Transport and control factors of suspended sediment in Penglai offshore area in summer
-
摘要:
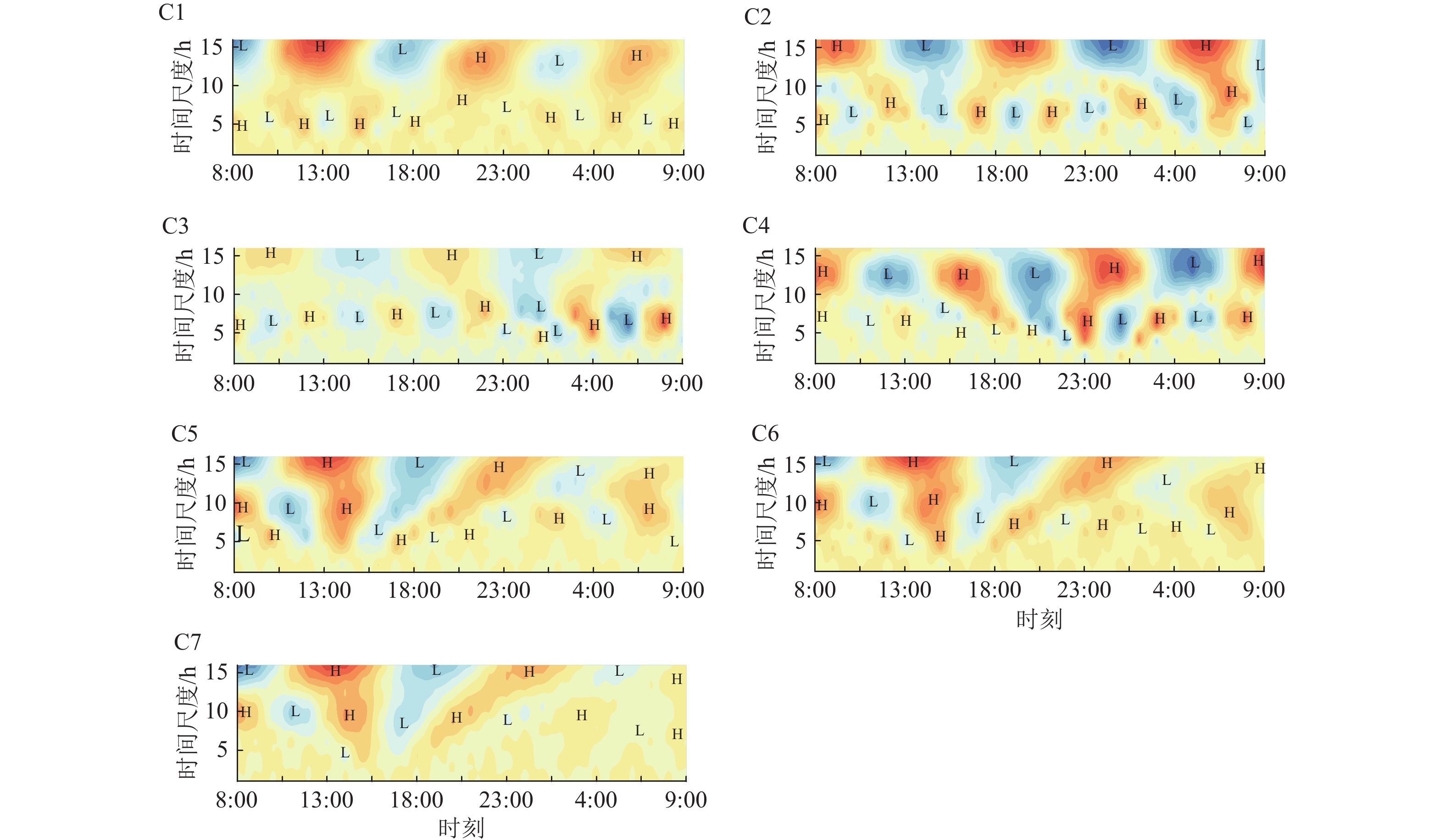
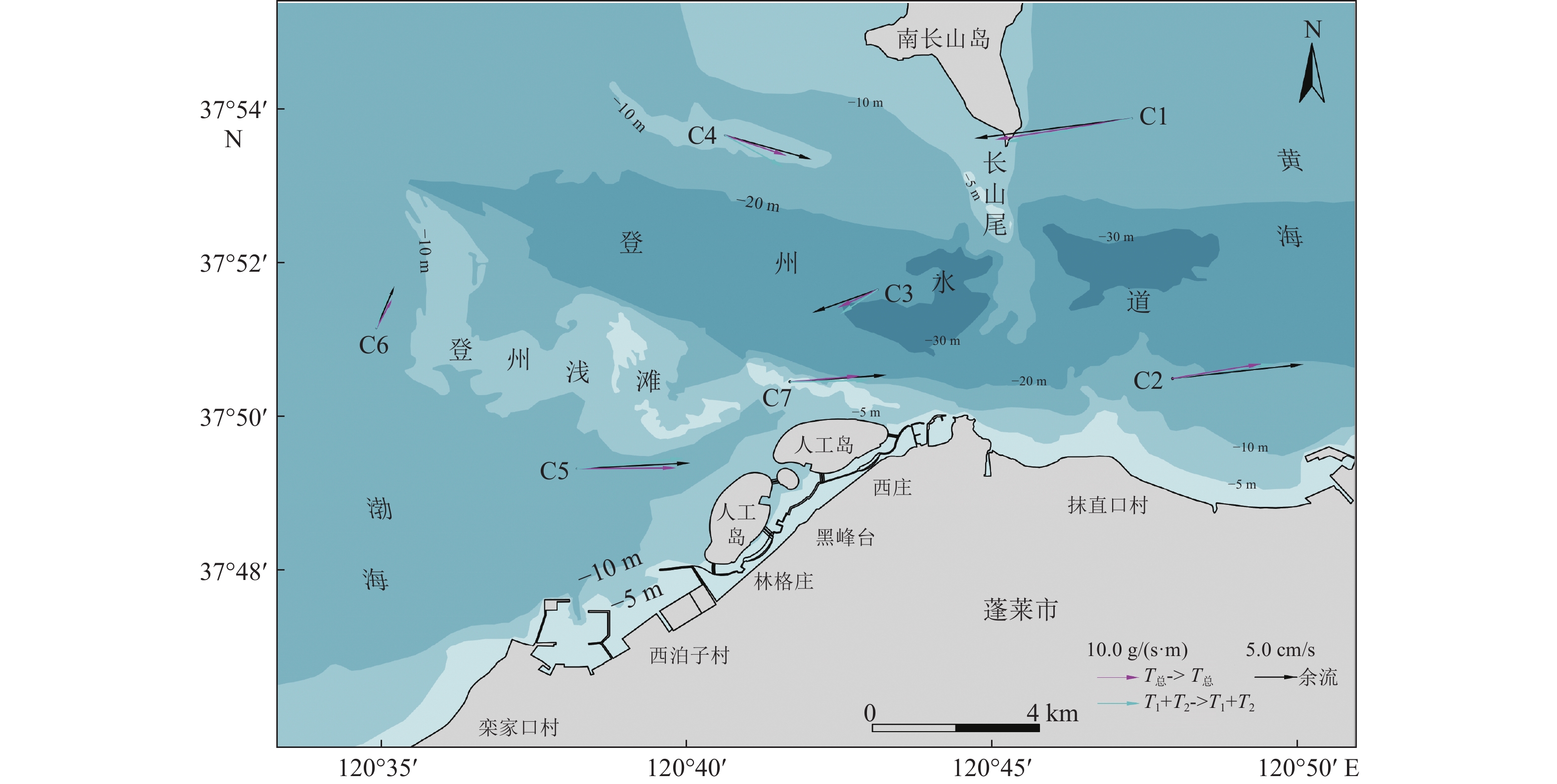
基于2019年6月在蓬莱近岸海域实地观测获取的样品和数据,研究了海流、温度、盐度和悬浮泥沙的时空分布特征,利用小波分析、单宽通量机制分解和Richardson数等方法,探讨了悬浮泥沙的输运机制和控制因素。研究区悬浮泥沙在平面上呈以登州浅滩为中心向周围海域逐渐降低的分布特征,垂向上呈由表层至底层逐渐升高的趋势。悬浮泥沙浓度变化与潮流变化具有较好的正相关关系,但在时间上滞后1~2 h。研究区单宽净输沙率为7.84~43.12 g/(s·m)。平流输运在研究区悬浮泥沙输运过程中占主导地位,垂向净环流输运次之。潮流是研究区悬浮泥沙输运的主要动力,悬浮泥沙净输运方向与余流方向一致,登州水道南部悬浮泥沙由西向东输运,水道中部悬浮泥沙由东向西输运,南长山岛两侧悬浮泥沙呈向水道输运的趋势。研究区海域部分水体层化现象明显,水体混合受到抑制,悬浮泥沙的分布和输运受到潮流、水体混合和地形地貌共同控制。
-
关键词:
- 蓬莱近岸海域 /
- 悬浮泥沙输运 /
- 控制因素 /
- 梯度Richardson数 /
- 通量机制分解
Abstract:Based on the hydrological and sediment observation data in spring tide period in Penglai coastal waters in Bohai Sea in June 2019, we studied the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of ocean current, temperature, salinity, and suspended sediment, and discussed the transport mechanism and control factors of suspended sediment by using wavelet analysis, single width flux mechanism decomposition, and the Richardson number. Results show that the concentration of suspended sediment in the study area is characterized by a gradual horizontal decrease from Dengzhou shoal to the surrounding sea area, and a gradual vertical increase from the surface layer to the bottom layer. There is a good positive correlation between suspended sediment concentration change and tidal current change with a time lag of 1~2 h. The net sediment transport rate per unit width is 7.84~43.12 g/(s·m). Advection transport plays a dominant role in suspended sediment transport in the study area, followed by vertical net circulation transport. Tidal current is the main driving force of suspended sediment transport. The net transport direction of suspended sediment is consistent with the residual current direction. The suspended sediment in the south of Dengzhou waterway is transported from west to east, while that in the middle of the waterway is transported from east to west, and those on both sides of Nanchangshan Island is transported to the waterway. The stratification phenomenon of some water bodies in the study area is obvious, the mixing of water bodies is suppressed, and the distribution and transportation of suspended sediment are controlled by the tide, the mixing of water bodies, and the topography.
-

-
表 1 海流特征值一览表
Table 1. List of current eigenvalues
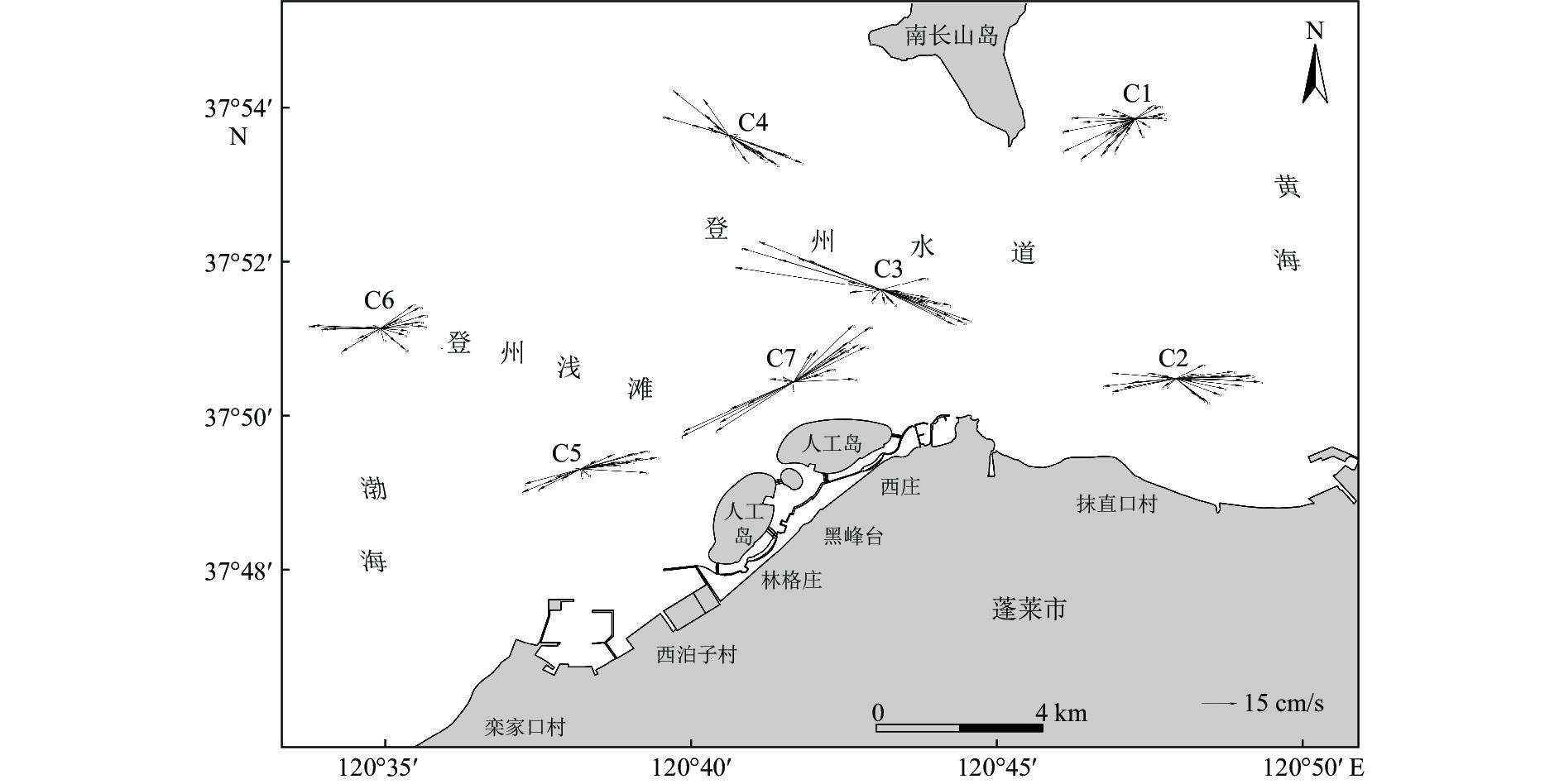
站位 层位 涨潮 落潮 最大 平均 最大 平均 流速/(cm/s) 流向/(°) 流速/(cm/s) 流向/(°) 流速/(cm/s) 流向/(°) 流速/(cm/s) 流向/(°) C1 表层 48.23 44.66 40.15 44.69 81.92 264.76 45.07 244.62 0.6H 27.73 35.75 21.51 71.96 75.52 240.93 34.46 256.21 底层 11.12 71.72 8.29 62.78 57.61 235.90 26.18 239.46 C2 表层 108.19 92.33 60.28 86.59 95.21 270.96 55.32 242.78 0.6H 78.51 87.01 43.43 93.98 73.60 273.04 40.37 193.71 底层 37.80 90.91 19.73 124.12 15.84 252.30 8.01 128.24 C3 表层 109.41 104.56 65.88 80.63 166.07 281.57 83.45 294.99 0.6H 93.36 115.15 52.15 118.86 146.56 275.44 74.19 276.47 底层 68.00 114.53 31.57 131.51 112.32 284.38 43.28 288.41 C4 表层 83.97 108.65 46.89 130.04 90.06 301.04 41.70 283.84 0.6H 76.14 109.55 38.55 109.02 68.98 312.00 34.08 290.40 底层 64.18 113.25 29.78 116.47 54.01 289.38 26.42 309.85 C5 表层 90.25 68.38 49.32 76.44 74.29 246.98 30.84 230.88 0.6H 72.69 76.65 38.35 85.17 63.24 246.90 26.44 224.33 底层 68.78 72.79 26.06 82.43 51.02 251.02 22.13 242.54 C6 表层 68.20 69.14 36.96 78.69 83.74 271.71 38.40 277.21 0.6H 59.72 73.27 31.15 81.65 75.53 274.48 34.04 266.81 底层 31.76 73.07 10.30 104.81 32.31 271.42 11.16 273.52 C7 表层 121.18 64.58 64.79 53.82 118.46 242.08 53.24 263.71 0.6H 121.16 48.52 60.01 53.27 115.28 247.65 50.76 234.90 底层 117.40 49.18 35.98 65.89 113.10 247.91 45.55 254.37 表 2 各站位调和结果一览表
Table 2. List of reconciliation results of each station
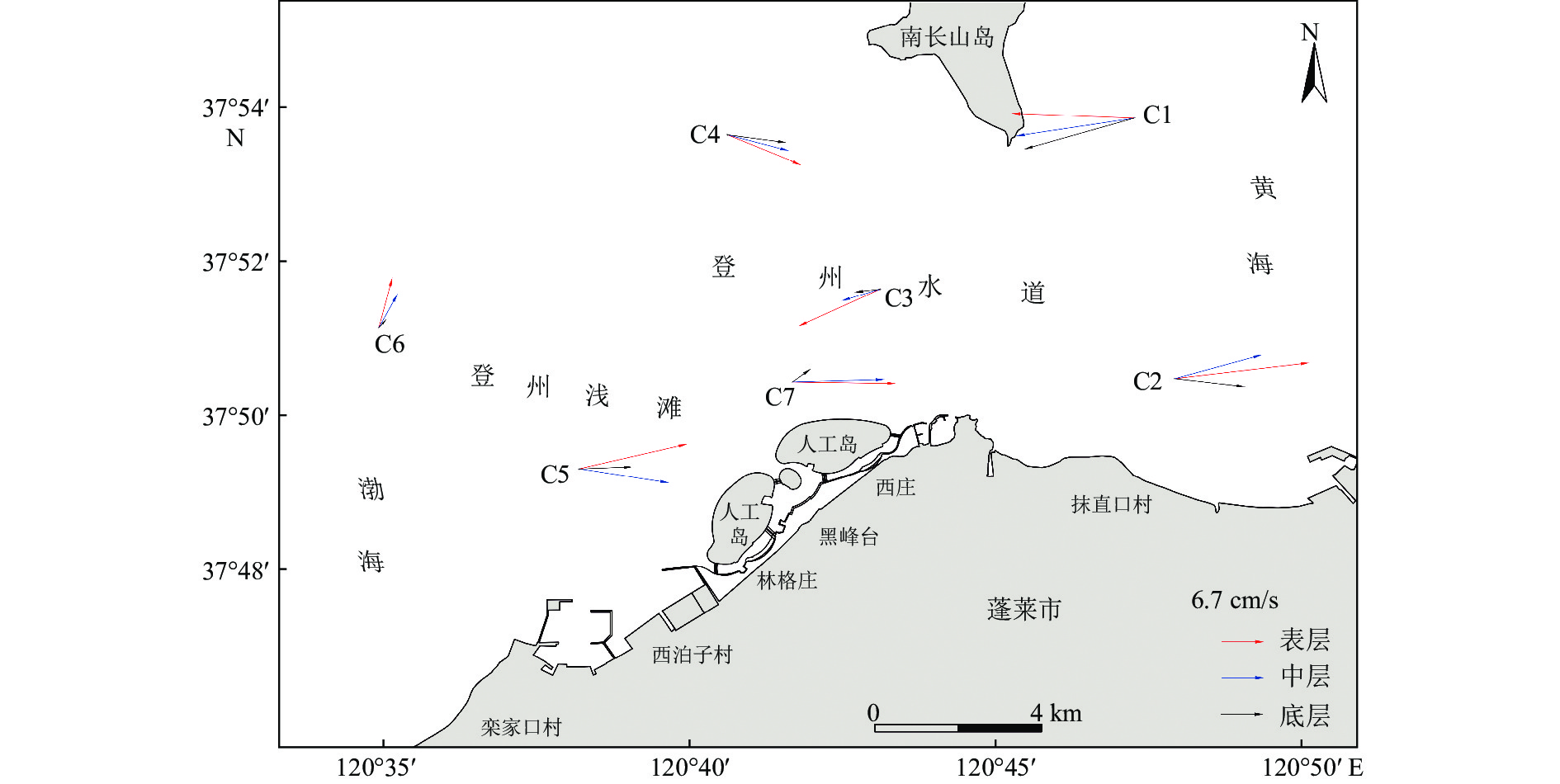
站位 潮流系数 K值 表层 中层 底层 流速/(cm/s) 流向/(°) 流速/(cm/s) 流向/(°) 流速/(cm/s) 流向/(°) C1 1.37 −0.57 19.61 272.22 19.1 261.41 18.33 254.22 C2 1.29 0.14 21.62 83.32 14.44 74.67 11.33 96.61 C3 1.31 0.01 14.28 245.6 6.39 253.34 4.06 263.33 C4 0.62 −0.11 12.74 112.13 10.08 104.6 9.45 97.64 C5 0.96 0.06 17.66 77.08 14.52 98.78 8.51 88.01 C6 1.28 0.12 8.26 15.14 6.22 29.01 1.77 41.56 C7 1.17 −0.05 16.5 90.78 14.73 88.44 3.63 54.79 表 3 典型站位温度、盐度特征值一览表
Table 3. List of characteristic values of temperature and salinity at typical stations
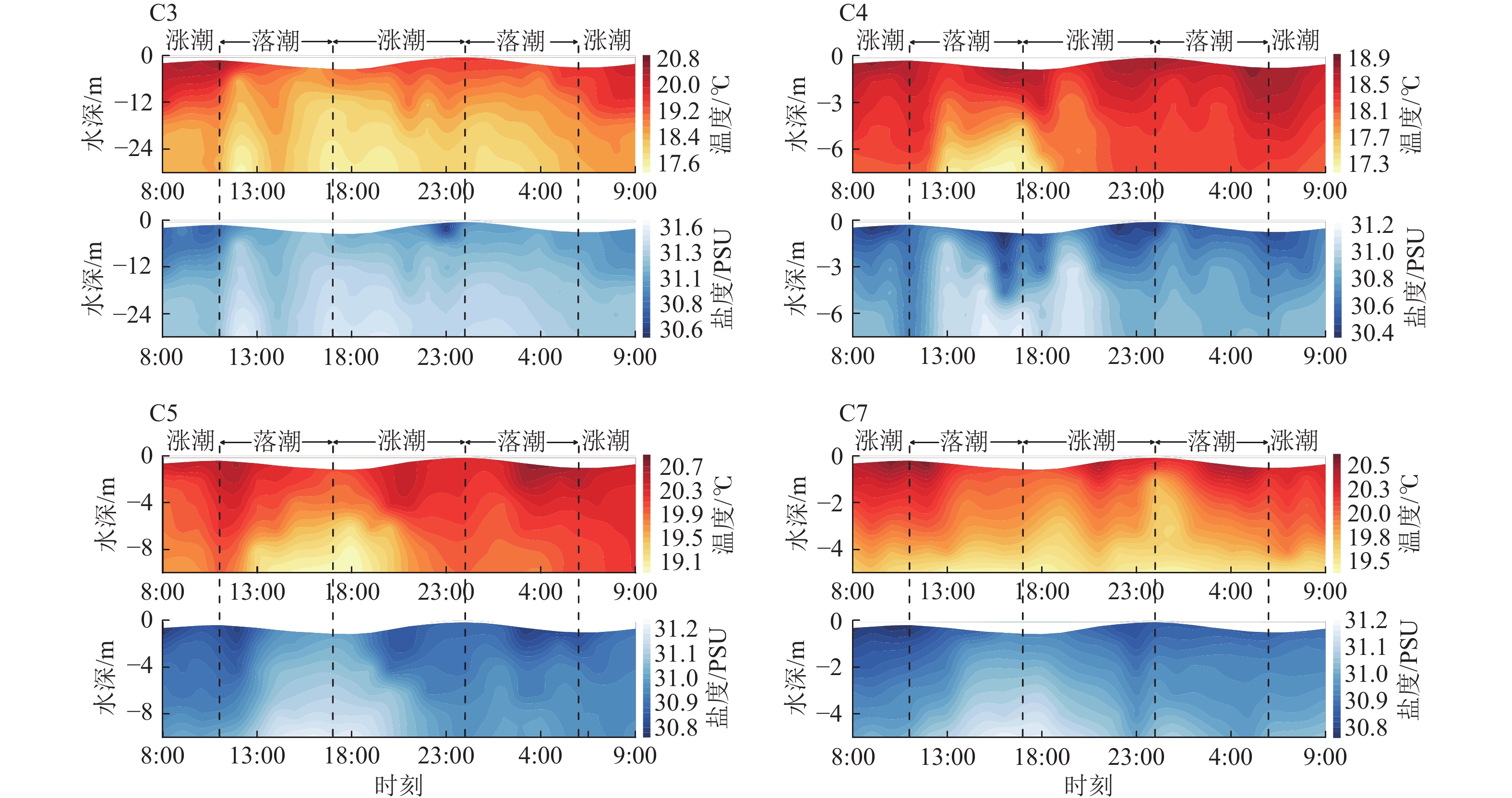
站位 温度/℃ 盐度/PSU 最大值 最小值 平均值 最大值 最小值 平均值 C3 20.57 17.42 18.76 31.56 30.52 31.23 C4 18.91 17.24 18.30 31.14 30.35 30.77 C5 20.85 18.91 19.99 31.25 30.81 31.02 C7 20.58 19.44 19.94 31.24 30.83 31.02 表 4 C1-C7站位悬浮泥沙输运项及单宽输沙率
Table 4. Suspended sediment transport items and single-width sediment transport rates at stations C1-C7
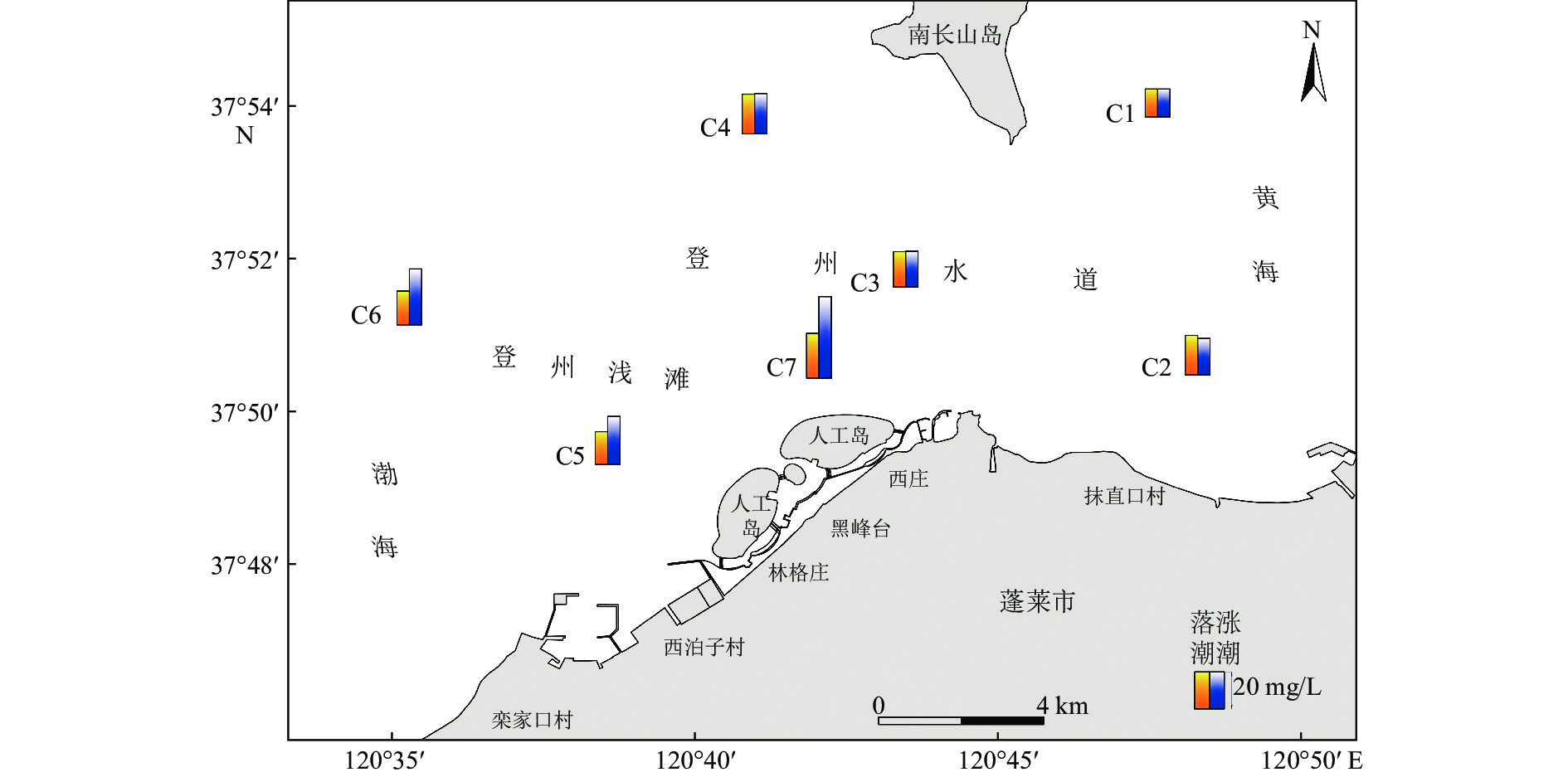
站位 项目 T1 T2 T1+T2 T3+T4 T5 T6+T7+T8 T总 T涨潮 T落潮 C1 输沙率/(g/(s·m)) 30.02 0.91 30.77 0.09 6.74 0.09 33.23 49.30 41.16 方向/(°) 259.24 222.78 259.44 251.11 180.9 165.33 261.19 271.73 234.50 C2 输沙率/ (g/(s·m)) 49.37 0.77 49.06 0.17 6.09 0.24 43.12 45.08 140.71 方向/(°) 82.71 328.64 81.83 295.49 268.88 73.82 80.73 288.10 87.39 C3 输沙率/ (g/(s·m)) 21.86 0.99 21.38 0.06 3.94 0.44 20.89 297.64 173.60 方向/(°) 235.89 296.47 236.72 146.68 200.26 168.21 245.8 281.71 118.07 C4 输沙率/ (g/(s·m)) 17.05 1.05 16.03 0.06 2.82 0.04 15.52 23.61 47.14 方向/(°) 94.72 284.83 95.46 127.58 11.37 62.24 86.41 276.35 121.69 C5 输沙率/ (g/(s·m)) 26.5 0.91 25.62 0.35 3.25 0.07 23.68 35.87 56.44 方向/(°) 84.8 256.43 84.64 75.28 227.76 158.07 89.54 268.95 86.84 C6 输沙率/ (g/(s·m)) 8.52 0.67 8.38 0.35 1.46 0.04 7.84 63.75 34.32 方向/(°) 22.31 337.72 17.85 76.84 145.75 10.6 28.53 277.16 73.30 C7 输沙率/ (g/(s·m)) 19.94 1.35 18.91 0.13 2.61 0.06 16.75 63.51 46.85 方向/(°) 91.67 251.02 89.34 85.09 236.41 24.17 85.08 268.99 52.77 表 5 各悬浮泥沙输运项在净输沙率中占比
Table 5. Percentage of suspended sediment transport items in net sediment transport rate
% 站位 T1 T2 T1+T2 T3+T4 T5 T6+T7 +T8 C1 90.34 2.74 92.61 0.27 20.29 0.28 C2 114.50 1.78 113.79 0.39 14.13 0.55 C3 104.66 4.78 102.35 0.29 18.86 2.10 C4 106.35 6.52 103.28 0.37 17.59 0.25 C5 103.45 3.55 108.16 1.36 12.68 0.27 C6 101.71 7.95 106.88 4.21 17.43 0.48 C7 105.45 7.14 105.71 0.67 13.81 0.31 注:各悬浮泥沙输运项均为矢量,具有方向性,因此部分悬沙输运项占比>100%。 -
[1] ZHANG J,LIU S M,XU H,et al. Riverine sources and estuarine fates of particulate organic carbon from North China in late summer[J]. Estuarine,Coastal and Shelf Science,1998,463(3):439-448.
[2] MA M,FENG Z,GUAN C,et al. DDT,PAH and PCB in sediments from the intertidal zone of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2001,42(2):132-136. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(00)00118-1
[3] BIAN C W,JIANG W S,QUAN Q,et al. Distributions of suspended sediment concentration in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea based on field surveys during the four seasons of 2011[J]. Journal of Marine Systems,2013,121-122:24-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2013.03.013
[4] 宋泽坤,张俊彪,施伟勇,等. 杭州湾口门中部水沙输运机制初探:以岱衢洋为例[J]. 海洋通报,2015,34(3):267-274.
[5] 陈斌,高飞,刘健. 夏季浙江沿岸陆架区泥沙输运机制[J]. 海洋学报,2017,39(3):96-105.
[6] 乔璐璐. 冬季大风事件下渤黄海环流及泥沙输运过程研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2008.
[7] 陈勇,韩震,杨丽君,等. 长江口水体表层悬浮泥沙时空分布对环境演变的响应[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),2012,34(1):145-152.
[8] 吕纪轩,胡日军,李毅,等. 烟台北部近岸海域表层沉积物粒度分布及沉积动力环境特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2020,36(4):27-36.
[9] 伊兆晗,胡日军,李毅,等. 福宁湾海域夏季大潮期悬浮泥沙输运特征及控制因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2021,41(6):53-66.
[10] 江文胜,苏健,杨华,等. 渤海悬浮物浓度分布和水动力特征的关系[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),2002(S1):212-217.
[11] 杨作升,郭志刚,王兆祥,等. 黄东海陆架悬浮体向其东部深海区输送的宏观格局[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),1992(2):81-90.
[12] 秦蕴珊,李凡. 渤海海水中悬浮体的研究[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),1982,4(2):191-200.
[13] 赵保仁,庄国文,曹德明,等. 渤海的环流、潮余流及其对沉积物分布的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼,1995,26(5):466-473. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1995.05.003
[14] 魏泽勋,李春雁,方国洪,等. 渤海夏季环流和渤海海峡水体输运的数值诊断研究[J]. 海洋科学进展,2003,21(4):454-464.
[15] JIANG W S,POHLMANN T,SUN J,et al. SPM transport in the Bohai Sea:field experiments and numerical modelling.[J]. Journal of Marine Systems,2004,44(3/4):175-188.
[16] BI N S,YANG Z S,WANG H J,et al. Seasonal variation of suspended-sediment transport through the southern Bohai Strait.[J]. Estuarine,Coastal and Shelf Science,2011,93(3):239-247. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.03.007
[17] 尹延鸿,周青伟. 渤海东部地区沉积物类型特征及其分布规律[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,1994,14(2):47-54.
[18] 石强. 渤、黄海冬、夏季节风生流场年际变化时空模态与环流变异[J]. 应用海洋学学报,2019,38(1):93-108.
[19] 王勇智,乔璐璐,杨作升,等. 夏、冬季山东半岛东北部沿岸悬浮物输送机制的初步研究[J]. 泥沙研究,2012(5):49-57.
[20] 李福林,夏东兴,王文海,等. 登州浅滩的形成、动态演化及其可恢复性研究[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),2004,26(6):65-73.
[21] 尹东晓,吴建政,胡日军,等. 登州浅滩近期演变及沉积物输运趋势[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2013,29(8):25-32.
[22] 王庆,仲少云,刘建华,等. 山东庙岛海峡的峡道动力地貌[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2006,26(2):17-24.
[23] 董超. 登州浅滩表层沉积物输运特征的研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2011.
[24] 邱恒清,孙宜超,秦巧丽,等. 蓬莱西海岸近海岸滩泥沙运移趋势和冲淤演变研究[J]. 海岸工程,2017,36(2):36-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2017.02.005
[25] 陈雪英,胡泽建. 山东蓬莱西庄附近海域波浪与海岸侵蚀[J]. 黄渤海海洋,1992,10(2):19-26.
[26] 林纪江,胡日军,朱龙海,等. 潮流作用下蓬莱近岸海域悬浮泥沙的时空分布及变化特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2017,33(12):13-23.
[27] 刘成,胡日军,朱龙海,等. 庙岛群岛海域沉积动力环境分区及沉积物输运趋势[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2018,34(8):24-33.
[28] 林霄沛,吴德星,鲍献文,等. 渤海海峡断面温度结构及流量的季节变化[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2002,32(3):355-360.
[29] 魏皓,武建平,POHLMANN T. 渤海环流与输运季节变化的数值模拟(英文)[J]. 黄渤海海洋,2001(2):1-9.
[30] 张志欣,乔方利,郭景松,等. 渤海南部沿岸水运移及渤黄海水体交换的季节变化[J]. 海洋科学进展,2010,28(2):142-148.
[31] 张立奎,吴建政,李巍然,等. 渤海湾西部与南部海岸线和潮滩演变及其影响因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2014,34(1):21-27.
[32] 吴培强,张杰,马毅,等. 2010—2015年环渤海海岸线时空变迁监测与分析[J]. 海洋科学进展,2018,36(1):128-138.
[33] 陈沈良. 崎岖列岛海区的水文泥沙及其峡道效应[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),2000,22(3):123-131. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2000.03.017
[34] 袁晓东,胡日军,朱龙海,等. 夏季庙岛海峡海域悬浮泥沙浓度时空变化及其对潮流的响应[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2018,34(6):19-27.
[35] KUMAR P, FOUFOULA‐GEORGIOU E. Wavelet analysis for geophysical applications [J]. Reviews of Geophysics 1997, 35 (4): 385-412.
[36] 牛艳蓉. 小波分析与应用综述[J]. 科技信息,2009(3):158-159.
[37] PRASAD L, IYENGAR S S. Wavelet Analysis with Applications to Image Processing[M]. Florida, USA: CRC Press, 2020.
[38] DYER K R. The salt balance in stratified estuaries[J]. Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science,1974,2(3):273-281. doi: 10.1016/0302-3524(74)90017-6
[39] INGRAM R G. Characteristics of the great Whale River Plume[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans,1981,86(C3):2017-2023. doi: 10.1029/JC086iC03p02017
[40] UNCLES R J,ELLIOTT R C A,WESTON S A. Dispersion of salt and suspended sediment in a partly mixed estuary[J]. Estuaries,1985,8(3):256-269. doi: 10.2307/1351486
[41] TROWBRIDGE J H. A simple description of the deepening and structure of a stably stratified flow driven by a surface stress[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans,1992,97(C10):15529-15543. doi: 10.1029/92JC01512
[42] 林纪江,胡日军,王平,等. 庙岛海峡周边海域表层沉积物再悬浮及悬浮泥沙输运机制[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2022,42(3):9-24.
[43] 刘波,胡日军,袁晓东,等. 龙口近岸海域潮流作用下悬浮泥沙时空分布特征及输运机制[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2020,40(4):55-66.
[44] 刘波,胡日军,李毅,等. 夏季潮流作用下龙口湾海域悬浮泥沙时空变化特征及其输运机制[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2020,36(3):20-30.
[45] 卢鹏飞,岳英洁,朱龙海,等. 南黄海西部日照近海悬浮泥沙分布、输运及控制因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2022,42(3):36-49.
[46] 朱颖涛,冯秀丽,朱龙海,等. 山东半岛东北部海域悬浮体季节分布及控制因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2021,41(2):30-42.
[47] 陆建忠. 遥感反演与数值模拟耦合的渤海悬浮泥沙输移研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2010.
[48] 刘焘,朱龙海,胡日军,等. 基于遥感反演的山东半岛东北部海域悬浮体时空变化规律探讨[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2021,52(3):624-634.
[49] 姚弘毅,李九发,戴志军,等. 长江河口北港河道泥沙特性及河床沙再悬浮研究[J]. 泥沙研究,2013(3):6-13.
[50] 冷星,朱龙海,胡日军. 山东半岛东部海域泥质区冬季悬浮泥沙时空变化及输运机制[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2019,49(4):106-116,8.
[51] 孟令鹏,胡日军,李毅,等. 福宁湾海域冬季大潮期悬浮泥沙输运特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2020,40(3):61-73.
[52] 庞重光,李坤,于炜. 渤海表层悬沙的时空分布特征及其动力成因[J]. 海洋科学进展,2014,32(4):450-458.
-




 下载:
下载: