On the change of coastline and underwater terrain of the southern Laizhou Bay since 1958
-
摘要:
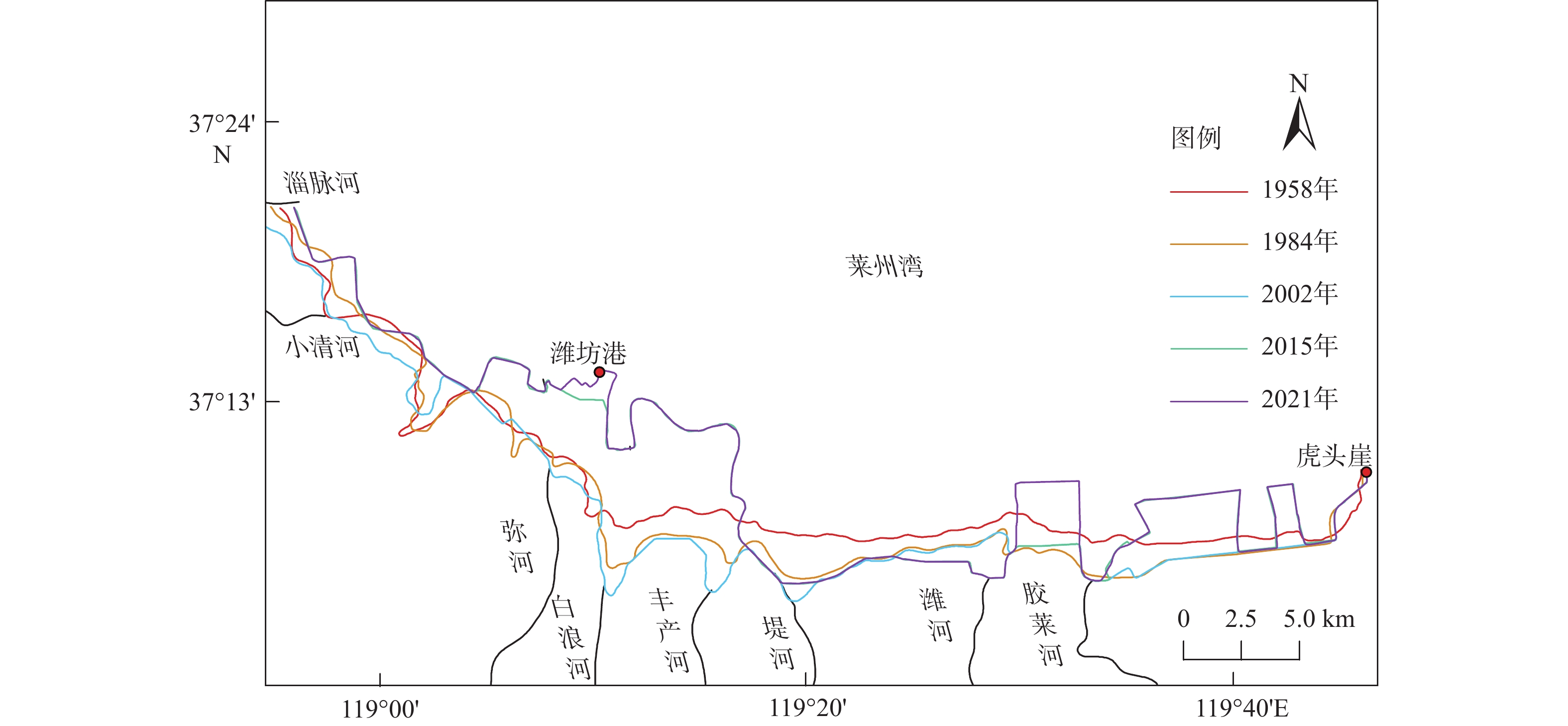
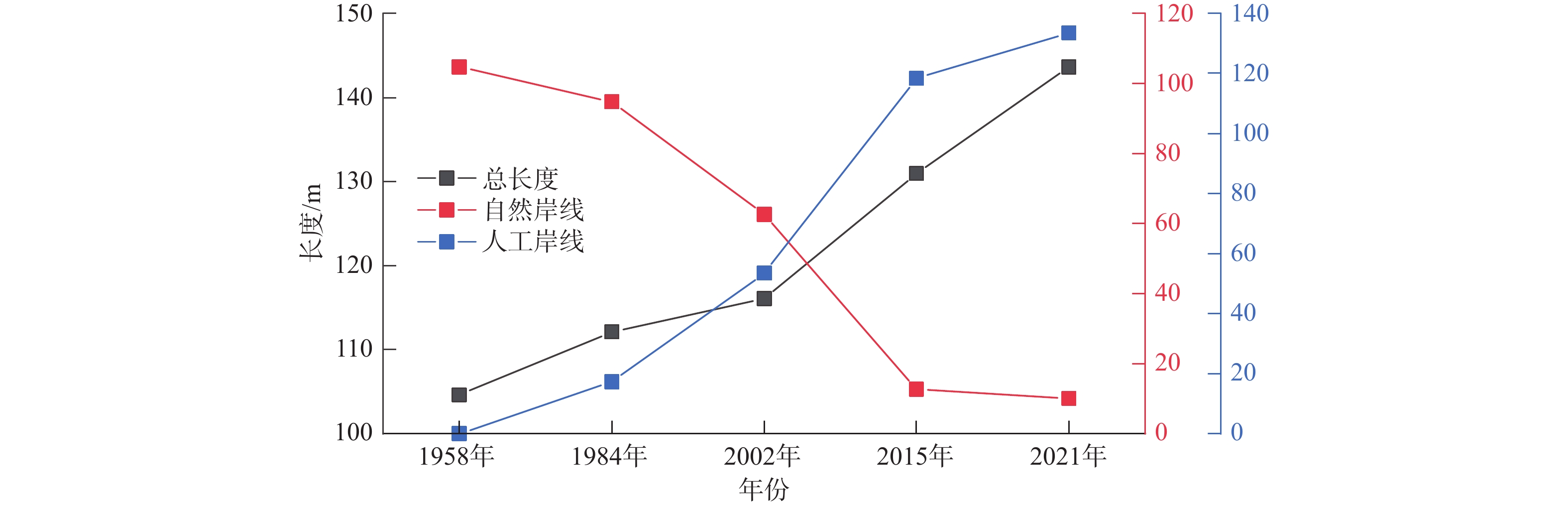
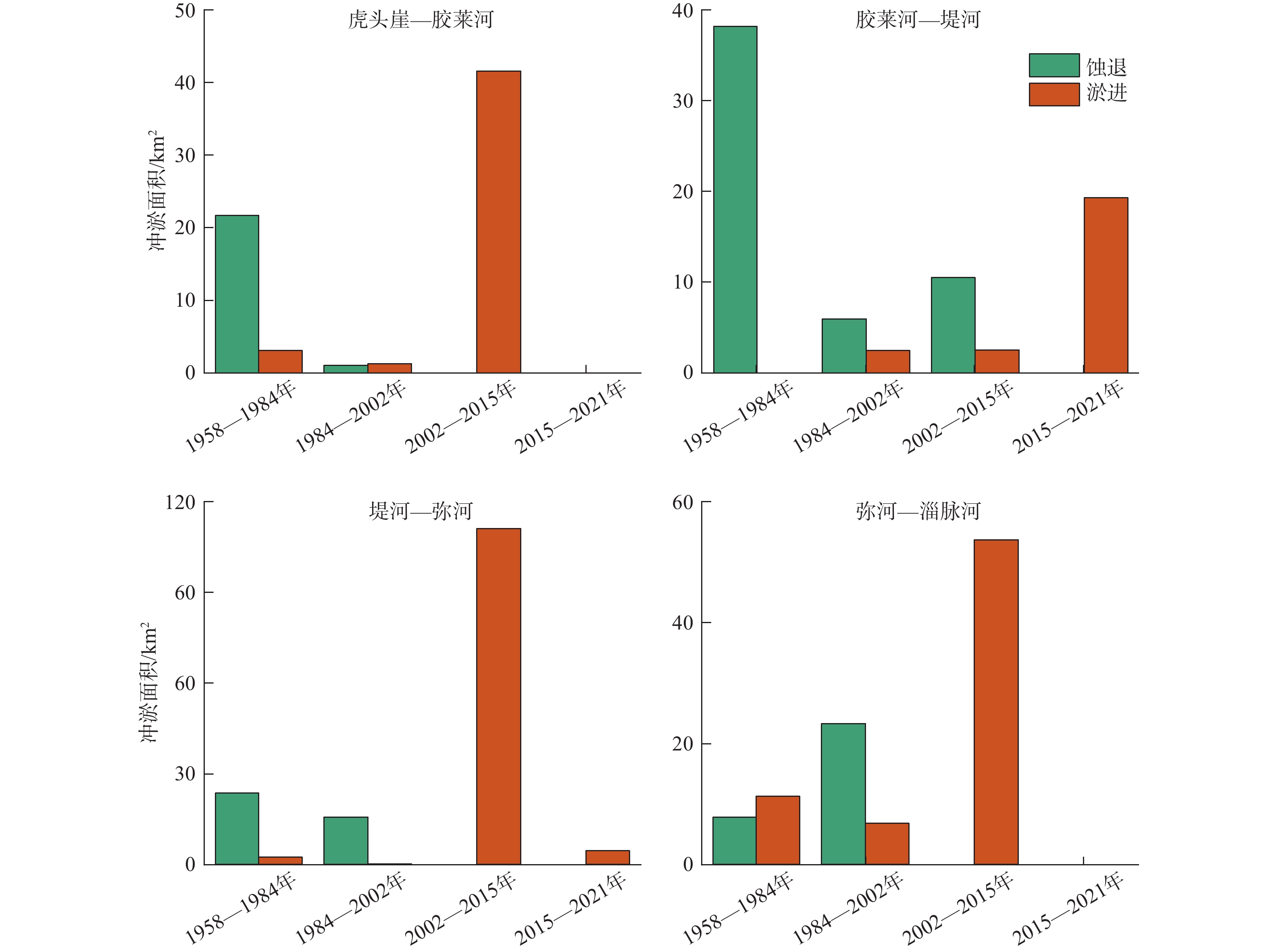
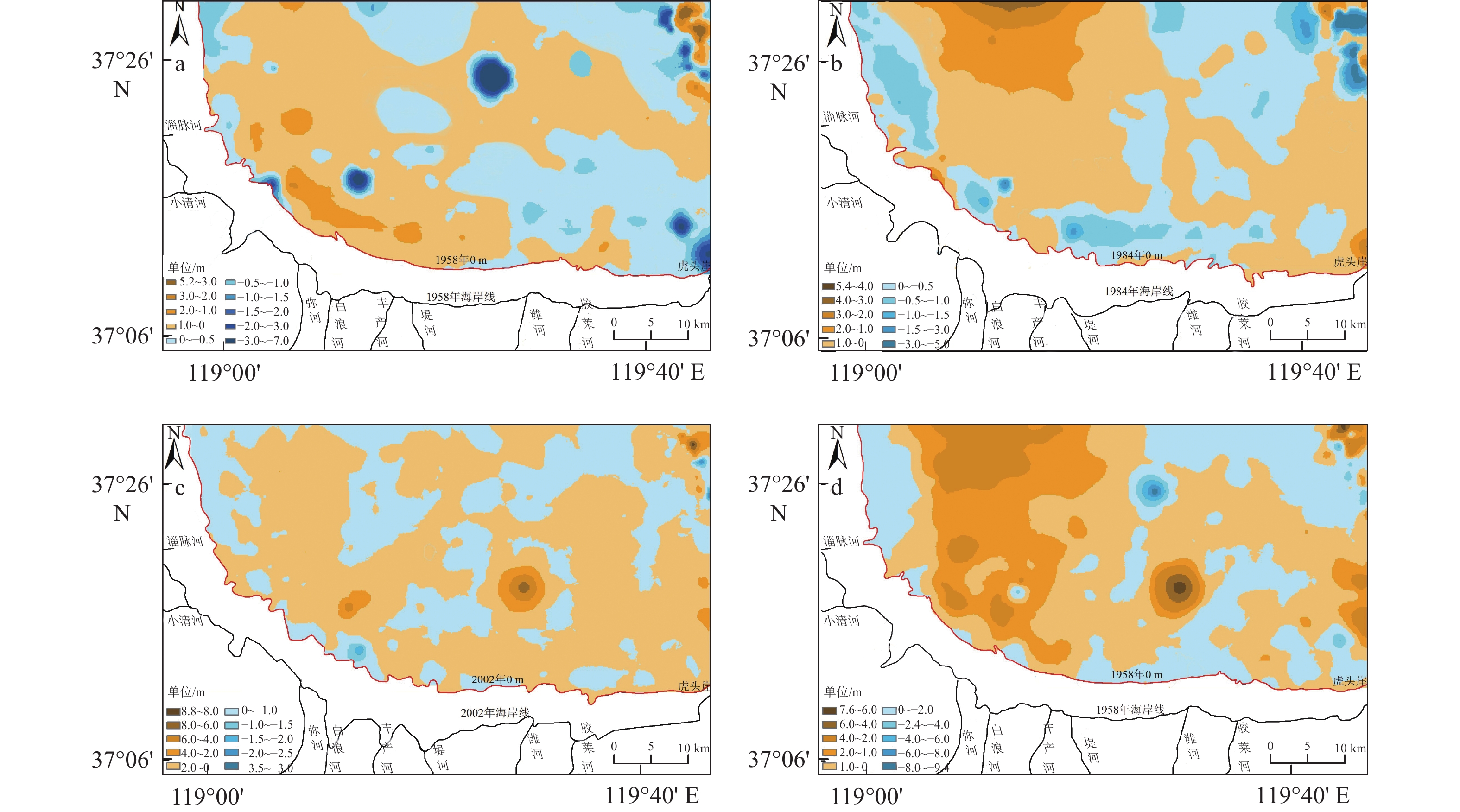
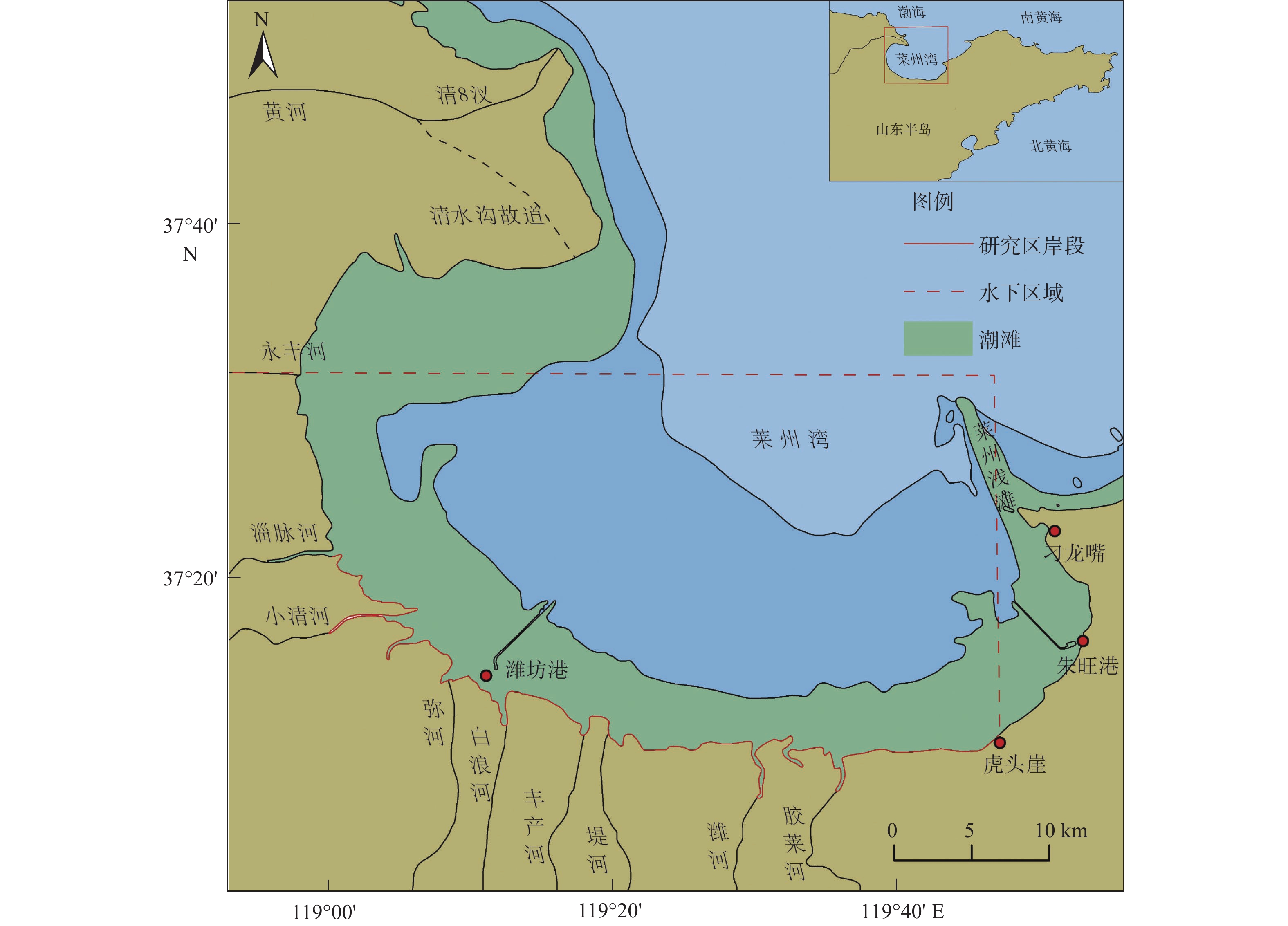
莱州湾南部自20世纪80年代以来海岸地貌发生了显著变化,研究海岸地貌的演变规律对海岸防护和海岸带资源可持续利用具有重要意义。本文以不同时期测量或成像的海图和遥感影像为数据源,基于RS和GIS技术对海岸线和水下岸坡演变进行定量研究。结果表明:①1958–2021年自然岸线逐渐减少,人工岸线逐渐增加,到2021年人工岸线长度约占总长度的87%,海岸线演化与海岸带建设密切相关;②以1984年为界,1984年前以自然演变为主,1984年后人类活动起主导作用,自然演变下海岸线以向陆蚀退为主,人为干预下以向海推进为主;③水下岸坡冲淤分布极不平衡,总体呈侵蚀–淤积–淤积减缓的趋势。南部河流入海口处在1984年后基本呈侵蚀状态。0 m和2 m等深线有前进有后退,但变化幅度相对较小;5~9 m等深线在堤河以西海域向海前进显著,其冲淤演变复杂;10 m等深线以堤河为界表现出西淤东蚀的状态。河流来沙是导致海岸线和水下岸坡演变的重要物质基础,波浪和潮流是主要的驱动力。人工设施在引起河流输沙减少的同时,也导致海岸线大幅向海推进、入海河口受到侵蚀。东北部莱州浅滩附近受人为影响处于侵蚀、解体状态,未来将会继续受到侵蚀。
Abstract:The coastal geomorphology of the southern coast of Laizhou Bay, Shandong, has changed greatly since the 1980s. It is of great significance to study the evolution of coastal geomorphology for coastal protection and sustainable utilization of coastal resources. We used the charts and remote sensing images measured or imaged in different periods as data sources, and quantitatively studied the coastline and offshore slope evolution based on remote sensing and GIS technology. The results show that: ① from 1958 to 2021, the natural shoreline gradually decreased and the artificial shoreline gradually increased. Until 2021, the length of artificial shoreline accounted for about 87% of the total length. Coastline evolution was closely related to the coastal construction; ② taking 1984 as the boundary, natural evolution dominated before 1984, and human activities played a leading role after 1984. Under natural evolution, the coastline was dominated by land erosion. Under human intervention, it was dominated by seaward advance; ③ the distribution of erosion and deposition on the subaqueous slope was extremely unbalanced, and the overall trend was from erosion, siltation, to slowed-down siltation. The southern river estuary was largely eroded after 1984. The 0 m and 2 m isobaths advanced or and retreated slightly. The 5~9 m isobaths advanced seaward significantly in the west of the Dihe River, and the evolution of erosion-siltation was complicated. The 10 m isobath was bounded by the Dihe River, showing the state of westward siltation and eastward erosion. River sediment is the important material basis for the evolution of coastline and subaqueous slope. Waves and tidal currents are the main driving forces. While causing a decrease in river sediment transport, artificial facilities have also led to a significant advance of the coastline and erosion of estuaries. The northeast Laizhou shoal is in a state of erosion and disintegration due to human influence, and will continue to be eroded in the future.
-
Key words:
- Laizhou Bay /
- coastline /
- subaqueous slope /
- isobath
-

-
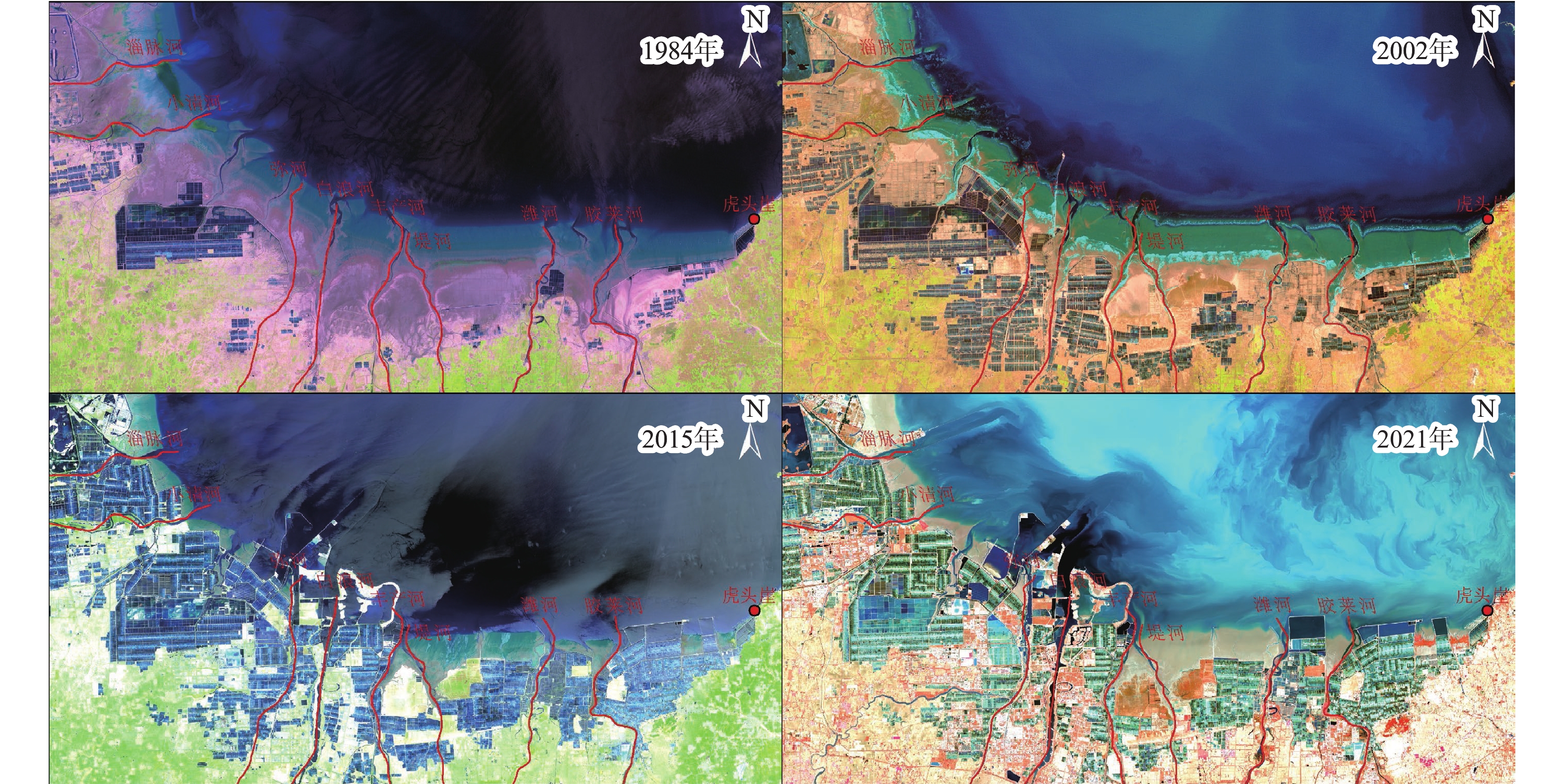
表 1 遥感影像资料信息
Table 1. Remote sensing image data
序号 卫星/传感器 分辨率/m 成像日期 波段数 1 Landsat5/TM 30 1984-07-17 7 2 Landsat5/TM 30 2002-11-24 7 3 Landsat8/OLI 15 2015-06-21 11 4 Landsat8/OLI 15 2021-11-12 11 表 2 不同时期莱州湾及附近海域海图信息
Table 2. Sea charts of Laizhou Bay and nearby areas in different periods
序号 区域 测量年份 比例尺 测量基准面 1 老黄河口–龙口港 1958 1:150 000 理论最低潮面 2 岐河口–龙口港 1984 1:250 000 理论最低潮面 3 莱州湾 2002 1:150 000 理论最低潮面 4 莱州湾 2015 1:150 000 理论最低潮面 -
[1] 夏东兴,王文海,武桂秋,等. 中国海岸侵蚀述要[J]. 地理学报,1993,48(5):468-476. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1993.05.010
[2] THAMPANYA U,VERMAAT J E,SINSAKUL S,et al. Coastal erosion and mangrove progradation of southern Thailand[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science,2006,68(1/2):75-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2006.01.011
[3] DADA O A,QIAO L,DING D,et al. Evolutionary trends of the Niger Delta shoreline during the last 100 years:responses to rainfall and river discharge[J]. Marine Geology,2015,367:202-211. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.06.007
[4] 战超,于君宝,王庆,等. 近60年莱州湾东部砂质海岸地貌的时空动态[J]. 海洋学报,2017,39(9):90-100.
[5] AIELLO A,CANORA F,PASQUARIELLO G,et al. Shoreline variations and coastal dynamics:a space-time data analysis of the Jonian littoral,Italy[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science,2013,129(1):124-135.
[6] CONWAY B. Rapid sea-level change and coastal evolution on the Pacific margin of Canada[J]. Sedimentary Geology,2002,150:171-183. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(01)00274-3
[7] 尹砚军,吴建政,朱龙海,等. 莱州湾东岸三山岛—石虎嘴近岸海域冲淤演变[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2016,32(9):41-46. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2016.09006
[8] 刘世昊,丰爱平,杜军,等. 莱州湾东岸三山岛段砂质海岸沉积物运移动力机制[J]. 海洋科学进展,2014,32(3):343-354. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2014.03.006
[9] 仲少云,王庆,战超,等. 最近50年来莱州湾东部典型砂岸潮上带土地利用变化研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2015,46(2):410-419. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20140900245
[10] 李雪艳,王庆,王红艳,等. 莱州湾东部潮上带土地利用对海岸蚀退的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2015,46(6):1347-1357.
[11] 孙伟富. 1978—2009年莱州湾海岸线变迁研究[D]. 青岛: 国家海洋局第一海洋研究所, 2012.
[12] 彭远新,邓振利,姜亚俊,等. 近50年莱州湾南岸海岸线变迁遥感监测研究[J]. 安徽农业科学,2019,47(3):54-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2019.03.018
[13] 丁小松,单秀娟,陈云龙,等. 基于数字化海岸分析系统(DSAS)的海岸线变迁速率研究:以黄河三角洲和莱州湾海岸线为例[J]. 海洋通报,2018,37(5):565-575. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2018.05.010
[14] 崔钰磊,王庆,金秉福,等. 最近40年来莱州湾东南岸地貌演变研究[J]. 鲁东大学学报,2015,31(2):7-13.
[15] 中国海湾志编委会. 中国海湾志(第三分册)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1993 : 1-81.
[16] 庄振业,许卫东,李学伦. 渤海南岸6000年来的岸线演变[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报,1991,2:99-110.
[17] 王文海,吴桑云,陈雪英. 山东省9216号强热带气旋风暴期间的海岸侵蚀灾害[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,1994,14(4):71-78. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1994.04.008
[18] 朱学明,鲍献文,宋德海,等. 渤、黄、东海潮汐、潮流的数值模拟与研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2012,43(6):1103-1113. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201206011011
[19] 张永强,迟万清,胡泽建,等. 黄河清水沟流路大嘴的形成对莱州湾潮流场影响的数值研究[J]. 海洋科学进展,2010,28(2):149-157. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2010.02.003
[20] 李晓炜,侯西勇,邸向红,等. 从生态系统服务角度探究土地利用变化引起的生态失衡:以莱州湾海岸带为例[J]. 地理科学,2016,36(8):1197-1204.
[21] 王庆. 全新世以来山东半岛东北部海面变化的河流地貌响应[J]. 地理科学,1999,19(3):34-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.1999.03.007
[22] 王李娟,牛铮,赵德刚,等. 基于ETM遥感影像的海岸线提取与验证研究[J]. 遥感技术与应用,2010,25(2):235-239. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2010.2.235
[23] 卢薇艳,罗鹏,龚淑云. 基于遥感技术的海岸线提取及应用研究综述[J]. 华南地质与矿产,2019,35(3):393-397.
[24] 吕立蕾,董玉磊,奉定平,等. 海岸线自动提取方法研究[J]. 海洋测绘,2019,39(4):57-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2019.04.014
[25] 梁立,刘庆生,刘高焕,等. 基于遥感影像的海岸线提取方法综述[J]. 地球信息科学学报,2018,20(12):1745-1755. doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2018.180152
[26] 夏东兴,段焱,吴桑云. 现代海岸线划定方法研究[J]. 海洋学研究,2009,27(1):28-33.
[27] 林起忠. WGS-84坐标系到地方坐标系的转换方法及精度分析[J]. 城市勘测,2016,2:108-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8262.2016.02.030
[28] 谢建春,陈同峰,姚磊,等. 1980西安坐标系与2000坐标系坐标成果转换方法及精度分析[J]. 山东国土资源,2012,28(8):58-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2012.08.015
[29] 杨鸣. 莱州湾南岸海岸带环境退化及治理对策研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2005.
[30] 陈翠霞,安催花,罗秋实,等. 黄河水沙调控现状与效果[J]. 泥沙研究,2019,44(2):69-74. doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2019.02.010
[31] 王庆,杨华,仲少云,等. 山东莱州浅滩的沉积动态与地貌演变[J]. 地理学报,2003,58(5):749-756. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2003.05.014
[32] CHEN J Y,CHEN S L. Estuarine and coastal challenges in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology,2002,2:174-181.
[33] 夏菲,张永战,吴蔚. EOF分析在海岸地貌与沉积学研究中的应用进展[J]. 地理科学进展,2009,28(2):174-186. doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2009.02.003
[34] 韩美,孟庆海. 莱州湾沿岸的地貌类型[J]. 山东师范大学学报(自然科学版),1996,3:64-68.
[35] 秦亚超,李日辉. 表层沉积物粒度所指示的渤海现代沉积体系[J]. 第四纪研究,2017,37(3):654-666. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2017.03.20
[36] 崔金瑞,夏东兴. 山东半岛海岸地貌与波浪、潮汐特征的关系[J]. 海洋科学进展,1992,10(3):20-25.
[37] ZHAN C,WANG Q,CUI B,et al. The morphodynamic difference in the western and southern coasts of Laizhou Bay:responses to the Yellow River Estuary evolution in the recent 60 years[J]. Global and Planetary Change,2020,187(3):103138.
-



 下载:
下载: