Cenozoic fault characteristics and hydrocarbon accumulation potential of the Panyu Low Uplift in the Pearl River Mouth Basin
-
摘要:
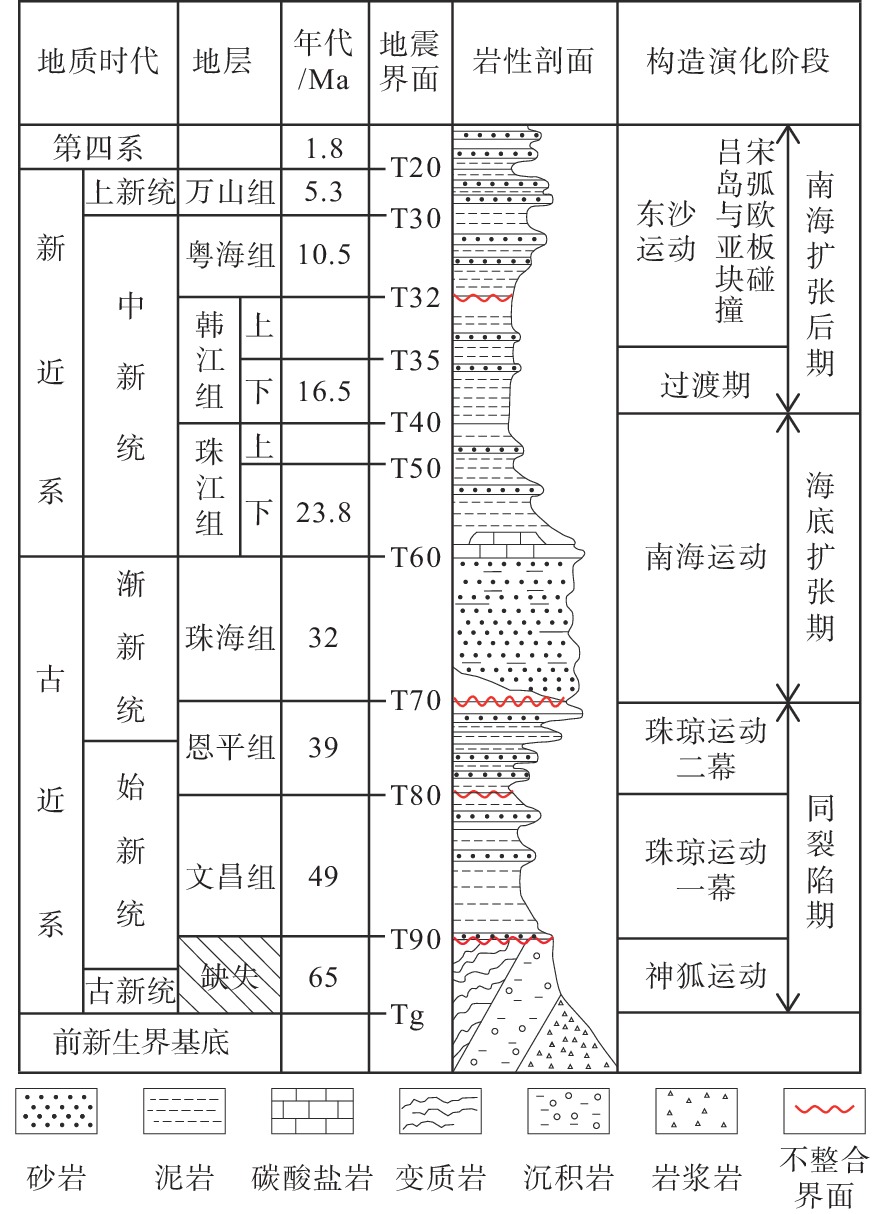
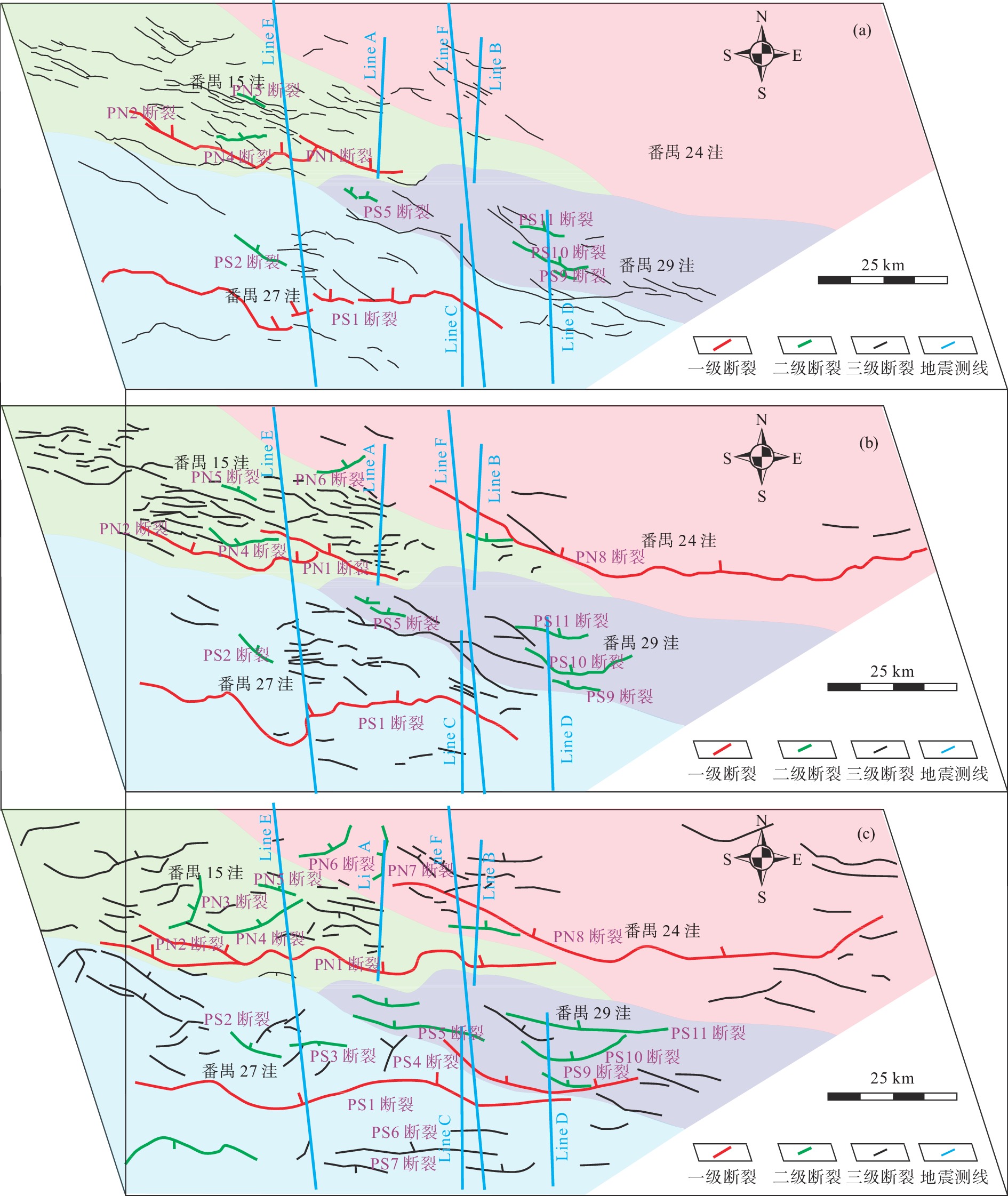
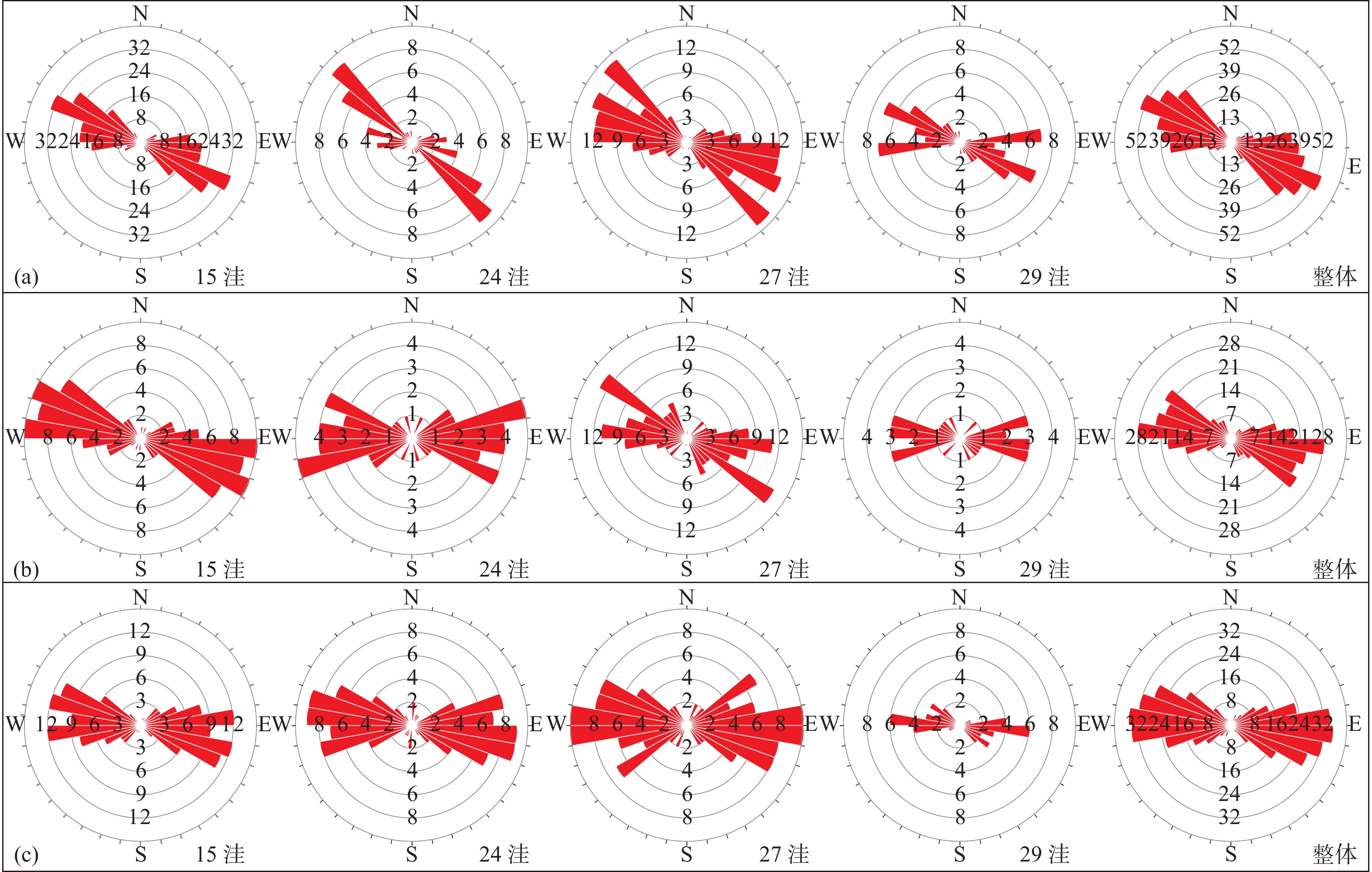
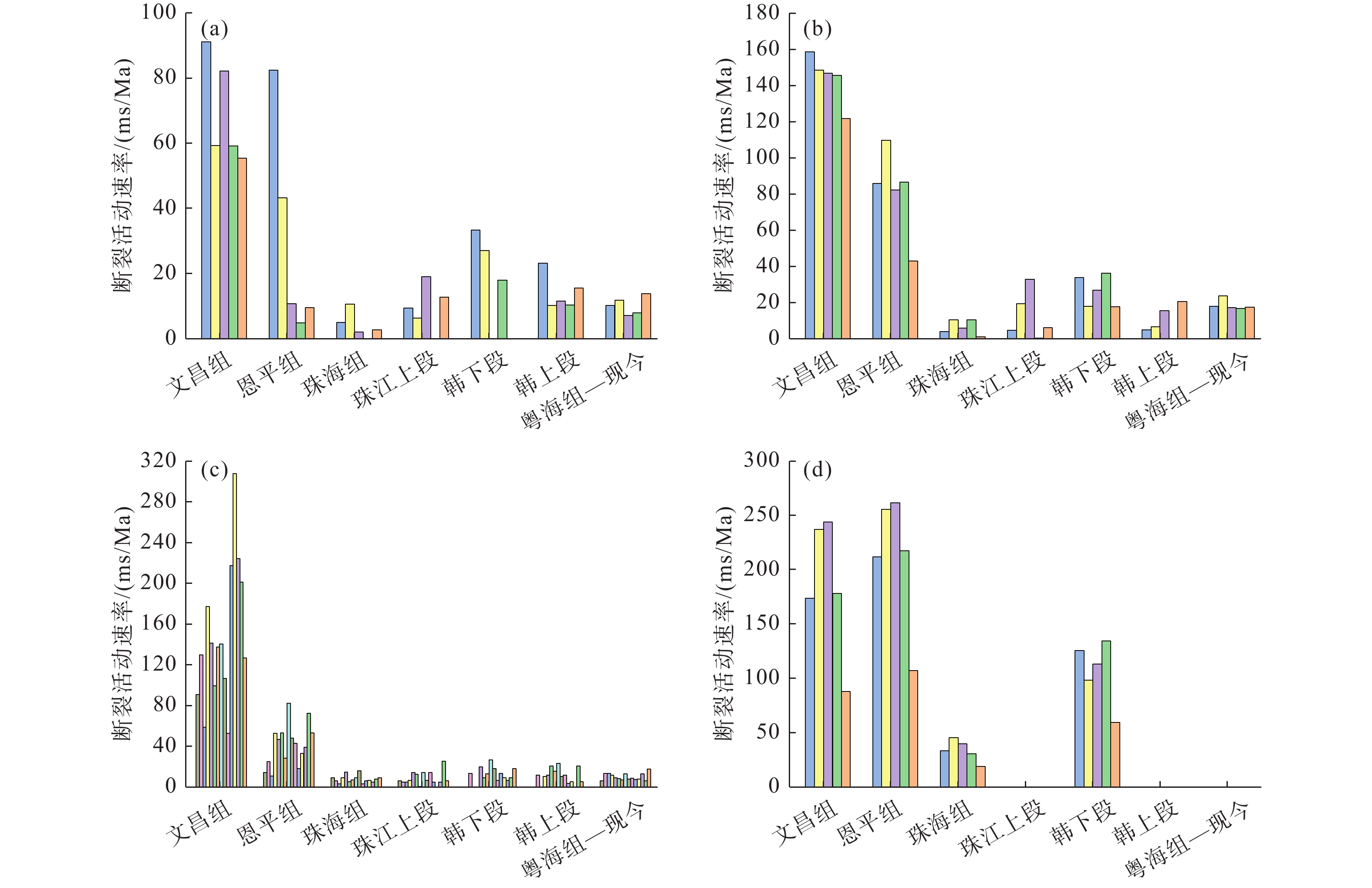
番禺低隆起的油气勘探潜力受新生代断裂体系控制,目前对其断裂特征和演化过程的研究较为匮乏。利用覆盖番禺低隆起的三维地震资料,对研究区的结构特征、断裂平面展布、断裂剖面变形样式等进行分析;定量计算了新生代以来各洼陷边界断裂的活动速率,划分了断裂活动期次;对研究区新生代演化过程进行了复原,分析了不同时期断裂发育的动力学成因。结果表明:番禺低隆起各洼陷均为“南断北超”结构,控洼断裂沿走向的不连续导致洼陷具有多个沉积中心;控洼断裂新生代活动可划分为初始裂陷期、加速裂陷期、裂后拗陷期、构造复活期和构造平静期;其中,文昌组沉积期和韩江组下段沉积期为断层活动的两大高峰期;番禺低隆起新生代断裂的发育受到基底先存断裂的严格控制,断裂走向自深到浅发生顺时针偏转,与南海区域应力场的偏转密切相关。裂陷期断裂活动强烈,使得番禺低隆起具备发育优质烃源岩的潜力。
Abstract:The potential for oil and gas accumulation in the Panyu Low Uplift is strongly controlled by the development and activity of faults. At present, research on its fault characteristics and evolution process is relatively scarce. Using three-dimensional seismic data covering the Panyu Low Uplift, the structural characteristics, fault plane distribution, and the deformation styles at fault profile of the study area were analyzed. The activity rates of boundary faults in various sags since the Cenozoic were calculated based on the division of the fault activity periods. The evolution process of the Cenozoic in the research area was reconstructed and the dynamic causes of fault development in different periods were analyzed. Results show that all the sags in the Panyu Low Uplift are characterized by faulting in the south and stratigraphic overlapping in the north, and the discontinuous distribution of depression-controlling faults along the strike leads to multiple subsidence centers of depression. The Cenozoic activity of depression-controlling fault could be divided into periods from initial rift, accelerated rift, post rift, tectonic reactivation, to tectonic quiescence. The sedimentation periods of the Wenchang Formation and the lower Hanjiang Formation are two peak periods of faulting. The development of the Cenozoic faults in the Panyu Low Uplift is strictly controlled by the pre-existing faults in the basement, and the fault direction deviates clockwise from deep to shallow in depth, which is closely related to the deviation of the stress field of the South China Sea. The strong activity of faults during rifting in this area has given the low uplift the potential to develop high-quality source rocks.
-
Key words:
- Panyu Low Uplift /
- fault characteristics /
- activity period /
- structural evolution /
- subsidence center
-

-
[1] 米立军,张功成,傅宁,等. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷北坡-番禺低隆起油气来源及成藏分析[J]. 中国海上油气(工程). 2006,18(3):161-168.
[2] 施和生,秦成岗,张忠涛,等. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷北坡-番禺低隆起油气复合输导体系探讨[J]. 中国海上油气. 2009,21(6):361-366.
[3] 施和生,秦成岗,高鹏,等. 珠江口盆地番禺低隆起—白云凹陷北坡天然气晚期成藏特征[J]. 中国海上油气. 2008,20(2):73-76,95.
[4] 陈国俊,杜贵超,张功成,等. 珠江口盆地番禺低隆起第三系储层成岩作用及物性影响因素分析[J]. 天然气地球科学. 2009,20(6):854-861.
[5] 刘勇,都小芳,胡鹏,等. 基于“层序矢量滑距”的生长断层活动强度定量表征:以珠江口盆地番禺低隆起M区为例[J]. 石油地球物理勘探. 2018,53(6):1256-1262,1114.
[6] 舒梁锋. 番禺低隆起东南缘珠江组下部陆架边缘沉积体系与坡折带地貌研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2019.
[7] 吴智平,胡阳,钟志洪. 珠一坳陷番禺4洼新生代断裂特征及其区域动力背景[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2015,39(4):1-9.
[8] 于水明,陈雪芳,梅廉夫,等. 珠一坳陷断层特征及对油气成藏的作用[J]. 石油天然气学报. 2012,34(1):50-54,166.
[9] 彭光荣,刘从印,吴建耀,等. 珠江口盆地番禺4洼晚期断裂系统对油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 特种油气藏. 2013,20(3):41-45,152.
[10] 蓝倩. 珠江口盆地番禺4洼结构,构造特征及其与油气成藏关系[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学(武汉),2011.
[11] 代一丁. 珠江口盆地西江南洼古近系构造演化与沉积特征[J]. 中国海上油气,2013,25(3):1-7.
[12] 陈长民. 珠江口盆地(东部)第三系油气藏形成条件[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2003
[13] 漆家福,吴景富,马兵山,等. 南海北部珠江口盆地中段伸展构造模型及其动力学[J]. 地学前缘,2019,26(2):203-221.
[14] 郑金云,高阳东,张向涛,等. 珠江口盆地构造演化旋回及其新生代沉积环境变迁[J]. 地球科学,2022,47(7):2374-2390.
[15] 刘从印,周平兵,曾驿,等. 番禺4洼地区新近系油气成藏主控因素分析[J]. 中国海上油气,2009,21(2): 91-94.
[16] 陈雪芳,李洪博,高鹏,等. 珠-坳陷浅层新领域油气勘探潜力条件分析[J]. 石油天然气学报,2012,34(4):52-56,166.
[17] 余烨,张昌民,李少华,等. 惠州凹陷珠江组泥岩地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2014,38(1):40-49.
[18] 钟志洪,中海石油,钟志洪,等. 珠江口盆地构造-地层格架及成因机制探讨[J]. 中国海上油气,2014,26(5):20-29.
[19] 吴智平,李伟,郑德顺,等. 沾化凹陷中、新生代断裂发育及其形成机制分析[J]. 高校地质学报,2004,10(3):405-417.
[20] 吴婷婷,张丽丽,吴哲,等. 珠江口盆地前新生代先存断裂特征及动力背景:以惠州凹陷和番禺4洼为例[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2022,38(6):54-62.
[21] 包汉勇,郭战峰,张罗磊,等. 太平洋板块形成以来的中国东部构造动力学背景[J]. 地球科学进展,2013,28(3):337-338,340-346. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2013.03.0337
[22] 周蒂,陈汉宗,吴世敏,等. 南海的右行陆缘裂解成因[J]. 地质学报,2002,76(2):180-190. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2002.02.005
[23] 任纪舜,陈廷愚,牛宝贵,等. 中国东部及邻区大陆岩石圈的构造演化与成矿[Z]. 北京:地质矿产部地质研究所,2008.
[24] 童亨茂,聂金英,孟令箭,等. 基底先存构造对裂陷盆地断层形成和演化的控制作用规律[J]. 地学前缘. 2009,16(4):78-104.
[25] TAPPONNIER P,LACASSIN R,LELOUP P H,et al. The Ailao Shan/Red River metamorphic belt:Tertiary left-lateral shear between Indochina and South China[J]. Nature,1990,343(6257):431-437.
[26] ENGEBRETSON D C,COX A,GORDON R G. Relative motions between oceanic and continental plates in the Pacific Basin[J]. Geological Society of America Special Papers,1985,206(9):1-60.
[27] MARUYAMA S, SEND T. Orogeny and relative plate motions:example of the Japanese Islands[J]. Tectonophysics. 1986,127(3/4):305-329.
[28] 张亮. 南海构造演化模式及其数值模拟[D]. 青岛:中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所),2012.
[29] HALL R. Late Jurassic-Cenozoic reconstructions of the Indonesian region and the Indian Ocean[J]. Tectonophysics. 2012,570/571(11):1-41.
[30] 赵淑娟,吴时国,施和生,等. 南海北部东沙运动的构造特征及动力学机制探讨[J]. 地球物理学进展,2012,27(3):1008-1019.
[31] 耿威,张训华,温珍河,等. 台湾东部海岸山脉对弧陆碰撞的响应[J]. 地质论评,2013,59(1):129-136.
[32] 傅宁,米立军,张功成. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷烃源岩及北部油气成因[J]. 石油学报,2007,28(3):32-38.
[33] 胡润. 珠江口盆地东沙隆起珠江组灰岩成藏主控因素研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2016.
-




 下载:
下载: