Response of high-resolution sedimentary records to East Asian winter monsoon in the inner shelf of the East China Sea over the past 8 000 years
-
摘要:
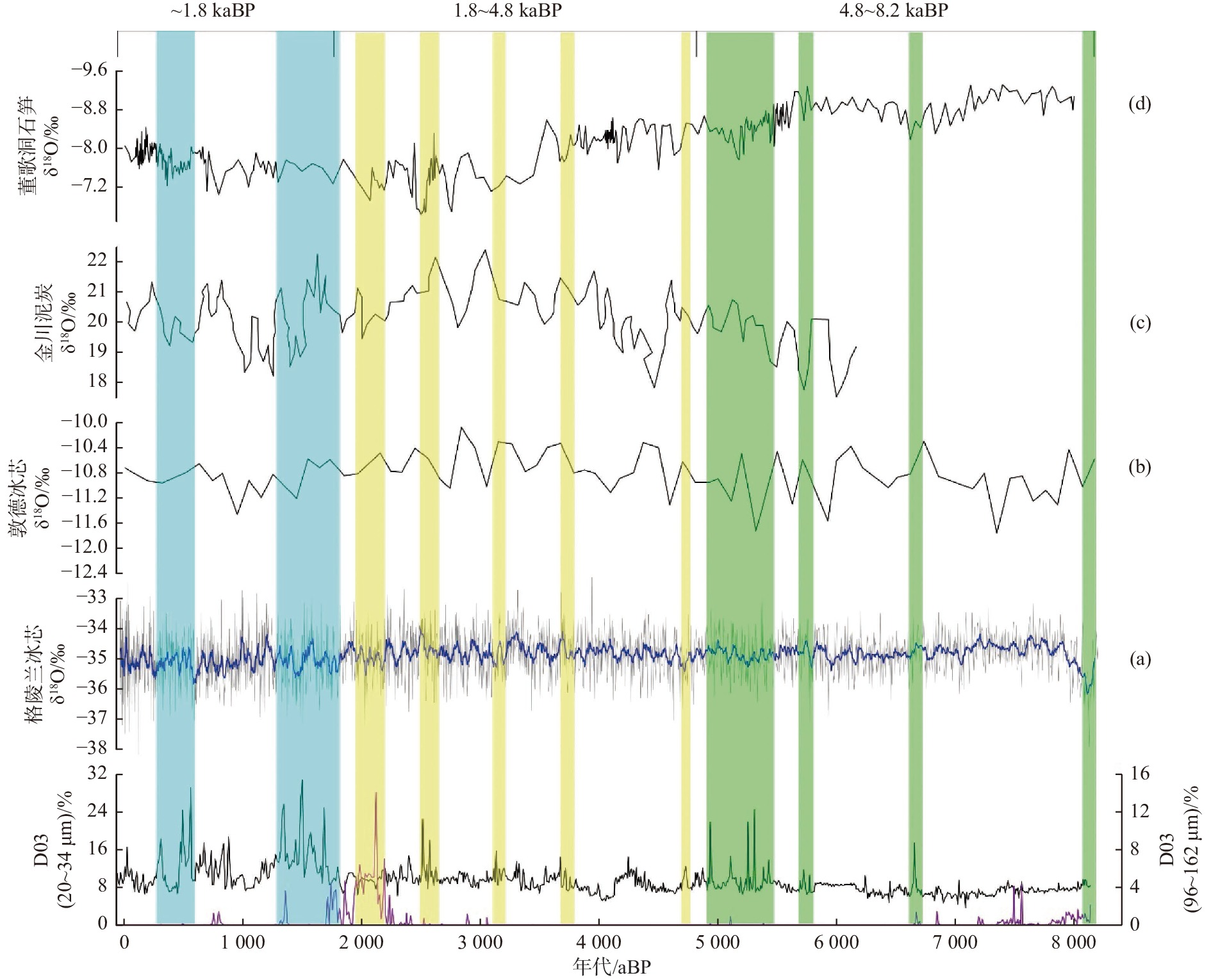
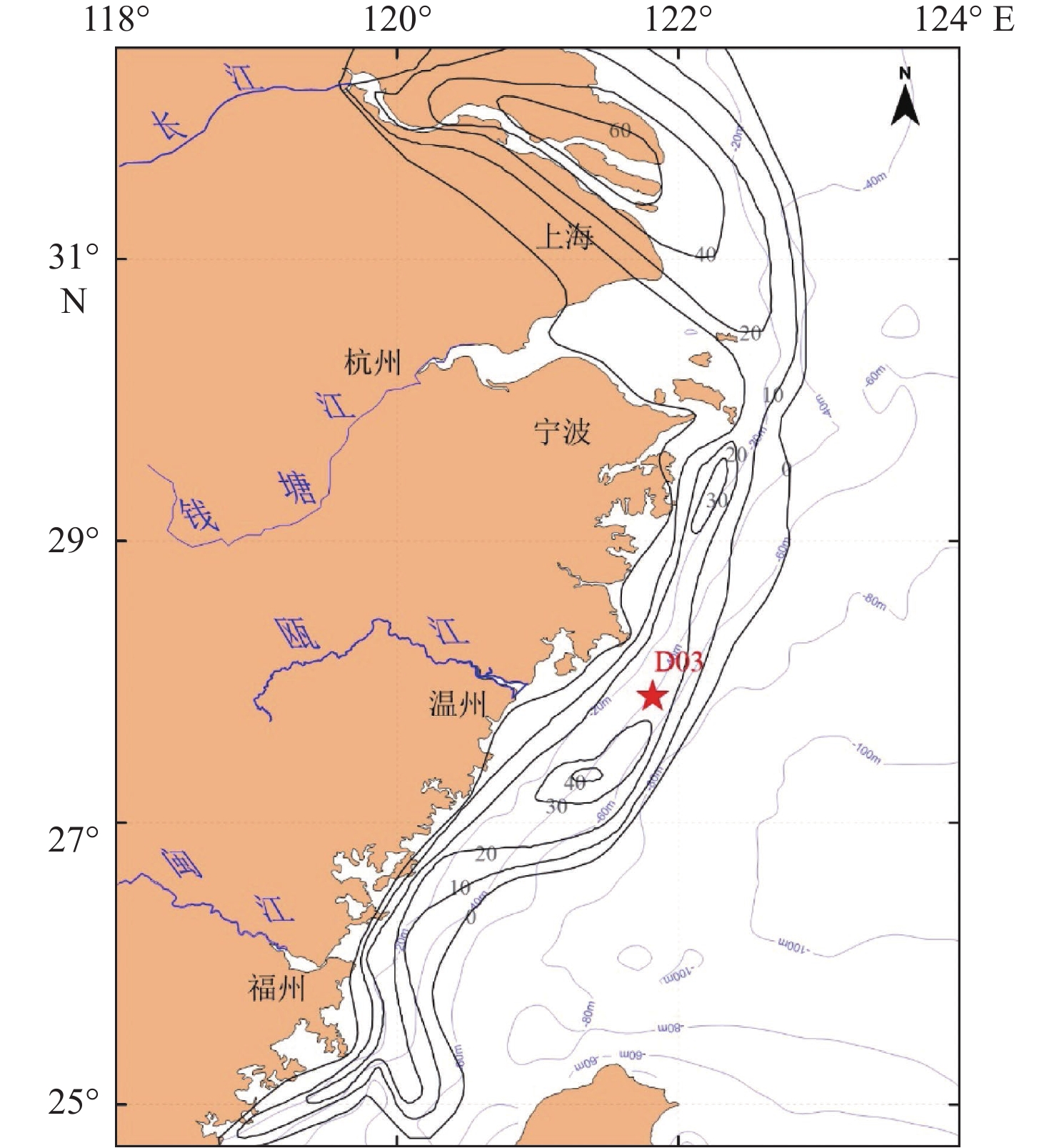
依据东海内陆架泥质区D03钻孔岩芯沉积物高分辨率粒度分析结果,筛选了对东亚冬季风有良好显示的敏感粒级,结合高精度年代框架,揭示了近8 ka以来东亚冬季风波动在泥质区的沉积记录,包括11个千年尺度的气候波动事件和5.4~4.9、1.8 kaBP以来的百年尺度的快速气候波动。与石笋、冰芯和泥炭的氧同位素曲线对比发现,东亚冬季风增强与世界范围的“8.2 ka”、“4.9 ka”、“3.8 ka”、“1.4 ka”和小冰期事件均有良好的对应关系,建立了全新世东亚冬季风增强与气候变冷事件的内在联系。8 ka以来东亚冬季风的演化大致可以分为3个阶段,即8.2~4.8 kaBP中高频波动期、4.8~1.8 kaBP波动较弱稳定期和1.8 kaBP以来的高频波动期。
Abstract:Through high resolution AMS14C dating and grain size analysis on upper layer sediments of the core D03 in the muddy area of inner shelf of the East China Sea, three sensitive grain groups were extracted and used as proxies of East Asian winter monsoon strength. During the past 8 ka, eleven millennium scale events and centennial scale rapid climatic events during 5.4~4.9 kaBP and in the past 1.8 kaBP were revealed. By comparison with records of other proxies from oxygen isotopes of stalagmites, ice cores and peat, it is indicated that the enhancement of East Asian winter monsoon in the study area was well correlated with the global cooling events, e.g. "8.2 ka", "4.9 ka", "3.8 ka","1.4 ka" and Little Icea Age.The inner relationship between the East Asian winter monsoon enhancement and the climate cooling event during the Holocene was established. The evolution of the East Asian winter monsoon in the past 8000 years can be roughly divided into three stages, including the intermediate and high frequency fluctuation stage during 8.2~4.8 kaBP, the weak and stable stage during 4.8~1.8 kaBP, and the high frequency fluctuations stage since 1.8kaBP.
-

-
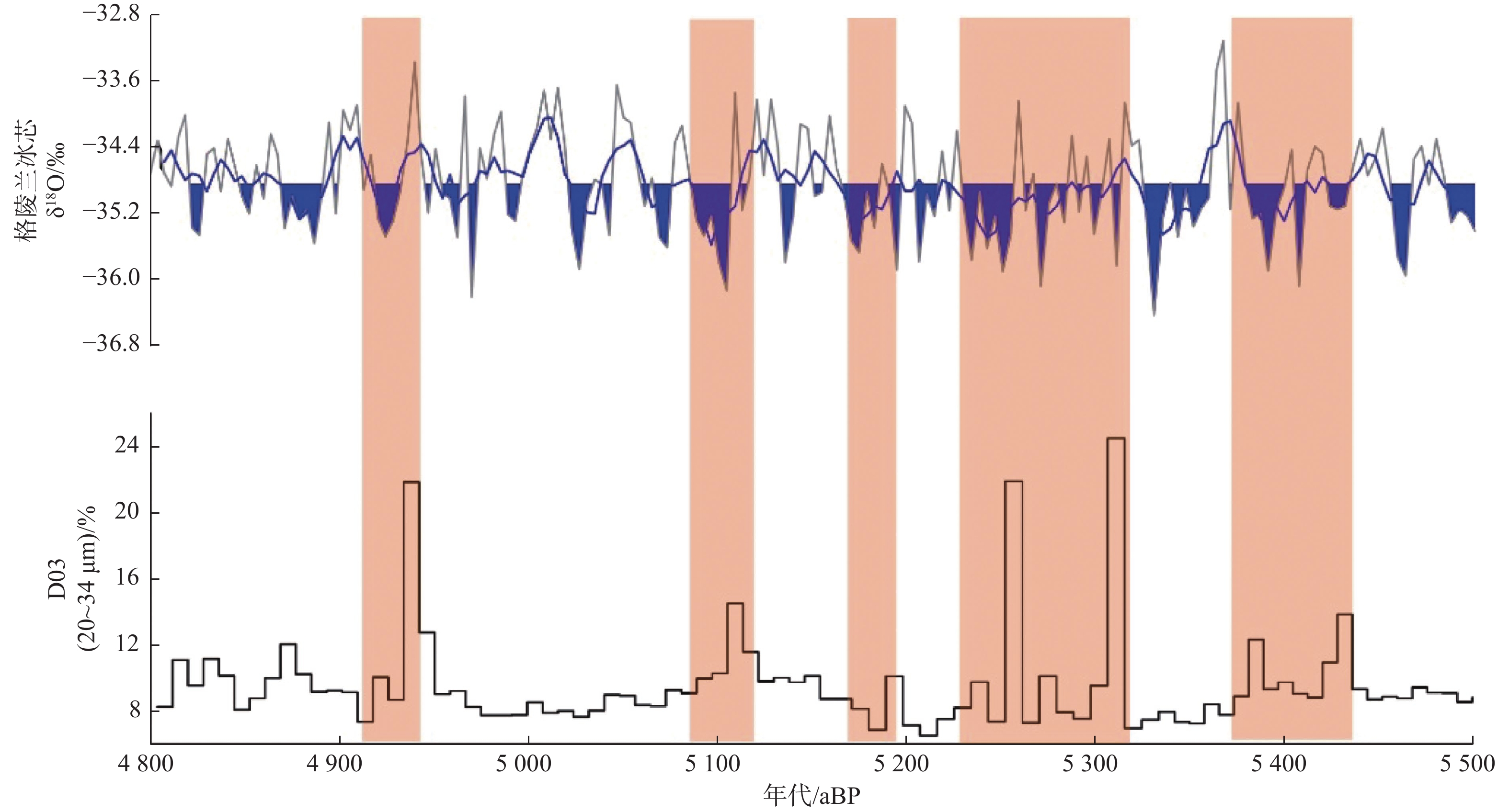
图 9 5.4~4.9 kaBP D03岩芯敏感粒级与格陵兰冰芯氧同位素记录[25]对比
Figure 9.
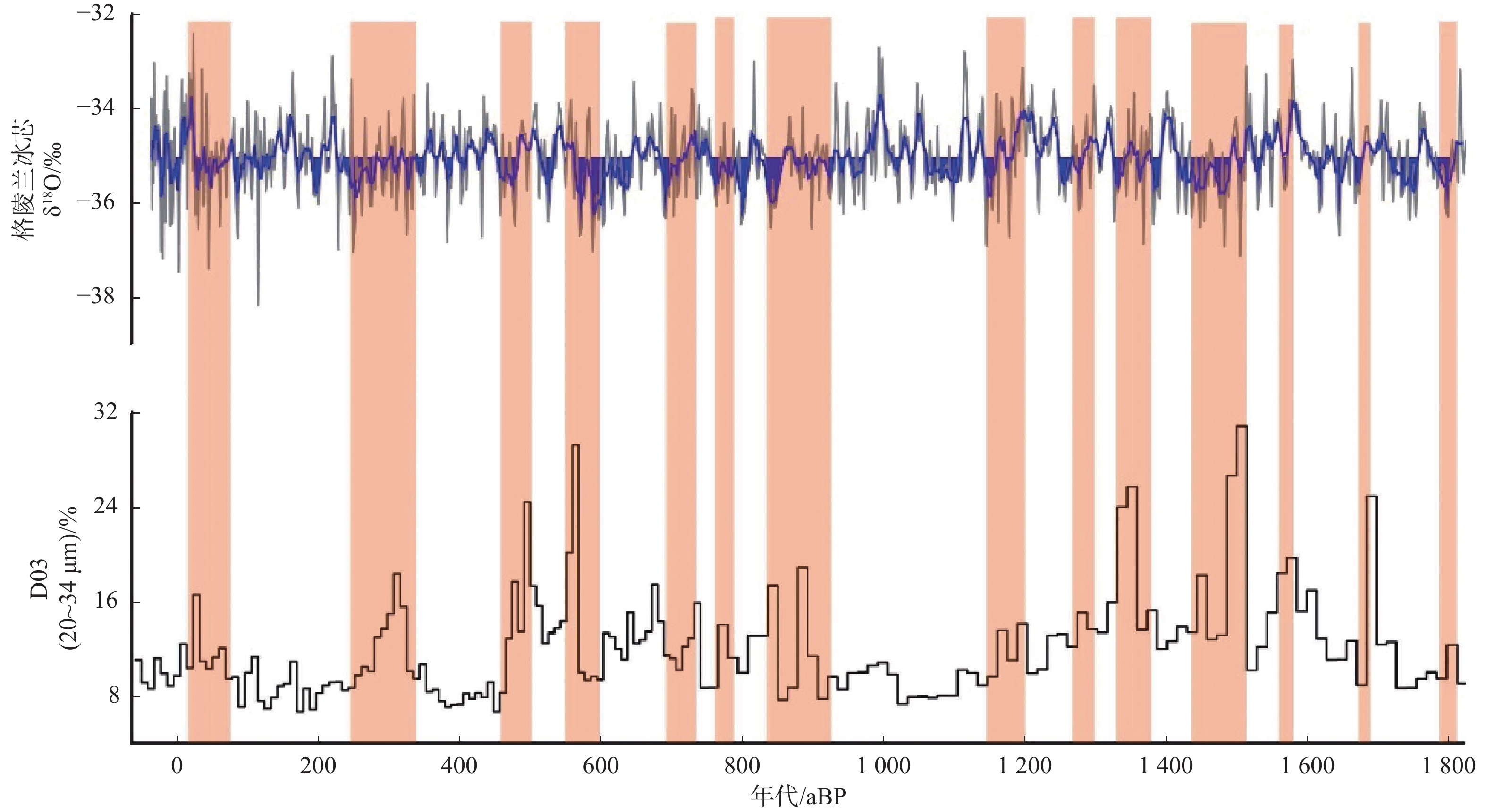
图 10 1.8 ka以来D03岩芯敏感粒级与格陵兰冰芯氧同位素记录[25]对比
Figure 10.
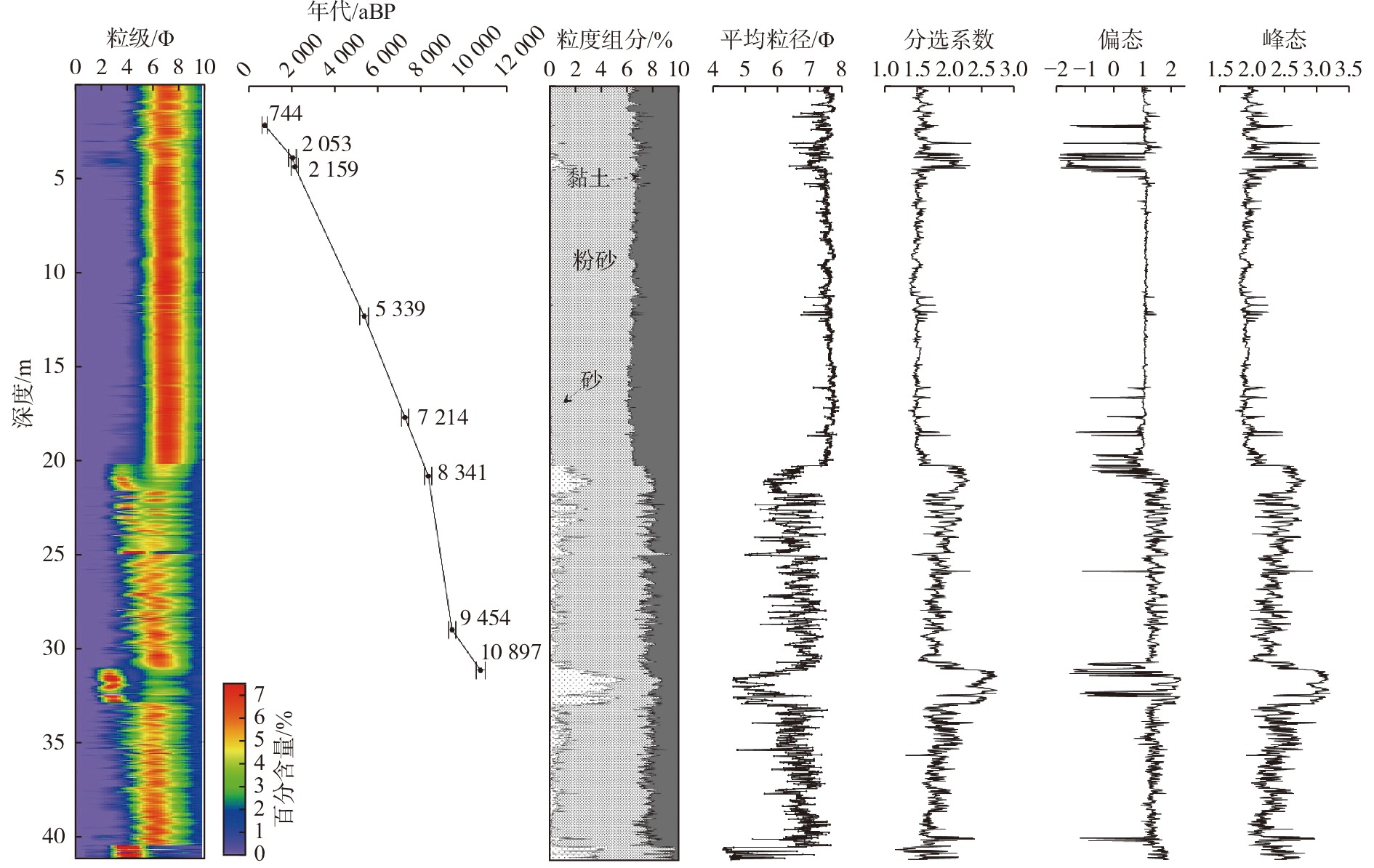
表 1 D03岩芯AMS14C测年数据和沉积速率
Table 1. AMS14C dating and calculated sedimention rate of the core D03
深度
/m测年材料 14C年龄
/aBP (14C)日历年龄
/aBP沉积速率
/(cm/a)2.07 压扁卷转虫 1 290±30 744(622~900) 0.26 3.80 压扁卷转虫 2 490±30 2 053(1 879~2 260) 0.13 4.28 压扁卷转虫 2 570±30 2 159(1 986~2 321) 0.45 12.23 希望虫 5 100±30 5 339(5 138~5 513) 0.25 17.64 压扁+希望虫 6 830±30 7 214(7 037~7 379) 0.29 20.75 压扁+希望虫 7 980± 0 8 341(8 180~8 493) 0.28 28.95 压扁卷转虫 8 880±30 9 454(9 289~9 588) 0.74 31.10 压扁卷转虫 9 940±30 10 897(10 684~11 102) 0.15 表 2 D03上部岩芯沉积物粒度参数
Table 2. Grain size parameters of the upper layer sediments of core D03
参数 砂/% 粉砂/% 泥/% 平均粒径/Φ 分选系数 偏态 峰态 最小值 0 52.35 19.54 6.38 1.37 −1.91 1.75 最大值 22.98 79.53 42.63 7.90 2.34 1.68 3.05 平均值 0.52 64.11 35.38 7.55 1.54 0.99 1.97 表 3 D03上部岩芯沉积物敏感粒级组成
Table 3. The composition of sensitive grain size of upper layer sediments of the core D03
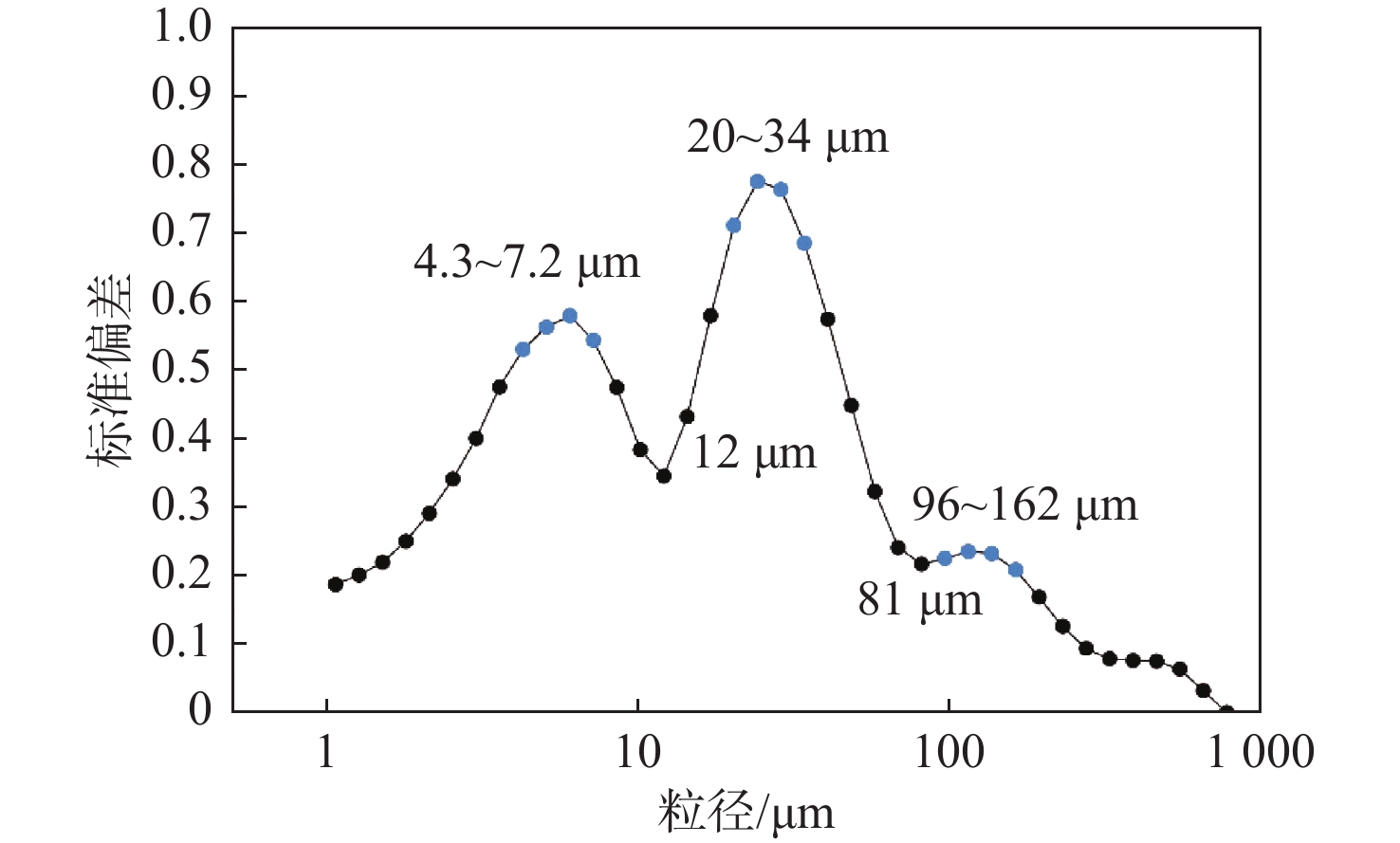
参数值 粒径区间/μm 峰值/μm 百分含量/% 最大值 最小值 平均值 敏感粒级1 4.3~7.2 6 30.5 10.5 25.2 敏感粒级2 20~34 24.1 31.8 3.7 9.1 敏感粒级3 96~162 114.6 14 0 0.2 -
[1] 孙东怀,安芷生,苏瑞侠,等. 古环境中沉积物粒度组分分离的数学方法及其应用[J]. 自然科学进展,2001,11(3):269-276. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2001.03.008
[2] 孙有斌,高抒,李军. 边缘海陆源物质中环境敏感粒度组分的初步分析[J]. 科学通报,2003,48(1):83-86. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.01.021
[3] 肖尚斌,李安春,蒋富清,等. 近2 ka 来东海内陆架的泥质沉积记录及其气候意义[J]. 科学通报,2004,49(21):2233-2238. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.21.017
[4] 苏纪兰. 中国近海水文[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2005: 229-246.
[5] 杨作升,郭志刚,王兆祥,等. 黄东海陆架悬浮体向其东部深海区输运的宏观格局[J]. 海洋学报,1992,14(2):81-90.
[6] HU B Q,YANG Z S,ZHAO M X,et al. Grain size records reveal variability of the East Asian winter monsoon since the Middle Holocene in the central Yellow Sea mud area,China[J]. Science China Earth Science,2012,55(10):1656-1668. doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4447-7
[7] XIAO S B,LI A C,LIU J P,et al. Coherence between solar activity and the East Asian winter monsoon variability in the past 8000 years from Yangtze River-derived mud in the East China Sea[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology,2006,237(2/4):293-304. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.12.003
[8] ZHOU X,YANG W,XIANG R,et al. Re-examining the potential of using sensitive grain size of coastal muddy sediments as proxy of winter monsoon strength[J]. Quaternary International,2014,333(4):173-178.
[9] 徐方建,李安春,万世明,等. 东海内陆架泥质区中全新世环境敏感粒度组分的地质意义[J]. 海洋学报,2009,31(3):95-102.
[10] 向荣,杨作升,SAITO Y,等. 济州岛西南泥质区近2300a来环境敏感粒度组分记录的东亚冬季风变化[J]. 中国科学(D辑):,2006,36(7):654-662.
[11] 孙晓燕,李广雪,刘勇,等. 东海北部泥质区敏感粒度组分对东亚季风演变的响应[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2008,28(4):11-17.
[12] 肖尚斌,李安春,陈木宏,等. 近8 ka 东亚冬季风变化的东海内陆架泥质沉积记录[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报,2005,30(5):573-581.
[13] Liu,J P,Li A C,Xu K H,et al. Sedimentary features of the Yangtze River-derived along-shelf clinoform deposit in the East China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2006,26:2141-2156. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2006.07.013
[14] 肖尚斌,李安春. 东海内陆架泥区沉积物的环境敏感粒度组分[J]. 沉积学报,2005,23(1):122-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.01.016
[15] LIU J P,XU K H,LI A C,et al. Flux and fate of Yangtze River sediment delivered to the East China Sea[J]. Geomorphology,2007,85:208-224. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.03.023
[16] 张晓东,许淑梅,翟世奎,等. 东海内陆架沉积气候信息的端元分析模型反演[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2006,26(2):29-36. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2006.02.004
[17] BISCAYE P E. Mineralogy and sedimentation of recent deep-sea clay in the Atlantic Ocean and adjacent seas and oceans[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin,1965,76(7):803-32. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1965)76[803:MASORD]2.0.CO;2
[18] YONEDA M,UNO H,SHIBATA Y,et al. Radiocarbon marine reservoir ages in the western Pacific estimated by pre-bomb molluscan shells[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B:Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms,2007,259(1):432-437.
[19] 朱亚美. 中全新世以来东海内陆架泥质区南部沉积演化及其气候环境响应[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2020.
[20] 肖尚斌,李安春,陈木宏,等. 全新世东亚季风变化的百年尺度周期[J]. 科技导报,2006,24(4):40-43. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7857.2006.04.011
[21] 王亮. 东海典型泥质区高分辨沉积记录及其对气候环境变化的响应[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.
[22] 田元,范德江,张喜林,等. 东海内陆架沉积物敏感粒级构成及其地质意义[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2016,47(2):30-37.
[23] ZHOU X,LIU Z H,YAN Q,et al. Enhanced tropical cyclone intensity in the western north Pacific during warm periods over the last two millennia[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2019,46(15):9145-9153. doi: 10.1029/2019GL083504
[24] 姚檀栋,谢自楚,武筱舲,等. 敦德冰帽中的小冰期气候记录[J]. 中国科学(B辑),1990,20(11):1196-1201.
[25] STUIVER M,GROOTES P M,BRAZIUNAS T F. The GISP2 δ18O climate record of the past 16,500 years and the role of the sun,ocean,and volcanoes[J]. Quaternary Research,1995,44(3):341-354. doi: 10.1006/qres.1995.1079
[26] 洪业汤,姜洪波,陶发祥,等. 近5 ka温度的金川泥炭δ18O记录[J]. 中国科学(D辑),1997,27(6):525-530.
[27] WANG Y J,CHENG H,EDWARDS R L. The Holocene Asian monsoon:links to solar changes and North Atlantic climate[J]. Science,2005,308:854-857. doi: 10.1126/science.1106296
[28] BEGET J E. Radiocarbon-dated evidence of worldwide early Holocene climate change[J]. Geology,1983,11(7):389-393. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1983)11<389:REOWEH>2.0.CO;2
[29] SEPPÄ H,BLRKS H J B,GLESECKE T,et al. Spatial structure of the 8 200 cal yr BP event in Northern Europe[J]. Clim Past Discuss,2007,3:165-195.
[30] 蔡演军,彭子成,安芷生,等. 贵州七星洞全新世石笋的氧同位素记录及其指示的季风气候变化[J]. 科学通报,2001,46(16):1398-1401. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2001.16.020
[31] DENTON G H,KARLÉN W. Holocene climatic variatons:their pattern and possible cause[J]. Quaternary Research,1973,3:155-205. doi: 10.1016/0033-5894(73)90040-9
[32] 覃嘉铭,袁道先,程海,等. 新仙女木及全新世早中期气候突变事件:贵州茂兰石笋氧同位素记录[J]. 中国科学(D辑),2004,34(1):39-74.
[33] 沈吉, 刘兴起, MATSUMOTO R, 等. 晚冰期以来青海湖沉积物多指标高分辨率的古气候演化[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 34(6): 582-589.
[34] 杨怀仁. 第四纪地质[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1987: 1-428.
[35] 葛全胜,王顺兵,郑景云. 过去5000 年中国气温变化序列重建[J]. 自然科学进展,2006,16:689-696. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2006.06.008
[36] 侯甬坚,祝一志. 历史记录提取的近5~2.7 ka黄河中下游平原重要气候事件及其环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2000,20(4):23-29.
[37] 葛全胜,方修琦,郑景云. 中国历史时期气候变化影响及其应对的启示[J]. 地球科学进展,2014,29(1):23-29. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2014.01-0023
[38] 葛全胜,朱会义. 两千年来中国自然与人文地理环境变迁及启示[J]. 地理学报,2021,76(1):3-14. doi: 10.11821/dlxb202101001
[39] BOND G,SHOWERS W,CHESEBY M,et al. A pervasive millennial-scale cycle in North Atlantic Holocene and glacial climates[J]. Science,1997,278:1257-1266. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5341.1257
[40] 樊耘畅, 丁旋, 樊加恩, 等. 东海陆架浙闽沿岸泥质区不同属种底栖有孔虫对14C测年的影响及其原因初探[J], 第四纪研究, 2018, 38(3): 792-798.
-



 下载:
下载: