Seismic prediction of tide-controlled sand reservoir in Pinghu Formation coal seam, W Gas Field, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin
-
摘要:
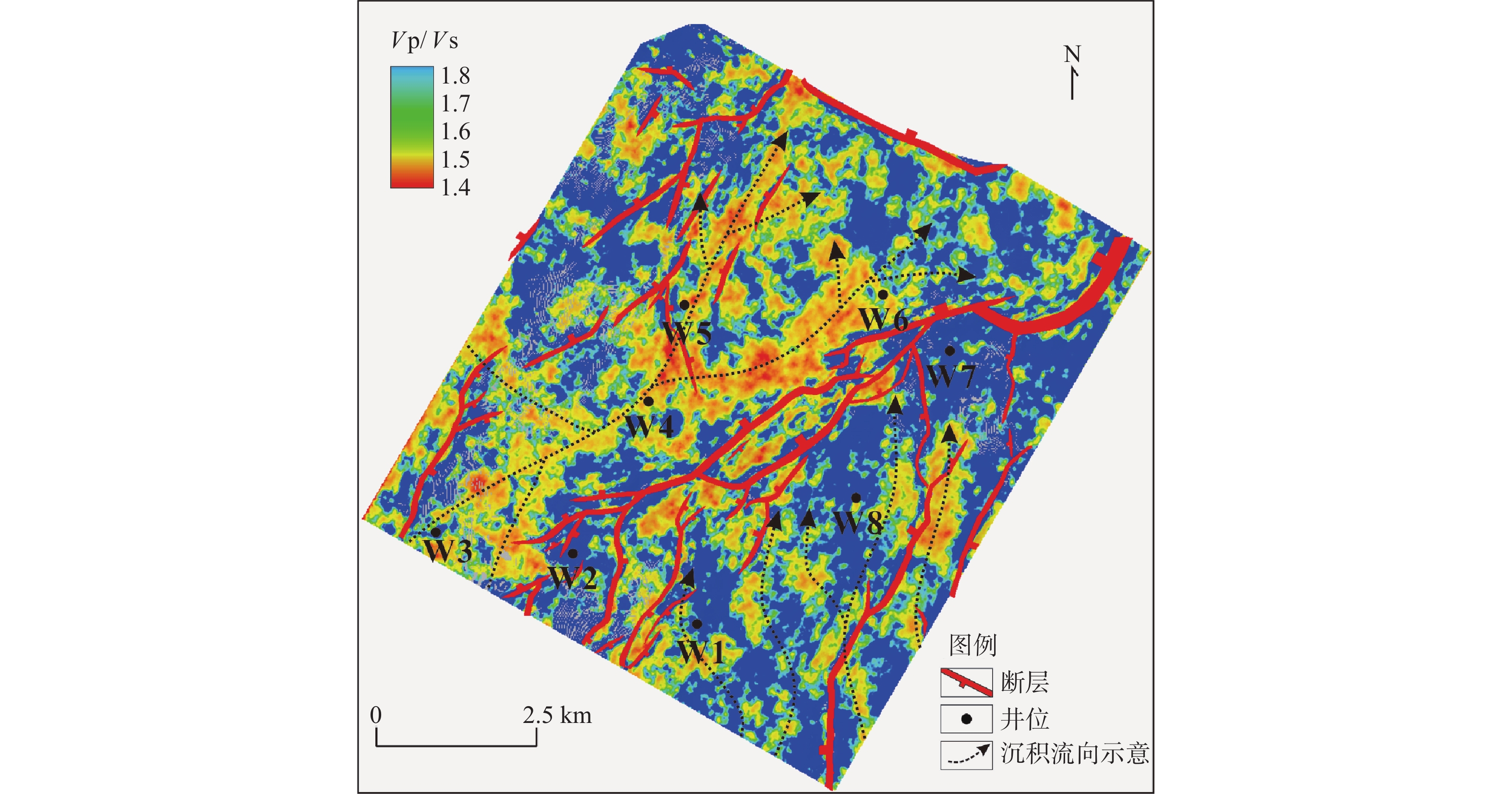
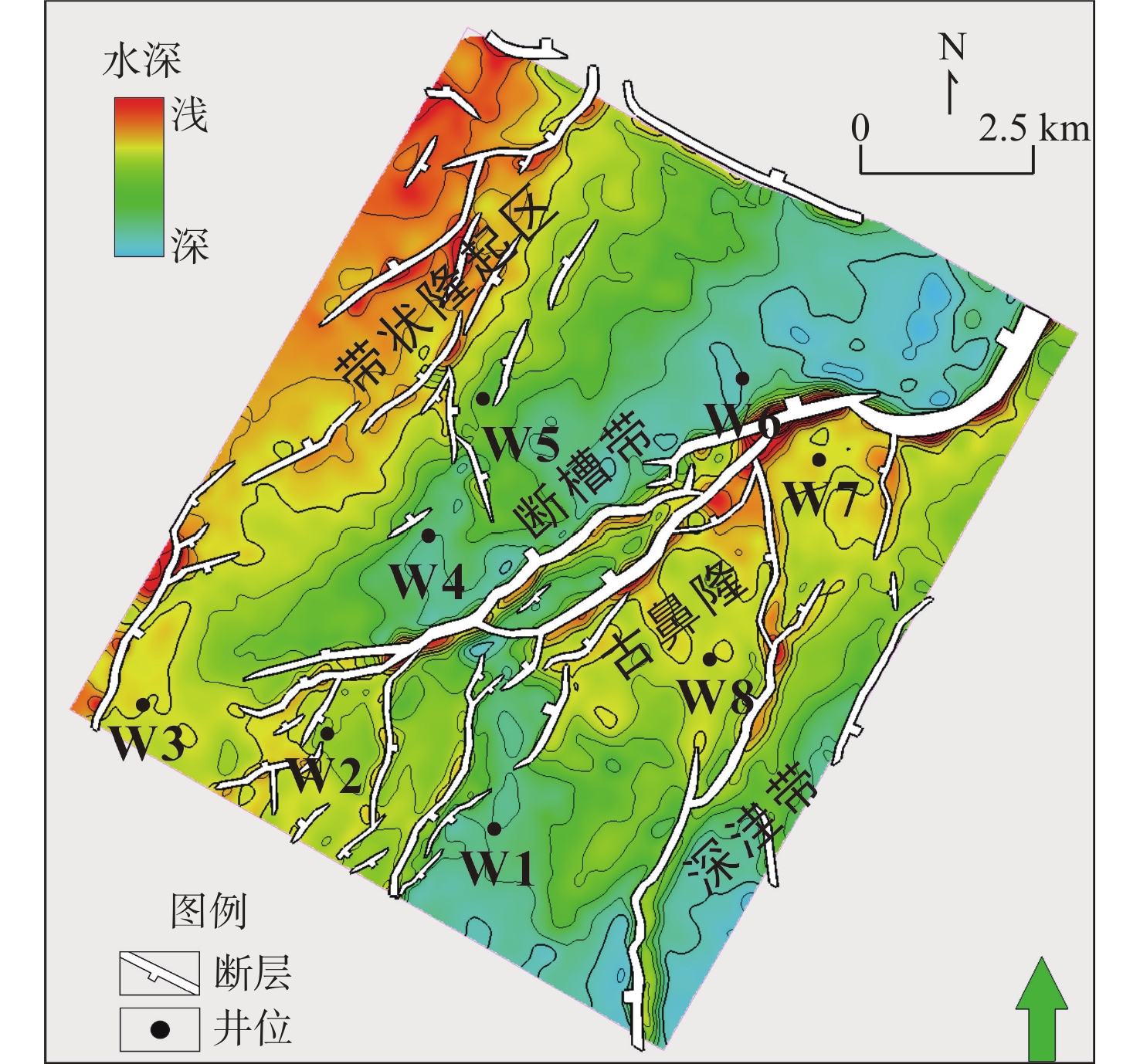
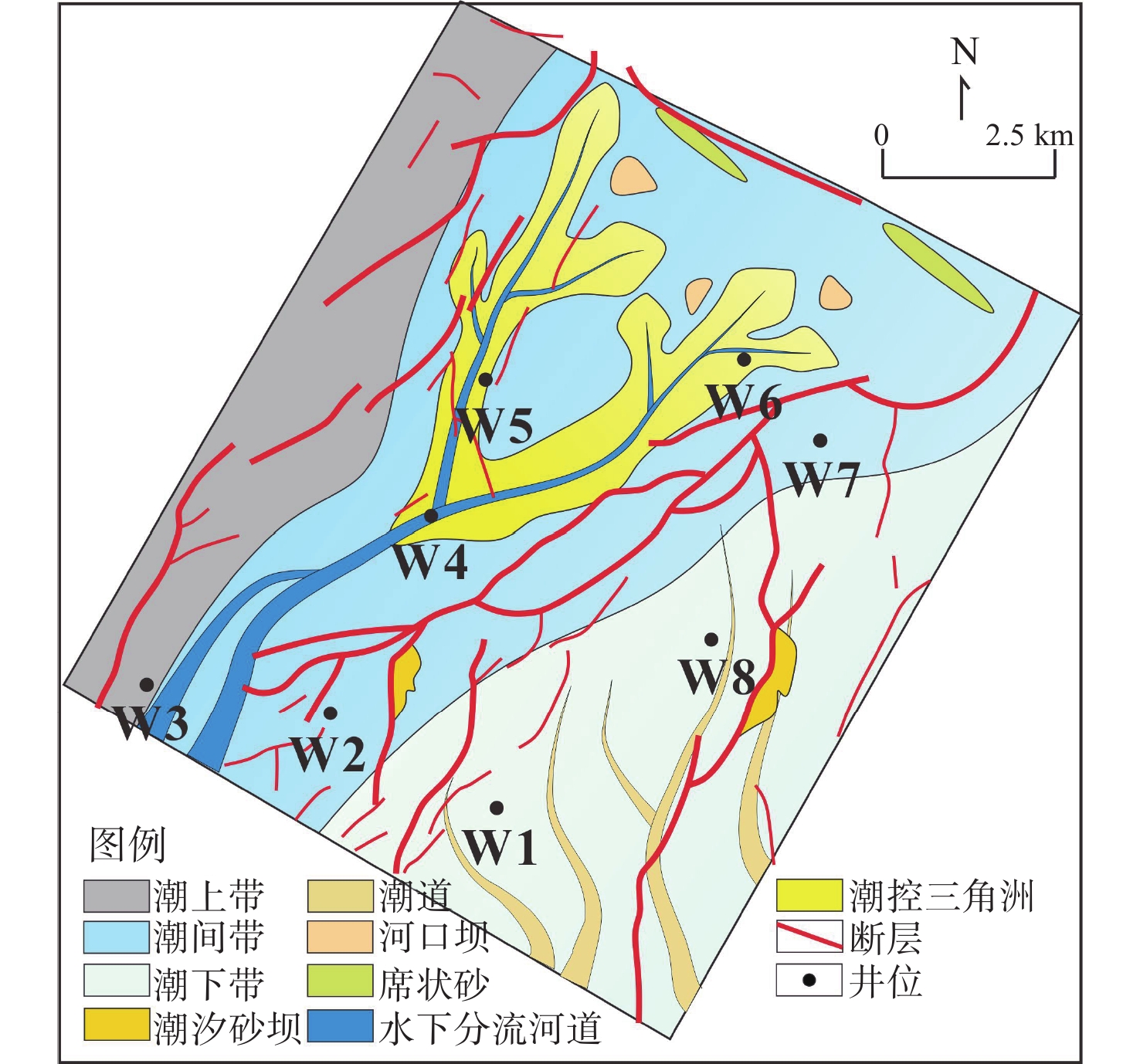
东海西湖凹陷油气资源丰富,具有较好的勘探开发潜力,其中平湖组作为重要的含油气层系,已成为近期勘探开发的焦点。平湖组普遍发育薄煤层,导致含油气砂体的地震响应存在多解性,严重制约着开发生产。为了识别薄煤层影响下的含油气砂岩,开展了储层地震预测研究工作。首先,通过岩芯、测井和分析化验资料解析了潮控沉积环境特征;然后,利用岩石物理分析技术归纳总结了在薄煤层影响下含水砂岩、含气砂层的叠前道集响应规律;最后,利用地球物理属性完成了潮控砂体储层预测,并结合沉积特征实现研究区有利目标优选。研究表明:平湖组以潮控三角洲-潮汐沉积环境为主,其中,水下分流河道、河口坝和潮汐砂坝等沉积微相是优势储集体;砂体储层受到薄煤层影响呈现近道为波峰、远道为波谷的Ⅱ -p类AVO特征;利用叠前道集响应规律指导叠前纵波速度/横波速度(Vp/Vs)反演,完成潮控储层定量预测;综合古地貌和沉积微相认识,实现了研究区潮控环境下潜力精细描述,明确③号砂体属于一类有利目标,可作为潜力目标。本研究方法有效提高了研究区储层预测工作的精确度,为该区块下一步深层煤系潮控砂体的井位部署提供了技术支撑。
Abstract:The Xihu Sag in the East China Sea is rich in oil and gas resources and has good exploration and development potential. Pinghu Formation, as an important oil-bearing horizon, has become the focus of exploration and development in the near future. Thin coal seams are widely developed in Pinghu Formation, which leads to multiple solutions of seismic amplitude, phase, and frequency of oil-bearing sand bodies, which seriously restricts the development and production. To identify oil-bearing sandstone under the influence of thin coal seams, reservoir earthquake prediction was carried out. First, the characteristics of tide-controlled sedimentary environment were analyzed in detail through core, well logging, and analytical laboratory data. Then, using rock physical analysis technology, the characteristics of pre-stack collection response of water-bearing sandstone and gas-bearing sand under the influence of thin coal seams were summarized. Finally, the geophysical properties were used to predict the reservoir of tide-controlled sand body, and the favorable target selection in the study area was realized in combination with the sedimentary characteristics. Results show that the Pinghu Formation mainly developed tide-controlled delta-tidal sedimentary environment, in which underwater distributary channel, estuary bar, and tidal sand bar were the dominant sedimentary microfacies. Under the influence of thin coal seam, the sand-body reservoir shows AVO type-Ⅱ response characteristics with wave crest in the short path and trough in the far path. Using prestack gathers response law to guide the P/S velocity ratio inversion, control reservoir quantitative prediction was completed. Based on the understanding of paleo-geomorphology and sedimentary microfacies, the potential of the tidal control environment in the study area could be accurately described, and No.3 sand body is a favorable and potential target. This method improved effectively the accuracy of reservoir prediction in the study area, and provided a technical support for the well location deployment of the deep coal measure tidal control sand body in the block.
-

-
图 1 西湖凹陷区域构造特征(a)、基岩分布(b)及研究区断裂与气田位置(c)[10]
Figure 1.
图 2 西湖凹陷新生代地层综合柱状图及平湖组三级层序、砂层组地层单元[10]
Figure 2.
表 1 研究区不同沉积微相岩芯和测井相特征
Table 1. Characteristics of different sedimentary microfacies in the study area on cores and logging curves
特征类型 沉积微相 水下
分流河道支流间湾 水下天然堤 河口坝 席状砂 潮汐砂坝 潮道 泥坪 颜色 灰白 深灰白 灰白
灰色灰白 灰白
灰色灰白 灰白
灰色深灰白 岩性 含砾石中砂岩 泥岩 粉砂岩 细砂岩 细砂岩 细砂岩、中砂岩 粉砂岩、细砂岩 泥岩 沉积构造 槽状层理
交错层理平行层理
植物碎屑爬升层理 沙纹层理
交错层理脉状层理 块状层理 波状层理 生物扰动层理 岩芯 







岩电特征 







表 2 不同岩相弹性参数
Table 2. Elastic parameters of different lithofacies
岩性 纵波时差/(μs/ft) 横波时差/(μs/ft) 密度/(g/cm3) 纵波阻抗/(g/cm3·m/s) Vp/(m/s) Vs/(m/s) Vp/Vs 泥岩 85 150 2.56 9 182 3 586.8 2 032.5 1.76 水砂 78 132 2.36 9 224 3 908.7 2 309.7 1.69 气砂 80 132 2.36 8 993 3 810.9 2 309.7 1.65 煤层 98 169 2.25 6 999 3 111.0 1 804.1 1.72 表 3 平下段有利目标评价表
Table 3. Favorable target evaluation
砂体 评价指标 优势古地貌区 有利相带分布区 断砂匹配 构造高低 ① 水下分流河道 较好 高部位 ② 水下分流河道 高部位 ③ 断槽带 水下分流河道 较好 高部位 ④ 断槽带 ⑤ 潮汐砂坝 较好 高部位 ⑥ 潮汐砂坝 较好 ⑦ -
[1] 江东辉,蒲仁海,苏思羽,等. 断陷盆地斜坡带大型油气田成藏条件:西湖凹陷平北缓坡断裂与岩性控藏有利区[J]. 天然气工业,2021,41(11):33-42. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2021.11.004
[2] 周荔青,江东辉,张尚虎,等. 东海西湖凹陷大中型油气田形成条件及勘探方向[J]. 石油实验地质,2020,42(5):803-812. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005803
[3] 周心怀. 西湖凹陷地质认识创新与油气勘探领域突破[J]. 中国海上油气,2020,32(1):1-12.
[4] 王泽宇,徐清海,侯国伟,等. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷W井区平湖组潮汐沉积模式[J]. 海相油气地质,2021,26(2):159-169. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2021.02.008
[5] 王红岩,周祥林,胡伟,等. 西湖凹陷平北斜坡带含煤系地层储层预测[J]. 石油物探,2021,60(4):595-603. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2021.04.008
[6] 刘英辉,蔡华,段冬平,等. 西湖凹陷平湖地区平湖组海侵体系域潮控三角洲-潮坪沉积特征及模式[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2022,38(1):33-40. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2021.147
[7] 胡云亭,刘灵童,王文升,等. 基于沉积相控的优质储层预测:以鄂尔多斯盆地X区块下石盒子组致密砂岩气为例[J]. 断块油气田,2020,27(6):705-709.
[8] 张兰,汪文基,何贤科,等. 东海西湖凹陷平湖组富煤环境相控储层预测技术[J]. 现代地质,2019,33(2):337-344. doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.02.09
[9] 李上卿,李纯洁. 东海西湖凹陷油气资源分布及勘探潜力分析[J]. 石油实验地质,2003,25(6):721-728. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2003.06.015
[10] 蔡华,秦兰芝,刘英辉. 西湖凹陷平北斜坡带海陆过渡相源-汇系统差异性及其耦合模式[J]. 地球科学,2019,44(3):880-897.
[11] 常吟善,段冬平,张兰,等. 西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带A气田沉积体系定量表征及海平面变化周期性探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2021,41(3):12-21. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2020081302
[12] 吴峰,任培罡,谈明轩,等. 东海西湖凹陷孔雀亭地区平湖组沉积相演变及其主控因素分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2022,42(2):119-130. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2021052401
[13] 徐长贵,赖维成. 渤海古近系中深层储层预测技术及其应用[J]. 中国海上油气,2005,17(4):231-236. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2005.04.004
[14] 王华,白云风,黄传炎,等. 歧口凹陷古近纪东营期古物源体系重建与应用[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报,2009,34(3):448-456.
[15] 侯国伟,李帅,秦兰芝,等. 西湖凹陷西部斜坡带平湖组源-汇体系特征[J]. 中国海上油气,2019,31(3):29-39.
[16] 刘金水,陆永潮,秦兰芝. 源—汇系统分析方法在大型储集体研究中的应用:以西湖凹陷中央反转带花港组为例[J]. 石油实验地质,2019,41(3):303-310. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201903303
[17] 漆家福. 裂陷盆地中的构造变换带及其石油地质意义[J]. 海相油气地质,2007,12(4):43-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2007.04.007
[18] 王启明,黄晓波,宛良伟,等. 石臼坨凸起东倾末端沙一、二段汇聚体系特征及砂体展布规律[J]. 中国海上油气,2017,29(4):60-67.
[19] 张建林,林畅松,郑和荣. 断陷湖盆断裂、古地貌及物源对沉积体系的控制作用:以孤北洼陷沙三段为例[J]. 油气地质与采收率,2002,9(4):24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2002.04.009
-




 下载:
下载: