Organic facies characteristics of Miocene marine source rocks in Yinggehai Basin
-
摘要:
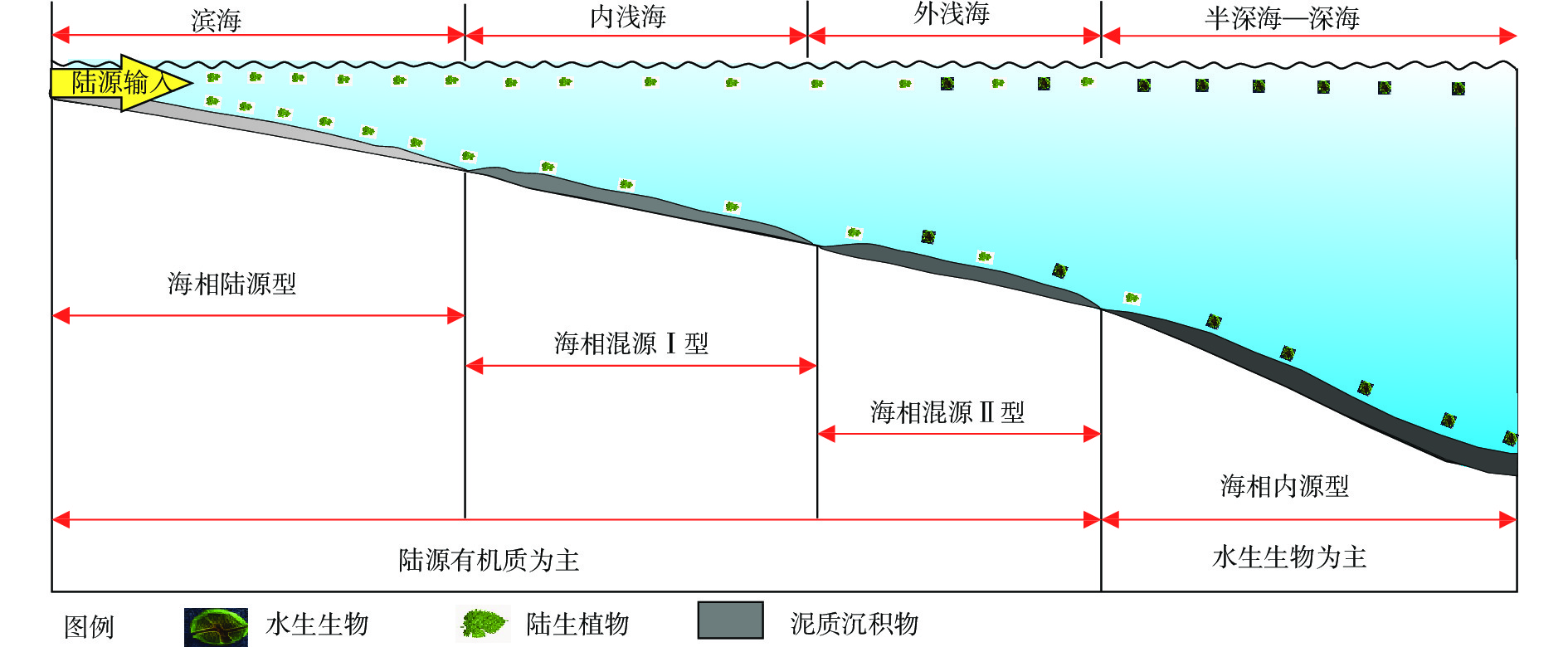
为了实现莺歌海盆地中新统海相烃源岩的精细划分与评价,结合地球化学测试资料,对莺歌海盆地中新统烃源岩进行有机相划分,建立了有机相与沉积相的对应关系,进而预测烃源岩的平面展布。研究结果表明,按照有机质来源与沉积环境可将莺歌海盆地中新统海相烃源岩分为4类:海相陆源型、海相混源Ⅰ型、海相混源Ⅱ型、海相内源型。不同有机相与沉积相对应关系较好,其中,扇三角洲、滨海相对应海相陆源型,内浅海对应海相混源Ⅰ型,外浅海、半深海对应海相混源Ⅱ型,外浅海、半深海和深海对应海相内源型。海相混源Ⅱ型烃源岩分布广,厚度大,有机质丰度较高,有机质类型以Ⅱ2型干酪根为主,少量Ⅲ型干酪根,保存条件较好,是莺歌海盆地的主要气源岩。研究成果为预测莺歌海盆地中新统海相优质烃源岩的平面展布并准确评价其资源潜力提供了重要依据。
Abstract:To evaluate the Miocene marine source rocks in the Yinggehai Basin, based on the geochemical data of source rocks, the organic facies of the Miocene source rocks were classified, the corresponding relationship between organic facies and sedimentary facies was clarified, and the planar distribution of the source rocks was predicted. Results show that the Miocene marine source rocks could be divided into four types according to the source of organic matter and sedimentary environments: marine terrestrial type, marine mixed source type Ⅰ, marine mixed source type Ⅱ, and marine endogenous type. The corresponding relationship between different organic facies and sedimentation is good, among which fan delta and coastal areas correspond to marine terrigenous types, inner shallow sea corresponds to marine mixed source type Ⅰ, outer shallow sea and half deep sea corresponds to marine mixed source type Ⅱ, and outer shallow sea, semi deep sea and deep sea corresponds to marine endogenous types. Type Ⅱ hydrocarbon source rocks are widely distributed with large thickness and rich organic matters. The organic matter is mainly type Ⅱ2, and a small amount of type Ⅲ, and have good preservation conditions. They are the main gas source rocks in the Yinggehai Basin. This study provided an important basis for predicting the planar distribution of high-quality marine source rocks in the Yinggehai Basin and accurately evaluating their resource potential.
-

-
表 1 莺歌海盆地中新统不同沉积相烃源岩有机质丰度评价
Table 1. Statistics in organic matter abundance of the Miocene source rocks of different facies in Yinggehai Basin
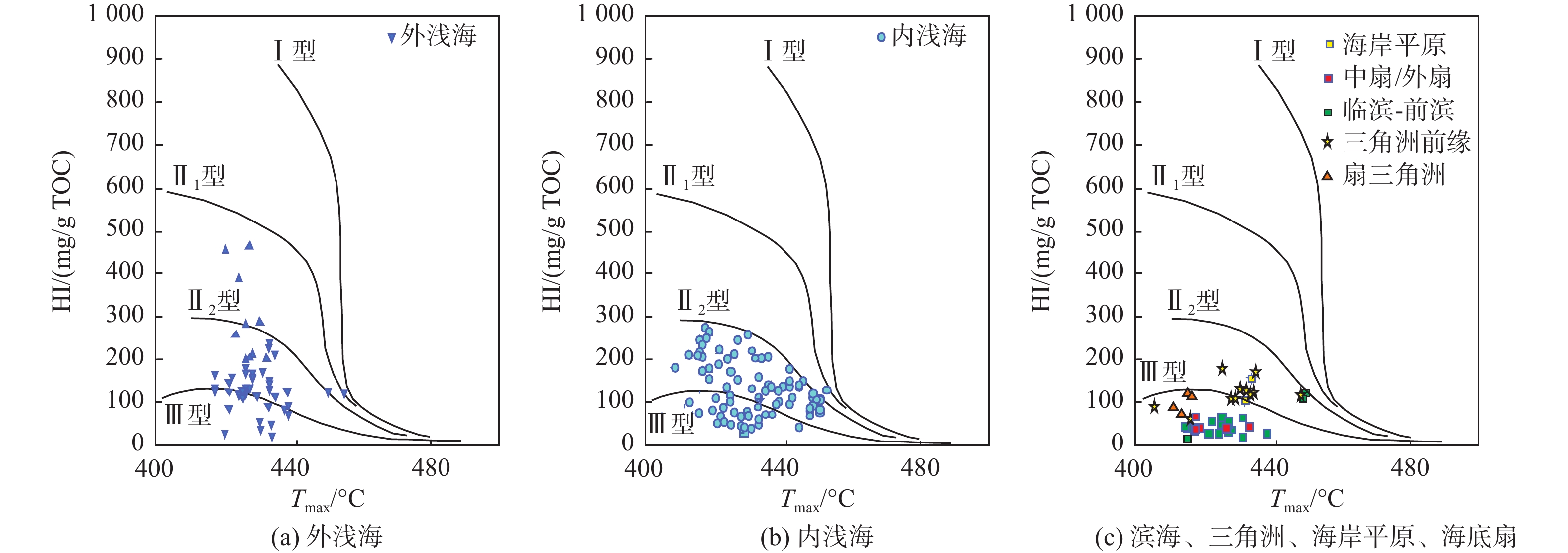
层位 岩性 沉积相 TOC/% S1+S2/(mg/g) 氯仿沥青“A”/% HI/(mg/gTOC) 梅山组 泥岩 外浅海相 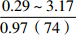
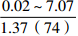
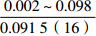
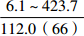
内浅海相 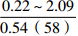
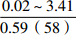
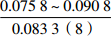
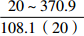
扇三角洲、滨海、海底扇相 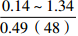
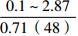
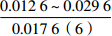
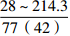
三亚组 泥岩 内浅海相 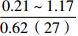
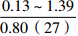
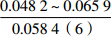
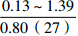
三角洲、滨海、海岸平原 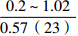
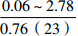
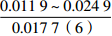
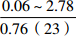
注:表中数据格式为 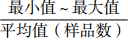 。
。表 2 莺歌海盆地不同沉积环境下烃源岩生源构成参数表
Table 2. Source rock composition parameters of different sedimentary environments in the Yinggehai Basin
沉积相 井号 层位 菌藻类生源/陆源生源总量 藿烷/陆源萜类 甾烷/藿烷 生源构成比例/% 高等植物 菌藻 细菌 其他 外浅海 X1-1_1 梅山组 1.41 1.46 0.34 36.9 28.3 23.9 10.9 X1-1_2 梅山组 1.16 1.52 0.32 43.5 26.6 23.6 6.3 X1-6 梅山组 1.29 1.12 0.3 38.8 29.1 21 11.1 内浅海 H29-1_1 梅山组 0.76 1.31 0.26 53.2 21.9 18.8 6.1 H29-1_2 梅山组 1.03 1.28 0.29 44.9 27.6 18.7 8.8 H29-1_3 三亚组 0.81 1.64 0.25 49.7 19.8 20.6 10 H29-1_4 梅山组 0.62 1.75 0.25 55.7 18.4 16.3 9.5 H29-1_5 梅山组 0.7 1.15 0.4 52.5 20.9 16.1 10.5 L26-2_1 梅山组 0.78 1.27 0.21 50.9 21.1 18.5 9.6 L26-2_2 梅山组 0.76 0.93 0.35 53.4 24.5 16.1 6 L20-1 梅山组 0.85 1.68 0.19 48.6 24.7 16.6 10.1 扇三角洲、滨海 H29-1_6 三亚组 0.71 1.11 0.42 55.3 23.3 15.9 5.5 H29-1_7 梅山组 0.79 2.01 0.3 49.6 20.6 18.5 11.3 L20-1_1 三亚组 0.82 1.23 0.3 52.2 27.1 16 4.7 L20-1_2 三亚组 0.82 1.5 0.34 49.9 24.4 16.7 9 L33-1 梅山组 0.69 1.16 0.36 53.1 14.5 21.9 10.5 表 3 莺歌海盆地中新统海相烃源岩有机相类型划分
Table 3. Classification of the Miocene marine source rocks in the Yinggehai Basin
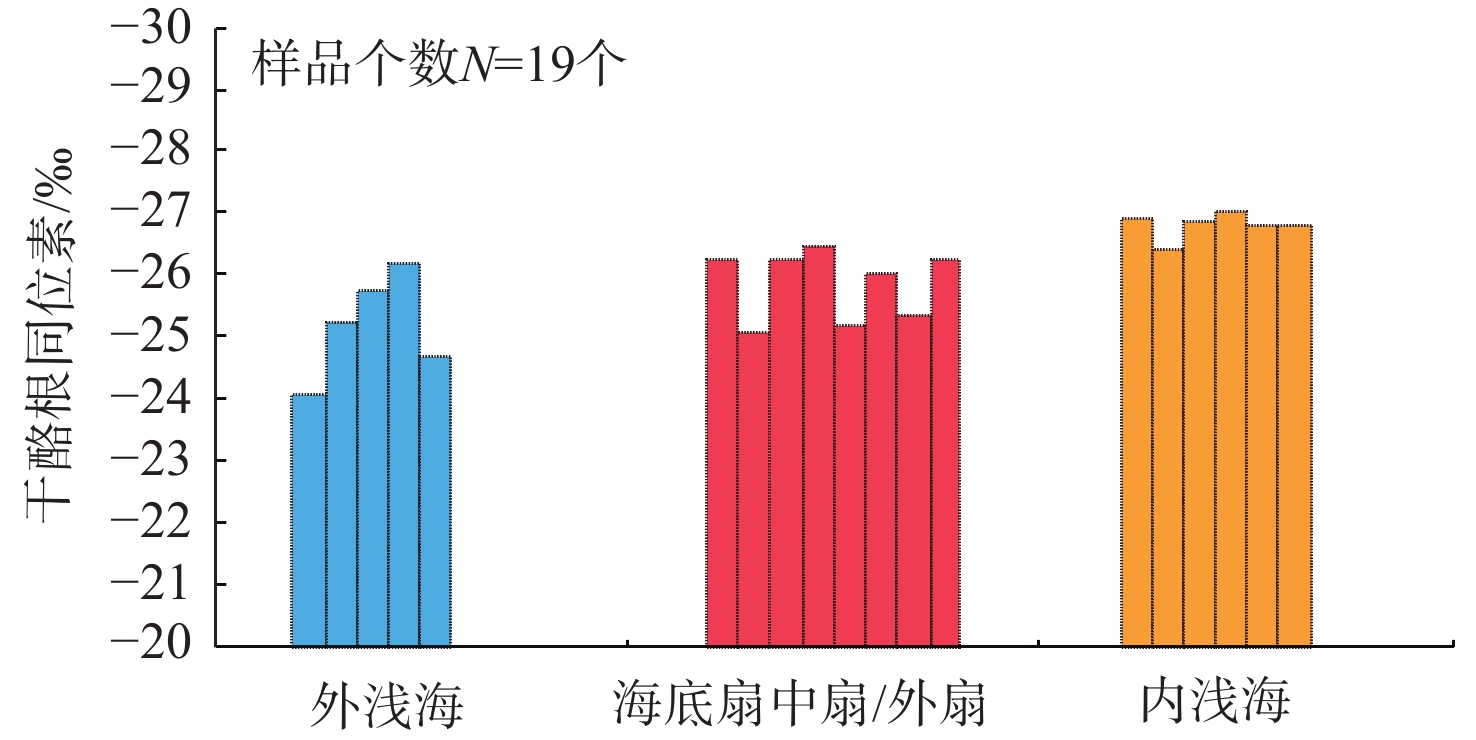
烃源岩特征 海相陆源型 海相混源Ⅰ型 海相混源Ⅱ型 海相内源型 沉积相 扇三角洲、滨海 内浅海 外浅海、半深海 外浅海、半深海和深海 有机质丰度 0.14%~1.34%,平均0.53% 0.22%~2.09%,平均0.59% 0.29%~3.17%,平均0.97% / 干酪根类型 以Ⅲ型为主 以Ⅲ型为主,少量Ⅱ2型 以Ⅱ2型为主,少量Ⅲ型 推测干酪根以Ⅱ1和Ⅱ2型为主 干酪根同位素 平均值为−26.8‰ 平均值为−25.8‰ 平均值为−25.1‰ / 特殊生物
标志物丰富的奥利烷
OL/C30藿烷:0.49~1.62/0.88一定丰度的奥利烷
OL/C30藿烷:0.10~0.98/0.46少量的奥利烷
OL/C30藿烷:0.08~0.41/ 有机质生源 陆源有机质为主;菌藻类生源总量/陆源生源总量为0.54~1.45,平均 0.76 海陆混源,陆源有机质居多;菌藻类生源总量/陆源生源总量为0.62~1.03,平均 0.79 海陆混源,海源有机质居多;菌藻类生源总量/陆源生源总量为1.16~1.41,平均1.29 推测海源有机质为主 生源构成比例 高等植物占比为49.6%~55.3%,
平均 52.02%;低等生物占比为36.4%~43.1%,平均 39.8%高等植物占比为44.9%~55.7%,
平均 51.7%;低等生物占比为34.7%~46.3%,平均40.1%高等植物占比为36.9%~43.5%,
平均39.7%;低等生物占比为39.2%~43.1%,平均 50%/ -
[1] 邓鸣放,张宏友,梁可明,等. 琼东南、莺歌海盆地油气特征及其烃源岩研究[J]. 中国海上油气(地质),1990,4(1):15-22.
[2] 黄保家,肖贤明,董良伟. 莺歌海盆地烃源岩特征及天然气生烃演化模式[J]. 天然气工业,2002,22(1):26-30.
[3] 王元,李贤庆,王刚,等. 莺琼盆地中新统海相烃源岩地球化学特征及生烃潜力评价[J]. 现代地质,2018,32(3):500-510.
[4] 黄保家,黄合庭,李里,等. 莺-琼盆地海相烃源岩特征及高温高压环境有机质热演化[J]. 海相油气地质,2010,15(3):11-18.
[5] 姜建群,胡建武,李明葵. 莺琼盆地高温超压环境有机质热演化及成烃模式探讨[J]. 特种油气藏,2000,7(2):4-8.
[6] 徐新德,杨计海,刘海钰,等. 莺歌海盆地浅海环境下烃源岩有机质形成机制[J]. 地球科学,2019,44(8):2643-2653.
[7] 徐建永,赵牛斌,徐仕琨,等. 莺歌海盆地中新统海相烃源岩发育主控因素及模式[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(2):54-63.
[8] ROGERS M A. Application of Organic Facies Concepts to Hydrocarbon Source Rock Evaluation[C]. Bucuresti: 10th World Petroleum Congress, 1979: 25-30.
[9] 郝芳,陈建渝,孙永传,等. 有机相研究及其在盆地分析中的应用[J]. 沉积学报,1994,12(4):77-86.
[10] 崔涛,解习农,任建业,等. 莺歌海盆地异常裂后沉降的动力学机制[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报,2008,33(3):351-356.
[11] 李思田, 解习农, 焦养泉. 南海北部边缘盆地充填序列和充填样[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997: 70-74.
[12] 朱伟林,张功成,高乐. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地油气地质特征与勘探方向[J]. 石油学报,2008,29(1):1-9.
[13] 龚再升, 李思田. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地油气成藏动力学研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004: 149-153.
[14] 谢玉洪,王振峰,解习农,等. 莺歌海盆地坡折带特征及其沉积体系的控制[J]. 地球科学,2004,29(5):569-574.
[15] 张建新,范彩伟,谭建财,等. 莺歌海盆地中新世沉积体系演化特征及勘探意义[J]. 地质科技情报,2019,38(6):51-59.
[16] 傅家谟, 秦匡宗. 干酪根地球化学[M]. 广州: 广东省科技出版社, 1995.
[17] 肖贤明. 有机岩石学及其在油气评价中的应用[M]. 广州: 广东科技出版社, 1992.
[18] HUANG B J,XIAO X M,LI X X. Geochemistry and origins of natural gases in the Yinggehai and Qiongdongnan Basins,Offshore South China Sea[J]. Organic Geochemistry,2003,34:1009-1025. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(03)00036-6
[19] 黄第藩. 陆相烃源岩有机质中碳同位素组成的分布特征[J]. 中国海上油气(地质),1993,7(4):1-5.
[20] MOLDOWAN J M,SEIFERT W K,GALLEGOS E J. Relationship between petroleum composition and depositional environment of petroleum source rocks[J]. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin,1985,69:1255-1268.
[21] PETERS K E, MOLDOWAN J M. The Biomarker Guide: Interpreting Molecular Fossils in Petroleum and Ancient Sediments [M]. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 1993.
[22] PHILIP R P, GILBERT T D. Biomarker distribution in oils predominantly derived from terrigenous source material[M]//LEYTHAEUSER D, RULLKOTTER J. Advances in Organic Geochemistry. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1985: 73-84.
[23] 王铁冠. 生物标志物地球化学研究[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1990.
[24] 王铁冠. 生物标志物组合与生源构成在天然气源岩研究中的应用[M]//天然气地质研究. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1992: 130-137.
[25] 戴娜,钟宁宁,邓运华,等. 中生代—新生代大陆边缘盆地海相烃源岩成因类型[J]. 石油学报,2015,36(8):941-953.
[26] 李丹,康洪全,郝立华,等. 西南非海岸盆地过渡期海相烃源岩有机相特征及其平面预测[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2019,35(5):21-60.
[27] 陈践发,张水昌,鲍志东,等. 海相优质烃源岩发育的主要影响因素及沉积环境[J]. 海相油气地质,2006,11(3):49-54.
[28] 杨海风,涂翔,赵弟亮,等. 渤海湾盆地莱州湾沙河街组第三、第四段烃源岩有机相特征[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,48(1):72-81.
-




 下载:
下载: