Mineral distribution characteristics and provenance of surface sediments in Sanmen Bay
-
摘要:
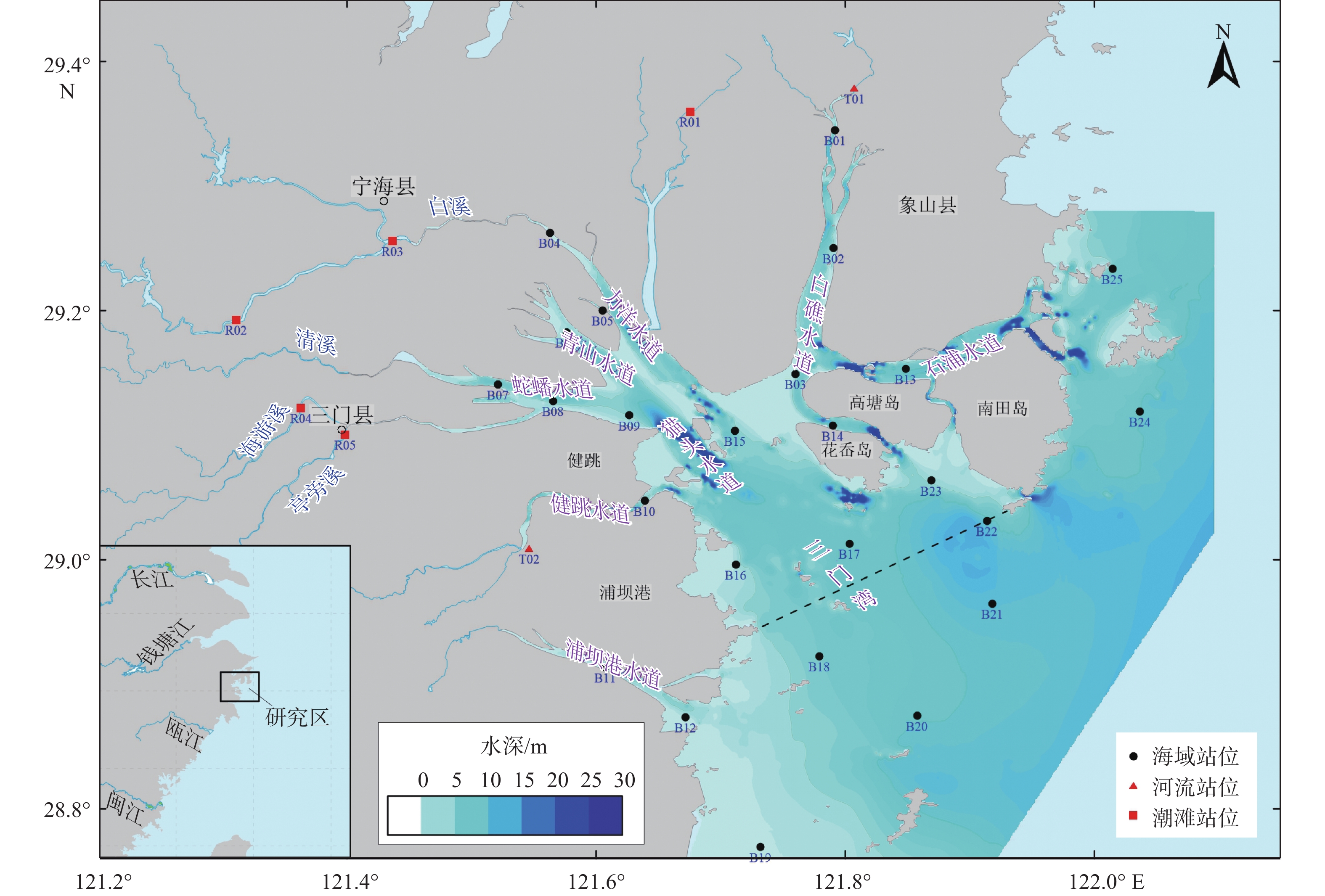
由于沉积环境和物质来源的差异,不同海域矿物组成及分布各异。为查明三门湾海域表层沉积物碎屑矿物和黏土矿物的含量、分布特征,在三门湾海域采集了25个海域表层沉积物、5个河流沉积物和2个潮滩沉积物样品,对沉积物样品进行63~125 μm粒级颗粒的碎屑矿物鉴定分析和<2 μm粒级颗粒的黏土矿物含量分析。结果显示,海域表层沉积物中共鉴定出27种重矿物、11种轻矿物。金属矿物、绿帘石、岩屑、普通角闪石、片状矿物含量占据重矿物的93.0%。轻矿物中81.1%为岩屑、斜长石、石英和片状矿物。三门湾黏土矿物以伊利石为主(平均61.1%),绿泥石和高岭石次之(19.3%和15.8%),含少量蒙脱石(3.8%)。根据Q型聚类,可将三门湾沉积物分为河口矿物区(Ⅰ区)、潮流通道矿物区(Ⅱ区)和浅水水下平原矿物区(Ⅲ区)。Ⅰ区以绿帘石、金属矿物和斜长石含量高为特征,受到河流输入直接影响,碎屑矿物与河流沉积物类似;Ⅱ区以金属矿物含量极高、片状矿物含量低为特征(80.6%),指示湾内潮汐通道的强水动力状况;Ⅲ区以金属矿物和片状矿物含量高为主要特征,显示出陆架碎屑矿物的重要影响。矿物物源分析结果表明,研究区内细颗粒沉积物以长江来源为主,沿岸河流输入影响较小,未改变以伊利石为主的黏土矿物组合格局;而粗颗粒沉积物主要受到湾外内陆架和沿岸河流输入沉积物的共同影响,沿岸河流输入使得研究区内岩屑和绿帘石含量高,在靠近基岩海岸的区域,还可能受到部分基岩风化输入的影响。
Abstract:To identify the content and distribution characteristics of detrital and clay minerals in surface sediments of Sanmen Bay, Zhejiang, East China, where 25 surface sediments, 5 river sediments, and 2 tidal flat sediments were collected. Detrital mineral grains in size of 63~125 μm and clay mineral particles of < 2 μm were analyzed, from which 27 heavy minerals and 11 light minerals were identified. Among heavy minerals, metal minerals, epidote, rock debris, hornblende, schistose mineral accounted for 93.0%; and among light minerals, 81.1% were rock debris, plagioclase, quartz, and flaky minerals. Clay minerals were dominated by illite (61.1%), followed by chlorite (9.3%), kaolinite (15.8%), and a small amount of smectite (3.8%). According to Q-type clustering, the sediments in Sanmen Bay could be divided into estuary mineral area (I), tidal channel mineral area (II), and shallow underwater plain mineral area (III). The mineral provenance analysis showed that fine-grained sediments in the area are mainly from the Yangtze River and are affected by the input of coastal rivers. However, the influence of rivers is very limited as clay mineral pattern dominated by illite has not been changed. The coarse-grained sediments are mainly affected by inner shelf sediments and coastal rivers sediments. The input of coastal rivers increased the content of rock debris and epidote in the study area. In addition, the areas near the bedrock coast in the study area were also affected by some bedrock weathering inputs.
-
Key words:
- Sanmen Bay /
- surface sediment /
- detrital mineral /
- clay mineral /
- provenance
-

-
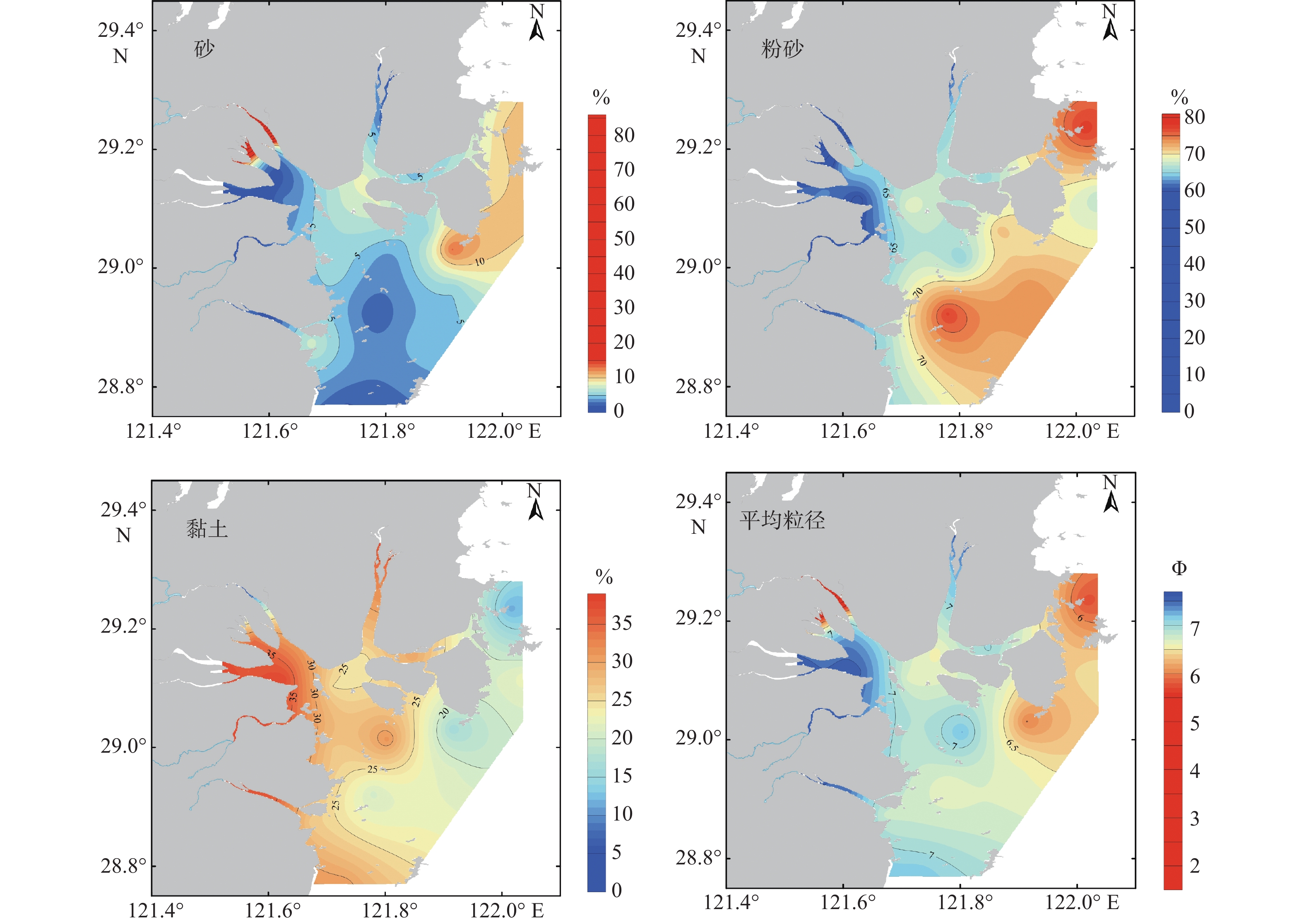
表 1 三门湾表层沉积物粒度特征
Table 1. Grain size of surface sediments in the Sanmen Bay
砂/% 粉砂/% 黏土/% 平均粒径/Φ 63~125 μm
体积百分含量/%63~125 μm
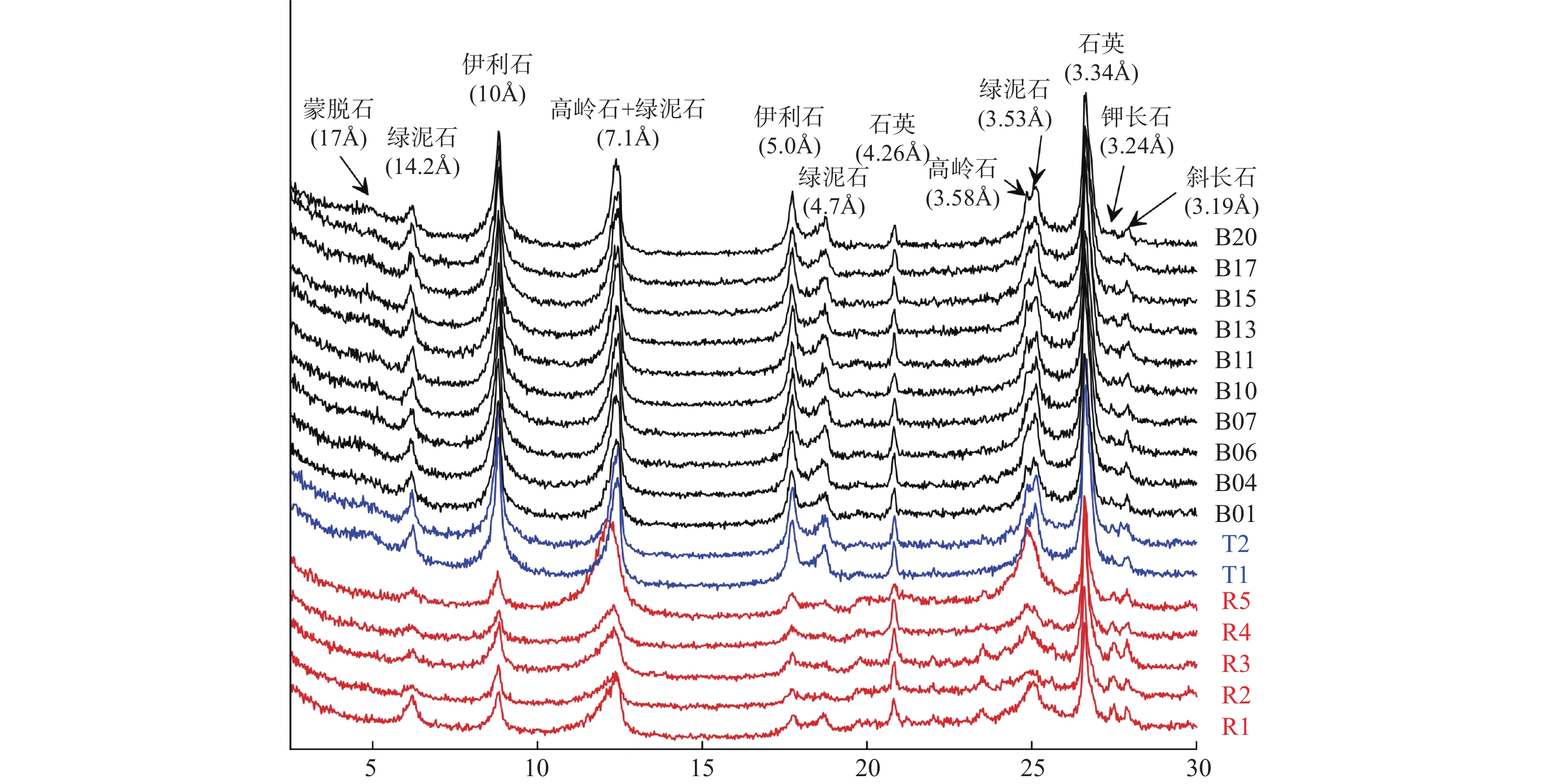
重量百分含量/%最小值 1.34 9.70 5.48 7.56 1.34 0.13 最大值 84.82 77.71 37.72 1.89 9.33 11.47 平均值 8.58 64.32 27.11 6.70 3.82 1.07 变异系数/% 189.0 19.5 30.5 16.5 57.9 207 表 2 沉积物黏土矿物组成
Table 2. Content of clay minerals in the surface sediments
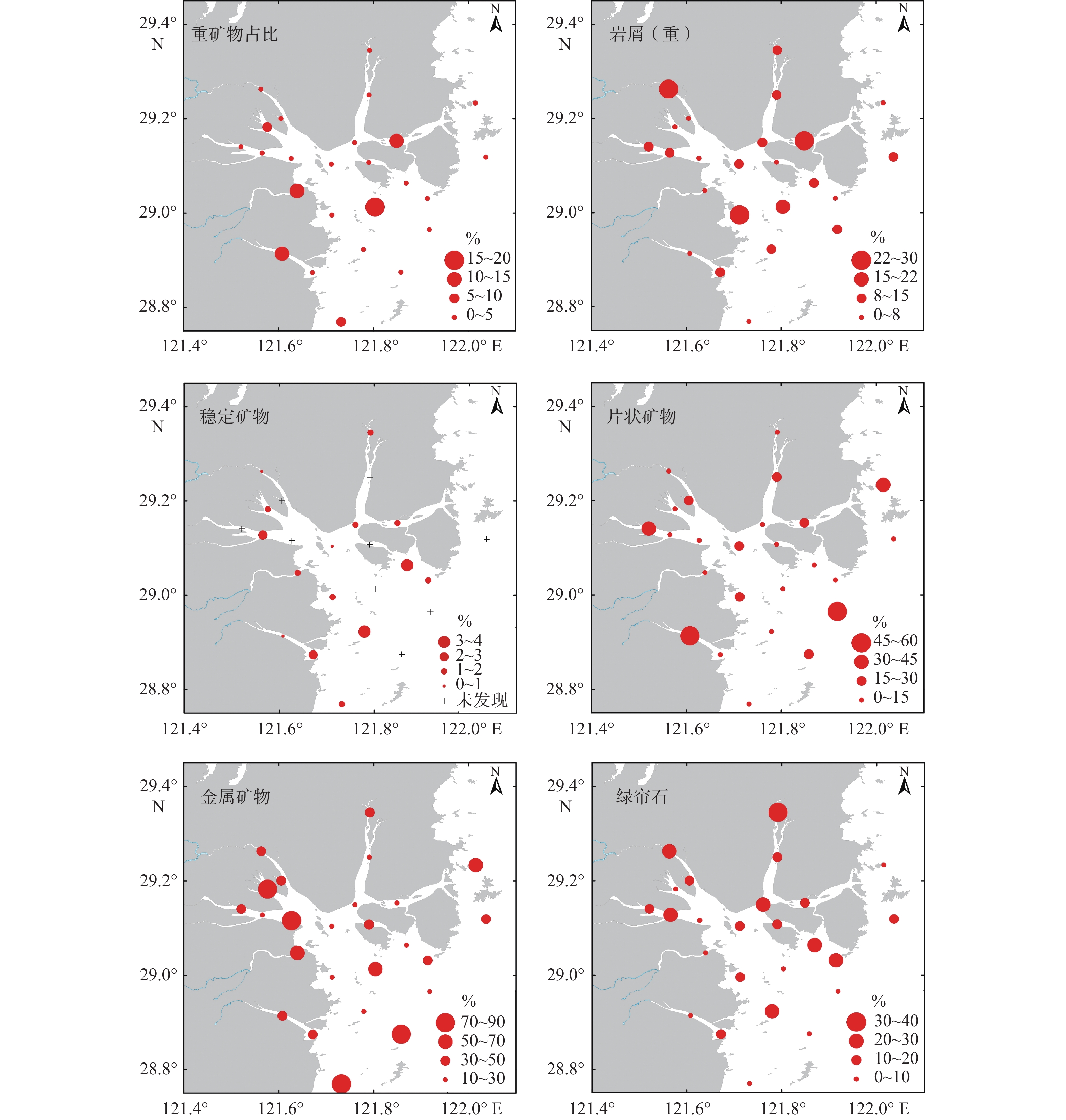
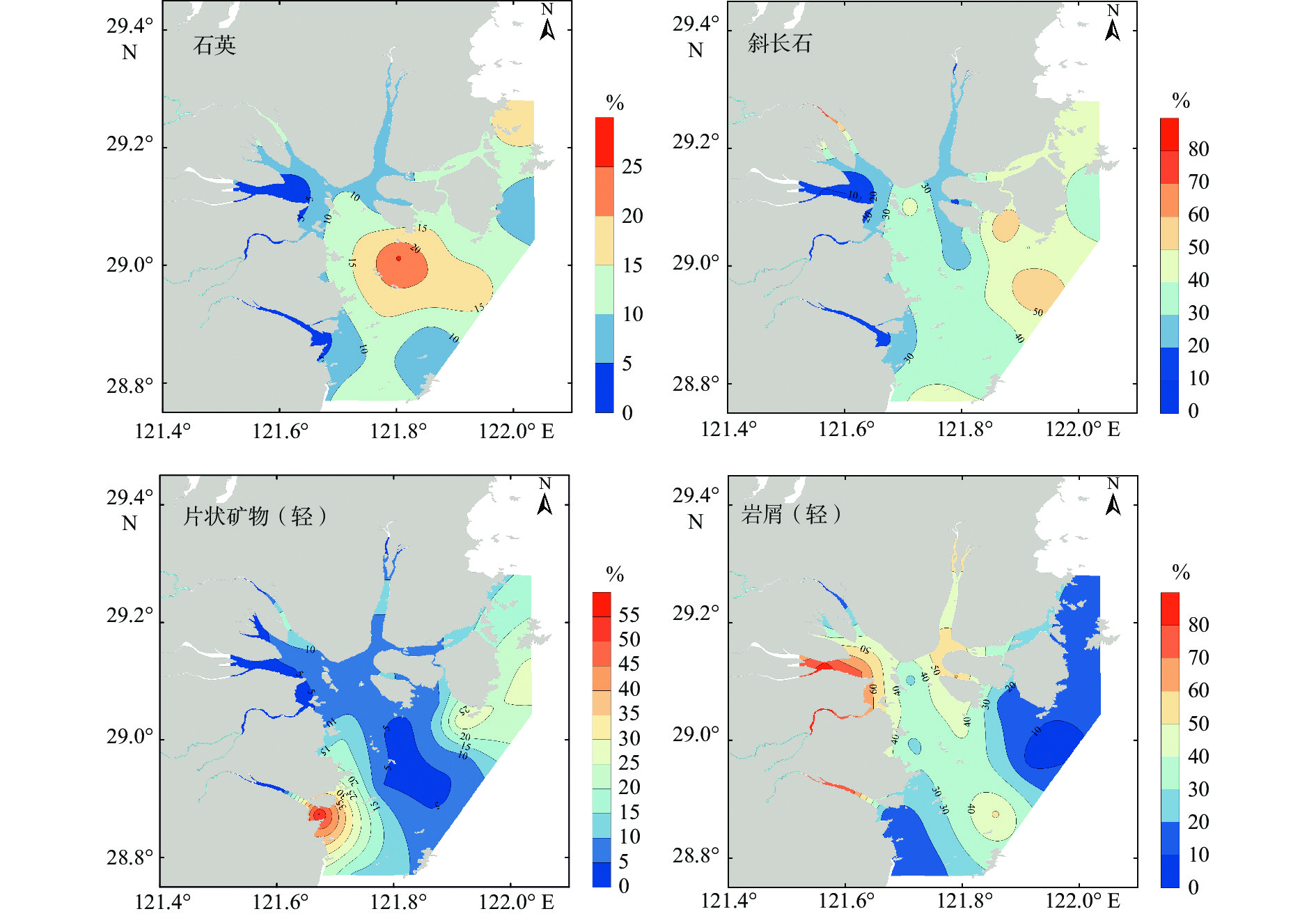
表 3 沉积物主要碎屑矿物含量
Table 3. Contents of major detrital minerals in the sediments
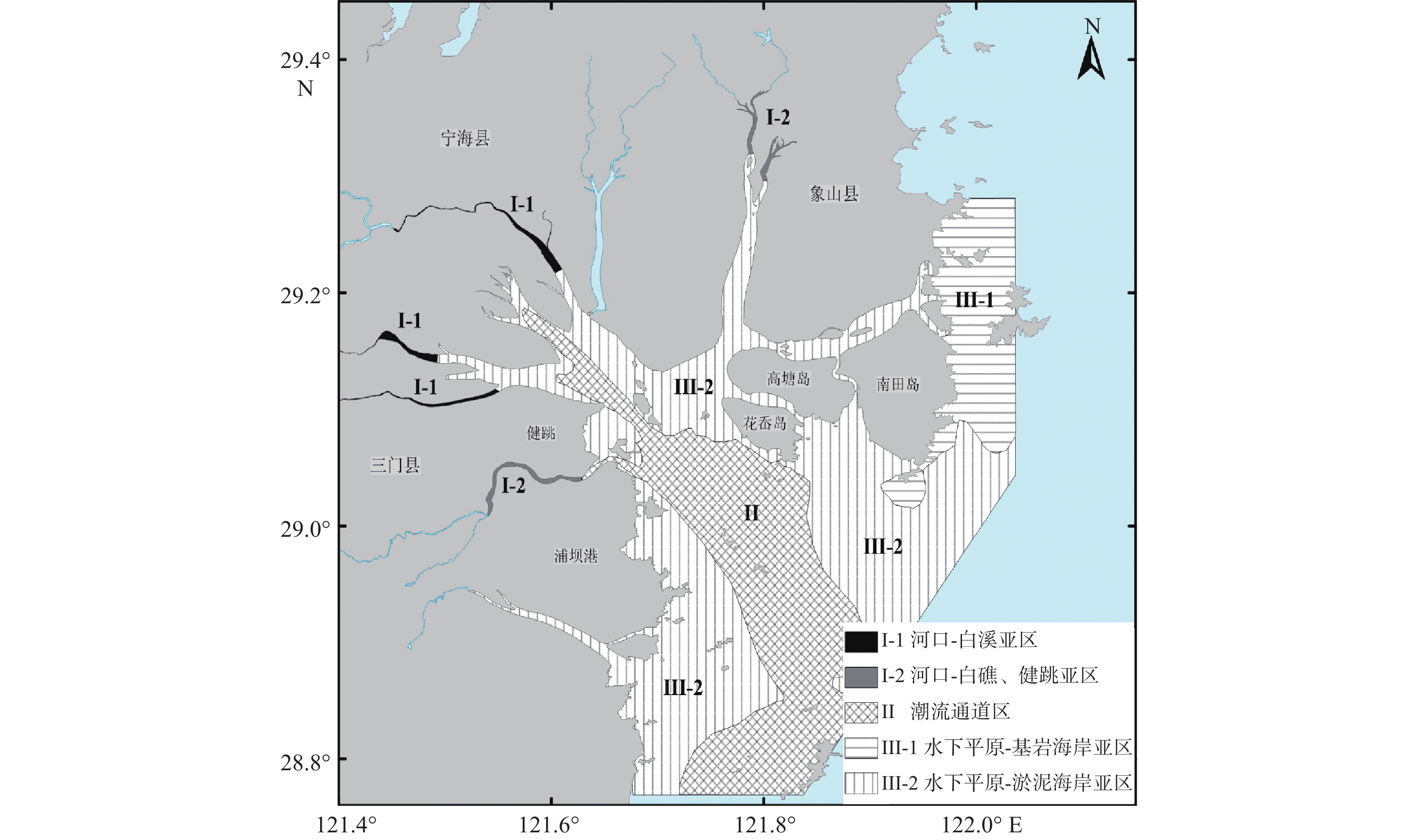
% 海域 河流 Ⅰ-1 Ⅰ-2 Ⅱ Ⅲ-1 Ⅲ-2 内陆架[6] 长江[33] 碎屑矿物 0.9(0.1~11.4) 34.5(0.8~64.7) 0.8 11.4 0.5 0.4 0.6 重矿物 4.2(0.6~18.8) 4.6(0.6~12.7) 0.9 3.4 8.6 2.2 3.2 8.8 12.6 岩屑(重) 10.8(0~27.6) 26.2(8.5~52.8) 14.3 23.8 5.7 7.0 14.1 金属矿物 40.8(13.6~89.4) 24.5(15.6~37.5) 36.9 57.8 80.6 45.7 24.6 稳定矿物 1(0~3.8) 1.7(0.4~3.7) 1.2 0.9 0.9 0.8 1.7 片状矿物(重) 16.5(0.8~55.3) 1(0~2.9) 7.7 1.9 9.5 16.0 26.6 26.4 28.0 绿帘石 15.1(1.5~38.8) 40.8(20~65.7) 45.2 35.7 4.4 17.0 20.6 8.0 8.0 普通角闪石 9.8(0.9~30.1) 2.8(0~4.5) 3.0 1.5 3.6 14.7 14.6 30.5 24.4 辉石类 0.3(0~1.2) 0.5(0.3~0.8) 0.0 0.4 0.0 0.3 0.4 2.0 2.1 岩屑(轻) 38.3(6~83.5) 51.6(33.1~91.1) 59.4 7.7 45.7 23.2 43.4 石英 9.9(1.2~25.6) 10.5(2.8~12.6) 20.9 13.9 20.4 12.4 17.7 32.9 42.3 斜长石 32.9(8.9~78.2) 35.7(6.1~51.1) 70.3 84.7 58.4 43.8 62.1 44.9 31.5 钾长石 1(0.1~2.6) 1.4(0.1~2.5) 2.2 0.7 1.6 1.6 1.9 5.6 14.1 片状矿物(轻) 10.6(0.3~55.7) 0.7(0.3~0.9) 5.5 0.3 9.1 36.1 13.3 14.6 9.6 注:表中海域和河流沉积物矿物含量,在括号前为平均值,括号内为含量范围;各分区(Ⅰ-1 —Ⅲ-2)和参考文献中的碎屑矿物含量为去除岩屑后的百分含量。 -
[1] 李安春,张凯棣. 东海内陆架泥质沉积体研究进展[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2020,51(4):705-727.
[2] 高抒. 中国东部陆架全新世沉积体系:过程-产物关系研究进展评述[J]. 沉积学报,2013,31(5):845-855.
[3] LIM D,CHOI J,JUNG H,et al. Recent sediment accumulation and origin of shelf mud deposits in the Yellow and East China Seas[J]. Progress in Oceanography,2007,73(2):145-159. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2007.02.004
[4] 郭志刚,杨作升,张东奇,等. 冬、夏季东海北部悬浮体分布及海流对悬浮体输运的阻隔作用[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),2002(5):71-80.
[5] ZHANG K K,LI A C,ZHANG J,et al. Recent sedimentary records in the East China Sea inner shelf and their response to environmental change and human activities[J]. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology,2018,36(5):1537-1555. doi: 10.1007/s00343-018-7028-6
[6] 张凯棣,李安春,董江,等. 东海表层沉积物碎屑矿物组合分布特征及其物源环境指示[J]. 沉积学报,2016,34(5):902-911.
[7] 周晓静,李安春,万世明,等. 东海陆架表层沉积物黏土矿物组成分布特征及来源[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2010,41(5):667-675.
[8] 周晓静. 浙江沿岸黏土矿物与长江物质示踪标记的初步研究 [D]. 青岛, 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2003.
[9] NAIDU A S,HAN M W,MOWATT T C,et al. Clay minerals as indicators of sources of terrigenous sediments,their transportation and deposition:Bering Basin,Russian-Alaskan Arctic[J]. Marine Geology,1995,127(1/4):87-104.
[10] PETSCHICK R,KUHN G,GINGELE F. Clay mineral distribution in surface sediments of the South Atlantic:sources,transport,and relation to oceanography[J]. Marine Geology,1996,130(3/4):203-229.
[11] 张尧,韩宗珠,艾丽娜,等. 黄海全新世泥质体表层沉积物重矿物特征及其指示意义[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2018,48(11):108-118.
[12] 刘金庆,张勇,印萍,等. 青岛近岸海域表层沉积物重矿物分布及物源[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2016,36(1):69-78.
[13] 林明祥,蔡廷禄,王欣凯,等. 近百年来浙江三门湾海岸线时空演变特征[J]. 海洋学研究,2021,39(1):47-55.
[14] 中国海湾志编纂委员会. 中国海湾志(第五分册)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1992.
[15] 应超,王乐乐,黄世昌. 三门湾猫头深潭对“烟花”台风的冲淤响应[J]. 水利水运工程学报,2021,190(6):43-50.
[16] KRUMBEIN W C. Size frequency distributions of sediments[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research,1934,4(2):65-77.
[17] UDDEN J A. Mechanical composition of clastic sediments[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of America,1914,25(1):655-744. doi: 10.1130/GSAB-25-655
[18] WENTWORTH C K. A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments[J]. The Journal of Geology,1922,30(5):377-392. doi: 10.1086/622910
[19] MCMANUS J. Grain size determination and interpretation [M]//TUCKER M E. Techniques in Sedimentology. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1988.
[20] 陆凯,秦亚超,王中波,等. 东海中南部海域表层沉积物碎屑重矿物组合分区及其物源分析[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2019,35(8):20-26.
[21] BISCAYE P E. Mineralogy and sedimentation of recent deep-sea clay in the Atlantic Ocean and adjacent seas and oceans[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin,1965,76(7):803-832. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1965)76[803:MASORD]2.0.CO;2
[22] 李艳,李安春,黄朋. 大连湾近海表层沉积物重矿物组合分布特征及其物源环境指示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2011,31(6):13-20.
[23] 张凯棣. 东海陆架近代泥质沉积源汇过程的矿物学响应 [D]. 青岛, 中国科学院大学(中国科学院海洋研究所), 2017.
[24] 刘勇,李广雪. 东海北部陆架表层沉积物重矿物组合、迁移路径对底层水团的示踪响应研究[J]. 地学前缘,2021,29(5):1-14.
[25] 王中波,杨守业,张志珣,等. 东海西北部陆架表层沉积物重矿物组合及其沉积环境指示[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),2012,34(6):114-125.
[26] 韩宗珠,王一冰,孙苑高,等. 黄海表层沉积物的矿物组成特征及其物源分析[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2022,38(4):10-19.
[27] XU K,MILLIMAN J D,LI A,et al. Yangtze- and Taiwan-derived sediments on the inner shelf of East China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2009,29(18):2240-2256. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2009.08.017
[28] 范德江,杨作升,毛登,等. 长江与黄河沉积物中黏土矿物及地化成分的组成[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2001,21(4):7-12.
[29] 薛成凤,贾建军,高抒,等. 中小河流对长江水下三角洲远端泥沉积的贡献:以椒江和瓯江为例[J]. 海洋学报,2018,40(5):75-89.
[30] 王昆山,王国庆,蔡善武,等. 长江水下三角洲沉积物的重矿物分布及组合[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2007,105(1):7-12.
[31] 陈丽蓉,申顺喜,徐文强,等. 中国海的碎屑矿物组合及其分布模式的探讨[J]. 沉积学报,1986,4(3):87-96,145.
[32] ZHANG X,DALRYMPLE R W,YANG S Y,et al. Provenance of Holocene sediments in the outer part of the Paleo-Qiantang River estuary,China[J]. Marine Geology,2015,366(8):1-15.
[33] 陈丽蓉. 中国海沉积矿物学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2008.
-



 下载:
下载: