The roles of anisotropy in production increasing in low porosity and low permeability reservoir: an example in Sag A, East China Sea
-
摘要:
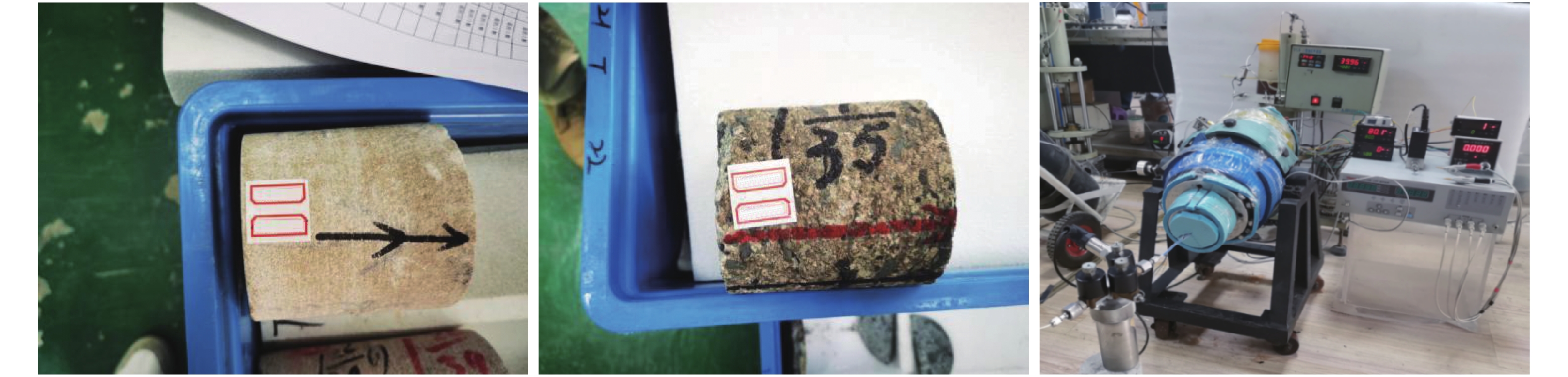
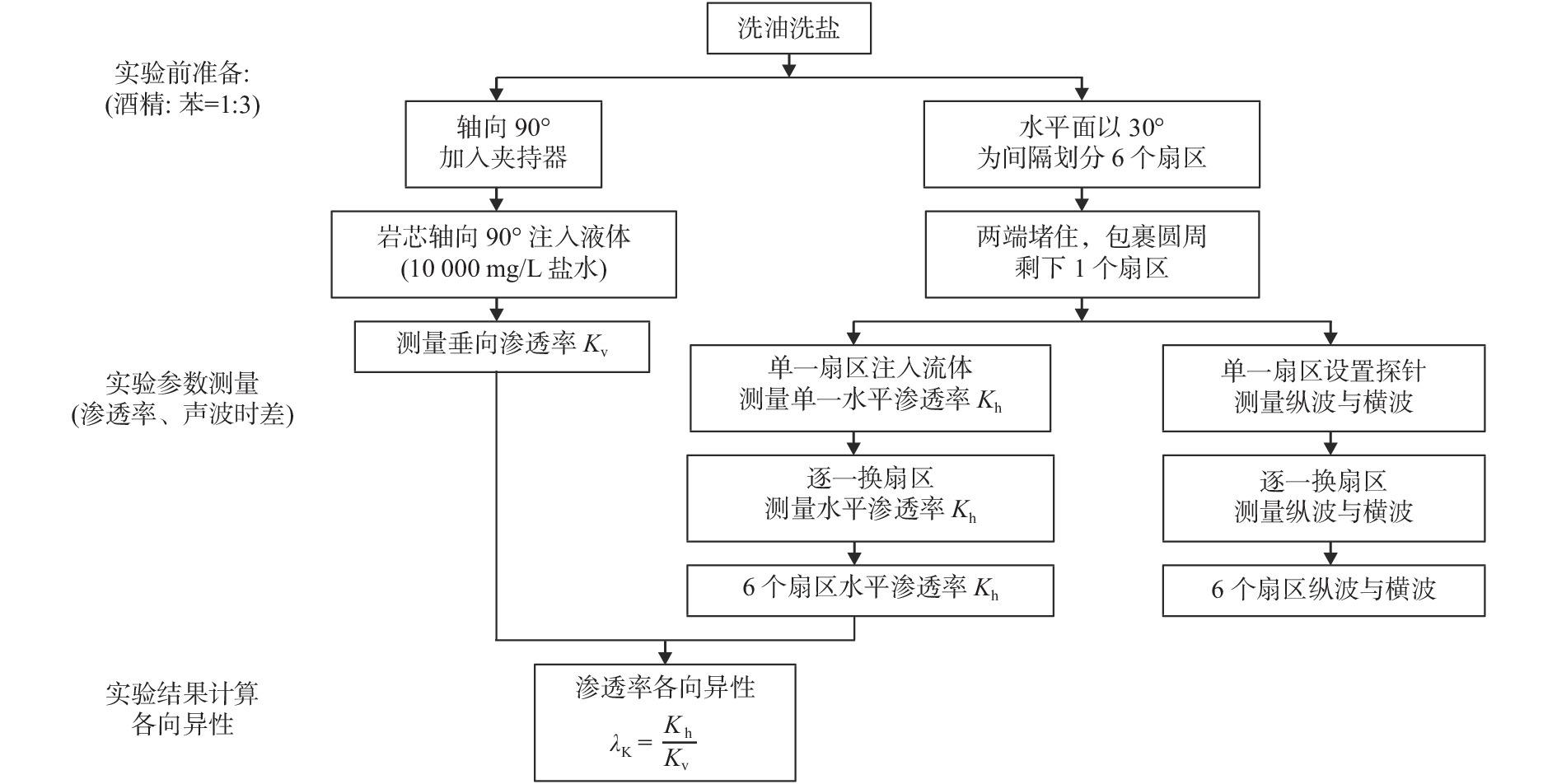
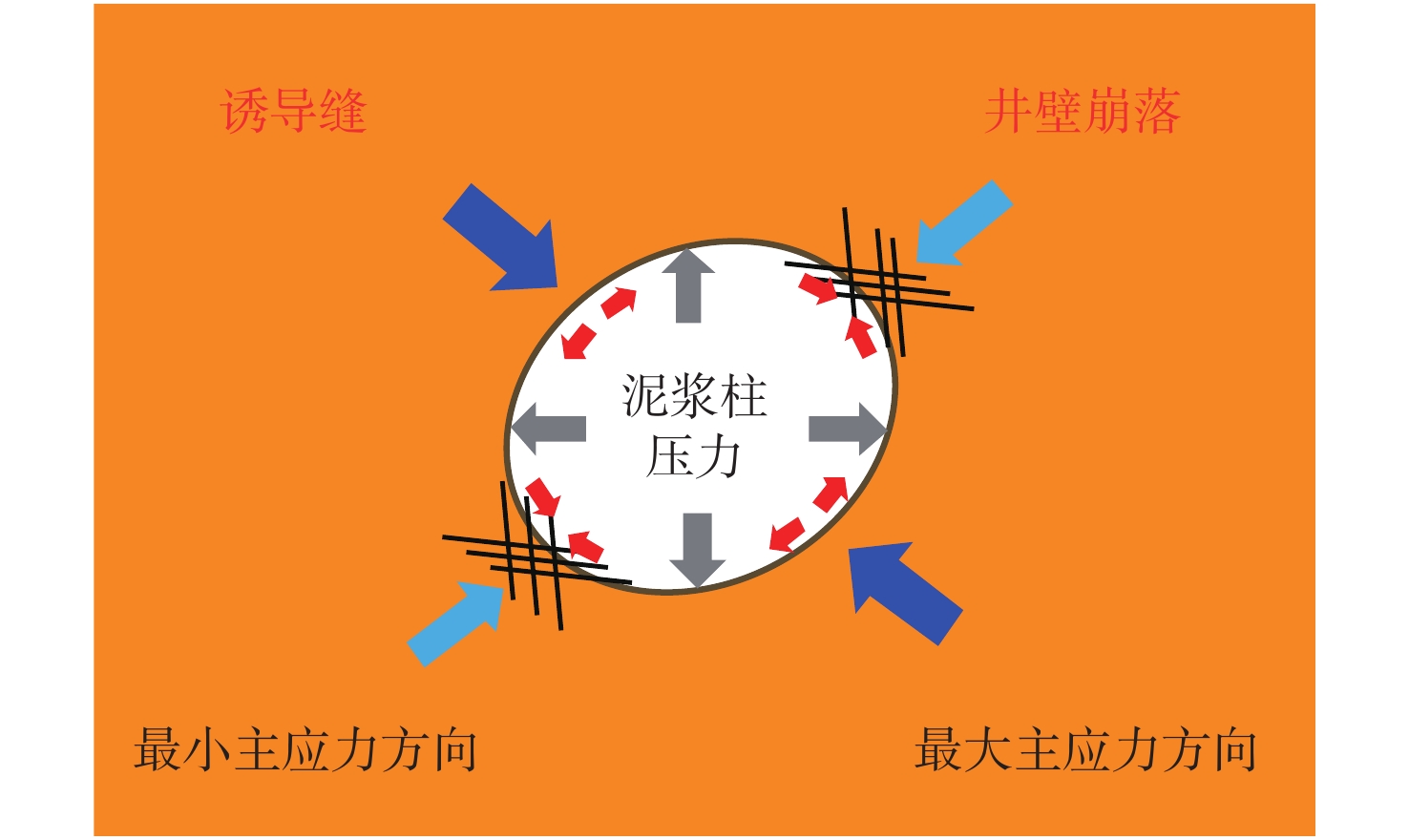
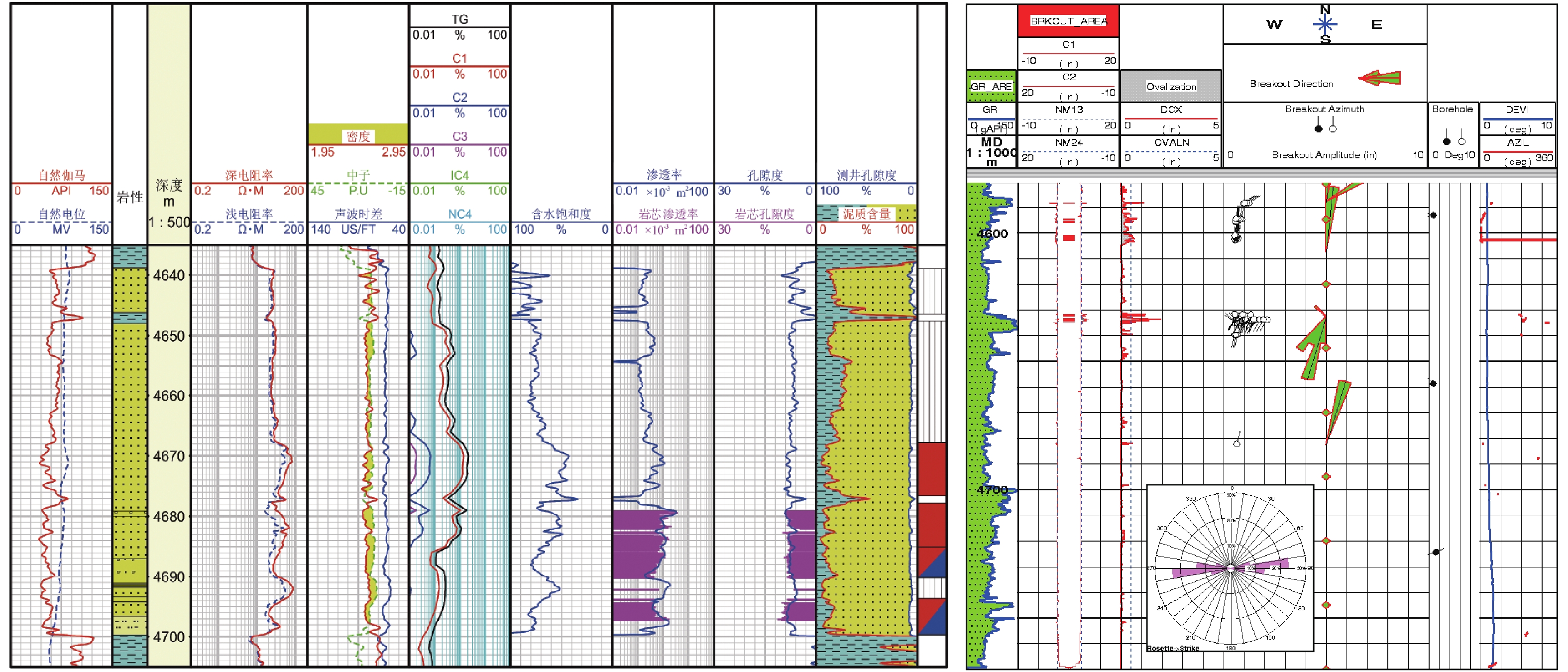
东海盆地A凹陷主要以低孔低渗储层发育为主,经生产实践证实,该类储层运用常规直井或低角度定向井(产能低)难以实现商业产能,因此,渗透率各向异性和储层“甜点”攻关显得尤为重要。碎屑岩储层各向异性特征普遍存在,基于全直径岩芯360°分扇区各向异性实验(渗透率、声波时差)结果表明:6个扇区的水平渗透率分布范围为(3.7~17.3)×10−3 μm2,轴向90°渗透率为0.06×10−3 μm2,渗透率各向异性分布范围为62~288,其中水平优势方向的渗透率是非优势方向的3~5倍,且渗透率高值与纵波时差、横波时差低值存在较小夹角。进一步利用成像测井资料与区域地应力分析证实,最大水平主应力方向与构造裂缝发育方向(渗透率优势方向)存在较小夹角,结合“甜点”储层展布形态,并垂直于最大水平主应力方向布井有利于产能释放,助力低渗储层的经济有效开发。
Abstract:The Sag A of the East China Sea Basin is dominated by low porosity and low permeability reservoirs. Production practice has proved that such reservoirs cannot be economically and effectively developed in conventional vertical wells or low-angle directional wells (low productivity). Therefore, it is particularly important to tackle permeability anisotropy and reservoir "sweet spot". The anisotropy characteristics of clastic rock reservoir are common in the Sag A. The results of the anisotropy experiment of 360° sub-sector of full-diameter core (permeability and sonic time difference) show that: the horizontal permeability distribution range of six sectors is (3.7~17.3)×10−3 μm2, the axial permeability of 90° is 0.06×10−3 μm2, and the permeability anisotropy distribution range is 62~288. The permeability in the horizontal dominant direction is 3~5 times of that in non-dominant direction. Moreover, the high permeability has a small angle between the P-wave time difference and the low S-wave time difference. Further imaging logging data and regional stress analysis confirm that the direction of maximum horizontal principal stress has a small angle with the development direction of structural fracture (permeability predominant direction). Combined with the distribution pattern of the "sweet spot" reservoir, the well distribution perpendicular to the direction of maximum horizontal principal stress is conducive to productivity release, which facilitate the economical and effective development of low permeability reservoir.
-

-
表 1 全直径岩芯不同角度渗透率、声波时差对比表
Table 1. Comparison of permeability and acoustic transit time difference of full-diameter core at different angles
样号 长度/cm 直径/cm 角度/(°) 渗透率/10−3 μm2 纵波时差/(μs/ft) 横波时差/(μs/ft) 样品1 9.502 9.986 轴向 0.419 118.71 169.30 0 1.513 104.64 137.55 30 2.393 108.74 141.01 60 2.588 109.64 139.22 90 2.763 110.60 141.59 120 2.682 109.45 137.80 150 2.039 105.02 133.70 样品2 9.508 10.018 轴向 0.060 75.33 110.21 0 4.636 86.52 128.87 30 17.317 135.06 185.68 60 14.876 121.40 160.90 90 7.183 100.72 146.60 120 4.735 85.50 125.22 150 3.759 83.44 122.30 表 2 A凹陷4个含油气构造裂缝识别数量统计
Table 2. Statistics of identification number of 4 hydrocarbon-bearing structural fractures in Sag A
裂缝类型 XX-1 XX-2 XX-3 XX-4 合计 构造缝 328 225 41 53 647 层理缝 491 327 103 202 1123 合计 819 552 144 255 1770 -
[1] 李潮流,袁超,李霞,等. 致密砂岩电学各向异性测井评价与声电各向异性一致性分析[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2020,47(2):427-434. doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.02.22
[2] 李道品. 低渗透砂岩油田开发[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1977: 28-31.
[3] 丁云宏,陈作,曾斌,等. 渗透率各向异性的低渗透油藏开发井网研究[J]. 石油学报,2002,23(2):64-67. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2002.02.014
[4] 罗健,胡文亮,何玉春,等. 不同泥浆体系下东海低渗储层测录井评价[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2019,39(6):216-227. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2019070403
[5] LOGAN T L. Horizontal drainhole drilling techniques used, for coal seam resource exploitation[C]//SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, 1988.
[6] MARICIC N,MOHAGHEGH S D,ARTUN E. A parametric study on the benefits of drilling horizontal and multilateral wells in coalbed methane reservoirs[J]. SPE Reservoir Evaluation and Engineering,2008,11(6):976-983. doi: 10.2118/96018-PA
[7] 唐晓明,李盛清,许松,等. 页岩气藏水平测井裂缝识别及声学成像研究[J]. 测井技术,2017,41(5):501-505. doi: 10.16489/j.issn.1004-1338.2017.05.001
[8] 李思亦,唐晓明,何娟,等. 基于声波远探测和岩石力学分析的井旁裂缝有效性评价方法[J]. 石油学报,2020,41(11):1388-1395. doi: 10.7623/syxb202011008
[9] 许松,唐晓明,苏远大,等. 斯通利波和弯曲波联合反演地层VTI各向异性的阵列声波处理方法[J]. 地球物理学报,2018,61(12):5105-5114. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0521
[10] 许松,苏远大,唐晓明. 含定向裂缝横向各向同性介质的弹性特征及其在各向异性测量中的应用(英文)[J]. Applied Geophysics,2020,17(2):182-191.
[11] 古锐瑶,许松,唐晓明,等. VTI各向异性地层偶极横波测井及其应用[J]. 测井技术,2017,41(3):364-368. doi: 10.16489/j.issn.1004-1338.2017.03.021
[12] 高伟中,孙鹏,田超,等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷地应力场与油气运移关系探讨[J]. 油气藏评价与开发,2015,5(1):1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1426.2015.01.001
[13] 张建培,徐发,钟韬,等. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖组-花港组层序地层模式及沉积演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2012,32(1):35-41.
[14] 叶素娟,杨映涛,张玲. 四川盆地川西坳陷上三叠统须家河组三段和五段“甜点”储层特征及分布[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2021,42(4):829-840. doi: 10.11743/ogg20210405
[15] 宋婷. X73油区长3油藏储层非均质性与水淹特征研究[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2021.
[16] 刘君龙,胡宗全,刘忠群,等. 四川盆地川西坳陷新场须家河组二段气藏甜点模式及形成机理[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2021,42(4):852-862. doi: 10.11743/ogg20210407
[17] 冯强. 下寺湾区山西组致密砂岩储层微观非均质性与含气性研究[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2021.
[18] 李庆昌,薛连达,裘亦楠. 裂缝性低渗透率储层的开发地质研究问题:以克拉玛依油田八区乌尔禾组油层为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,1988,15(5):46-52,60.
[19] 陈建军,翁定为. 中石油非常规储层水平井压裂技术进展[J]. 天然气工业,2017,37(9):79-84. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2017.09.010
[20] 姜瑞忠,黄磊,崔永正,等. 考虑应力敏感效应的裂缝性复合油藏水平井压力动态分析[J]. 东北石油大学学报,2018,42(3):84-91,128-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2018.03.009
[21] 刘忠华,宋连腾,王长胜,等. 各向异性快地层最小水平主应力测井计算方法[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2017,44(5):745-752. doi: 10.11698/PED.2017.05.09
[22] 李潮流,周灿灿,张莉,等. 一种定量评价碎屑岩储层各向异性的新方法[J]. 地球物理学进展,2012,27(5):2043-2050. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.05.027
[23] 张旭东. 高密度各向异性速度分析在琼东南海域的应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2014,30(9):64-69. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2014.09.021
[24] 崔刚,李秀容,王津津,等. 叠前方位各向异性技术在潜山储层裂缝预测中的应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2022,38(10):59-68. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2021.331
[25] 吴志强,曾天玖,肖国林,等. 各向异性叠前时间偏移在南黄海海相油气勘探中的应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2013,29(1):61-65,70. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2013.01.006
-



 下载:
下载: