Differential diagenetic evolution and quantitative characterization of pores in the third Member of Dongying Formation in the western section of Shijiutuo Uplift
-
摘要:
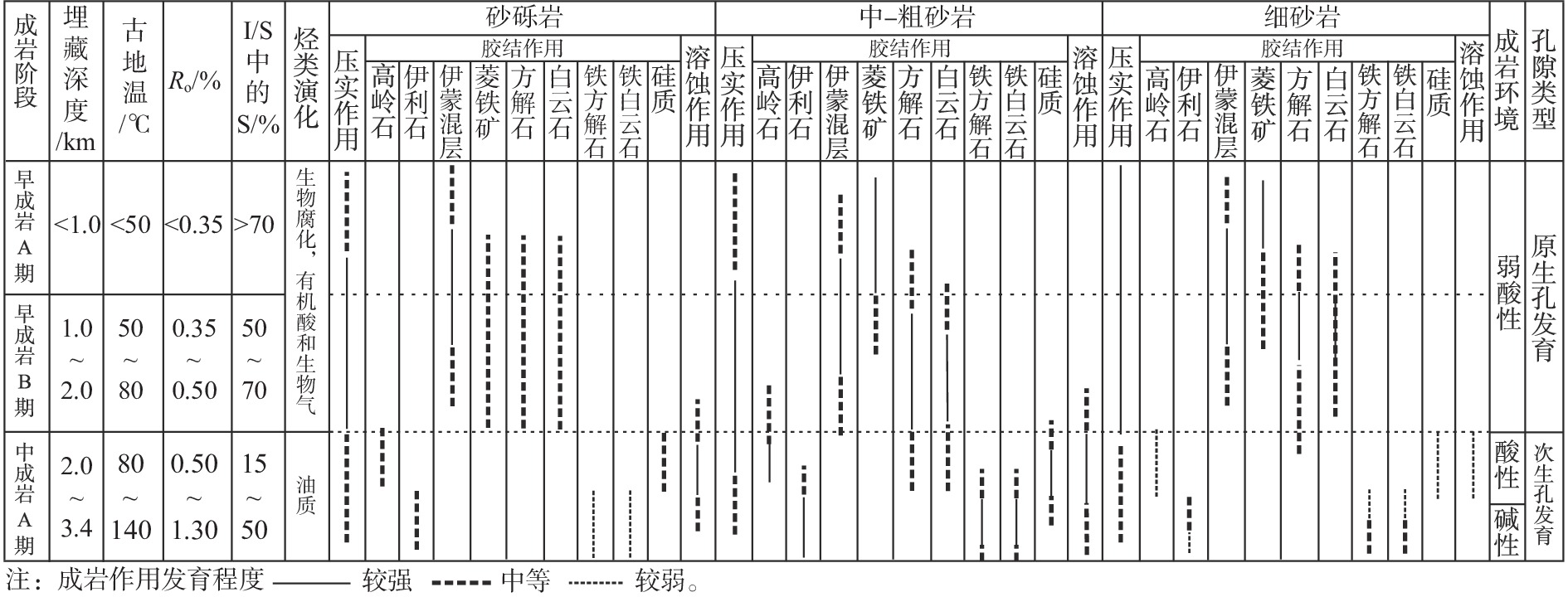
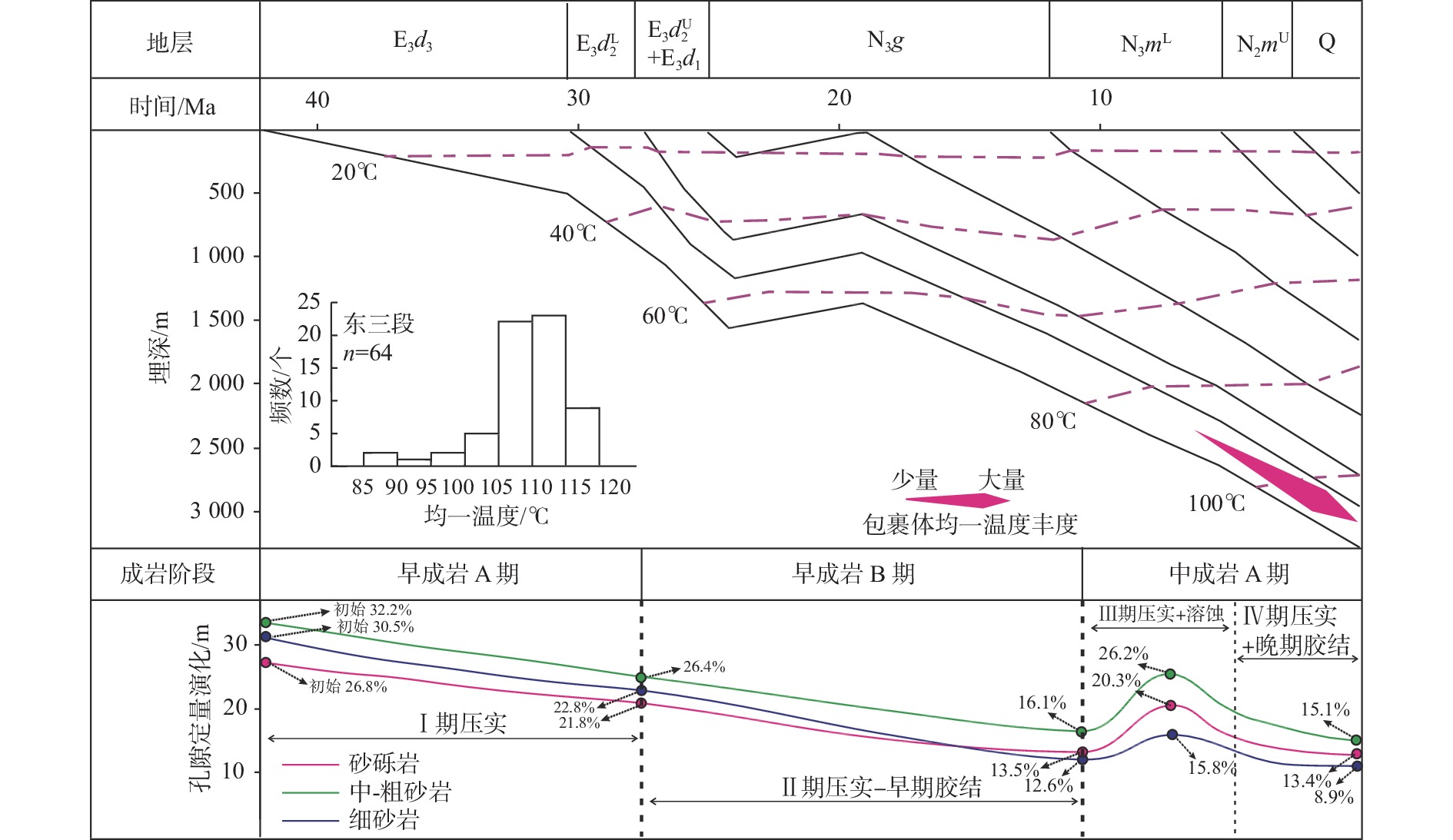
为了定量评价成岩作用对石臼坨凸起西段X-1井区东三段不同粒级储层孔隙发育的影响,利用铸体薄片、扫描电镜、常规物性、X射线衍射等资料,分析了不同粒级储层孔隙演化的差异及原因。结果表明,中-粗砂岩以较高含量的自生高岭石和次生溶蚀孔发育为特征,砂砾岩胶结物含量中等,但次生溶蚀孔较发育,细砂岩胶结物和次生溶蚀孔欠发育。中-粗砂岩经历的成岩作用类型较完整,砂砾岩整体具有较弱压实、弱溶蚀、弱胶结的成岩特征,而细砂岩以压实作用为主,中成岩A期溶蚀、胶结作用基本不发育。东三段同生期-早成岩B期以机械压实为主,对细砂岩孔隙演化影响最大;中成岩A期早期以溶蚀作用为主,对中-粗砂岩溶蚀增孔效应最明显;中成岩A期晚期以含铁碳酸盐胶结为特色,对中-粗砂岩孔隙演化的影响较大,但其总体孔隙度仍然最高。东三段不同粒级储层中的中-粗砂岩平均孔隙度为15.1%,砂砾岩为13.4%,细砂岩为8.9%。由于中-粗砂岩受压实影响较弱,溶蚀作用最强,故孔隙最为发育;砂砾岩虽然受压实作用较弱,但由于孔隙结构复杂,非均质性强,限制了成岩流体的活动性,影响了储层的溶蚀作用强度;细砂岩泥质含量较高,受压实作用影响最大,孔隙发育相对最差。该研究对于中国湖盆近源快速堆积背景下中深层有效储层的预测与评价具有参考价值。
Abstract:In order to quantitatively evaluate the influence of diagenesis on the pore development of different grain size reservoirs in the third Member of Dongying Formation of Well X-1 in the western section of Shijiutuo Uplift, the differences in pore evolution of different grain size reservoirs and their causes were analyzed by using cast thin sections, scanning electron microscopy, conventional physical properties and X-ray diffraction data.The results show that the middle-coarse grained sandstone is characterized by high content of authigenic kaolinite and secondary dissolution pores, the content of glutenite cements is medium but the secondary dissolution pores are relatively developed, and the fine-grained sandstone cements and secondary dissolution pores are underdeveloped. The diagenesis type of medium-coarse grained sandstone is relatively complete, and the sandstone is characterized by weak compaction, weak dissolution and weak cementation, while the fine-grained sandstone is dominated by compaction, and the dissolution and cementation of the mid-diagenetic stage A are not developed. From syngenetic stage to early diagenetic stage B, the diagenesis of the third Member of Dongying Formation is mainly mechanical compaction, which has the greatest influence on pore evolution of fine-grained sandstone. In the late stage A of middle diagenesis, it is characterized by iron-bearing carbonate cementation, which has A great influence on the pore evolution of middle-coarse grained sandstone, but its overall porosity is still the highest. The average porosity of the medium-coarse grained sandstone is 15.1%, 13.4% for conglomerate and 8.9% for fine-grained sandstone. Medium-coarse-grained sandstone has weak compaction effect, the strongest dissolution effect and the most developed pores. Although the compaction of conglomerate is weak, due to the complex pore structure and strong heterogeneity, the activity of diagenetic fluid is limited and the dissolution intensity of reservoir is affected. The fine-grained sandstone has high mud content, and the influence of compaction is the biggest, but the pore development is relatively worst. The research results have reference value for the prediction and evaluation of middle-deep effective reservoirs under the background of rapid accumulation near lacustrine basin in China.
-

-
表 1 东三段不同岩石类型填隙物类型及含量统计
Table 1. Types and contents of interstitial materials of different rock types of the third Member of Dongying Formation
岩石类型 样品数n /个 菱铁矿 白云石 铁白云石 方解石 铁方解石 高岭石 伊利石 石英次生加大 泥质 砂砾岩 38 ◆ ◆ (0.5~4)/1 (0.5~3)/1.4 (1~3)/2.2 (0.9~2.8)/1.5 ◆ ▲ (1~8)/2.8 中-粗砂岩 58 ◆ ◆ (1~6)/2.9 (2~4)/2.5 (2~7)/3.1 (1~5)/2.1 ◆ ▲ (1~6)/3.5 细砂岩 47 △ △ ▲ (0.2~1)/0.4 (0.5~2)/1 (0.5~2)/1 △ △ (3~15)/6.9 注:表中数据含义(最小值~最大值)/平均值,单位%;◆表示少见,▲表示偶见,△表示极少见。 表 2 东三段不同岩石类型孔隙类型及面孔率统计
Table 2. Statistics of pore types and face rates of different rock types of the third Member of Dongying Formation
岩石类型 样品数n/个 残余粒间孔 粒内溶孔 胶结物晶间孔 总面孔率 砂砾岩 38 (1~18)/6.2 (1~6)/8.9 ▲ (5~31)/19.5 中-粗砂岩 58 (5~32)/9.1 (2~25)/15.1 ◆ (6~32)/24.6 细砂岩 47 (2~16)/7.5 (1~5)/3.1 △ (1~27)/12.3 注:表中数据含义(最小值~最大值)/平均值,单位%;◆表示少见,▲表示偶见,△表示极少见。 表 3 东三段不同成岩作用对孔隙发育定量表征计算公式[9,12-17]
Table 3. The formula for calculating the quantitative influence of different diagenesis on porosity development of the third Member of Dongying Formation[9,12-17]
孔隙演化参数 定量表征公式 初始孔隙度 分选系数(Sd) Sd=(P25/P75)/2 未固结沉积物初始孔隙度(θ1)/% θ1=20.91+22.90/Sd 压实作用 经过压实作用后剩余孔隙度(θ2)/% θ2=θce+(θori+θmatr)×θmp/θpor 压实过程损失的孔隙度(φco)/% φco=θ1-θ2 压实减孔率(Pco)/% Pco=φco×100%/θ1 胶结作用 早期损失孔隙度(φce1)/% φce1=θce1 中晚期损失孔隙度(φce2)/% φce2=θce2 胶结过程损失孔隙度(φce)/% φce =φce1+φce2 胶结减孔率(Pce)/% Pce=φce×100%/θ1 溶蚀作用 溶蚀增加的孔隙度(φdiss)/% φdiss=θdiss×θave/θpor 溶蚀增孔率(Pdiss)/% Pdiss=θ4×100%/θ1 不同样品计算现今最终孔隙度(θn)/% θn=θ1-φco-φce+φdiss 注:P25和P75分别为粒度概率累积曲线上25%和75%处对应的颗粒直径,mm;θce为铸体薄片中现今胶结物含量,%;θce1和θce2分别为成岩早期和中晚期胶结物含量,%;θori和θmatr分别为铸体薄片中粒间孔和杂基微孔的面孔率,%;θmp为样品实测孔隙度,%;θpor为总孔隙面孔率,%;θdiss为溶蚀孔面孔率,%;n为样品数。 表 4 东三段深埋藏过程不同阶段压实减孔比率
Table 4. The ratio of compaction and pore reduction in different stages of deep burial process of the third Member of Dongying Formation
参数 C1 C2 C3 C4 n 0 0 1 1 α=2n 1 1 2 2 Ci /% 33.2 42.1 11.8 12.9 注:C1—C4分别为4个沉降阶段压实减孔比率[18]。 表 5 东三段样品不同成岩阶段孔隙演化统计表
Table 5. Statistical table of pore evolution during different diagenetic processes of samples from the third Member of Dongying Formation
储层类型 样品数n
/个θ1/% φco/% P1/% P2/% P3/% P4/% θn/% Φave/% E/% (φco×C1) (φco×C2+φce1) (φco×C3-φdiss) (φco×C4+φce2) 砂砾岩 38 26.8 15.1 5.0 6.5+1.8 1.8-6.8 1.9+3.2 13.4 12.9 3.7 中-粗砂岩 58 32.2 17.6 5.8 7.4+2.9 2.1-10.1 2.3+6.7 15.1 15.8 4.6 细砂岩 47 30.5 23.1 7.7 9.7+0.5 2.7-3.2 3.0+1.2 8.9 9.1 2.2 注:θ1为未固结沉积物初始孔隙度;φco为压实过程损失总孔隙度;P1—P4分别为4个孔隙演化阶段的孔隙度变化量;C1—C4分别为4个沉降阶段压实减孔比率;θn为不同样品计算现今最终孔隙度(θn=θ1-P1-P2-P3-P4);Φave为平均气测孔隙度值;相对误差E=|Φave-θn|×100%/Φave;表中孔隙数据为平均值。 -
[1] 王启明,李瑾,周晓光,等. 石臼坨凸起西南缘陡坡带东三段古地貌对沉积的控制[J]. 东北石油大学学报,2016,40(6):53-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2016.06.007
[2] 赵梦,徐长贵,杜晓峰,等. 石臼坨凸起西南陡坡带扇三角洲锆石定年与源汇示踪[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报,2017,42(11):1985-1991.
[3] 杜晓峰,王清斌,庞小军,等. 渤中凹陷石南陡坡带东三段源汇体系定量表征[J]. 岩性油气藏,2018,30(5):1-9.
[4] 庞小军,王清斌,张雪芳,等. 渤海海域石臼坨凸起西南缘断层特征对油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 东北石油大学学报,2016,40(3):32-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2016.03.005
[5] 江涛,黄晓波,陶莉,等. 石南断层分段特征及其对油气差异成藏的控制[J]. 断块油气田,2021,28(5):625-630.
[6] 万琳,王清斌,代黎明,等. 应用恒速压汞技术定量评价低渗-特低渗砂岩储层微观孔喉特征:以石臼坨凸起陡坡带东三段为例[J]. 高校地质学报,2018,24(4):584-592.
[7] 万琳,王清斌,赵国祥,等. 石臼坨凸起陡坡带东三段扇三角洲砂体成岩作用定量表征[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,2017,36(6):31-37.
[8] 孙藏军,别旭伟,聂玲玲,等. 渤海曹妃甸6-4油田东三段储层孔隙演化定量分析[J]. 中国海上油气,2019,31(6):44-51.
[9] 王琪,马东旭,余芳,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地临兴地区下石盒子组不同粒级砂岩成岩演化及孔隙定量研究[J]. 沉积学报,2017,35(1):163-172.
[10] XU L W,YANG K J,WEI H,et al. Pore evolution model and diagenetic evolution sequence of the Mesoproterozoic Xiamaling shale in Zhangjiakou,Hebei[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2021,207(12):109-115.
[11] ZINDORF M, ROOZE J, MEILE C, et al. Sulfur and carbon cycling in Fe dominated sediments from the Mozambique margin: past and current processes[C]//Goldschmidt Conference 2019, Barcelona, 2019.
[12] 王琪,禚喜准,陈国俊,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地盐池-姬源地区三叠系长4+5砂岩成岩演化特征与优质储层分布[J]. 沉积学报,2005,23(3):397-404. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.03.004
[13] 王瑞飞,陈明强. 储层沉积-成岩过程中孔隙度参数演化的定量分析:以鄂尔多斯盆地沿25区块、庄40区块为例[J]. 地质学报,2007,81(10):1433-1438.
[14] 潘高峰,刘震,赵舒,等. 砂岩孔隙度演化定量模拟方法:以鄂尔多斯盆地镇泾地区延长组为例[J]. 石油学报,2011,32(2):249-256. doi: 10.7623/syxb201102009
[15] 唐俊,王琪,廖朋,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地环县地区长8段砂岩储层孔隙度演化定量模拟[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2013,24(1):321-331.
[16] 张茜,孙卫,任大忠. 鄂尔多斯盆地华庆地区长63储层成藏期孔隙度定量演化及致密成因机理[J]. 地质与勘探,2017,53(4):807-817.
[17] 施振生,李熙喆,董大忠,等. 致密砂岩储层成岩作用与孔隙演化:以川西南上三叠统为例[J]. 地学前缘,2018,25(2):180-190. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.yx.2017-6-4
[18] SOMBRA C L, CHANG H K. Burial history and porosity evolution of Brazilian Upper Jurassic to Tertiary sandstone reservoirs[C]//American Association of Petroleum Geologists Memoir, 1997, 69: 79-89.
-




 下载:
下载: