Preliminary study on depositional and reservoir characteristics of high-saturation gas hydrate worldwide
-
摘要:
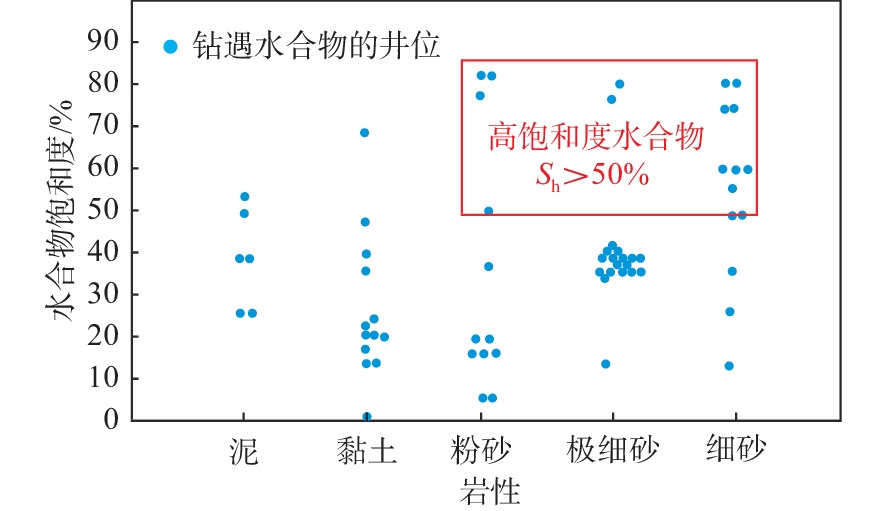
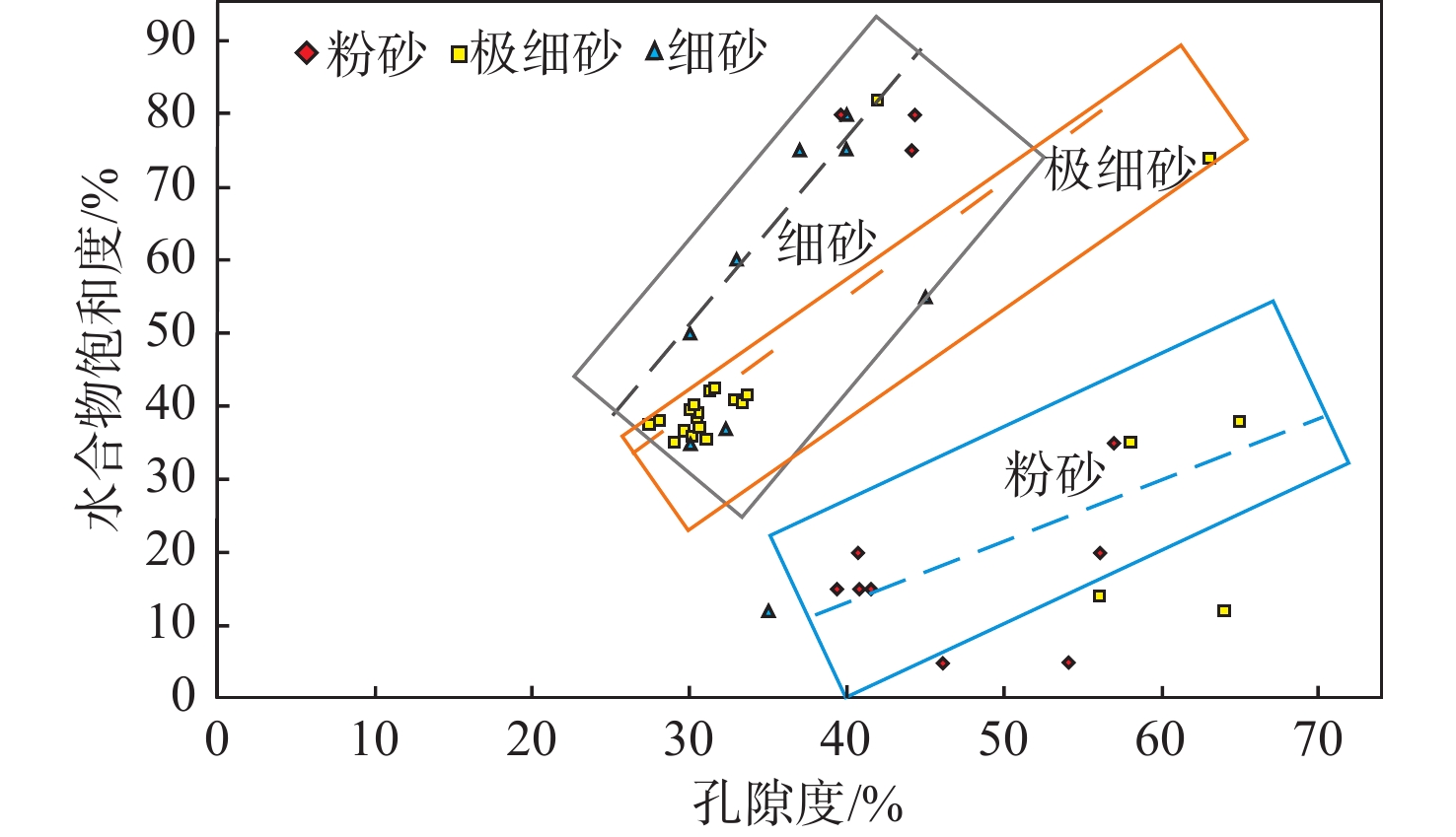
天然气水合物是全球未来能源的接替资源,高饱和度(Sh>50%)水合物储层是未来面向工业化开采的首要选择。截止到目前,高饱和度天然气水合物有利沉积相带与储层条件之间的关系仍缺乏系统研究。根据公开发表的文献资料,系统总结了墨西哥湾、日本南海海槽、韩国郁陵盆地、印度Krishna-Godavari盆地以及南海神狐海域等全球5个天然气水合物热点钻探区64口井取芯及井-震联合资料,对含水合物储层岩性、沉积环境、水合物饱和度等参数进行的详细总结分析表明:在必要的温压环境和气源条件下,深海平原区块体搬运沉积和浊流等高沉积速率的深水砂质沉积物赋存孔隙型水合物,水合物可分布在砂岩、极细砂岩、粉砂岩、粉砂质黏土和泥等粒级沉积物中,但高饱和度水合物主要赋存于粉砂-细砂岩中,储层孔隙度与饱和度具有一定的正相关性。中国南海神狐海域发现含有孔虫黏土质粉砂或粉砂质黏土这种特殊的细粒沉积物,其水合物饱和度可达到中高水平(20%~76 %)。上述研究成果及认识奠定了下一步寻找优质天然气水合物储层的地质基础,也可为高饱和度水合物商业化勘探开发提供理论依据。
Abstract:Natural gas hydrate resources have been a popular replacement object of global energy in the future. High-saturated (Sh>50%) hydrate reservoir is the first choice for industrial exploration and exploitation. However, relationship between saturation of gas hydrate and its reservoir facies lacks of systematic investigation at present. Based on published literatures, five gas hydrate-exploration hotpot areas in the word are systematically summarized, including the Gulf of Mexico, the Nankai Trough in Japan, the Ulleung Basin in South Korea, the Krishna-Godavari basin in India, and the Shenhu area of the South China Sea. The cores and logs of 64 penetrated wells were used to analyze the lithology, sedimentary environment, hydrate saturation and other parameters of the hydrate reservoir in detail. The results show that under suitable temperature and pressure conditions associated with gas sources, the deposits of MTDs (mass transport deposits) and turbidite in deep marine areas are facilitated with good gas hydrate resources. The reservoirs of gas hydrate include fine-grained sandstone, very fine-grained sandstone, siltstone, and silty mud and mud sediments. However, the high saturation hydrate mainly occurs in siltstone and fine-grained sandstone. The porosity and saturation of the gas hydrate reservoir have a relatively positive correlation. The Shenhu area of the South China Sea is mainly composed of fine-grained sediments, including clayed silt or foraminifera-rich silty clay. The sand content is low (less than 10%), but the hydrate saturation can reach a medium-to-high level (20%-48%). This study provides a geological base for large-scale exploration and development of high-quality and high-saturation hydrates gas reservoirs.
-
Key words:
- gas hydrate /
- depositional system /
- reservoir conditions /
- high saturation /
- worldwide
-

-
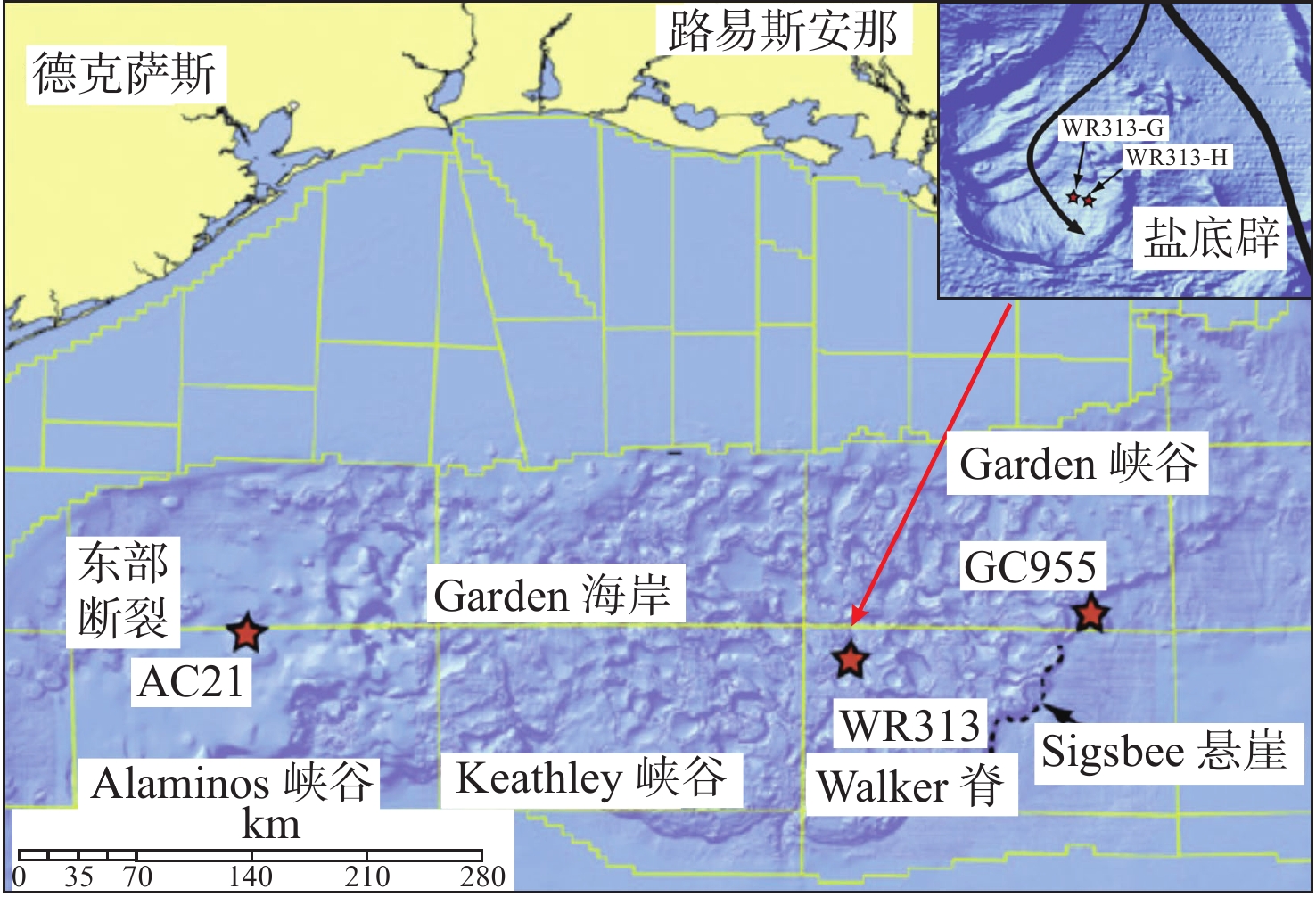
图 1 墨西哥湾JIP Leg II站位平面分布图[11]
Figure 1.
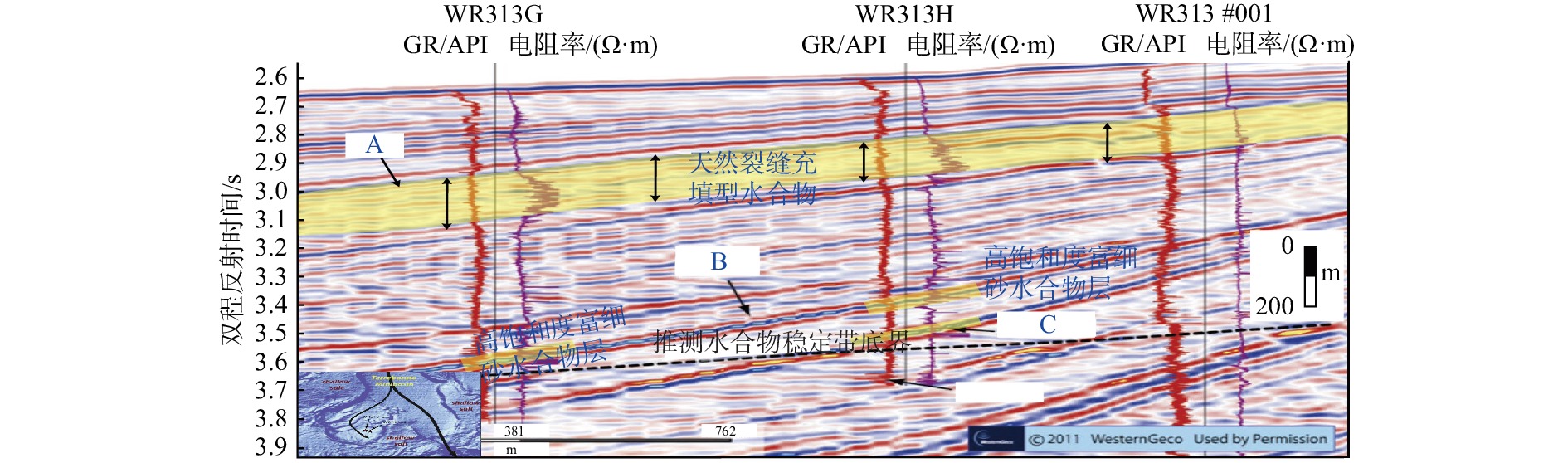
图 2 墨西哥湾Terrebonne盆地过WR313-G和WR313-H的井-震联合剖面以及WR313-#001工业井[11]
Figure 2.
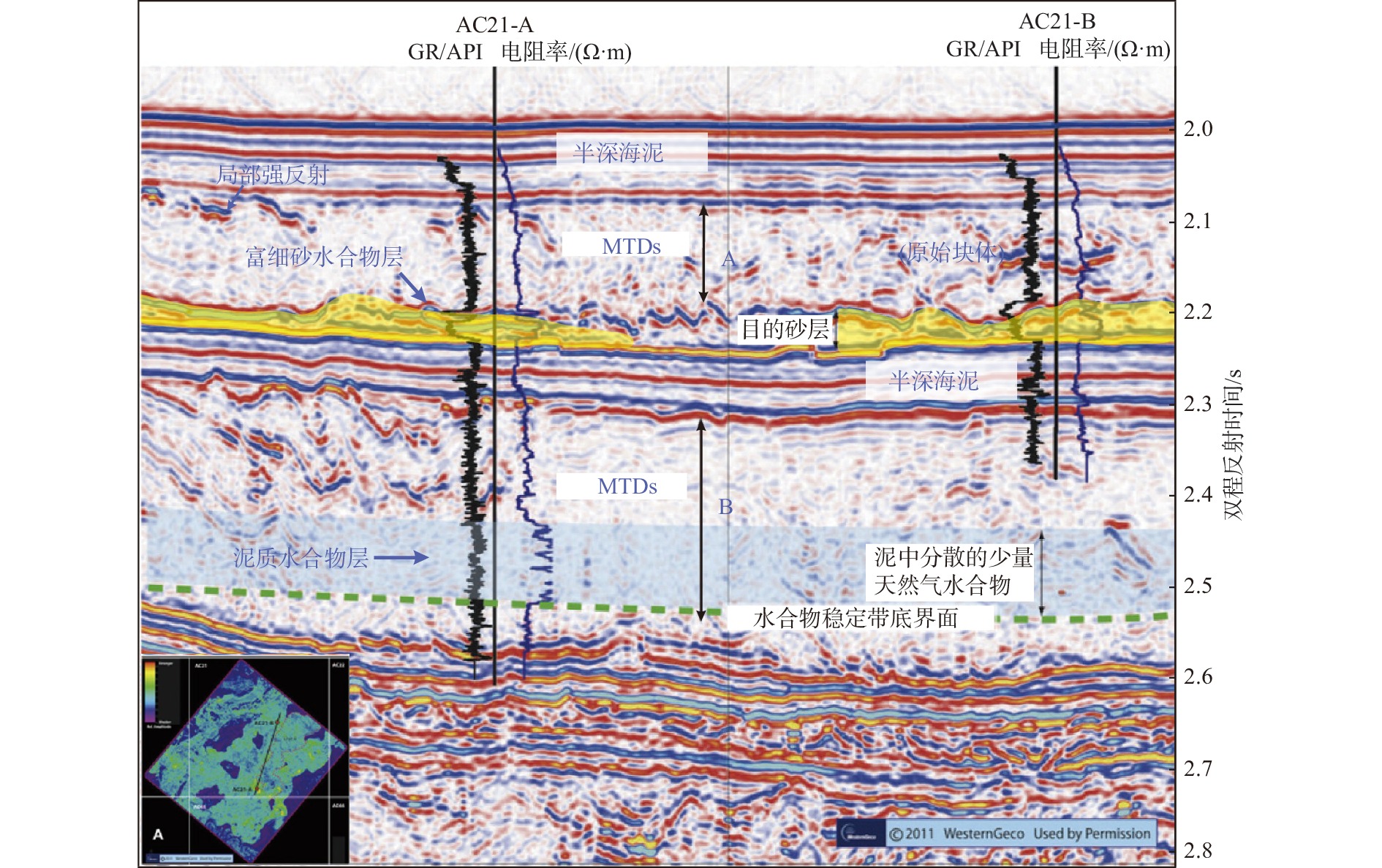
图 3 墨西哥湾Alaminos峡谷过水合物钻井AC21-A和AC21-B的井-震联合剖面[11]
Figure 3.
图 4 韩国郁陵盆地过UBGH2-6井的井-震联合剖面[36]
Figure 4.
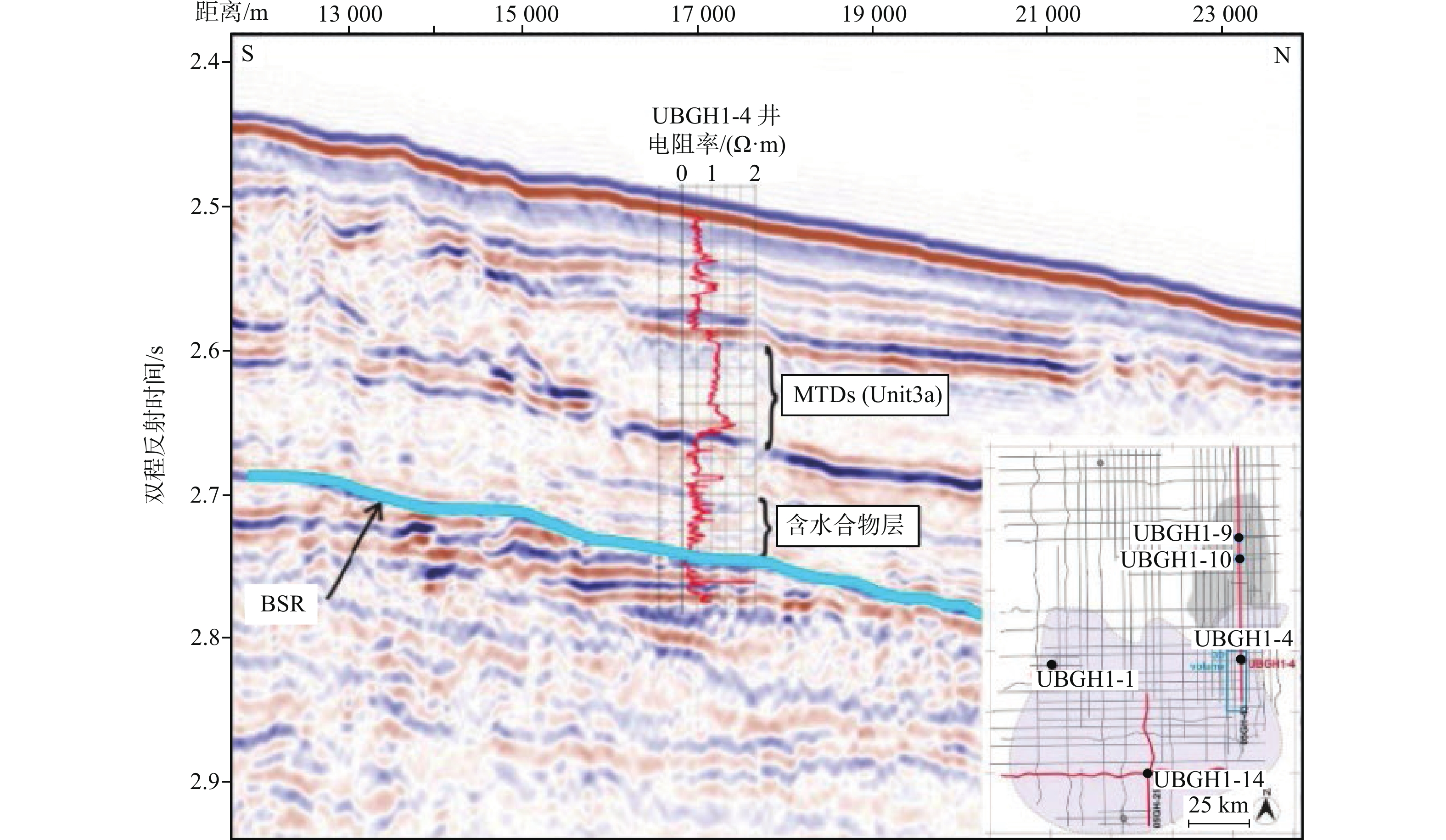
图 5 韩国郁陵盆地过UBGH1-4井的井-震联合剖面[37]
Figure 5.
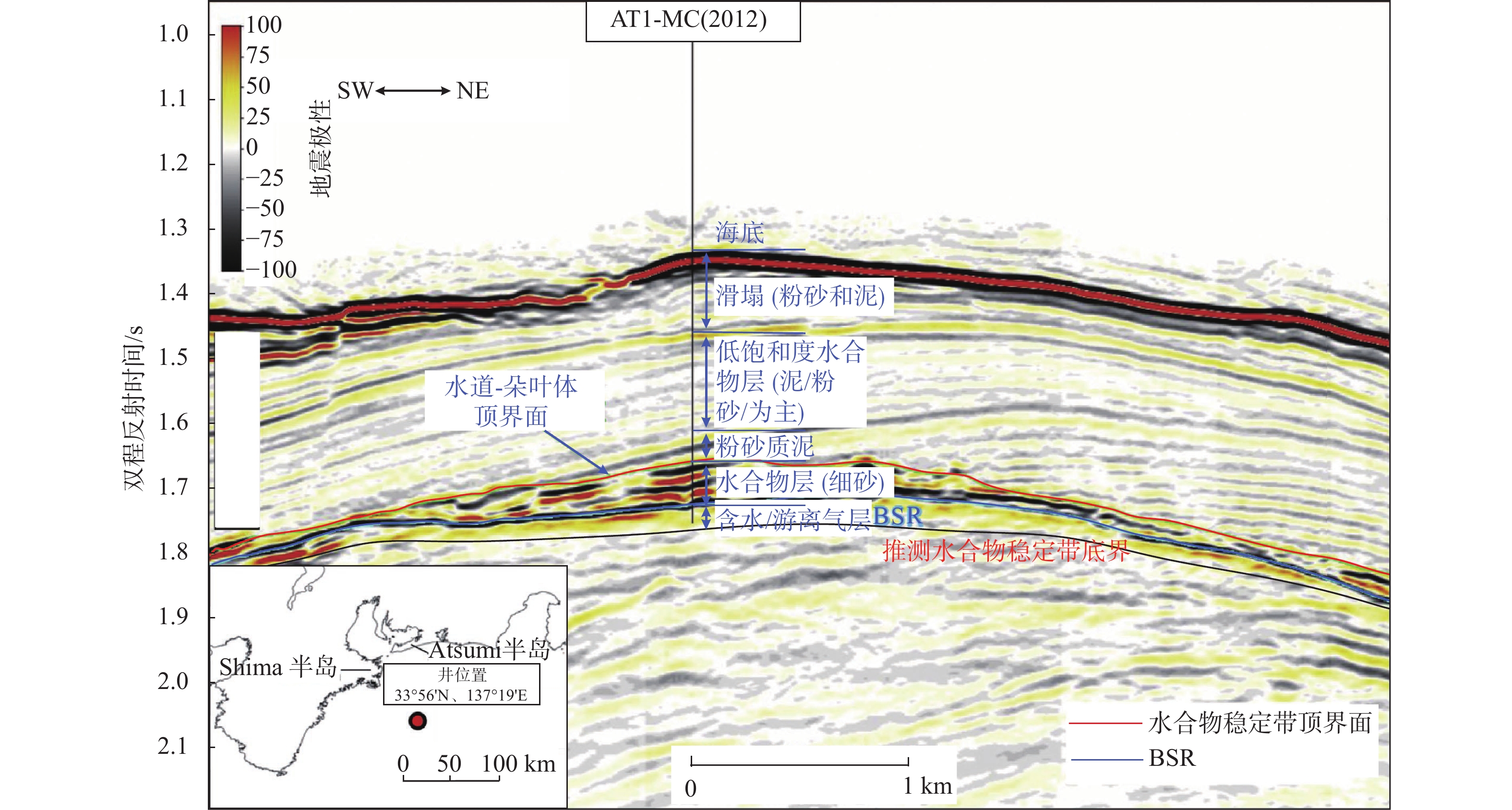
图 6 日本南海海槽过AT1-MC井的井-震联合剖面[43]
Figure 6.
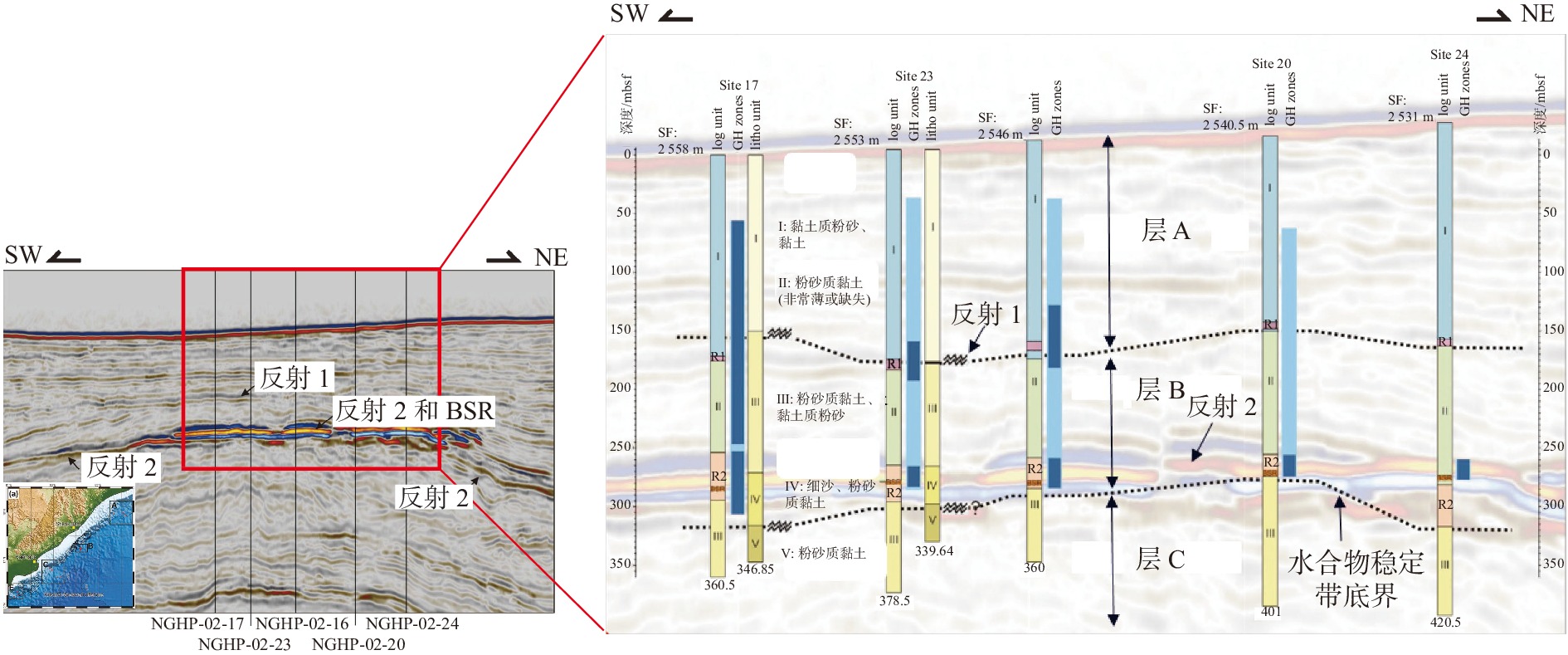
图 7 印度KG盆地过井NGHP2-17、NGHP2-23、NGHP2-16、NGHP2-20、NGHP2-24的井-震联合剖面[44]
Figure 7.
图 8 中国南海神狐海域GMGS1—4水合物钻探井位置图[45]
Figure 8.
表 1 本文选取的世界水合物勘探热点地区
Table 1. The hot spots of hydrate exploration areas worldwide selected in this study
国家 实例区 航次 取样深度/mbsf 水合物钻井 来源 日本 南海海槽 MITI 0.31~318.25 12 YONEDA等,2015[7] 墨西哥 Keathley峡谷 JIP leg I / 1 BOSWELL等,2009[8] Green 峡谷 JIP Leg II / 2 SSH等,2017[9] Alaminos峡谷 / / 4 PORTNOV等,2009[10]
;BOSWELL等,2012[11-12]Walker 脊 / / 2 HILLMAN等,2017[13] 中国 神狐海域 GMGS1 153~224.5 3 吴时国等,2015[14] GMGS3 47~257 5 张伟等,2017[15] GMGS4 45~221 3 WEI等,2017[16] 韩国 郁陵盆地 UBGH1 3 BAHK等,2009[17] UBGH2 0.8~236.2 8 RYU等,2013[18] 印度 KG盆地 NGHP1 29~213 13 COLLETT等,2014[19] Mahanadi盆地 / / 6 WINTERS等,2014[20] Andaman群岛 NGHP2 57~508 1 KK盆地 / / 1 表 2 中国南海神狐海域部分水合物取芯井统计[14-16, 49-54]
Table 2. Statistics of sampling analysis for hydrate core in the Shenhu area, South China Sea[14-16, 49-54]
年份 井位 含水合物层厚度/m 含水合物层深度/mbsf 地震剖
面特征水合物饱和度/% 储层岩性描述 平均值 最大值 2007 SH2 33.5 191~225 强BSR 25 47 黏土质粉砂、粉砂质黏土 SH3 11 190~201 强BSR 12.5 25.5 黏土质粉砂、粉砂质黏土 SH7 27 0~194 强BSR 48 / 黏土质粉砂、粉砂质黏土 2015 W02 20.1 127~151 强BSR 13.7 / 黏土质粉砂、粉砂质黏土 W07 14.3 140~156 强振幅 39 66 富含有孔虫的粉砂质黏土 W11 77.3 47~216 强振幅 22.9 53 富含有孔虫的粉砂质黏土 W17 45 207~257 强—中强振幅 19.4 76 富含有孔虫的粉砂质黏土 W18 16 50~174 强振幅 25 63 富含有孔虫的粉砂质黏土 W19 29.3 138~168 强—中强振幅 45.2 71 含硅质的钙质黏土质粉砂 2016 SC1 22 57~190 强BSR / 66 以粉砂质黏土和有孔虫砂为主 SC2 28 94~189 强BSR / 68 以粉砂质黏土和有孔虫砂为主 SC3 >90 45~221 强BSR / 72 以粉砂质黏土和有孔虫砂为主 表 3 世界水合物热点钻探区水合物储层沉积环境及储集特征等相关参数统计[7-19,23]
Table 3. Statistics of reservoir characteristics and depositional environments in hot hydrate drilling areas worldwide[7-19,23]
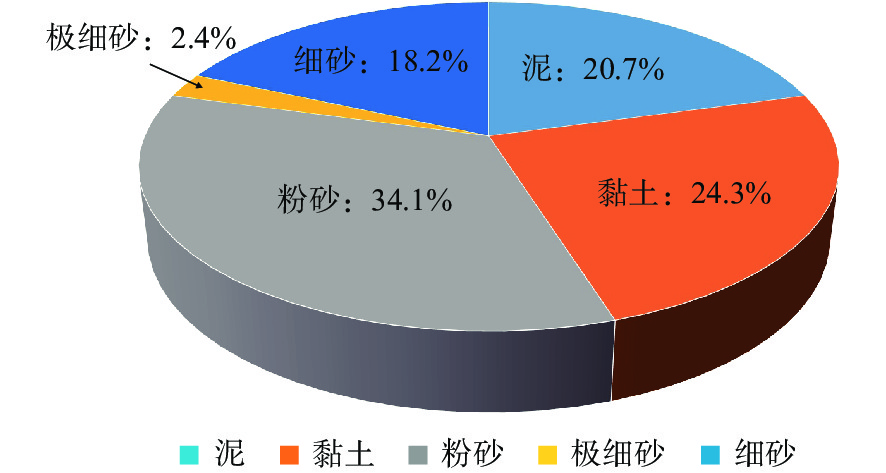
钻探位置 航次 站位 海底以下深度/mbsf BSR特征 分布范围 储集特征 厚度/m 面积/km2 墨西哥湾 Perdido峡谷 JIP Leg II AC818 275~325 强振幅,簇状BSR 10~18 0.8 分布在浊积砂体和深海泥的裂缝中,平均饱和度80%,地层孔隙度42% Terrebonne盆地 JIP Leg II WR313-G 106~134 强振幅,发育断裂、气烟囱 1~34 16 分布在细粒砂体中,且砂体被泥质沉积物包围,水合物饱和度通常>60% Green峡谷 JIP Leg II GC955 400 强振幅,发育底辟 21~30 7.5 分布在浊流沉积的水道-天然堤砂体中,平均水合物饱和度约80% Alaminos峡谷 JIP Leg II AC21 160 强振幅 18~30 0.8 分布在砂体中,低渗透性富黏土的MTDs覆盖在砂体上,水合物饱和度12%~15% Mississippi峡谷 JIP Leg II MC127,MC128 250~300 强振幅,簇状BSR 30 12.6 分布在富砂单元中,据估算水合物饱和度50%~90% 日本南海海槽 MH21 KIGAM 205~268 强BSR,发育气烟囱、麻坑 0.1~24 12 以孔隙型充填产出,分布在富砂层中,水合物饱和度50%~60%,最高达80%~90% 韩国郁陵盆地 UBGH1 UBGH1-9 63~151 强BSR 70 / 沉积环境为披覆泥和低密度浊流沉积相为主 UBGH2 UBGH2-2 68~155 强BSR,发育气烟囱 12.7 12 分布在含浊积砂的半深海泥中,粗粉砂至细砂为主,水合物饱和度约37% UBGH2 UBGH2-6 110~155 强BSR,发育气烟囱 12.7 12 分布在含浊积砂的半深海泥中,粗粉砂至细砂为主,水合物饱和度约52% 印度KG盆地 NGHP-02 NGHP-02 200~300 强BSR,发育断裂和浊积层 30~43 5 分布在砂体中,交替有泥、黏土、砾岩,水合物饱和度50% 中国南海 神狐海域 GMGS-1 SH2 191~224.5 强BSR 33.5 63 分布在黏土质粉砂细粒沉积物中,富含有孔虫壳体,水合物饱和度25%~46% GMGS-1 SH3 190~201 强BSR 11 63 分布在黏土质粉砂细粒沉积物中,富含有孔虫壳体,水合物饱和度12.5%~25.5% GMGS-1 SH7 153~180 强BSR 27 63 分布在黏土质粉砂细粒沉积物中,富含有孔虫壳体,水合物饱和度20%~43% GMGS-3 W19 134~202 强—中强BSR,发育气烟囱、杂乱反射、空白反射带等 68 63 分布在钙质黏土质粉砂岩、钙质粉砂岩、含钙质和硅质的黏土质粉砂岩及含硅质的钙质黏土质粉砂岩,平均饱和度46.2% -
[1] PAULL C K, DILLON W P. Natural gas hydrates: occurrence, distribution, and detection[M]. Woods Hole: American Geophysical Union, 2001.
[2] 徐华宁,杨胜雄,郑晓东,等. 南中国海神狐海域天然气水合物地震识别及分布特征[J]. 地球物理学报,2010,53(7):1691-1698. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.07.020
[3] LEE M W,COLLETT T S. Gas hydrate saturations estimated from fractured reservoir at Site NGHP-01-10,Krishna-Godavari Basin,India[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research,2009,114:261-281.
[4] BOSWELL R,SHIPP C,REICHEL T,et al. Prospecting for marine gas hydrate resources[J]. Interpretation,2016,4:13-24.
[5] ZHANG G X,YANG S X,ZHANG M,et al. GMG2 expedition investigates rich and complex gas hydrate environment in the South China Sea[J]. Fire in the Ice:Methane Hydrate Newsletter,2014,14(1):1-5.
[6] 吴能友,黄丽,胡高伟,等. 海域水合物开采的地质控制因素和科学挑战[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2017,37(5):1-11.
[7] YONEDA J,MASUI A,KONNO Y,et al. Mechanical properties of hydrate-bearing turbidite reservoir in the first gas production test site of the Eastern Nankai Trough[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2015,66:471-486. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.02.029
[8] BOSWELL R,SHELANDER D,LEE M,et al. Occurrence of gas hydrate in Oligocene Frio sand:Alaminos Canyon Block 818:Northern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2009,26:1499-1512. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.03.005
[9] HAINES S S,HART P E,COLLETT T S,et al. High-resolution seismic characterization of the gas and gas hydrate system at Green Canyon 955,Gulf of Mexico,USA[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2017,82:220-237. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.01.029
[10] PORTNOV A,COOK A E,SAWYER D E,et al. Clustered BSRs:evidence for gas hydrate-bearing turbidite complexes in folded regions,example from the Perdido Fold Belt,northern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2019,528:115843. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2019.115843
[11] BOSWELL R,COLLETT T S,FRYE M,et al. Subsurface gas hydrates in the northern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2012,34(1):4-30.
[12] BOSWELL R,FRYE M,SHELANDER D,et al. Architecture of gas-hydrate-bearing sands from Walker Ridge 313,Green Canyon 955,and Alaminos Canyon 21:northern deepwater Gulf of Mexico[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2012,34(1):134-149.
[13] HILLMAN J I T,COOK A E,DAIGLE H,et al. Gas hydrate reservoirs and gas migration mechanisms in the Terrebonne Basin,Gulf of Mexico[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2017,86:1357-1373. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.07.029
[14] 吴时国, 王秀娟, 陈端新, 等. 天然气水合物地质概论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015.
[15] 张伟,梁金强,陆敬安,等. 中国南海北部神狐海域高饱和度天然气水合物成藏特征及机制[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2017,44(5):670-680. doi: 10.11698/PED.2017.05.02
[16] WEI J G,FANG Y X,LU H L,et al. Distribution and characteristics of natural gas hydrates in the Shenhu Sea Area,South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2018,98:622-628. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.07.028
[17] BAHK J J,UM I K,HOLLAND M. Core lithologies and their constraints on gas hydrate occurrence in the Ulleung Basin,East Sea of Korea:results from the Site UBGH1-9[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2011,28:1943-1952. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.12.003
[18] RYU B J,COLLETT T S,RIEDEL M,et al. Scientific results of the Second Gas Hydrate Drilling Expedition in the Ulleung Basin (UBGH2)[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2013,47:1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.07.007
[19] COLLETT T S,BOSWELL R,COCHRAN J R,et al. Geologic implications of gas hydrates in the offshore of India:results of the National Gas Hydrate Program Expedition 01[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2014,58:1-2. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.07.020
[20] WINTERS W J,WILCOX-CLINE R W,LONG P,et al. Comparison of the physical and geotechnical properties of gas-hydrate-bearing sediments from offshore India and other gas-hydrate-reservoir systems[J]. Marine and petroleum geology,2014,58:139-167. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.07.024
[21] 苏丕波,梁金强,沙志彬,等. 神狐深水海域水合物成藏的气源条件[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2014,36(2):1-8.
[22] 张伟,何家雄,卢振权,等. 琼东南盆地疑似泥底辟与天然气水合物成矿成藏关系初探[J]. 天然气地球科学,2015,26(11):2185-2197. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2015.11.2185
[23] GAY A. Are polygonal faults the keystone for better understanding the timing of fluid migration in sedimentary basins? [C]. EPJ Web of Conferences, 2017, 140: 12009.
[24] 何家雄,苏丕波,卢振权,等. 南海北部琼东南盆地天然气水合物气源及运聚成藏模式预测[J]. 天然气工业,2015,35(8):19-29. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2015.08.003
[25] 于兴河,王建忠,梁金强,等. 南海北部陆坡水合物沉积成藏特征[J]. 石油学报,2014,35(2):253-264. doi: 10.7623/syxb201402005
[26] 陈芳,周洋,苏新,等. 南海神狐海域含水合物层粒度变化及与水合物饱和度的关系[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2011,31(5):95-100.
[27] CLAYPOOL G E,KAPLAN I R. The origin and distribution of methane in marine sediments[J]. Natural Gases in Marine Sediments,1974:99-139.
[28] KVENVOLDEN K A, MCMENAMIN M A. Hydrates of Natural Gas: A Review of Their Geologic Occurrence[M]. Arlington, Massachusetts: United States Geological Survey, 1980, 825: 1-11.
[29] MOUNTAIN G S, TUCHOLKE B E. Mesozoic and Cenozoic geology of the US Atlantic continental slope and rise[M]//POAG C W. Geologic Evolution of the United States Atlantic Margin. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1985: 293-341.
[30] 黄霞,祝有海,卢振权,等. 南海北部水合物钻探区烃类气体成因类型研究[J]. 现代地质,2010,24(3):576-580. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2010.03.023
[31] DILLON W P,DANFORTH W W,HUTCHINSON D R,et al. Evidence for faulting related to dissociation of gas hydrate and release of methane off the southeastern United States[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications,1998,137(1):293-302. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1998.137.01.23
[32] COLLETT T,LEE M,LEWIS R,et al. Gulf of Mexico gas hydrate joint industry project Leg II logging-while-drilling data acquisition and analysis[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2012,34:41-61. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.08.003
[33] FRYE M. Gas hydrate resource potential in the Terrebonne Basin,Northern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2012,34(1):150-168. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.08.001
[34] BOSWELL R,COLLETT T S. Current perspectives on gas hydrate resources[J]. Energy and Environmental Science,2011,4(4):1206-1215. doi: 10.1039/C0EE00203H
[35] FLEMINGS P B, PHILLIPS S C, COLLETT T, et al. Hydrate Pressure Coring Expedition Report[R]. Austin, TX: University of Texas Institute for Geo-physics, 2018.
[36] KIM K J,YI B Y,KANG N K,et al. Reservoir characterization of gas hydrate in the northwestern part of the Ulleung Basin,East Sea[J]. Marine Georesources and Geotechnology,2017,35(2):226-235. doi: 10.1080/1064119X.2016.1139644
[37] RIEDEL M,BAHK J J,SCHOLZ N A,et al. Mass-transport deposits and gas hydrate occurrences in the Ulleung Basin,East Sea - Part 2:Gas hydrate content and fracture-induced anisotropy[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2012,35(1):75-90. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2012.03.005
[38] TOBIN H,KINOSHITA M,ASHI J,et al. NanTroSEIZE stage 1 expeditions 314,315 and 316:first drilling program of the Nankai Trough seismogenic zone experiment[J]. Scientific Drilling,2009,8(8):4-17.
[39] SUZUKI K,SCHULTHEISS P,NAKATSUKA Y,et al. Physical properties and sedimentological features of hydrate-bearing samples recovered from the first gas hydrate production test site on Daini-Atsumi Knoll around eastern Nankai Trough[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2015,66:346-357. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.02.025
[40] TAKAHASHI H,TSUJI Y. Japan explores for hydrates in the Nankai Trough[J]. Oil and Gas Journal,2005,103(33):48-53.
[41] FUJII T NAKAMIZU M, TSUJI Y, et al. Methane-hydrate occurrence and saturation confirmed from core samples, eastern Nankai Trough, Japan[C]//COLLETT T S, JOHNSON A, KNAPP C, et al. Natural gas hydrates: energy resource potential and associated geologic hazards. AAPG Memoir, 2009, 89: 385-400.
[42] TSUJI Y, FUJII T, HAYASHI M, et al. Methane-hydrate occurrence and distribution in the eastern Nankai Trough, Japan: findings of the Tokai-Oki to Kumano-Nada methane hydrate drilling program[C]//Collett T S, Johnson A, Knapp C, et al. Natural gas hydrates: energy resources potential and associated geological hazards. AAPG memoir, 2009, 89: 228-246.
[43] FUJII T,SUZUKI K,TAKAYAMA T,et al. Geological setting and characterization of a methane hydrate reservoir distributed at the first offshore production test site on the Daini-Atsumi Knoll in the eastern Nankai Trough,Japan[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2015,66:310-322. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.02.037
[44] KAN-HSI H,SANIATSU S,TOSHIYA K,et al. Regional stratigraphic framework and gas hydrate occurrence offshore eastern India:core-log-seismic integration of National Gas Hydrate Program Expedition 02 (NGHP-02) Area-B drill sites[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2019,108:206-215. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.06.021
[45] 吴时国,王吉亮. 南海神狐海域天然气水合物试采成功后的思考[J]. 科学通报,2018,63(1):2-8.
[46] LI J F,YE J L,QIN X W,et al. The first offshore natural gas hydrate production test in South China Sea[J]. China Geology,2018,1(1):5-16. doi: 10.31035/cg2018003
[47] LIU C L,YE Y G,MENG Q G,et al. The characteristics of gas hydrates recovered from Shenhu area in the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology,2012,307:22-27.
[48] SUN J X,ZHANG L,NING F L,et al. Production potential and stability of hydrate-bearing sediments at the Site GMGS3-W19 in the South China Sea:a preliminary feasibility study[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2017,86:447-473. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.05.037
[49] YANG S X, LEI Y, LIANG J Q, et al. Concentrated gas hydrate in the Shenhu area, South China Sea: Results from drilling expeditions GMGS3 & GMGS4[C]//Proceedings of 9th International Conference on Gas Hydrates. 2017: 25-30.
[50] WANG X J,COLLETT T S,LEE M W,et al. Geological controls on the occurrence of gas hydrate from core,downhole log,and seismic data in the Shenhu area,South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology,2014,357:272-292. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.09.040
[51] ZHANG W,LIANG J Q,WEI J G,et al. Geological and geophysical features of and controls on occurrence and accumulation of gas hydrates in the first offshore gas-hydrate production test region in the Shenhu area,northern South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2020,114:104191. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.104191
[52] WU N Y, ZHANG H Q, SU X, et al. High concentrations of hydrate in disseminated forms found in very fine-grained sediments of Shenhu area, South China Sea[J]. Terra Nostra, 2007, 1: 236-237.
[53] WU S G, WANG X J, WONG H K. Low-amplitude BSRs and gas hydrate concentration on the northern margin of the SCS[J]. Marine Geophysical Researches, 2007, 28: 127-138.
[54] 王静丽,梁金强,宗欣,等. 南海北部神狐海域水合物差异性分布的控制因素[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2015,31(1):24-30.
[55] YANG S X,ZHANG M,LIANG J Q,et al. Preliminary results of China′s third gas hydrate drilling expedition:a critical step from discovery to development in the South China Sea[J]. Fire Ice,2015,15:1-5.
[56] 张伟,梁金强,苏丕波,等. 南海北部陆坡高饱和度水合物气源运聚通道控藏作用[J]. 中国地质,2018,45(1):1-14. doi: 10.12029/gc20180101
[57] 郭依群,杨胜雄,梁金强,等. 南海北部神狐海域高饱和度水合物分布特征[J]. 地学前缘,2017,24(4):24-31.
[58] BÜNZ S,MIENERT J,BERNDT C. Geological controls on the Storegga gas-hydrate system of the mid-Norwegian continental margin[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2003,209(3/4):291-307.
[59] TRÉHU A M,LONG P E,TORRES M E,et al. Three-dimensional distribution of gas hydrate beneath southern Hydrate Ridge:constraints from ODP Leg 204[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2004,222(3/4):845-862.
-



 下载:
下载: