Variation and source of heavy metals in surface sediment of Sanmen Bay in recent 10 years
-
摘要:
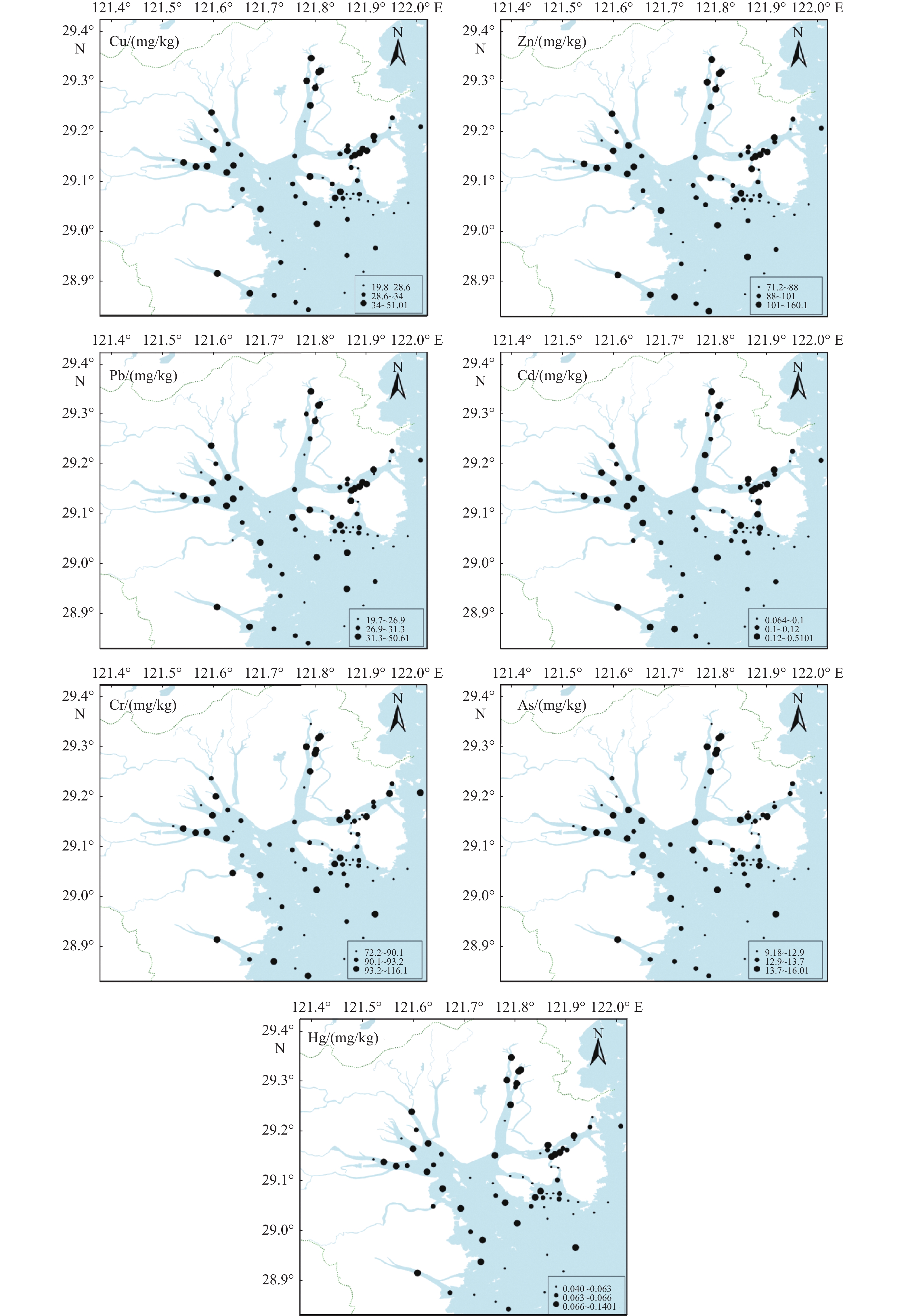
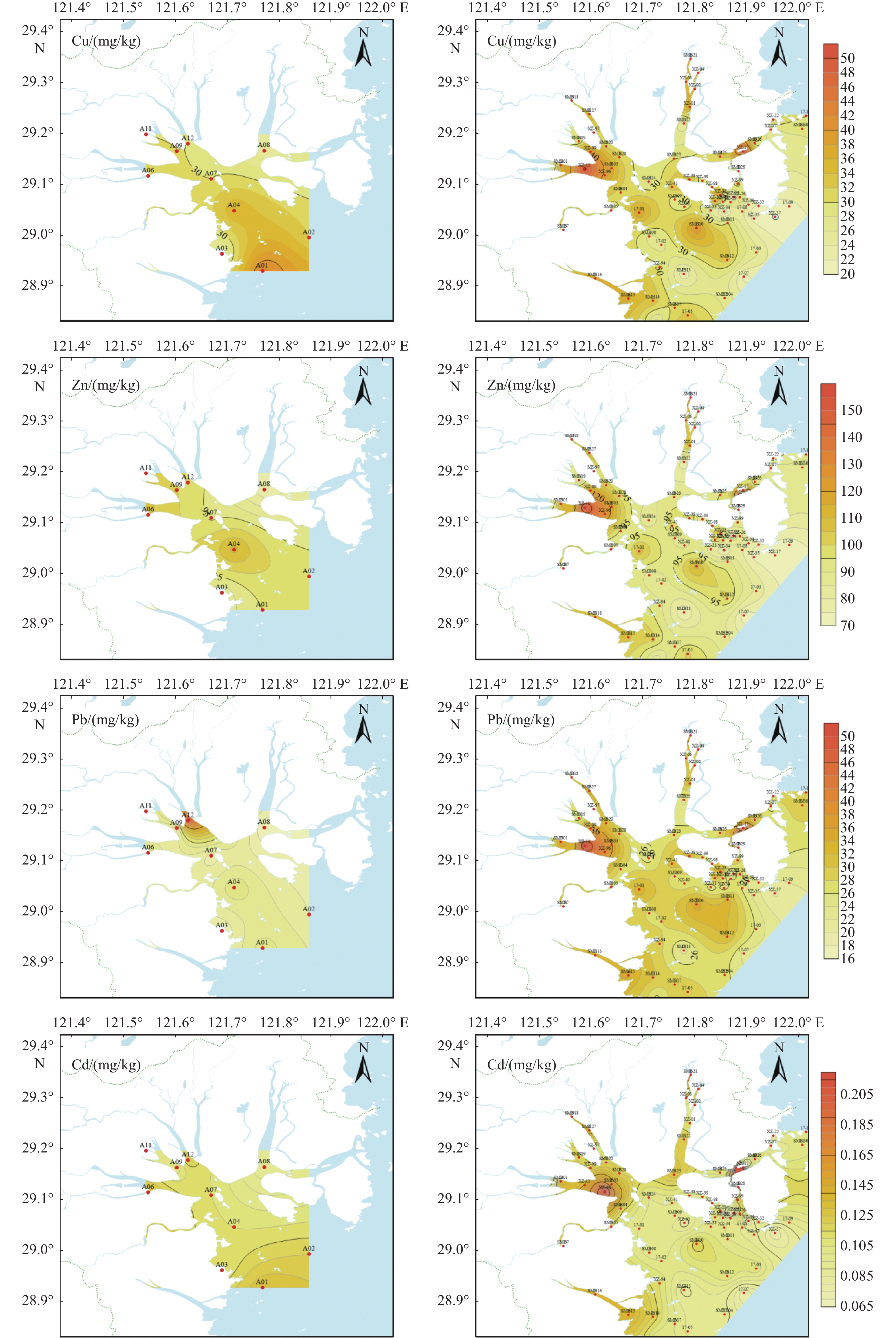
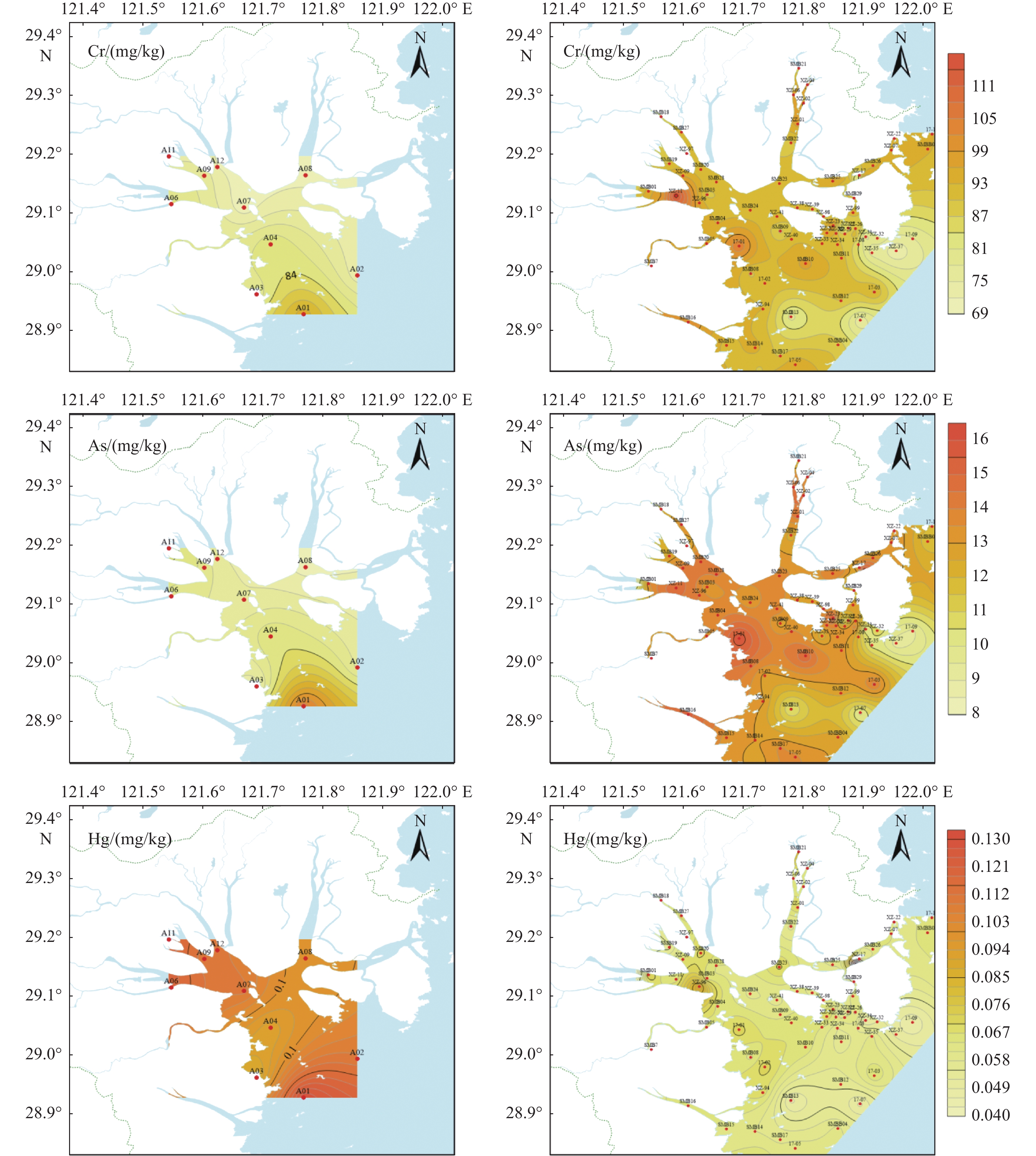
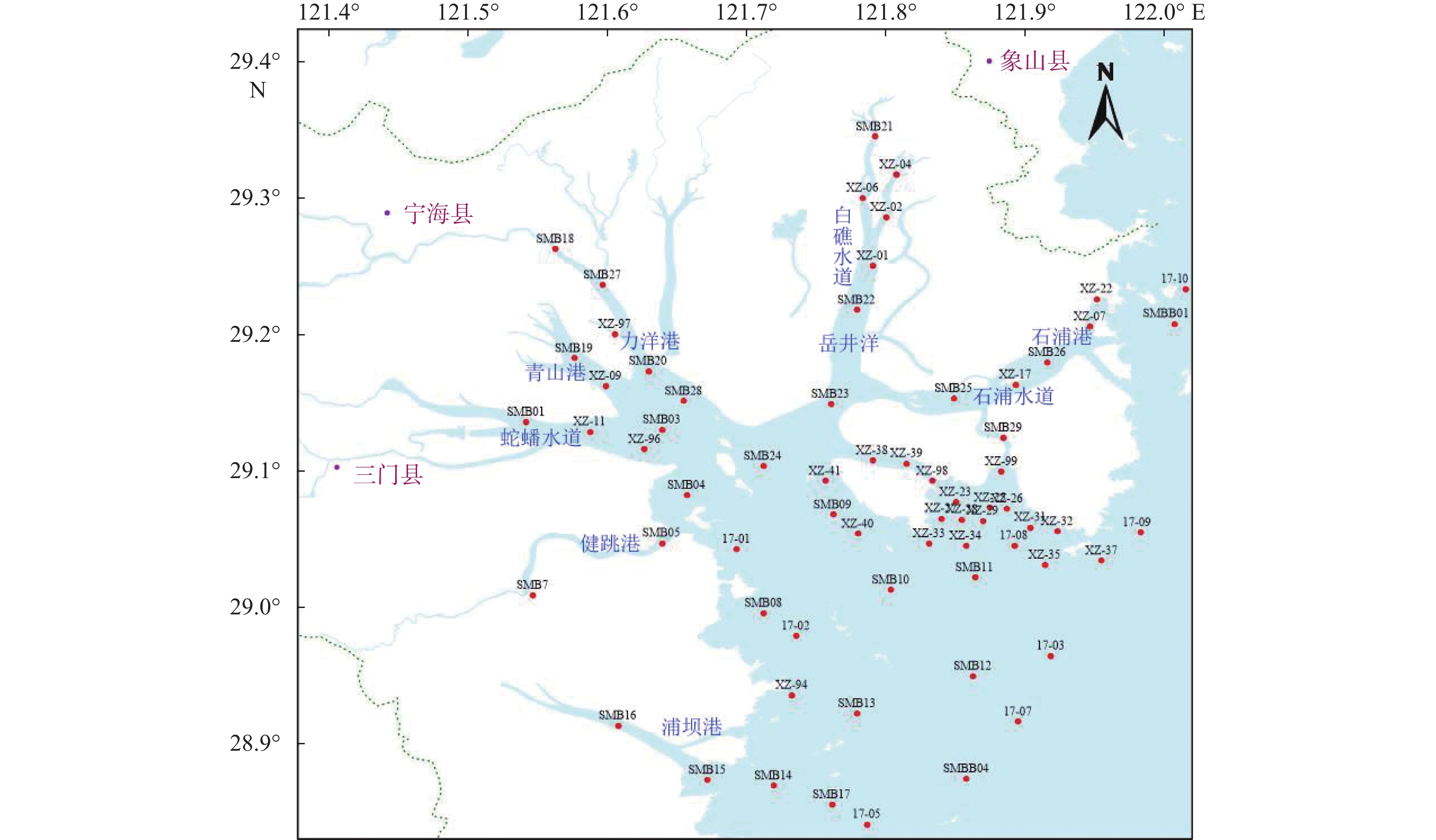
为了解三门湾海域表层沉积物重金属的含量和分布特征,本研究对三门湾海域2019年82个站位海域表层沉积物中的Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd、Cr、As及Hg共7种重金属元素的含量进行测定,并对比10年前的数据,分析了元素含量的变化情况,追溯了其主要物质来源。结果表明,三门湾海域表层沉积物中Cu、Zn、Pb、Cd、Cr、As、Hg的平均质量浓度分别是31.33、96.46、29.86、0.116、91.54、13.09、0.06 mg/kg,Cu、Cr的含量相对较高。与2009年相比,2019年三门湾海域表层沉积物Cu、Zn与Cd的含量大体上保持一致,Pb、Cr与As的含量有所上升,Hg的含量显著降低。沉积物重金属含量由近岸向外海依次降低,高值区主要集中在蛇蟠水道口、力洋港与健跳镇附近。运用主成分分析与因子分析对重金属物质来源进行解析的结果表明,重金属物质的来源与人类活动的影响密切相关。
Abstract:To clarify the distribution and concentration of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Sanmen Bay, Fujian, South China, Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd, Cr, As and Hg in the surface sediments of 82 stations in the Sanmen Bay waters in 2019 were analyzed. The concentration of the heavy metal elements were determined, and the data from 10 years ago were compared to show the changes in content of the elements, and their main material sources were analyzed. Results show that the average concentrations of Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, Cr, As, and Hg in the surface sediments were 31.33, 96.46, 29.86, 0.116, 91.54, 13.09, 0.06 mg/kg, respectively, and Cu and Cr contents were higher obviously. Compared with 2009, the contents of Cu, Zn, and Cd in 2019 were generally consistent, while those of Pb, Cr, and As increased, and that of Hg decreased significantly. The contents of heavy metals in sediments decreased gradually from the nearshore to the sea, and the high-value areas were mainly concentrated near the mouth of the Shepan Waterway, Liyang Port, and Jiantiao Town. The principal component analysis and factor analysis showed that the sources of heavy metals were closely related to the impact of human activities.
-
Key words:
- Sanmen Bay /
- heavy metals /
- spatial distribution /
- source analysis /
- human activities
-

-
表 1 2019年三门湾7种重金属元素的含量
Table 1. The contents of seven heavy metal elements in Sanmen Bay in 2019
/(×10−6) Cu Zn Pb Cd Cr As Hg 最小值 19.80 71.21 19.72 0.06 72.20 9.18 0.04 最大值 51.22 160.00 50.62 0.51 116.21 16.03 0.14 平均值 31.33 96.46 29.86 0.12 91.54 13.09 0.06 表 2 三门湾表层沉积物重金属Pearson相关性分析
Table 2. Pearson correlation analysis of heavy metals in surface sediments of Sanmen Bay
Cu Pb Zn Cr Cd As Hg Cu 1.000 Pb 0.870** 1.000 Zn 0.865** 0.952** 1.000 Cr 0.647** 0.483** 0.527** 1.000 Cd 0.345** 0.560** 0.633** 0.021 1.000 As 0.681** 0.524** 0.541** 0.808** 0.151 1.000 Hg 0.454** 0.587** 0.663** 0.196* 0.880** 0.393** 1.000 注:**表示p<0.01; *表示p<0.05。 表 3 主成分方差与方差贡献
Table 3. Principal component variance and variance contribution
成分 特征值 贡献率/% 累积贡献率/% 1 4.456 63.655 63.655 2 1.555 22.220 85.875 3 0.592 8.459 94.334 4 0.196 2.803 97.137 5 0.092 1.316 98.453 6 0.073 1.046 99.499 7 0.035 0.501 100.000 表 4 变量主成分分析的载荷和得分关系
Table 4. Relationship between loadings and scores of the principal components
重金属元素 PC1 PC2 PC3 Cu 0.825 0.470 0.182 Pb 0.873 0.241 0.378 Zn 0.810 0.289 0.478 Cr 0.307 0.901 0.002 As 0.253 0.900 0.187 Cd 0.269 −0.099 0.933 Hg 0.229 0.156 0.921 注:加粗数值代表高载荷 表 5 2009年与2019年土地利用分类遥感解译结果统计
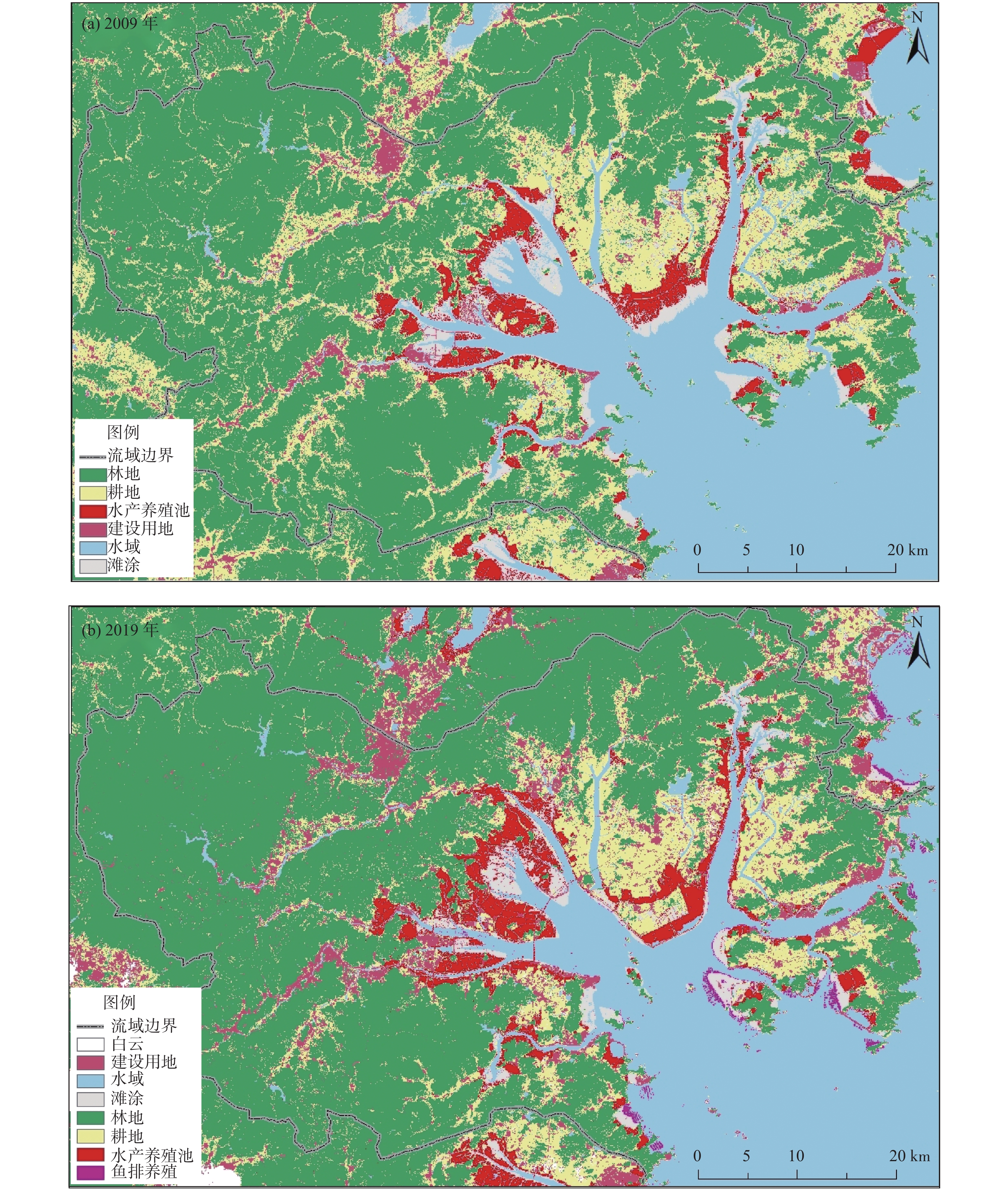
Table 5. Statistics of remote sensing interpretation results of land use classification in 2009 and 2019
/% 年份 建设用地 林地 耕地 滩涂 水产养殖池 鱼排 2009 4.81 49.33 20.71 5.21 3.24 / 2019 7.62 52.41 10.80 3.12 3.66 0.34 -
[1] ZENG J,HAN G,YANG K. Assessment and sources of heavy metals in suspended particulate matter in a tropical catchment,northeast Thailand[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2020,265:121898. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121898
[2] 付仁笼. 渤海海底表层沉积物重金属污染状况及来源分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019.
[3] SAKAI H,KOJIMA Y,SAITO K. Distribution of heavy metals in water and sieved sediments in the Toyohira River[J]. Water Research,1986,20(5):559-567. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(86)90019-9
[4] ALI M H. The relation of stream sediment grain sizes and its geochemical composition:a case study from Wadi Himur area,South Egypt[J]. Молодой ученый,2011(12/1):121-129.
[5] EDELSTEIN M,BEN-HUR M. Heavy metals and metalloids:sources,risks and strategies to reduce their accumulation in horticultural crops[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2018,234:431-444. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2017.12.039
[6] DAVUTLUOGLU O I,SECKIN G,ERSU C B,et al. Heavy metal content and distribution in surface sediments of the Seyhan River,Turkey[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2011,92(9):2250-2259. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.04.013
[7] SURESH G,SUTHARSAN P,RAMASAMY V,et al. Assessment of spatial distribution and potential ecological risk of the heavy metals in relation to granulometric contents of Veeranam Lake sediments,India[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2012,84:117-124. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.06.027
[8] ABRAHIM G M S,PARKER R J. Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary,Auckland,New Zealand[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,2008,136(1):227-238.
[9] 薛楚楚. 宁海三门湾新区主导产业的选择与空间布局研究[D]. 宁波: 宁波大学, 2013.
[10] 李铁军,刘士忠,郭远明,等. 三门湾沉积物重金属污染及其潜在生态危害评价[J]. 浙江海洋学院学报(自然科学版),2011,30(4):318-321.
[11] 吴春芳,宋伟华,陈立红,等. 三门湾海域环境质量现状监测与评价[J]. 科技创新导报,2014,11(27):95-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-098X.2014.27.055
[12] 梁静香,周永东,王忠明,等. 三门湾海域环境质量现状评价及其年际变化[J]. 浙江海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2021,40(2):121-127. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-830X.2021.02.004
[13] 朱荣,杨承虎,严峻,等. 浙江三门湾海域沉积物中重金属调查与评价[J]. 山东化工,2020,49(19):246-248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2020.19.110
[14] 林明祥,蔡廷禄,王欣凯,等. 近百年来浙江三门湾海岸线时空演变特征[J]. 海洋学研究,2021,39(1):47-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2021.01.006
[15] 中国海湾志编纂委员会. 中国海湾志 第五分册(上海市和浙江省北部海湾)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1982.
[16] 宋文杰,禹丝思,陈梅花,等. 近30年三门湾海岸线时空变化及人为干扰度分析[J]. 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版),2017,40(3):343-349.
[17] 王龙. 电感耦合等离子体质谱法在测定水中多种金属元素中的应用研究[J]. 世界有色金属,2019(8):213-215. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2019.08.123
[18] 陈思杨,宋琍琍,刘希真,等. 浙江典型海湾潮间带沉积物污染及生态风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学,2020,40(4):1771-1781. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.04.045
[19] 赵晨辉,胡佶,刘小涯,等. 浙江三门湾表层沉积物重金属含量分布、赋存形态及生态风险评价[J]. 海洋学研究,2018,36(2):64-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2018.02.009
[20] 柴小平,魏娜,任世军,等. 杭州湾及其邻近海域表层沉积物的沉积环境分区及重金属污染特征分析[J]. 海洋科学,2019,43(8):29-35. doi: 10.11759/hykx20190212004
[21] 白有成,高生泉,金海燕,等. 长江口及邻近海域沉积物重金属潜在生态风险评价[J]. 海洋学研究,2011,29(4):32-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2011.04.005
[22] LU Q,BAI J,GAO Z,et al. Spatial and seasonal distribution and risk assessments for metals in a Tamarix chinensis Wetland,China[J]. Wetlands,2016,36(1):125-136.
[23] 张伯镇,雷沛,潘延安,等. 重庆主城区次级河流表层沉积物重金属污染特征及风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报,2015,35(7):2185-2192.
[24] 柴小平. 杭州湾及其邻近海域表层沉积物重金属分布特征与污染评价研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2015.
[25] 李萌,熊尚凌,陈伟,等. 浙北海域表层沉积物中重金属的含量特征、来源和污染评价[J]. 海洋环境科学,2018,37(1):14-20.
[26] 刘晓凤,段晓勇,田元,等. 三门湾水体营养盐变化及其对人类活动的响应[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2021,37(5):46-56. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2020.052
[27] 赵玉庭,孙珊,由丽萍,等. 莱州湾沉积物粒度与重金属分布特征[J]. 海洋科学,2021,45(3):43-50.
[28] 师鹏飞,许东峰,王俊,等. 三门湾外海的潮汐和潮流特征[J]. 海洋学研究,2012,30(2):27-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2012.02.005
-



 下载:
下载: