The salt structure characteristics and formation mechanism of Early Permian Kungurian in Pre-Caspian Basin
-
摘要:
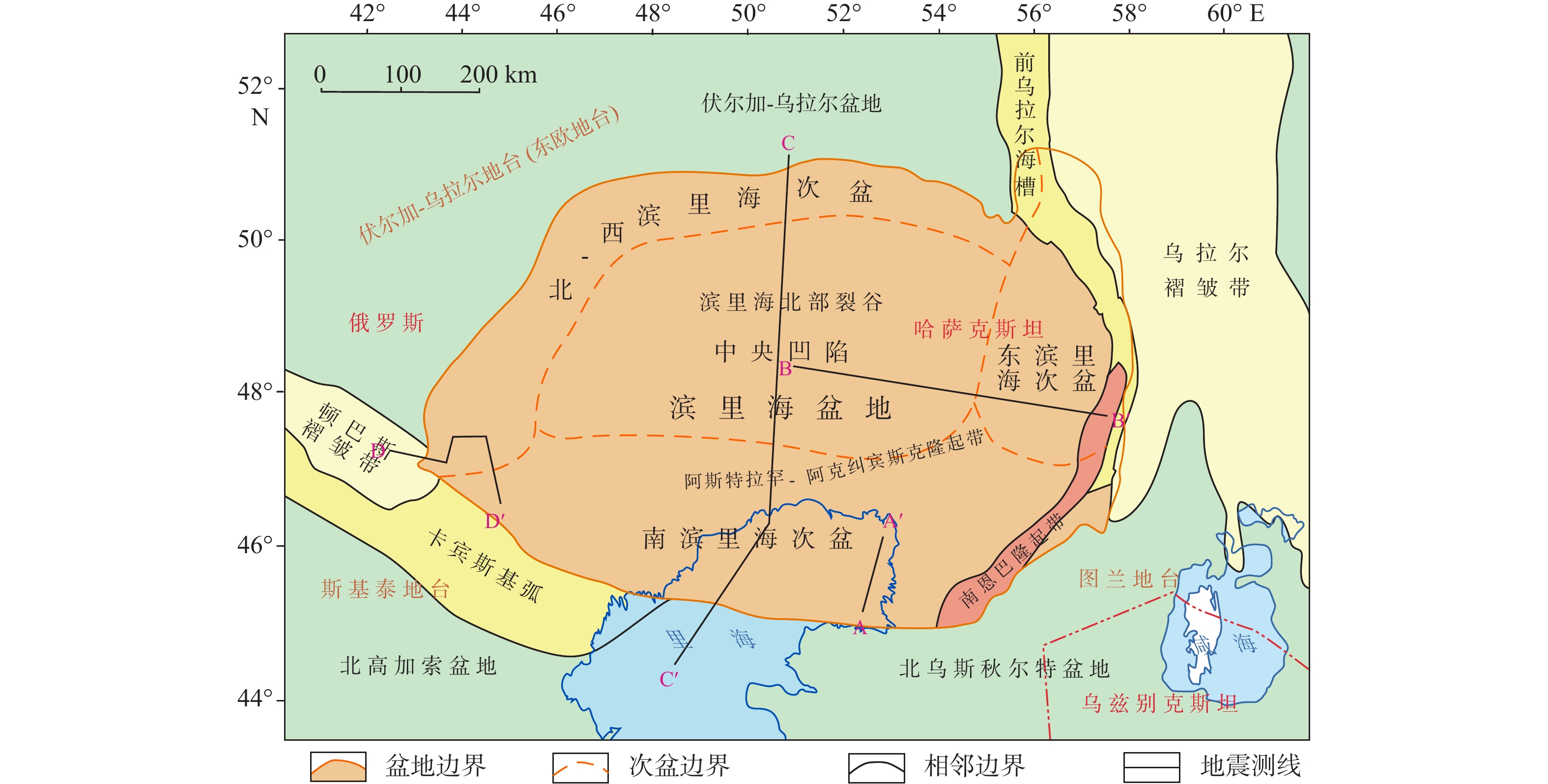
滨里海盆地为自寒武系以来多期沉降的大型叠合含盐盆地,也是世界上油气资源最丰富的大型沉积盆地之一。下二叠统孔谷阶含盐层系在全盆皆有分布,岩盐层具有厚度大、分布广、后期变形构造样式多等特征,但厚层岩盐形成机制尚有争议,盐构造变形类型、空间组合分布规律、变形主控因素等尚不明确。为了研究盆地巨厚盐构造的形成机制及分布规律,在深入了解区域地质背景基础上,利用二维地震剖面资料,采用平衡剖面恢复方法,从全盆地的角度分析盆地演化过程与盐构造变形样式及分布规律,并探讨了盆地盐构造形成演化过程及触发机制。结果表明,盐岩变形程度由盆地中央向盆地边缘减小,由盆缘盐滚、盐背斜构造向盆地中心盐墙构造变化,呈现分带特征。盐岩层的变形对盐下地层影响较小,地层连续性较好;对盐上地层穿插切割较强,导致盐上地层连续性差,形变剧烈。先存斜坡和盆缘的挤压作用是盐岩层最初开始形变的因素,而上覆地层的差异负载作用是盐岩层发生构造变形的主导因素。滨里海盆地连续且巨厚的致密盐岩层是一个天然盖层,阻止了油气向上运移,盐下地层应是未来油气勘探的重点目标,同时,局部岩盐变形消失后使上下地层连接,利于油气向上运移成藏,形成盐上油气勘探目标区。
Abstract:The Pre-Caspian Basin is a large superimposed salt-bearing basin, which is also one of the largest sedimentary basins with the richest oil and gas resources in the world. The Kungurian Stage salt-bearing strata are distributed throughout the basin. The salt beds are very thick and widely developed in salt structural units. There are many structural types and different influencing factors. Due to the nature of salt rock itself and the particularity of deformation, the factors affecting structural deformation are diverse and complex. To study the influencing factors on the deformation of the huge thick salt structures in the basin, we scrutinized the evolution process of the basin from the perspective of the whole basin and analyzed the characteristics of the salt structure in the whole basin by using 2D seismic profile data and regional geological data. The formation and evolution of salt structure in the basin and its triggering mechanism are discussed through the restoration of balanced profile. Results show that the deformation degree of salt rock decreases from the center of the basin to the edge of the basin, showing zoning characteristics. The compressional action of preexisting slope and basin margin is the factor of initial deformation of salt rock, and the differential loading of overlying strata is the dominant factor of structural deformation of salt rock. The strata beneath salt beds have good continuity and weak deformation duo to the existence of salt rock, while the upper salt layer is poorly continuous and severely deformed. Therefore, the continuous and extremely thick salt bed in the Pre-Caspian Basin is a natural cap rock, and the reservoir under the salt is good, which should be the focus of oil and gas exploration in the future.
-
Key words:
- Pre-Caspian Basin /
- salt structure /
- structural deformation /
- balanced profile /
- formation mechanism
-

-
图 8 寒武纪以来的海平面变化曲线[47]
Figure 8.
表 1 滨里海盆地地层层序简表 (据IHS数据库资料[28])
Table 1. Stratigraphic sequence of the Pre-Caspian Basin (according to IHS database[28])
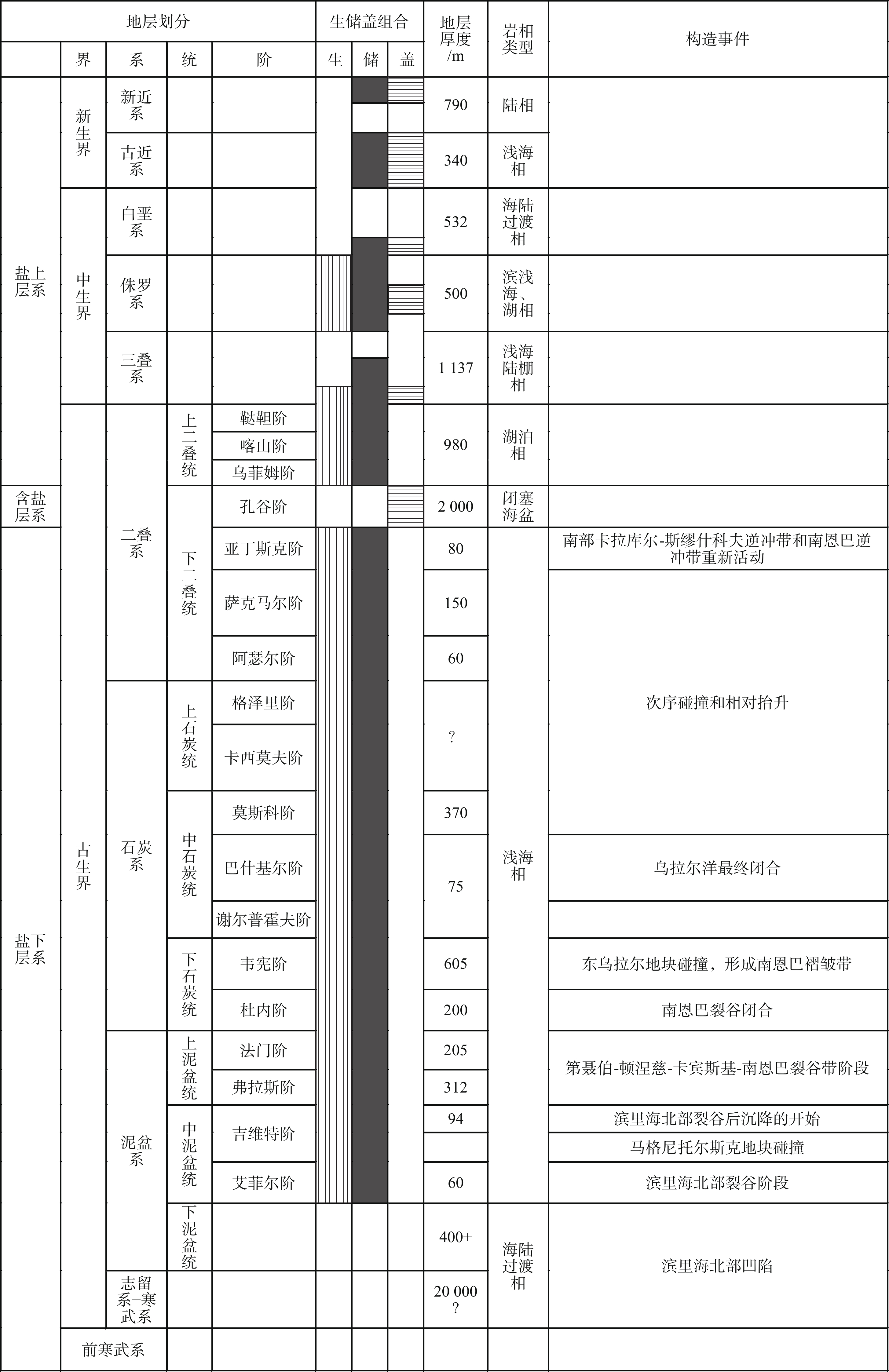
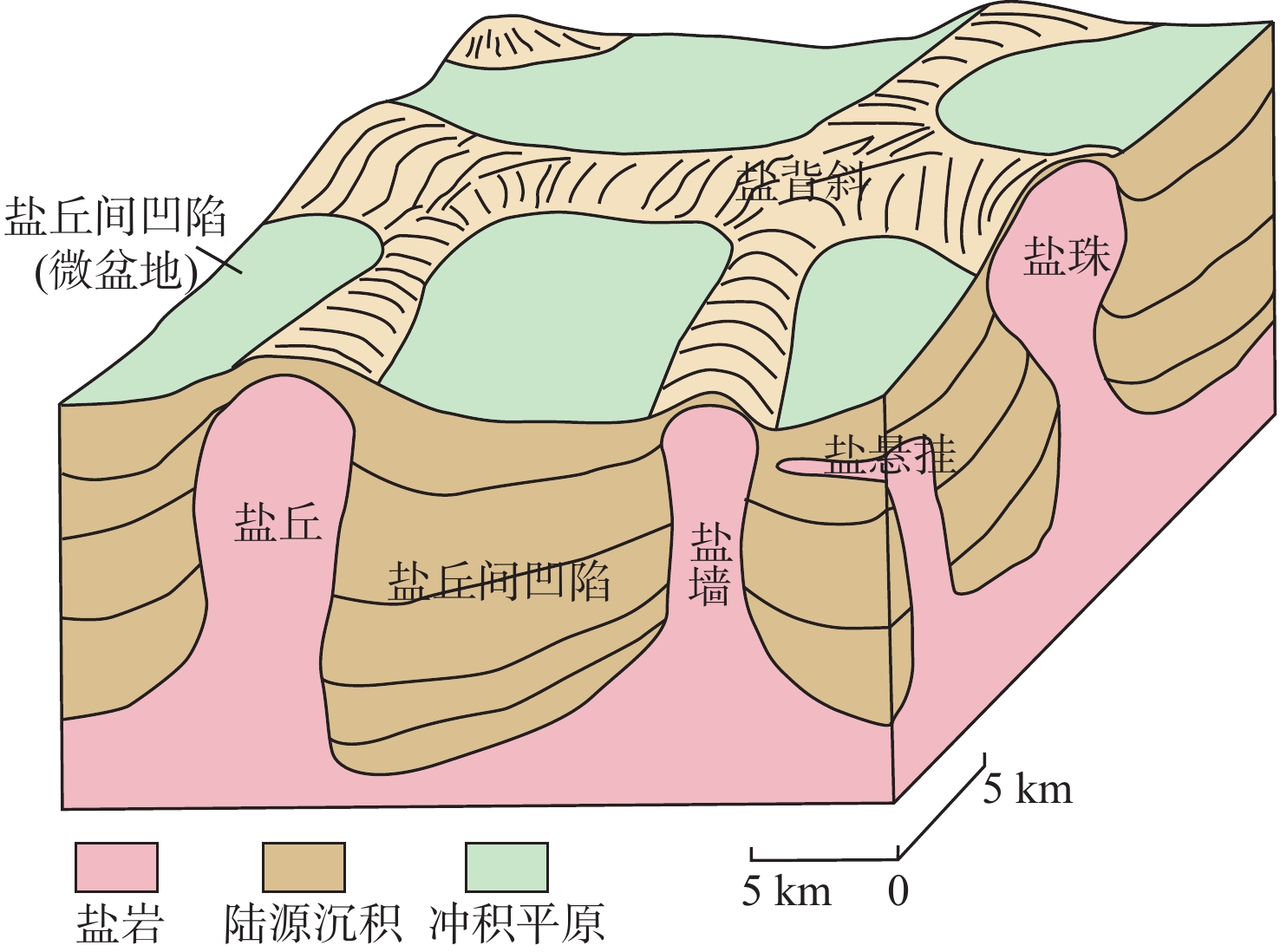
表 2 滨里海盆地盐构造类型分类及特征
Table 2. Classification and characteristics of salt structure types in the Pre-Caspian Basin
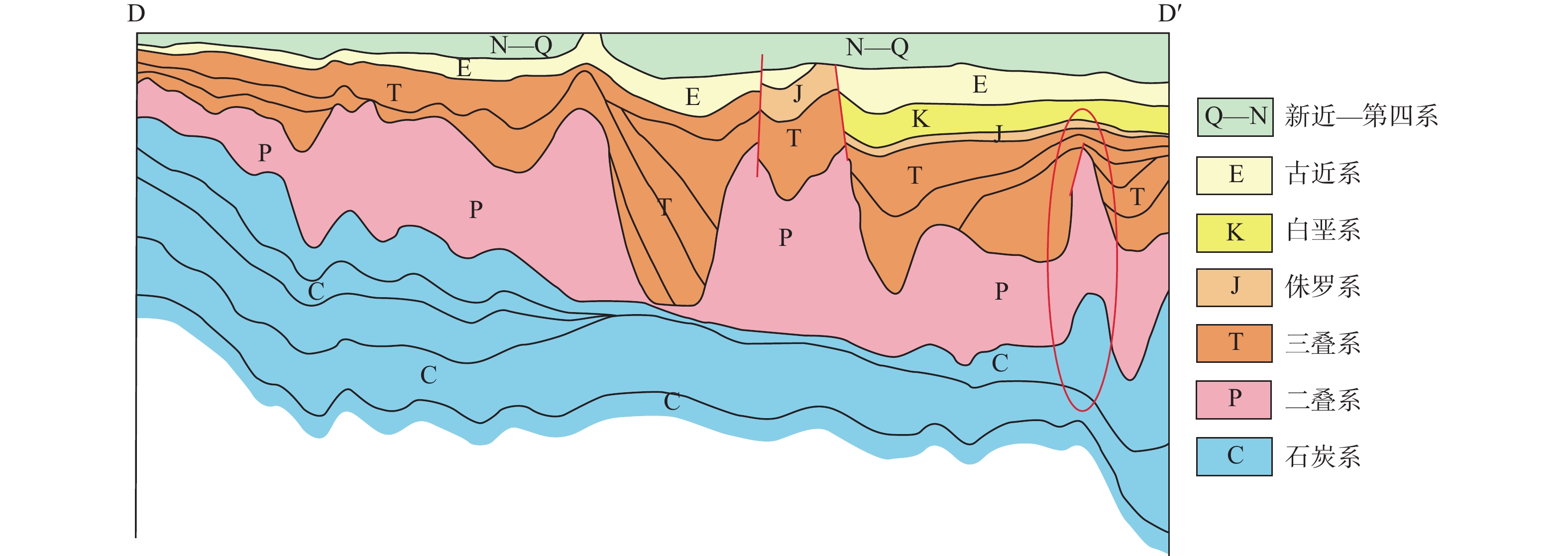
类型 名称 特征 整合接触非刺穿型盐丘 盐枕 早期盐构造,中间厚边缘薄的、平面上呈圆形的盐隆,剖面上呈枕状,形态上表现为上凸下平,继续活动形成盐珠 盐背斜 形态较为对称,盐枕构造因塑性流变而进一步发展,逐步汇聚形成盐背斜(图4) 隐刺穿型盐丘 盐滚构造 幅度低,两翼不对称,缓倾一翼与上覆地层整合接触,陡倾一翼由于存在断层使盐岩沿断层挤入,与上覆地层以正断层接触 非整合接触刺穿型盐丘 盐墙 狭长条带状,如墙体一样,沿断层发育,具深层盐核及延伸很长的长轴盐背斜构造形态(图4) 盐珠 顶部呈圆形的颈装刺穿体,成熟度高,幅度大(图4) 盐脊 在断层作用下盐岩沿着断面进一步向上运动,最终对上覆上二叠统甚至侏罗系产生刺穿 盐悬挂 或称盐悬边,一般和其他盐构造伴生,剖面形状不对称,岩盐朝着侧向延伸侵入,好象悬挂在地层中(图4) 盐蓬 一种复合型盐构造体,由多个盐悬挂侧向扩张连接起来组成的 盐焊接 发育于盐丘构造之间的凹陷底部,盐岩经过塑性流动,原先被盐岩层分隔的盐上地层与盐下地层直接接触(图5c) 其他与盐构造相关的构造
样式龟背构造 发育于盐源凹陷内,由于盐流动引起构造反转而形成,盐间凹陷的地层上隆变形,短轴状的为龟背构造,长轴的为背斜构造 残余盐高 具有盐芯的反形式,可能与相邻的圆顶断开连接。在这些结构中,高结构点始终处于高位,低点始终处于低位(图5b) 盐丘间凹陷 在两个或多个盐丘之间常发育由上二叠统—中生界组成的坳陷,可称之为“盐缘坳陷”或“盐丘间凹陷”,受控于盐构造运动(图4) 盐丘顶部断层 盐丘顶部形成断层密集分布的地带,形成于大规模的盐运动中所产生的局部张扭性构造作用,常与部分龟背构造伴生,剖面上表现为“Y”字形断裂,平面上呈环形围绕核部向四周呈放射状分布(图5b) -
[1] 汤良杰,余一欣,陈书平,等. 含油气盆地盐构造研究进展[J]. 地学前缘,2005,12(4):375-383. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.04.006
[2] 戈红星,JACKSON M P A. 盐构造与油气圈闭及其综合利用[J]. 南京大学学报,1996,32(4):640-649.
[3] JACKSON M P A. Retrospective salt tectonics[M]//JACKSON M P A, ROBERTS D G, SNELSON S. Salt Tectonics: A Global Perspective. AAPG Memoir, 1995, 65: 1-28.
[4] HUDEC M R,JACKSON M P A. Terra infirma:understanding salt tectonics[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2007,82(1/2):1-28.
[5] 葛智渊. 被动大陆边缘盐构造研究进展[J]. 地质论评,2021,67(1):159-172. doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2021.01.012
[6] 王迎,李江海,章雨,等. 南大西洋中段被动陆缘盆地下白垩统盐构造成因模式[J]. 地质学报,2022,96(4):1182-1196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.04.004
[7] 朱钇同,李爱山,陈亮,等. 墨西哥Burgos盆地Perdido构造带深浅双层盐分布特征及南北差异构造形变[J]. 中国海上油气,2021,33(6):62-70. doi: 10.11935/j.issn.1673-1506.2021.06.007
[8] 杨泰,汤良杰,余一欣,等. 滨里海盆地南缘盐构造相关油气成藏特征及其物理模拟[J]. 石油实验地质,2015,37(2):246-251,258. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201502246
[9] 刘洛夫,朱毅秀,胡爱梅,等. 滨里海盆地盐下层系的油气地质特征[J]. 西南石油学院学报,2002,24(3):11-15.
[10] 方甲中,吴林刚,高岗,等. 滨里海盆地碳酸盐岩储集层沉积相与类型:以让纳若尔油田石炭系KT-Ⅱ含油层系为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2008,35(4):498-508. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2008.04.017
[11] 雍天寿,杨瑞麒,关维东,等. 扎纳若尔油田石炭系划分及沉积特征[J]. 新疆石油地质,2003,24(1):92-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3873.2003.01.024
[12] 钱桂华. 哈萨克斯坦滨里海盆地油气地质特征及勘探方向[J]. 中国石油勘探,2005,10(5):60-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2005.05.011
[13] 刘洛夫,朱毅秀,张占峰,等. 滨里海盆地盐上层的油气地质特征[J]. 新疆石油地质,2002,23(5):442-447. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3873.2002.05.027
[14] 梁爽,王燕琨,金树堂,等. 滨里海盆地构造演化对油气的控制作用[J]. 石油实验地质,2013,35(2):174-178,194. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201302174
[15] 刘洛夫,郭永强,朱毅秀. 滨里海盆地盐下层系的碳酸盐岩储集层与油气特征[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版),2007,22(1):53-58,63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-064X.2007.01.013
[16] 王瑞,朱筱敏,陈烨菲,等. 滨里海盆地肯基亚克地区中、下石炭统碳酸盐岩储层特征与成岩作用[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2012,33(2):225-235. doi: 10.11743/ogg20120209
[17] 杨孝群,汤良杰,朱勇. 滨里海盆地东缘盐构造特征及其与乌拉尔造山运动关系[J]. 高校地质学报,2011,17(2):318-326. doi: 10.16108/j.issn1006-7493.2011.02.021
[18] 苗钱友,王燕琨,朱筱敏,等. 滨里海盆地东缘石炭系层序地层研究[J]. 新疆石油地质,2013,34(4):483-487.
[19] 古俊林,朱桂生,李永林. 滨里海盆地Sagizski区块盐上层系成藏条件及分布规律研究[J]. 中国石油勘探,2012,17(2):57-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2012.02.011
[20] 杨怀义, 张建球, 李永林. 滨里海盆地油气地质特征与勘探实践[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2020.
[21] FOMENKO K YE. Stroyeniye kristallicheskogo fundamental Prikaspiyskoy padiny po geofizicheskim damn ym. Geologiya Nefti Gaza[J]. Nedra,Moscow,Russian Federation,1972,10:39-46.
[22] 刘洛夫,朱毅秀,熊正祥,等. 滨里海盆地的岩相古地理特征及其演化[J]. 古地理学报,2003,5(3):279-290. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2003.03.002
[23] 侯珏,林雅平,赵文琪,等. 哈萨克斯坦北特鲁瓦油田石炭系碳酸盐岩储层测井评价[J]. 海相油气地质,2022,27(1):103-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2022.01.011
[24] 景紫岩,李国斌,张亚军,等. 滨里海盆地东缘盐构造及变形机制:物理模拟的启示[J]. 地质学报,2021,95(5):1459-1468. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.05.010
[25] 邓西里,汪红,鲍志东,等. 滨里海盆地油气分布规律及勘探潜力分析[J]. 石油实验地质,2012,17(5):36-47.
[26] MALUSHIN I I. Genesis of the North Caspian depression (in Russian)[J]. Sovetskaya Geologiya,Moscow,Nedra,1985,8(10):72-77.
[27] Blackbourn Geoconsulting. Petroleum Geology of the Precaspian Basin[DB/OL]. 2005.
[28] IHS. Precaspian Basin, Kazakhstan, Russia[DB/OL]. Basin Monitor. 2012.
[29] 贾小乐,何登发,童晓光,等. 全球大油气田分布特征[J]. 中国石油勘探,2011,16(3):1-7.
[30] 张家青. 哈萨克斯坦滨里海盆地东南部油气地质特征及勘探方向[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2011,27(7):50-56. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2011.07.005
[31] 李江海, 王洪浩, 周肖贝, 等. 盐构造[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015.
[32] YU Y X,TAO C Z,SHI S Y,et al. Physical modeling of salt structures in the middle south Atlantic marginal basins and their controlling factors[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2021,48(1):136-145. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(21)60010-1
[33] BARD E J P,CHAMBERLAIN P,GALAVAZI M,et al. Sedimentation during halokinesis:Permo-Triassic reservoirs of the Saigak field,Precaspian Basin,Kazakhstan[J]. Petroleum Geoscience,2002,8(2):177-187. doi: 10.1144/petgeo.8.2.177
[34] 张建培,唐贤君,张田,等. 平衡剖面技术在东海西湖凹陷构造演化研究中的应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2012,28(8):31-37.
[35] 肖维德,唐贤君. 平衡地质剖面技术发展现状与实际应用:以苏北盆地溱潼凹陷为例[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2014,30(5):58-63.
[36] CHAMBERLIN R T. The Appalachian folds of central Pennsylvania[J]. The Journal of Geology,1910,18(3):228-251. doi: 10.1086/621722
[37] 熊连桥,姚根顺,熊绍云,等. 基于平衡剖面对断裂带地层展布恢复的方法:以川西地区中泥盆统观雾山组为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2019,43(6):1079-1093. doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2019.06.001
[38] 李伟,郭甜甜,吴智平,等. 平衡剖面方法在伸展、走滑作用叠加、配比关系分析中的应用:以渤海海域辽东湾坳陷为例[J]. 地质论评,2019,65(6):1501-1514.
[39] 张田,朱伟林,钟锴,等. 南黄海盆地东北凹构造特征及伸缩率研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2021,41(2):118-125.
[40] 陈书平,汤良杰. 盐构造剖面的分层合并复原方法及应用[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版),2008,23(3):32-37.
[41] HOSSACK J. Geometric Rules of Section Balancing for Salt Structures[M]//JACKSON M P A, ROBERTS D G, SNELSON S. Salt Tectonics: A Global Perspective. AAPG Memoir, 1995, 65: 29-40.
[42] HSÜ K J,MONTADERT L,BERNOULLI D,et al. History of the Mediterranean salinity crisis[J]. Nature,1977,267(5610):399-403. doi: 10.1038/267399a0
[43] ROWAN M G. A systematic technique for the sequential restoration of salt structures[J]. Tectonophysics,1993,228(3/4):331-348.
[44] KUZNETSOV. Geological development of the Precaspian Basin and the distribution of reefs[J]. News from Higher Education Establishments,2007,32(2):6-14.
[45] SCHMALZ R F. Deep-water evaporite deposition:a genetic model[J]. AAPG Bulletin,1969,53(4):798-823.
[46] 禚喜准,郑旭,陈骁帅,等. 内陆湖盆“深水成盐”形成条件和识别标志:以东濮凹陷与现代盐湖为例[J]. 地学前缘,2021,28(1):43-59.
[47] 覃建雄,陈洪德,田景春. 二叠纪海平面变化研究[J]. 岩相古地理,1998,18(6):40-47.
[48] 刘洛夫,尚晓庆,孟江辉,等. 滨里海盆地东南部S区块下二叠统空谷阶盐岩特征及其对盐上层系油气成藏的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2012,42(2):304-311.
[49] VAIL P,MITCHUM R,THOMPSON S,et al. Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea level, part 3: relative changes of sea level from coastal onlap[J]. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotheraphy,1977,41(9):1859-1866.
[50] Hallam A,Wignall P B. Mass extinctions and sea-level changes[J]. Earth-Science Reveiews,1998,48(4):217-250.
[51] VOLOZH Y A,ANTIPOV M P,BRUNET M F,et al. Pre-Mesozoic geodynamics of the Precaspian Basin (Kazakhstan)[J]. Sedimentary Geology,2003,156(1/4):35-58.
[52] JACKSON M P A,VENDEVILLE B C. Regional extension as a geologic trigger for diapirism[J]. GSA Bulletin,1994,106(1):57-73. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1994)106<0057:REAAGT>2.3.CO;2
[53] 余一欣,郑俊章,汤良杰,等. 滨里海盆地东缘中段盐构造变形特征[J]. 世界地质,2011,30(3):368-374.
[54] 汤良杰,余一欣,杨文静,等. 库车坳陷古隆起与盐构造特征及控油气作用[J]. 地质学报,2007,81(2):145-150.
[55] VENDEVILLE B C,JACKSON M P A. The rise of diapirs during thin-skinned extension[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,1992,9(4):331-354. doi: 10.1016/0264-8172(92)90047-I
[56] TALBOT C J,POHJOLA V. Subaerial salt extrusions in Iran as analogues of ice sheets,streams and glaciers[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2009,97(1/4):155-183.
-



 下载:
下载: