Faults development controlled the Neogene hydrocarbon accumulation in the mid-Huanghekou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin
-
摘要:
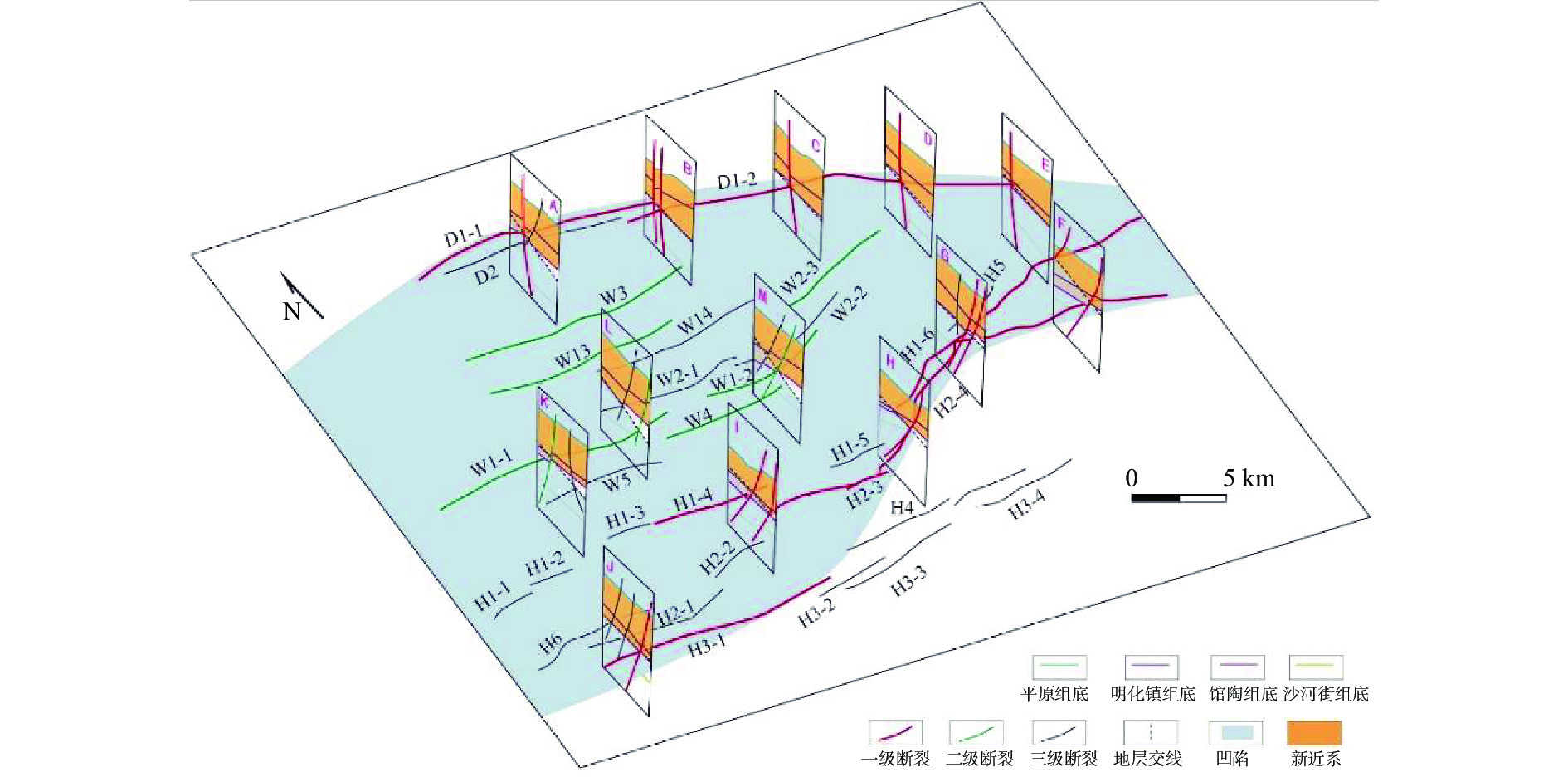
黄河口凹陷是渤海海域重要的富烃凹陷,区域主要的烃源岩沙三段在明化镇组沉积时期开始大规模生排烃,此时研究区内断裂发育,活动强度较高,因此,断裂有效性分析是确定区域油气输导体系、判断油气输导运移成藏的重要研究内容。通过三维地震数据及钻井分析,对黄河口凹陷中洼断裂分布、活动性及生长演化进行了系统的分析,结合区域烃源岩分布及钻井油气分布特征,总结断裂对新近系油气富集的控制作用。研究表明,黄河口凹陷中洼断裂活动生长具有“先变弱再变强”的特征−从沙河街组沉积时期到馆陶组沉积时期断裂活动强度逐渐减弱,断裂活动区域逐渐缩小;明化镇组沉积时,中洼断裂活动增强,区域内断裂全面活跃。研究区早期断裂多以长度短、断距小为特征;晚期洼陷中心联结组合形成大型断裂,油源断裂沟通源储,大部分油气沿着断裂运移至浅层馆陶及明化镇组砂体中,再向两侧砂体构造高部位运移,而南部缓坡带和北部陡坡带因为断裂活动速率不同而具有不同的油气聚集特征;南部缓坡带断裂晚期活动速率不高,能够对油气进行有效封堵,自深凹而来的油气沿着砂体构造脊在缓坡带馆陶及明化镇组砂体中聚集成藏;而北部陡坡带晚期断裂活动速率高,油气在断裂附近合适的明化镇组浅层圈闭中成藏。
Abstract:Huanghekou Sag is an important hydrocarbon-rich sag in Bohai Sea and can be divided into West-, Mid-, and East-Huanghekou sags. The source rocks of the third member of Shahejie Formation in the Mid-Huanghekou sag began to generate and expel hydrocarbons on large scale during the sedimentary period of Minghuazhen Formation. The analysis of active faults and their impact on the Mid-Huanghekou sag evolution is important to understand the regional hydrocarbon migration and accumulation. Based on 3D seismic and drilling data analyses, the distribution, activity, and growth evolution of the faults in the Mid-Huanghekou sag were systematically analyzed. Combined with the distribution characteristics of regional source rocks and oil-gas resources, the controlling effect of faults on hydrocarbon accumulation in the Neogene was summarized. The study shows that the development of faults in the mid-Huanghekou sag is characterized by “weakening first and then strengthening”. From the deposition period of Shahejie Formation to the deposition period of Guantao Formation, the intensity of fault activity gradually decreased and the fault activity area gradually shrank. During the deposition of Minghuazhen Formation, the fault activity was enhanced and the faults were fully active in the region. In the early stage, faults were small-sized; and in the late stage, they developed and merged into large ones in the central area of the sag, forming network of active faults-source rocks-reservoirs. Most of oil and gas migrated to the sand bodies of shallow facies of the Guantao and Minghuazhen Formations along active faults, and further to the both sides the structural highs of reservoirs. The north and south secondary structures have different hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics. In the southern gentle slope zone, the fault activity rate is small in the late stage, which effectively favored the sealing of the oil and gas, and finally formed large-scale oil-gas accumulation in the sand body along structural ridge. In the northern steep slope zone, the fault activity rate is great in the late stage, and the oil and gas formed in certain shallow structural traps nearby faults.
-
Key words:
- fault growth /
- Neogene /
- hydrocarbon /
- accumulation pattern /
- mid-Huanghekou Sag
-

-
[1] 吴哲,王文勇,张忠涛,等. 张扭性断裂带的生长过程与油气穿断运移评价:以珠江口盆地恩平凹陷为例[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2020,36(1):50-58.
[2] 蒋子文,罗静兰,王嗣敏,等. 郯庐断裂新生代构造演化及其对烃源岩生排烃的影响:以辽东湾坳陷辽中凹陷为例[J]. 高校地质学报,2018,24(4):573-583.
[3] 万桂梅,周东红,汤良杰. 渤海海域郯庐断裂带对油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2009,30(4):450-454+461. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2009.04.010
[4] 邓津辉,周心怀,魏刚,等. 郯庐走滑断裂带活动特征与油气成藏的关系:以金县地区为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2008,29(1):102-106. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2008.01.016
[5] 付广,王浩然. 不同时期油源断裂输导油气有利部位确定方法及其应用[J]. 石油学报,2018,39(2):180-188. doi: 10.7623/syxb201802006
[6] 吴智平,陈伟,薛雁,等. 断裂带的结构特征及其对油气的输导和封堵性[J]. 地质学报,2010,84(4):570-578.
[7] ROTEVATN A,JACKSON C A L,TVEDT A B M,et al. How do normal faults grow?[J]. Journal of Structural Geology,2018,125:174-184.
[8] FOSSEN H,ROTEVATN A. Fault linkage and relay structures in extensional settings:a review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2016,154:14-28. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.11.014
[9] LIU Y,CHEN Q,WANG X,et al. Influence of normal fault growth and linkage on the evolution of a rift basin:a case from the Gaoyou Depression of the Subei Basin,eastern China[J]. AAPG Bulletin,2017,101(02):265-288. doi: 10.1306/06281615008
[10] 范婕,蒋有录,刘景东,等. 长岭断陷龙凤山地区断裂与油气运聚的关系[J]. 地球科学,2017,42(10):1817-1829.
[11] HINDLE A. D. Petroleum migration pathways and charge concentration:a three-dimensional mode[J]. AAPG Bulletin,1997,81(9):1451-1481.
[12] 蒋有录,刘培,宋国奇,等. 渤海湾盆地新生代晚期断层活动与新近系油气富集关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2015,36(4):525-533. doi: 10.11743/ogg20150401
[13] 江涛,黄晓波,李慧勇,等. 渤西伸展背景下先存-新生断裂体系特征及控藏作用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2020,36(11):27-34.
[14] 姜丽娜,邹华耀. 郯庐断裂带渤中-渤南段新构造运动期断层活动与油气运聚[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2009,30(4):8.
[15] 王军,吴奎,樊建华,等. 辽中凹陷走滑断裂带原油来源、运移及分布层系[J]. 新疆石油地质,2017,38(6):707-714.
[16] 陈云锋. 东营凹陷八面河地区西南段断裂输导能力研究[J]. 天然气地球科学,2014,25(S1):39-45.
[17] 周心怀,牛成民,滕长宇. 环渤中地区新构造运动期断裂活动与油气成藏关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2009,30(4):469-475, 482. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2009.04.013
[18] 庄新兵,邹华耀,滕长宇. 新构造运动期断裂活动对油气的控制作用:以渤中地区为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2012,41(3):452-459.
[19] 刘涛,但志伟,方中于,等. 番禺4地区断裂发育期次与油气藏形成的关系[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2015,31(11):18-22.
[20] 孙和风,周心怀,彭文绪,等. 黄河口凹陷新近系浅水三角洲岩性油气藏成藏模式[J]. 大庆石油学院学报,2010,34(2):11-15, 37, 122-123.
[21] 于海波,王德英,牛成民,等. 层序—构造对黄河口凹陷新近系油气分布及成藏的控制作用[J]. 油气地质与采收率,2012,19(6):42-46, 113-114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2012.06.010
[22] 胡光义,杨希濮,古莉,等. 渤海海域黄河口凹陷新近系多油水系统油藏成因分析[J]. 地学前缘,2012,19(2):95-101.
[23] 孙和风,周心怀,彭文绪,等. 渤海南部黄河口凹陷晚期成藏特征及富集模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2011,38(3):307-313.
[24] 彭文绪,孙和风,张如才,等. 渤海海域黄河口凹陷近源晚期优势成藏模式[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2009,30(4):510-518. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2009.04.019
[25] 陈斌,邓运华,郝芳,等. 黄河口凹陷BZ34断裂带油气晚期快速成藏模式[J]. 石油学报,2006,27(1):37-41. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2006.01.008
[26] 田立新,余宏忠,周心怀,等. 黄河口凹陷油气成藏的主控因素[J]. 新疆石油地质,2009,30(3):319-321.
[27] 张新涛,周心怀,牛成民,等. 渤海湾盆地黄河口凹陷油气成藏模式[J]. 石油天然气学报,2014,36(3):30-36, 5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2014.03.007
[28] 傅强,刘彬彬,徐春华,等. 渤海湾盆地黄河口凹陷构造定量分析与油气富集耦合关系[J]. 石油学报,2013,34(S2):112-119. doi: 10.7623/syxb2013S2013
[29] 温宏雷,邓辉,李正宇,等. 渤海海域新近系明化镇组断裂控藏作用定量评价:以黄河口凹陷中央构造脊为例[J]. 油气地质与采收率,2017,24(4):36-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2017.04.006
[30] 姜治群,吴智平,李伟,等. 断裂对黄河口凹陷新近系油气分布的控制作用[J]. 特种油气藏,2016,23(6):50-54, 143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2016.06.011
[31] 赵梦,潘文静,郝轶伟,等. 渤海海域黄河口凹陷渤中29-6构造火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2019,35(1):22-34.
[32] 庞雄奇,郭永华,姜福杰,等. 渤海海域优质烃源岩及其分布预测[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2009,30(4):393-397. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2009.04.001
[33] 朱秀香,吕修祥,王德英,等. 渤海海域黄河口凹陷走滑转换带对油气聚集的控制[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2009,30(4):476-482. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2009.04.014
[34] 王应斌,黄雷,王强,等. 渤海浅层油气富集规律:以黄河口凹陷为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2011,32(5):637-641, 650.
[35] 雷宝华. 生长断层活动强度定量研究的主要方法评述[J]. 地球科学进展,2012,27(9):947-956.
[36] 张晓庆,吴智平,周心怀,等. 渤海南部新生代构造发育与演化特征[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2017,41(1):50-60.
[37] 贾博,吴智平,张晓庆,等. 黄河口凹陷新生代断裂体系与构造演化[J]. 特种油气藏,2017,24(1):76-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2017.01.015
[38] 滕长宇,邹华耀,郝芳. 渤海湾盆地构造差异演化与油气差异富集[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2014,44(4):579-590.
[39] 张新涛,牛成民,黄江波,等. 黄河口凹陷渤中34区明化镇组下段油气输导体系[J]. 油气地质与采收率,2012,19(5):27-30, 112-113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2012.05.007
[40] 何仕斌,朱伟林,李丽霞. 渤中坳陷沉积演化和上第三系储盖组合分析[J]. 石油学报,2001,22(2):38-43, 121-122. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2001.02.007
-




 下载:
下载: