Application of geostatistical inversion in prediction of conglomerate interlayer in heavy oil reservoir
-
摘要:
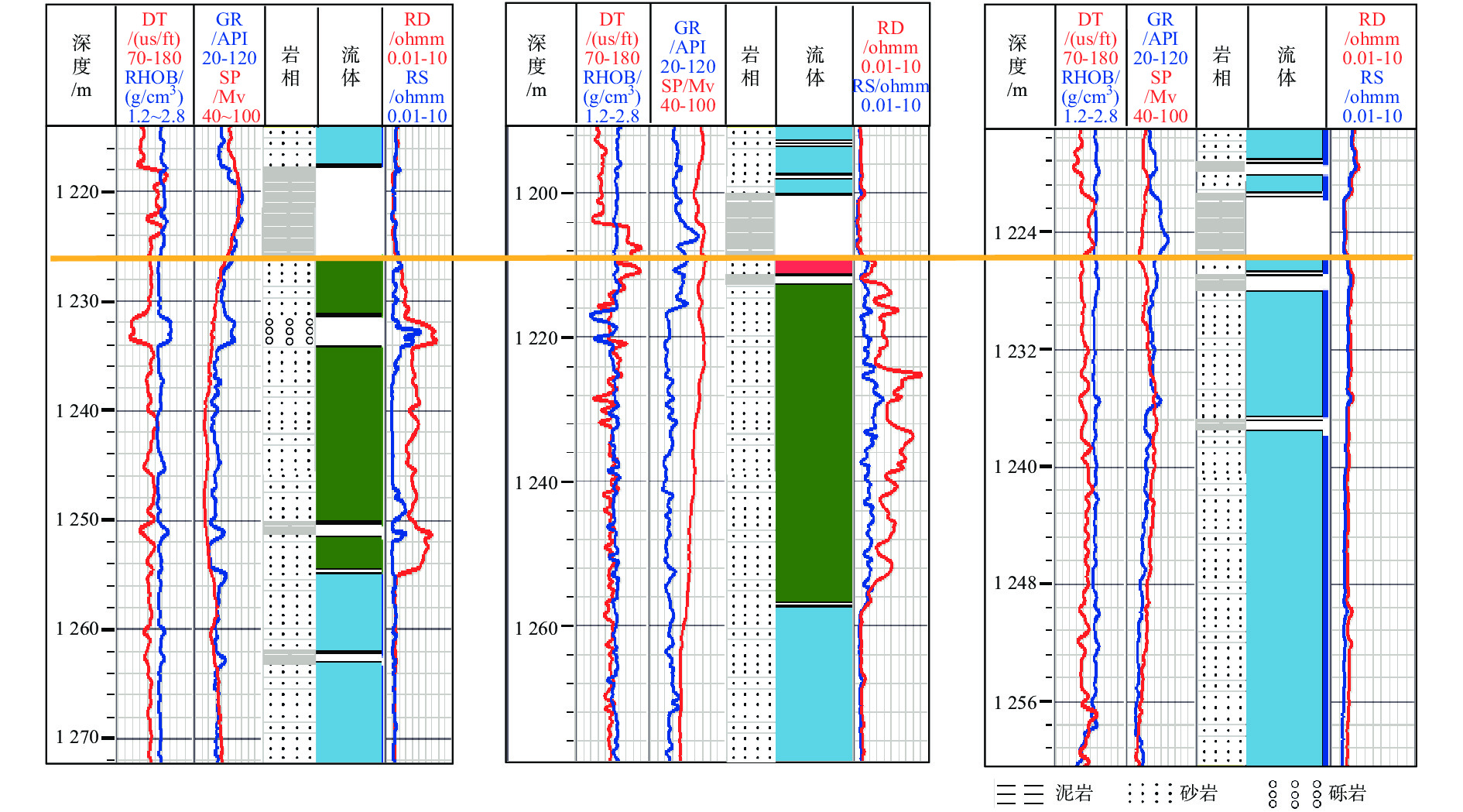
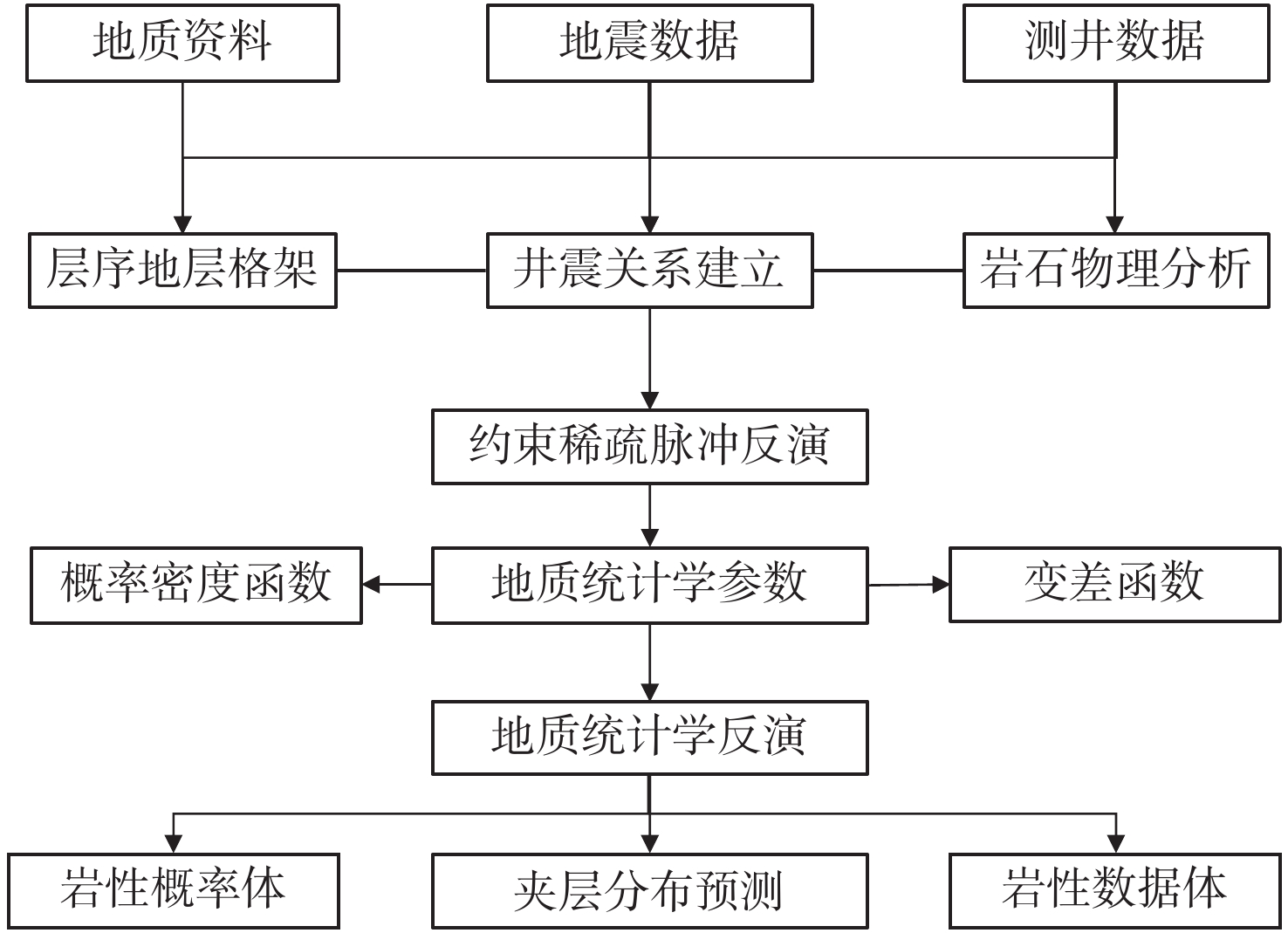
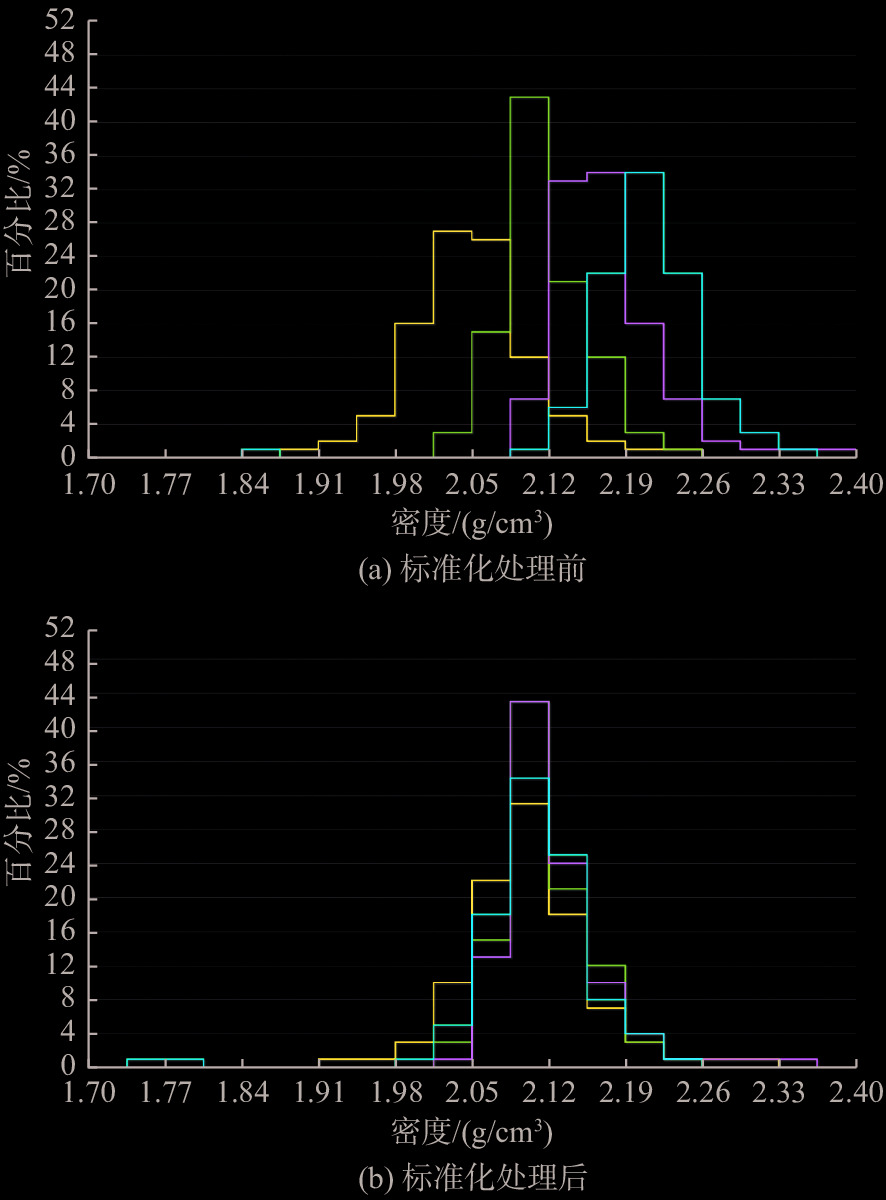
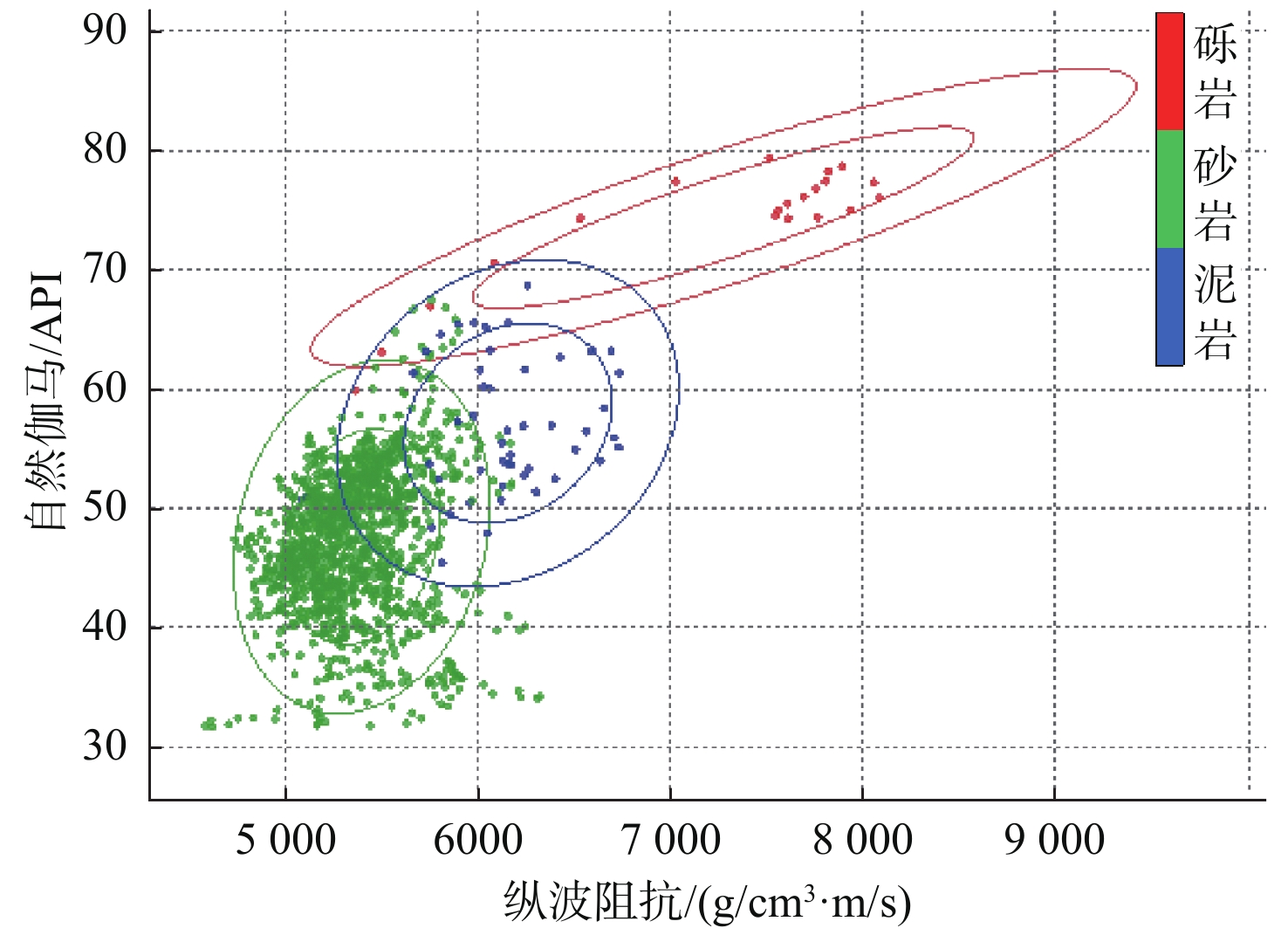
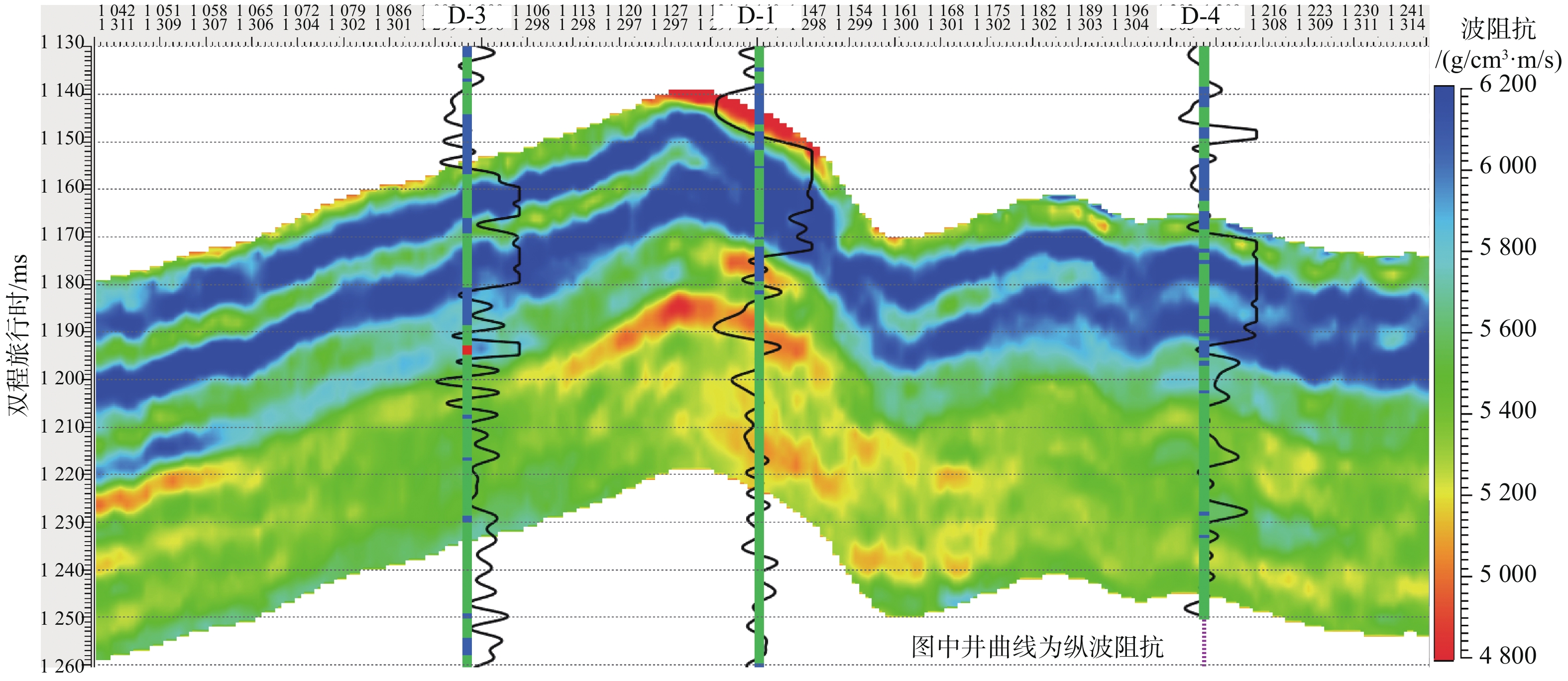
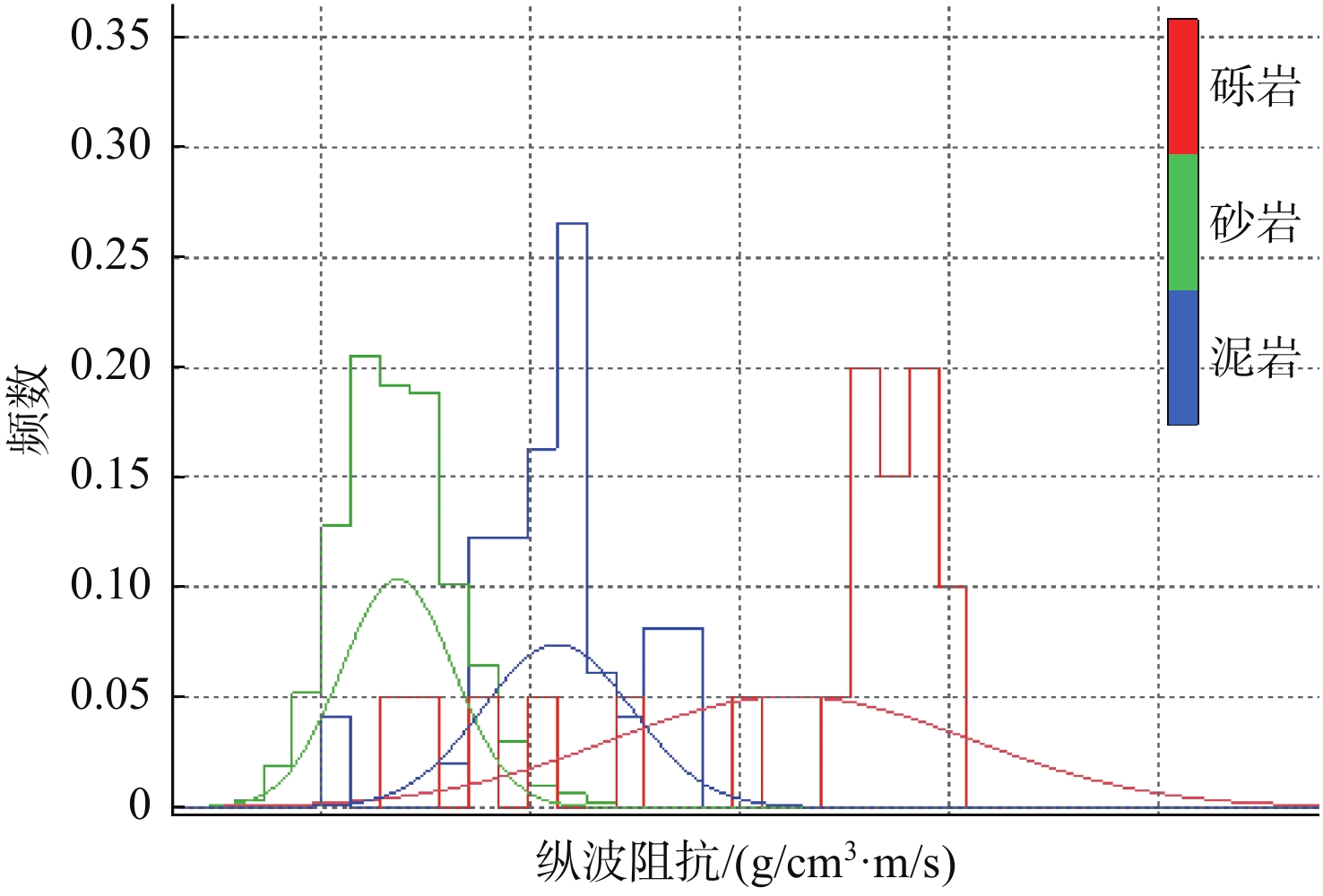
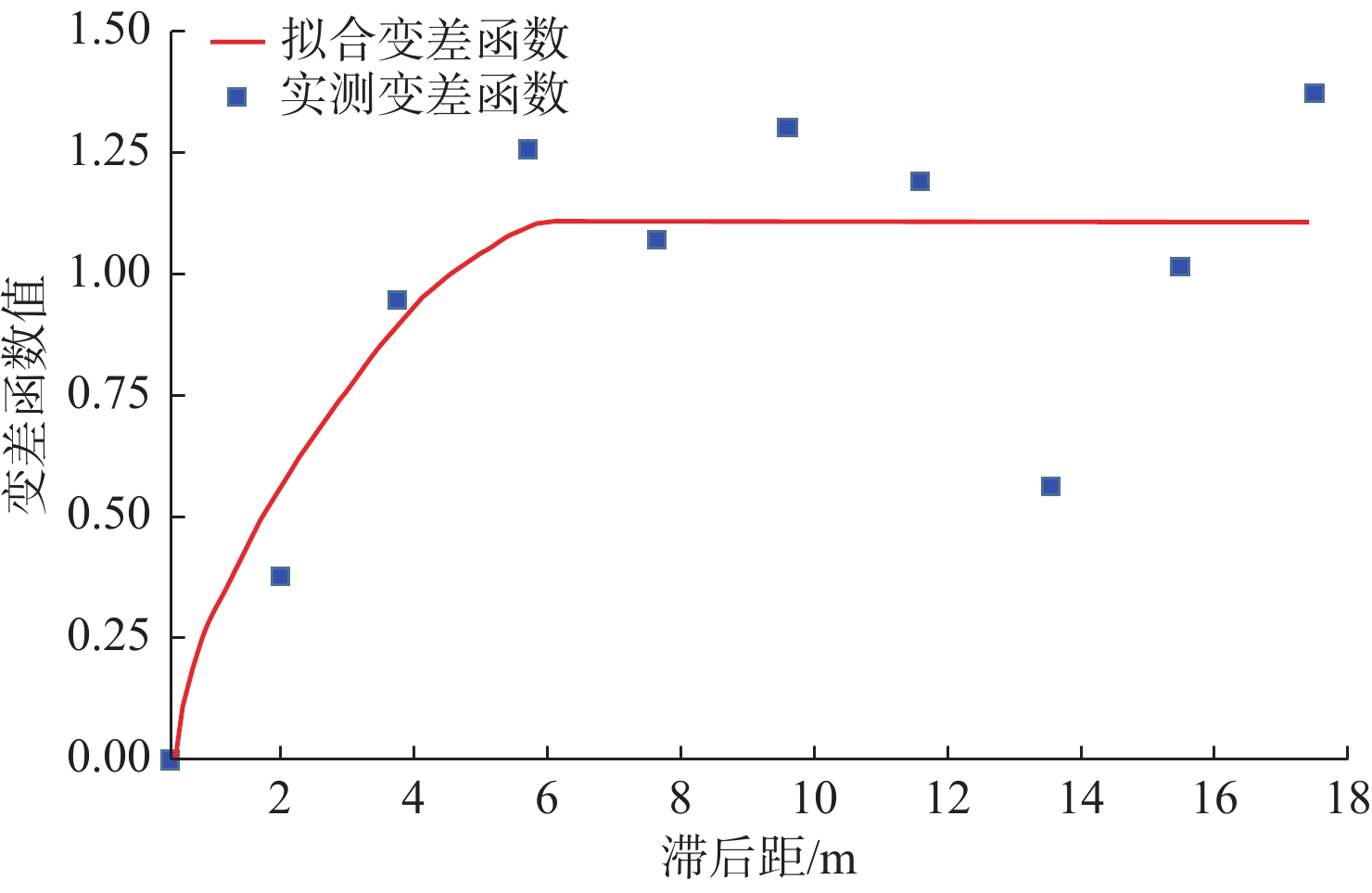
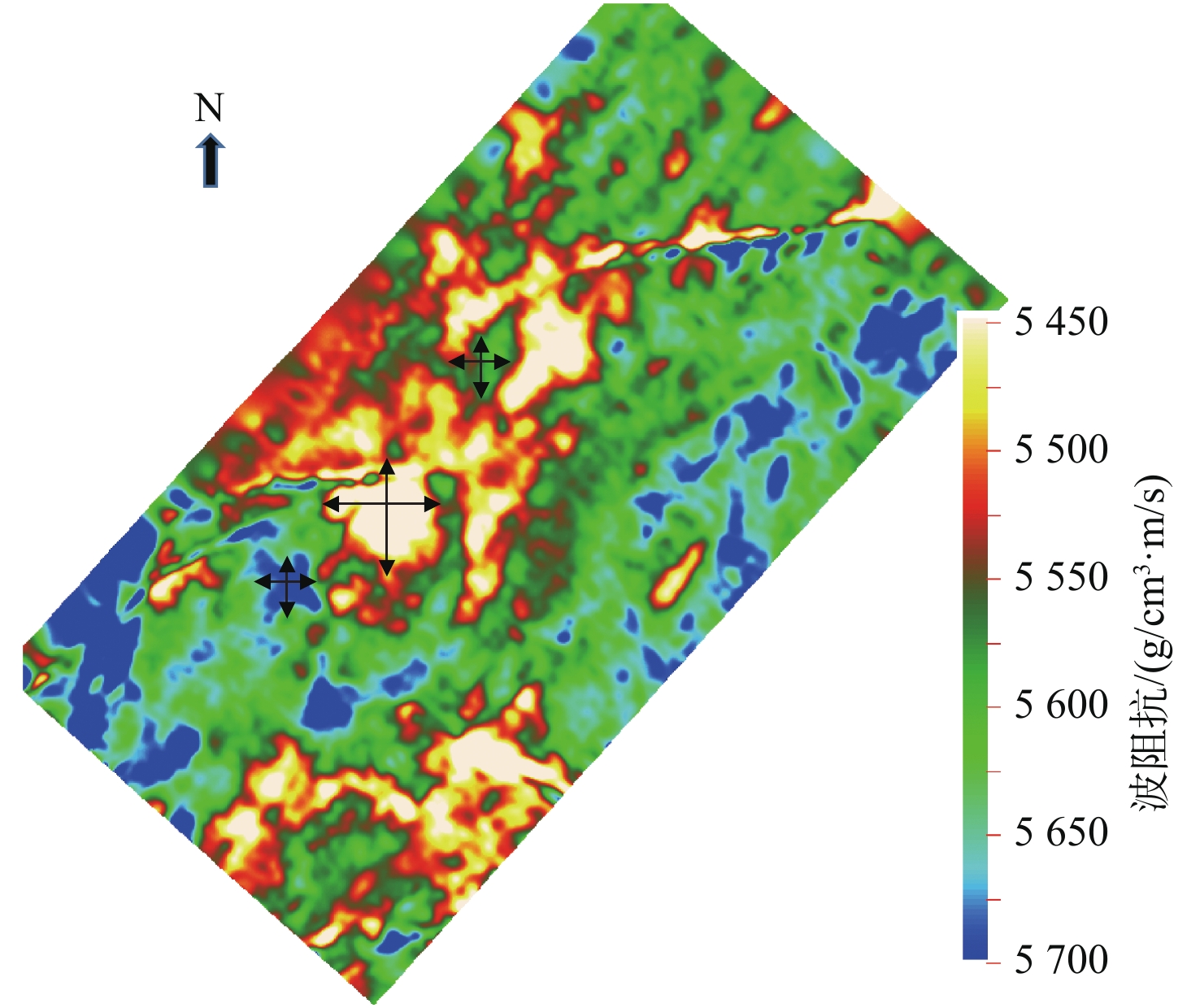
随着开发程度加剧,中海油增储上产不断突破下限,越来越走向深层、低渗、深水和稠油。渤海海域探明原油地质储量超60%为稠油,开发难度大。影响稠油油藏热采开发的关键地质因素有油藏类型、含油饱和度、隔夹层、小断层等,其中隔夹层影响最大。D油田为辫状河沉积、储集层非均质性强的厚层块状特超稠油油藏。针对D油田砾岩夹层薄、地震预测精度低的特点,采用高分辨率地质统计学反演技术,进行了测井曲线标准化、概率密度参数、变差函数研究,获得了岩性和厚度定量表征结果,识别了厚度<5 m的砾岩夹层,平面展布符合研究区地质特征,为心滩内部夹层三维地质模型构建提供了依据。
Abstract:With the intensification of development, CNOOC continues to break through the lower limit of production, and is increasingly moving towards deep, low permeability, deep water and heavy oil. More than 60 % of the proven crude oil geological reserves in the Bohai Sea are heavy oil, which is difficult to develop. The key geological factors affecting the thermal recovery development of heavy oil reservoirs include reservoir type, oil saturation, interlayer and small faults, among which interlayer has the greatest impact. D Oilfield is a thick block super heavy oil reservoir with braided river deposition and strong reservoir heterogeneity. Aiming at the characteristics of thin conglomerate interlayer and low seismic prediction accuracy in D Oilfield, high-resolution geostatistical inversion technology was used to study the standardization of logging curves, probability density parameters and variogram functions. The quantitative characterization results of lithology and thickness were obtained. The conglomerate interlayer with a thickness of less than 5 meters was identified. The plane distribution conforms to the geological characteristics of the study area, which provides a basis for the construction of a three-dimensional geological model of the interlayer inside the heart beach.
-
Key words:
- braided river /
- conglomerate /
- interlayer /
- geostatistical inversion
-

-
[1] 李久,明君,李宾,等. 渤海L油田隔夹层地球物理特征及识别[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,2017,36(1):150-155. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1000-3754.2017.01.028
[2] 陈程,孙义梅. 厚油层内部夹层分布模式及对开发效果的影响[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,2003,22(20):24-27,68.
[3] 王延章,林承焰,温长云,等. 夹层分布模式及其对剩余油的控制作用[J]. 西南石油学院学报,2006,28(5):6-10,109.
[4] 李琳,任作伟,林承焰,等. 曙二区缓坡浊积岩储层隔夹层研究[J]. 西安石油学院学报(自然科学版),1996,11(3):8-18.
[5] 周国文,谭成仟,郑小武,等. H油田隔夹层测井识别方法研究[J]. 石油物探,2006,45(5):542-545,18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2006.05.020
[6] 段冬平,候加根,郭素华,等. 塔河油田九区三叠系油气藏隔夹层识别及其展布研究[J]. 科技导报,2010,28(19):21-25.
[7] 高磊,明君,闫涛,等. 辫状河储集层夹层发育模式及其对开发的影响:以准噶尔盆地风城油田为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2015,42(3):101-105.
[8] 高磊,明君,闫涛,等. 地震属性综合分析技术在泥岩隔夹层识别中的应用[J]. 岩性油气藏,2013,25(4):364-373.
[9] 冯鑫,孟鹏,郭敬民,等. 海上油田稀疏井网辫状河薄泥砾隔夹层预测方法[J]. 中国海上油气,2020,32(1):95-102.
[10] HAAS A,DUBRULE O. Geostatistical inversion-A sequential method for stochastic reservoir modeling constrained by seismic data[J]. First Break,1994,13(12):61-569.
[11] DUBRULE O,THIBAUT M,LAMY P,et al. Geostatistical reservoir characterization constrained by 3D seismic data[J]. Petroleum Geoscience,1998,4(2):121-128. doi: 10.1144/petgeo.4.2.121
[12] 刘钰铭, 侯加根, 宋保全, 等. 辫状河厚砂层内部夹层表征: 以大庆喇嘛甸油田为例[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(5): 836-840.
[13] 何火华, 李少华, 杜家元, 等. 利用地质统计学反演进行薄砂体储层预测[J]. 物探与化探, 2011, 35(6): 804-808.
[14] 刘晓晨, 陆永潮, 杜学斌, 等. 层序格架约束下的地质统计学反演在薄砂体预测中的应用[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(3): 99-109.
[15] 赵继龙, 王俊鹏, 张先龙, 等. 基于地震多属性融合与地质统计学反演的薄层砂岩预测[J]. 地质科技情报, 2014, 33(5): 93-99.
[16] 沈洪涛, 郭乃川, 秦童, 等. 地质统计学反演技术在超薄储层预测中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2017, 32(1): 248-253.
[17] 周超宇. 地质统计学地震反演技术在溱潼南华地区薄砂层的预测应用[J]. 非常规油气, 2018, 5(4): 23-26.
[18] 王雅春, 王璐. 地质统计学反演在杏北西斜坡区储层预测中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2013, 28(5): 2554-2560.
[19] 黄明泉,徐景平,施林炜. ROV在海洋油气田开发中的应用及展望[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2021,37(2):77-84.
[20] 董奇, 卢双舫, 张学娟, 等. 地质统计学反演参数选取及反演结果可靠性分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2013, 37(2): 328-337.
[21] 隋佳铎,林承焰,任丽华,等. 基于地震沉积学方法的湖相浊积砂体识别:以东营凹陷牛20区块沙三中亚段为例[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2020,36(2):33-42.
[22] 徐立恒, 陈显森, 姜岩, 等. 不同变差函数变程下随机反演与随机模拟对比分析 [J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(2): 224-233.
[23] 郭丽娜,王龙,陈培元,等. 渤海P油田河流相多层砂岩油藏储层连通性分析[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2020,36(5):57-63.
[24] 黄江波,左中航,侯栋甲,等. 叠前密度反演技术在沙南凹陷中深层储层预测中的应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2021,37(2):46-53.
[25] 徐立恒, 马耀军, 朱遂珲, 等. 油田开发后期井间砂体识别 [J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2019, 54(2): 390-397.
[26] 赵鹏飞,王庆如,陈飞. 海上油气资源储量和潜在资源量分类[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2020,36(10):68-75.
[27] 祁鹏,黄饶,仝中飞,等. 宽频地震在东海盆地A凹陷油气勘探中的应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2020,36(6):69-75.
-




 下载:
下载: