Grain size characteristics of surface sediments and net transport patterns in the southeastern Andaman Sea
-
摘要:
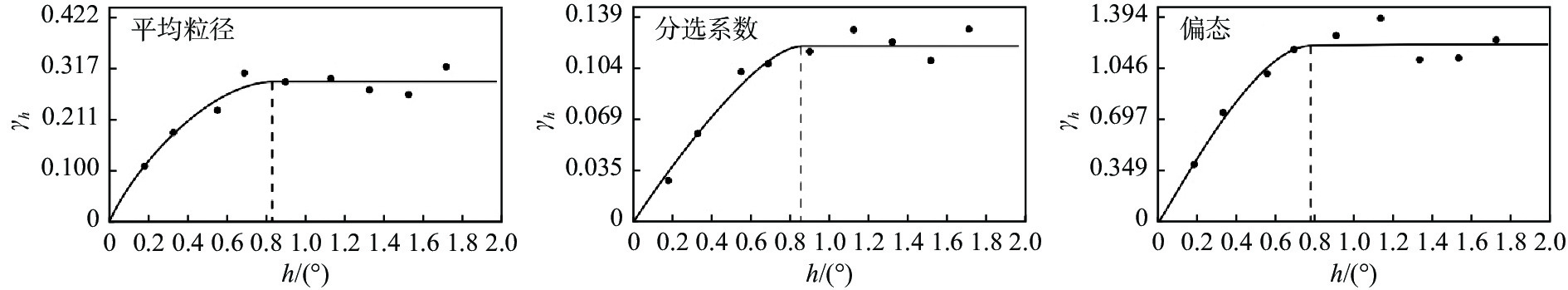
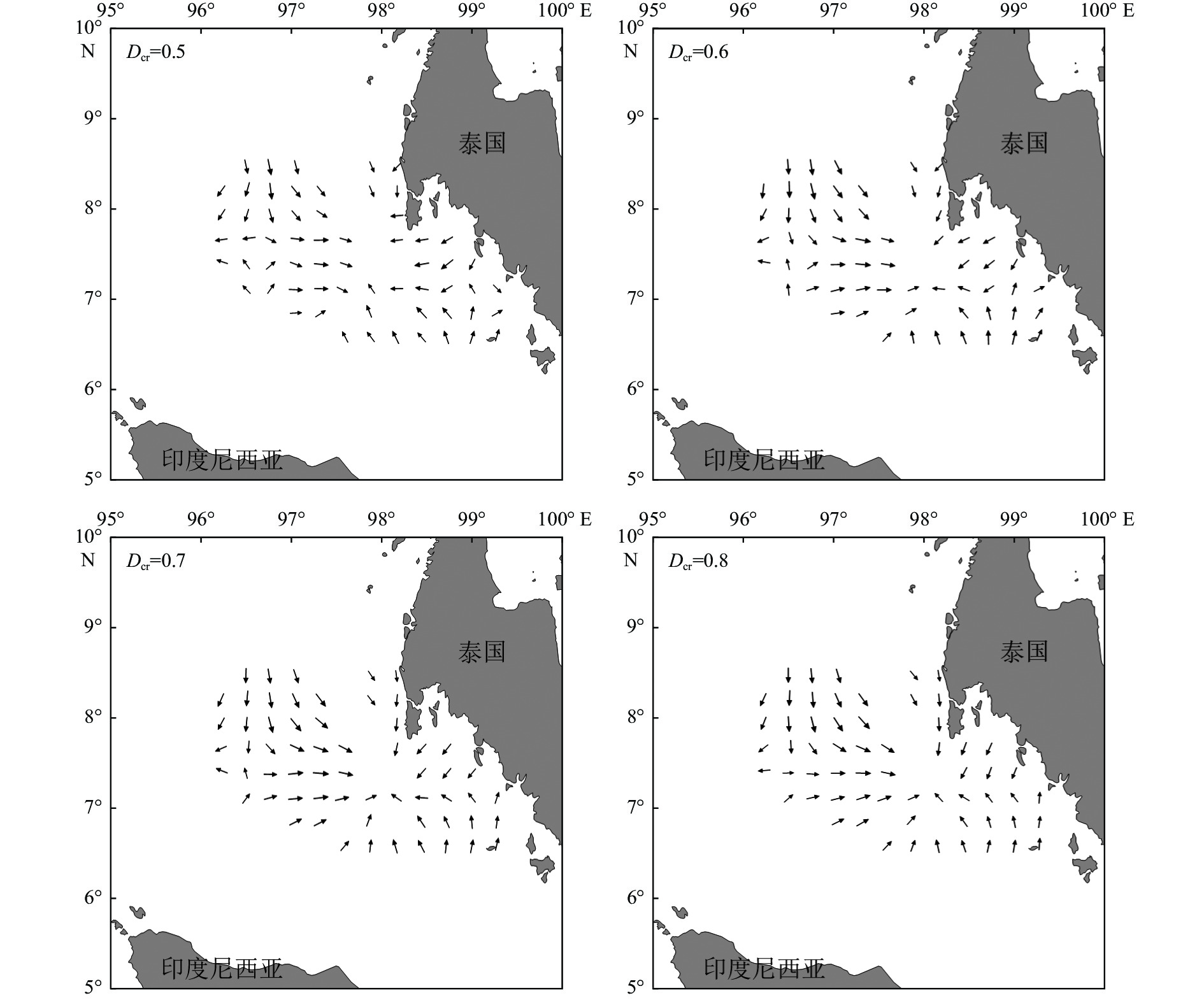
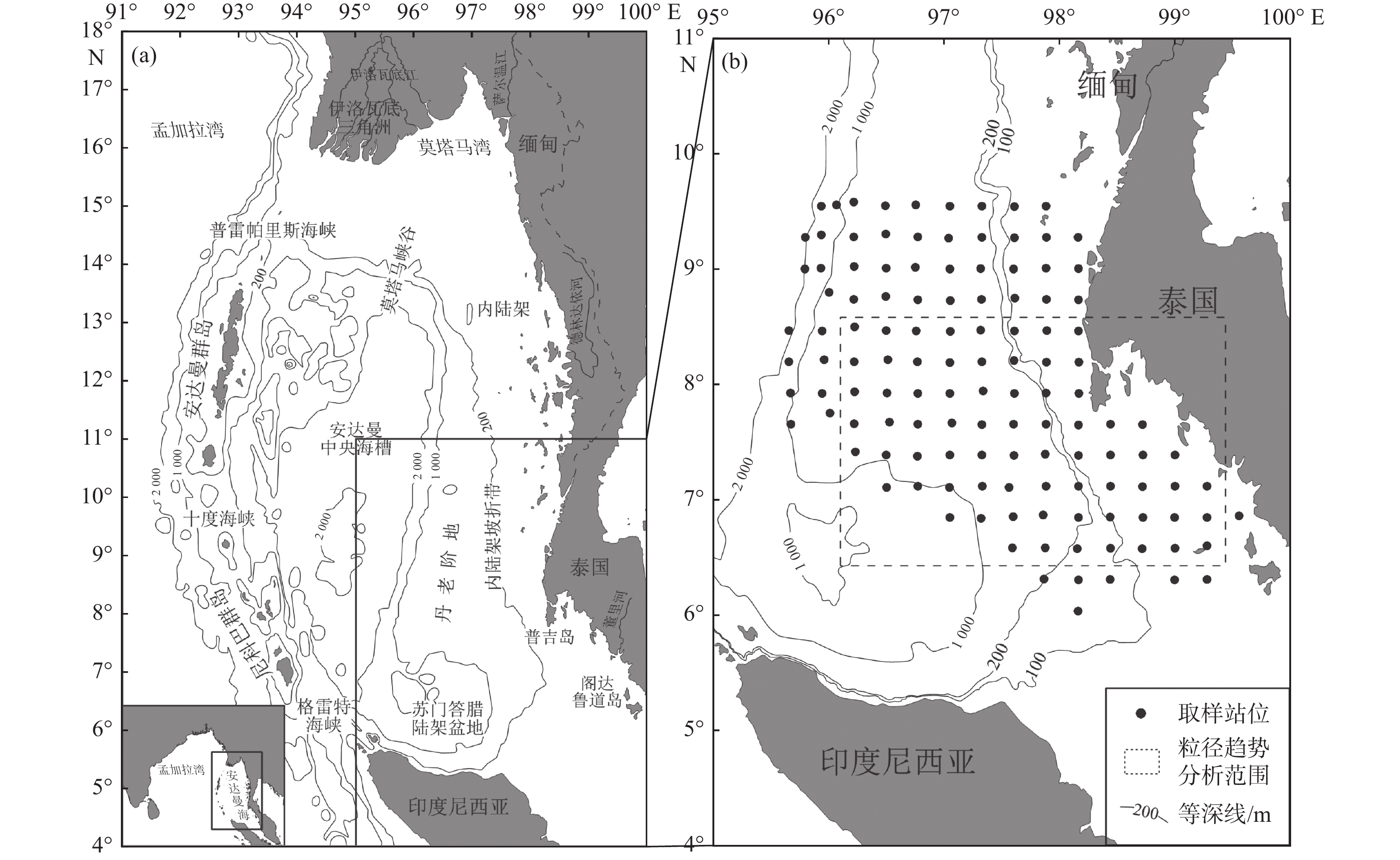
海底沉积物粒度是反映水动力格局最直接的指标,可以有效指示不同时间尺度陆源碎屑物质输运过程。利用激光粒度仪对取自安达曼海东南部海域的98个表层沉积物样品进行粒度分析,结果表明,研究区表层沉积物以粉砂、砂质粉砂及粉砂质砂为主,且粒度组成空间分区明显:北部陆架为粗粒级且分选差的残留砂质沉积区;南部内陆架为混合沉积区,以砂质粉砂、粉砂质砂和粉砂沉积为主;丹老阶地和陆坡为细粒级且分选较好的粉砂和泥质沉积区。在此基础上选用Gao-Collins“粒径趋势”方法分析了该区域表层沉积物的净输运趋势,结果显示,当特征距离<0.8°时,普吉岛东南部海域存在沉积中心,研究区沉积物有向该区域汇聚的明显趋势,沉积物分布特征和输运趋势主要受陆源物质供给、季节性变化的西南季风流以及潮流的综合影响。
Abstract:The grain size of seafloor sediments is the most direct indicator of hydrodynamic pattern, which could effectively indicate the transport process of terrestrial detritus material at different time scales. Grain size was analyzed with the Malvern Mastersize 2000 particle size analyzer for 98 surface sediment samples collected from the southeast continental shelf, Andaman Sea. Results show that sediments on the southeast continental shelf could be divided into four categories: silty sand, sandy silt, silt, and mud. The grain size distribution of the study area revealed four distinct zones in terms of sediment texture: the northern shelf zone with relict sands; the southern inner shelf zone of mixed sediments with silty sand, sandy silt and silt; the Mergui Terrace zone with silt; and the continental slope zone with fine-grained and well-sorted mud. Based on the grain size analysis and Gao-Collins grain size trend analysis, the net transport patterns in the study area were discussed. The characteristic distance was defined less than 0.8° by geostatistical analysis and the results indicate that southwest area near Phuket was the depositional center of the southeastern Andaman Sea and the sediments displayed a net transport trend toward it. It was believed that the distribution and transport pattern of sediments in the study area were controlled by source supply, southwest monsoon currents, and tidal movement.
-
Key words:
- sediment /
- grain size /
- sedimentary process /
- trend analysis /
- Andaman Sea
-

-
[1] 高抒,COLLINS M. 沉积物粒径趋势与海洋沉积动力学[J]. 中国科学基金,1998,12(4):241-246. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8217.1998.04.002
[2] McLaren P,BOWLES D. The effects of sediment transport on grain-size distribution[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology,1985,55:457-470.
[3] McLaren P,HILL S H,BOWLES D. Deriving transport pathways in a sediment trend analysis (STA)[J]. Sedimentary Geology,2007,202:489-498. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2007.03.011
[4] 高抒. 沉积物粒径趋势分析:原理与应用条件[J]. 沉积学报,2009,27(5):826-836. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2009.05.006
[5] LE ROUX J P,ROJAS E M. Sediment transport patterns determined from grain size parameters:overview and state of the art[J]. Sedimentary Geology,2007,202(3):473-488.
[6] ZHANG W,ZHENG J H,JI X M,et al. Surficial sediment distribution and the associated net sediment transport pattern in the Pearl River Estuary,South China[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2013,61/62:41-51.
[7] 王国庆,石学法,刘焱光,等. 粒径趋势分析对长江南支口外沉积物输运的指示意义[J]. 海洋学报,2007,29(6):161-166.
[8] DUMAN M,AVCI M,DUMAN Ş,et al. Surficial sediment distribution and net sediment transport pattern in İzmir Bay,western Turkey[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2004(24):965-981.
[9] 王华强,高抒. 杭州湾北岸高潮滩沉积与沿岸物质输运趋势[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2007,27(6):25-30. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2007.06.012
[10] PLOMARITIS T A,PAPHITIS D,COLLINS M. The use of grain size trend analysis in macrotidal areas with breakwaters:implications of settling velocity and spatial sampling density[J]. Marine Geology,2008,253:132-148. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2008.05.003
[11] 高建华,高抒,陈鹏,等. 海南岛博鳌港沉积物的沿岸输送[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2002,22(2):41-48. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2002.02.007
[12] 石学法,陈春峰,刘焱光,等. 南黄海中部沉积物粒径趋势分析及搬运作用[J]. 科学通报,2002,47(6):452-456. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2002.06.014
[13] 刘升发,刘焱光,朱爱美,等. 东海内陆架表层沉积物粒度及其净输运模式[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2009,29(1):1-6.
[14] RAMASWAMY V,GAYE B,SHIRODKAR P V,et al. Distribution and sources of organic carbon,nitrogen and their isotopic signatures in sediments from the Ayeyarwady (Irrawaddy) continental shelf,northern Andaman Sea[J]. Marine Chemistry,2008,111:137-150. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2008.04.006
[15] PETER G,WEEKS L A,BURNS R E. A reconnaissance geophysical survey in the Andaman Sea and across the Andaman-Nicobar Island Arc[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research,1966,71(2):495-509. doi: 10.1029/JZ071i002p00495
[16] RODOLFO K S. Sediments of the Andaman Basin,Northeastern Indian Ocean[J]. Marine Geology,1969,7:371-402. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(69)90014-0
[17] FRERICHS W E. Planktonic foraminifera in the sediments of the Andaman Sea[J]. Journal of Foraminiferal Research,1971,1(1):1-14. doi: 10.2113/gsjfr.1.1.1
[18] JINTASAERANEE P,WEINREBE W,KLAUCKE I,et al. Morphology of the Andaman outer shelf and upper slope of the Thai exclusive economic zone[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2012,46:78-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.11.003
[19] CURRAY J R. Tectonics and history of the Andaman Sea region[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2005,25:187-232. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.09.001
[20] SIJINKUMAR A V,NATH B N,GUPTHA M V S. Late Quaternary record of pteropod preservation from the Andaman Sea[J]. Marine Geology,2010,275:221-229. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2010.06.003
[21] RASHID H,FLOWER B P,POORE R Z,et al. A ~25ka Indian Ocean monsoon variability record from the Andaman Sea[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews,2007,26:2586-2597. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2007.07.002
[22] PRENDERGAST A,CUPPER M L,Jankaew K,et al. Indian Ocean tsunami recurrence from optical dating of tsunami sand sheets in Thailand[J]. Marine Geology,2012,295-298:20-27. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2011.11.012
[23] McManus J. Grain size determination and interpretation [C]// Techniques in Sedimentology. Oxford: Blackwell, 1988: 63-85.
[24] FOLK R,ANDREWS P,LEWIS D. Detrital sedimentary rock classification and nomenclature for use in New Zealand[J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics,1970,13(4):937-968. doi: 10.1080/00288306.1970.10418211
[25] POIZOT E,MÉAR Y. eCSedtrend:a new software to improve sediment trend analysis[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2008,34(7):827-837.
[26] 贾建军,程鹏,髙抒. 利用插值试验分析采样网格对粒度趋势分析的影响[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2004,24(3):135-141. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2004.03.017
[27] 乔淑卿,石学法,王国庆,等. 渤海底质沉积物粒度特征及输运趋势探讨[J]. 海洋学报,2010,32(4):139-147.
[28] POIZOT E,MÉAR Y,THOMAS M,et al. The application of geostatistics in defining the characteristic distance for grain size trend analysis[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2006,32:360-370.
[29] Brown B E. Coral reefs of the Andaman Sea-an integrated perspective[C]//Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review, Vol. 45. New York: Taylor & Francis, 2007: 173-194.
[30] RAO P S,RAMASWAMY V,THWIN S. Sediment texture distribution and transport on the Ayeyarwady continental shelf,Andaman Sea[J]. Marine Geology,2005,216:239-247. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2005.02.016
[31] 程鹏,高抒. 北黄海西部海底沉积物的粒度参数特征和净输运趋势[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2000,31(6):604-605.
[32] WYRTKI K. Physical oceanography of the Indian Ocean[C]// The Biology of the Indian Ocean. Berlin: Springer Verlag, 1973: 18-36.
[33] RAMASWAMY V,RAO P S,RAO K H,et al. Tidal influence on suspended sediment distribution and dispersal in the northern Andaman Sea and Gulf of Martaban[J]. Marine Geology,2004,208:33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2004.04.019
[34] VARKEY M J,MURTY V S N,SURYANARAYANA A. Physical oceanography of the Bay of Bengal and Andaman Sea[J]. Oceanography and Marine Biology:An Annual Review,1996,34:1-70.
[35] SUWANNATHATSA S,WONGWISES P,VONGVISESSOMJAI S,et al. Phytoplankton tracking by oceanic model and satellite data in the Bay of Bengal and Andaman Sea[J]. APCBEE Procedia,2012,2:183-189. doi: 10.1016/j.apcbee.2012.06.033
-



 下载:
下载: