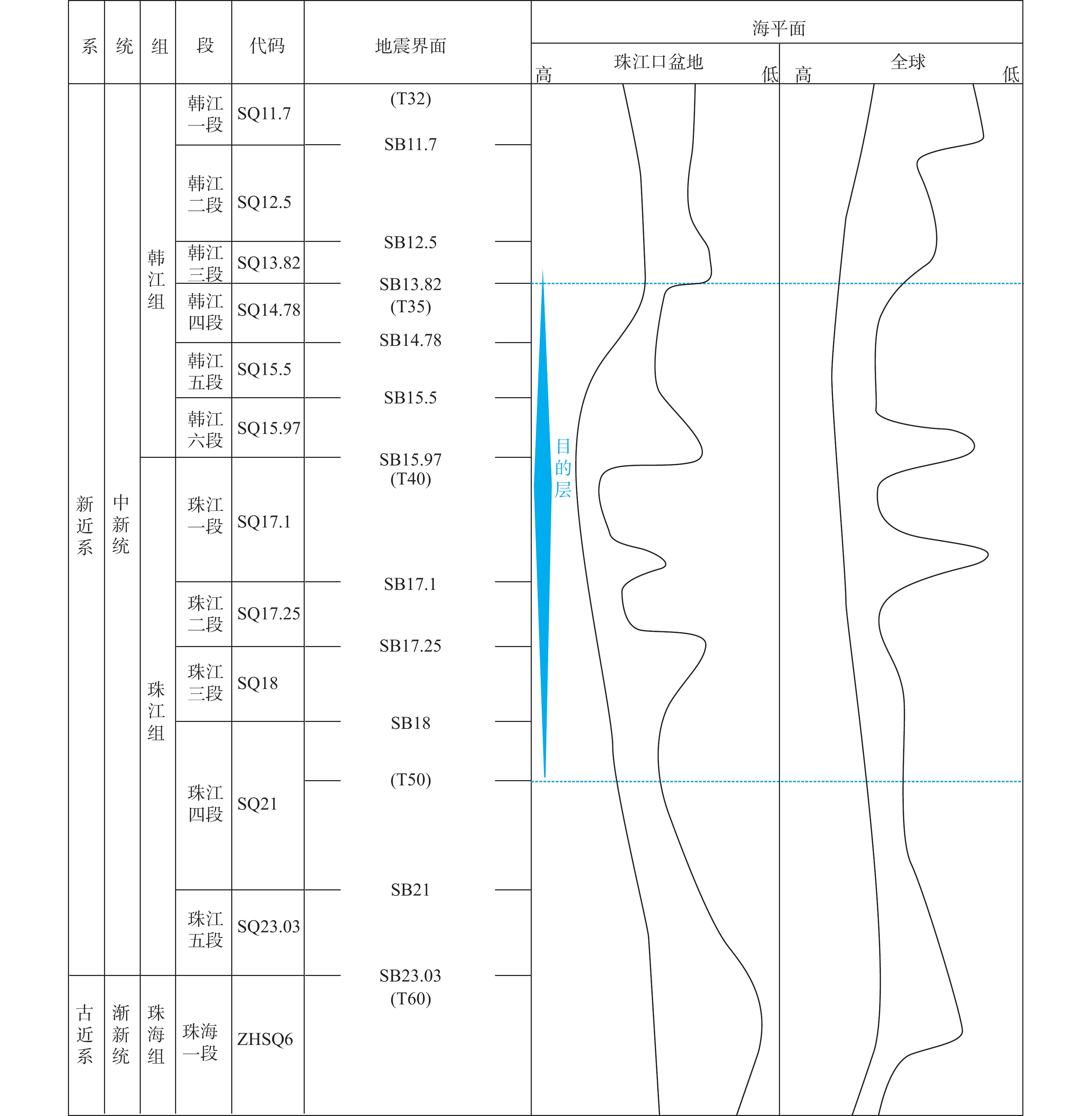
图 3 恩平凹陷四级层序划分方案[14]
Figure 3.
-
[1] 丁琳,杜家元,张向涛,等. 珠江口盆地岩性油气藏类型及形成条件:以惠西南地区中新统珠江组为例[J]. 海相油气地质,2017,22(2):67-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2017.02.009
[2] 朱明,陈维涛,杜家元,等. 珠江口盆地惠西南地区新近系岩性圈闭形成条件及发育类型[J]. 油气地质与采收率,2019,26(6):62-69.
[3] 陈维涛,杜家元,龙更生,等. 珠江口盆地惠州地区珠江组控砂机制及地层-岩性圈闭发育模式[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2012,33(3):449-458. doi: 10.11743/ogg20120315
[4] 丁琳,杜家元,张昌民,等. 古珠江三角洲岩性油藏主控因素分析:以惠西南地区为例[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2016,46(4):96-102.
[5] 许新明,陈胜红,王福国,等. 珠江口盆地恩平凹陷断层特征及其对新近系油气成藏的影响[J]. 现代地质,2014,28(3):543-550. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2014.03.011
[6] 龚再升,王国纯. 中国近海油气资源潜力新认识[J]. 中国海上油气地质,1997,11(1):1-12.
[7] SUN Z,ZHONG Z H,KEEP M,et al. 3D analogue modeling of the South China Sea:a discussion on breakup pattern[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2009,34:544-556. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.09.002
[8] 庞雄,陈长民,邵磊,等. 白云运动:南海北部渐新统—中新统重大地质事件及其意义[J]. 地质论评,2007,53(2):145-151. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2007.02.001
[9] 何敏,朱伟林,吴哲,等. 珠江口盆地新构造运动特征与油气成藏[J]. 中国海上油气,2019,31(5):9-20.
[10] POSAMENTIER H W,KOLLA V. Seismic geomorphology and stratigraphy of depositional elements in deep-water settings[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research,2003,73(3):367-388. doi: 10.1306/111302730367
[11] ZENG H,HENTZ T F. High-frequency sequence stratigraphy from seismic sedimentology:applied to Miocene,Vermilion Block 50,Tiger shoal area,offshore Louisiana[J]. AAPG Bulletin,2004,88:153-174. doi: 10.1306/10060303018
[12] BOURGET J,AINSWORTH R B,THOMPSON S. Seismic stratigraphy and geomorphology of a tide or wave dominated shelf-edge delta (NW Australia):process-based classification from 3D seismic attributes and implications for the prediction of deep-water sands[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2014,57:359-384. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.05.021
[13] CATUNEANU O. Principles of sequence stratigraphy[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science, 2006: 375 .
[14] 芮志锋,林畅松,郭佳,等. 珠江口盆地惠州地区珠江组砂体上倾尖灭的地质-地球物理“逐级预测”方法[J]. 现代地质,2019,33(6):1229-1240. doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.06.09
[15] 米立军,张向涛,丁琳,等. 海上成熟探区中浅层岩性油气藏分布特点与勘探策略:以珠江口盆地惠州凹陷为例[J]. 中国石油勘探,2018,23(6):10-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2018.06.002
[16] 杜家元,陈维涛,张昌民. 珠江口盆地新近系地层岩性圈闭形成条件及发育规律分析[J]. 石油实验地质,2014,36(5):555-561. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201405555
[17] 张向涛,杜家元,丁琳,等. 不同水动力机制下砂体沉积响应及岩性圈闭形成模式[J]. 石油学报,2019,40(S1):105-114. doi: 10.7623/syxb2019S1009
[18] 杜家元,施和生,丁琳,等. 珠江口盆地(东部)地层岩性油气藏勘探有利区域分析[J]. 中国海上油气,2014,26(3):30-36,55.
[19] 陈维涛,杜家元,施和生,等. 珠江口盆地惠西南地区复式油气成藏特征及富集规律[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2015,42(2):194-199,208. doi: 10.11698/PED.2015.02.08
[20] 朱定伟,彭光荣,张忠涛,等. 油气“穿断运移”模式、评价方法与应用:以珠江口盆地恩平凹陷为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2021,45(1):140-147.
[21] 赵鹏,彭光荣,吴静,等. 油气穿越未成岩断裂运移富集成藏模式与主控因素:以珠江口盆地恩平凹陷为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2021,45(1):148-157.
-




 下载:
下载: