Hydrochemical and hydrogen and oxygen isotope characteristics of subsurface water in the Maqu Plateau
-
摘要:
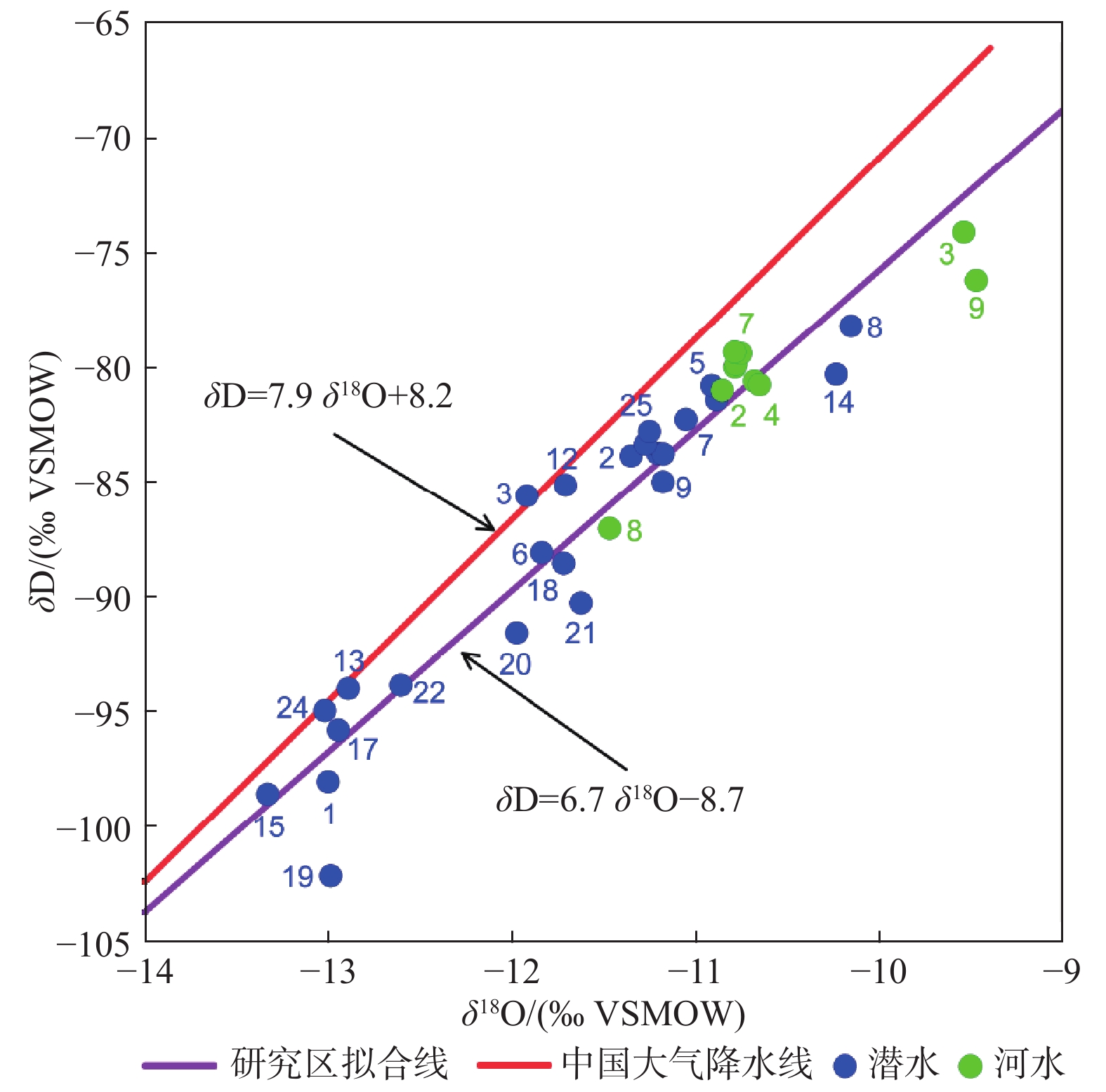
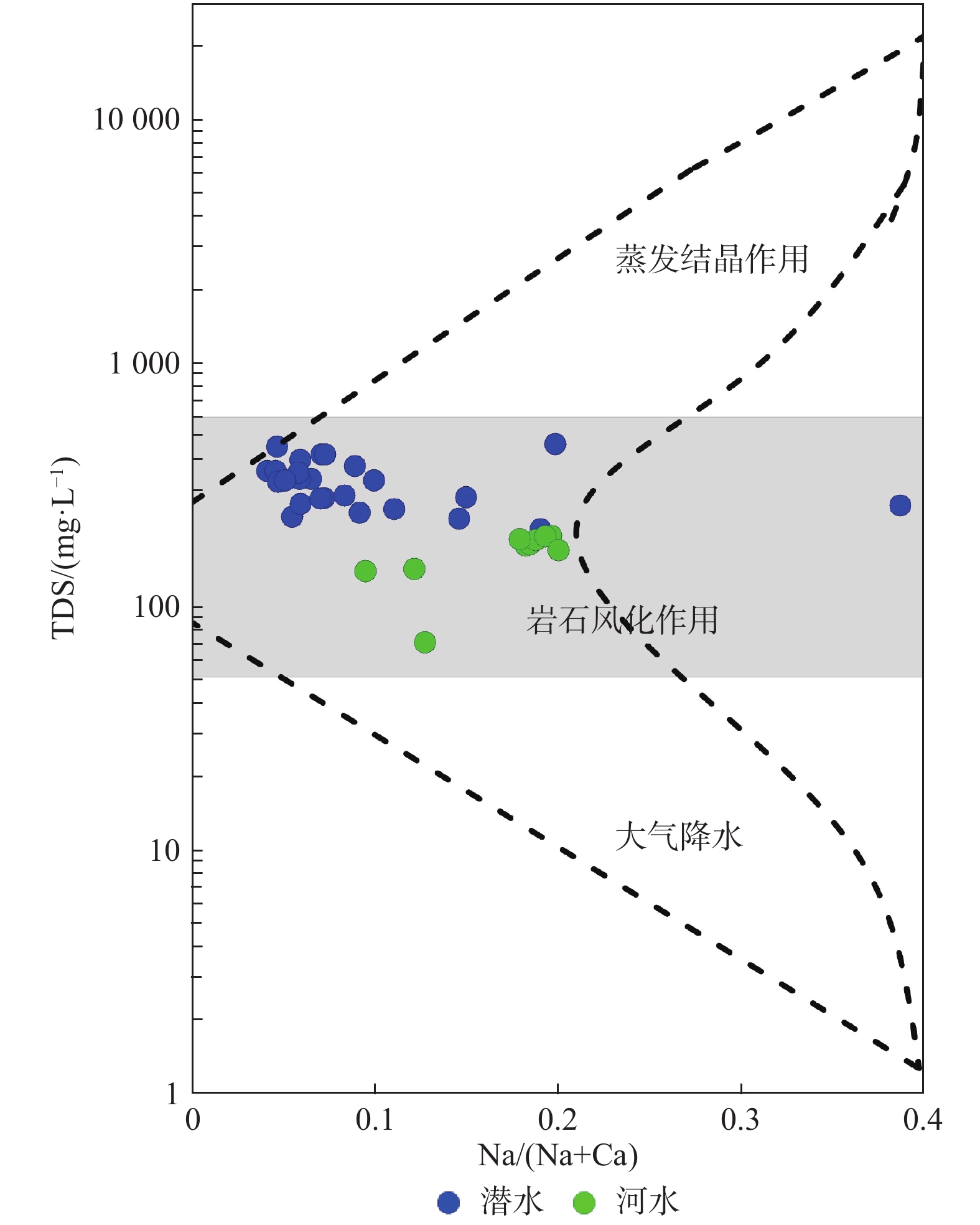
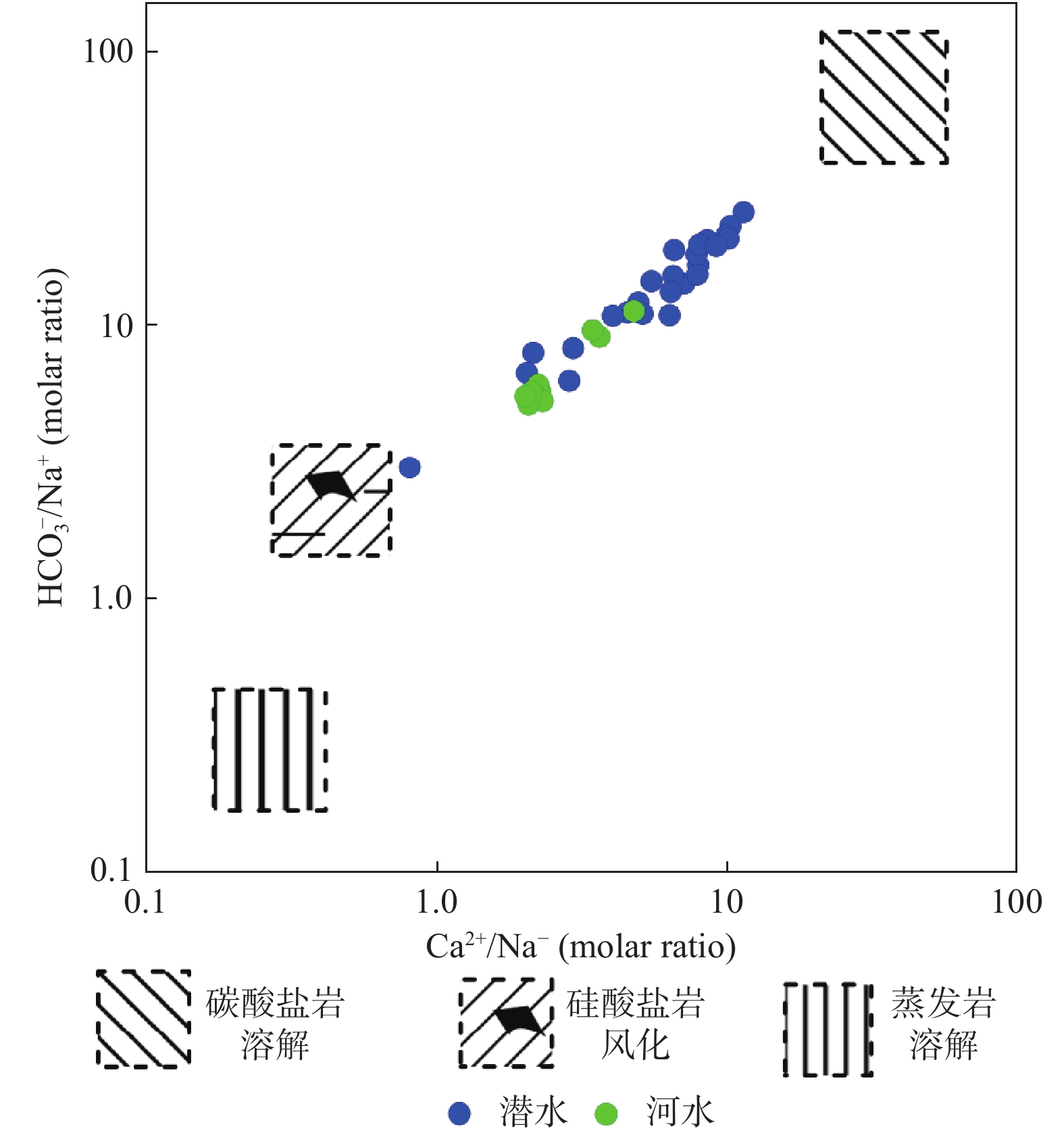
玛曲高原区地下水是黄河的重要补给水源,然而其水化学特征及形成机理认识还十分有限。通过采集玛曲潜水、河水和黄河河道沉积物,系统研究了玛曲高原区地下水水化学、同位素特征以及水文地球化学过程。结果表明:河水和潜水的溶解性总固体含量低,分别为72~195 mg/L和207~459 mg/L,水化学成分以Ca2+和
${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ Abstract:Groundwater is an important source of recharge to the Yellow River in the area of the Maqu Plateau, but little is known about the groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and the formation mechanism. Phreatic water samples, surface water samples and sediment samples were collected from the study area to investigate their hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics and hydrogeochemical processes. The results show that river water and phreatic water samples have low salinity with Ca2+ and
${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ -
Key words:
- the Yellow River catchment areas /
- Maqu Plateau /
- stable isotopes /
- water-rock interactions /
- aquifer
-

-
表 1 研究区水化学特征
Table 1. Hydrochemical eigenvalues of the study area
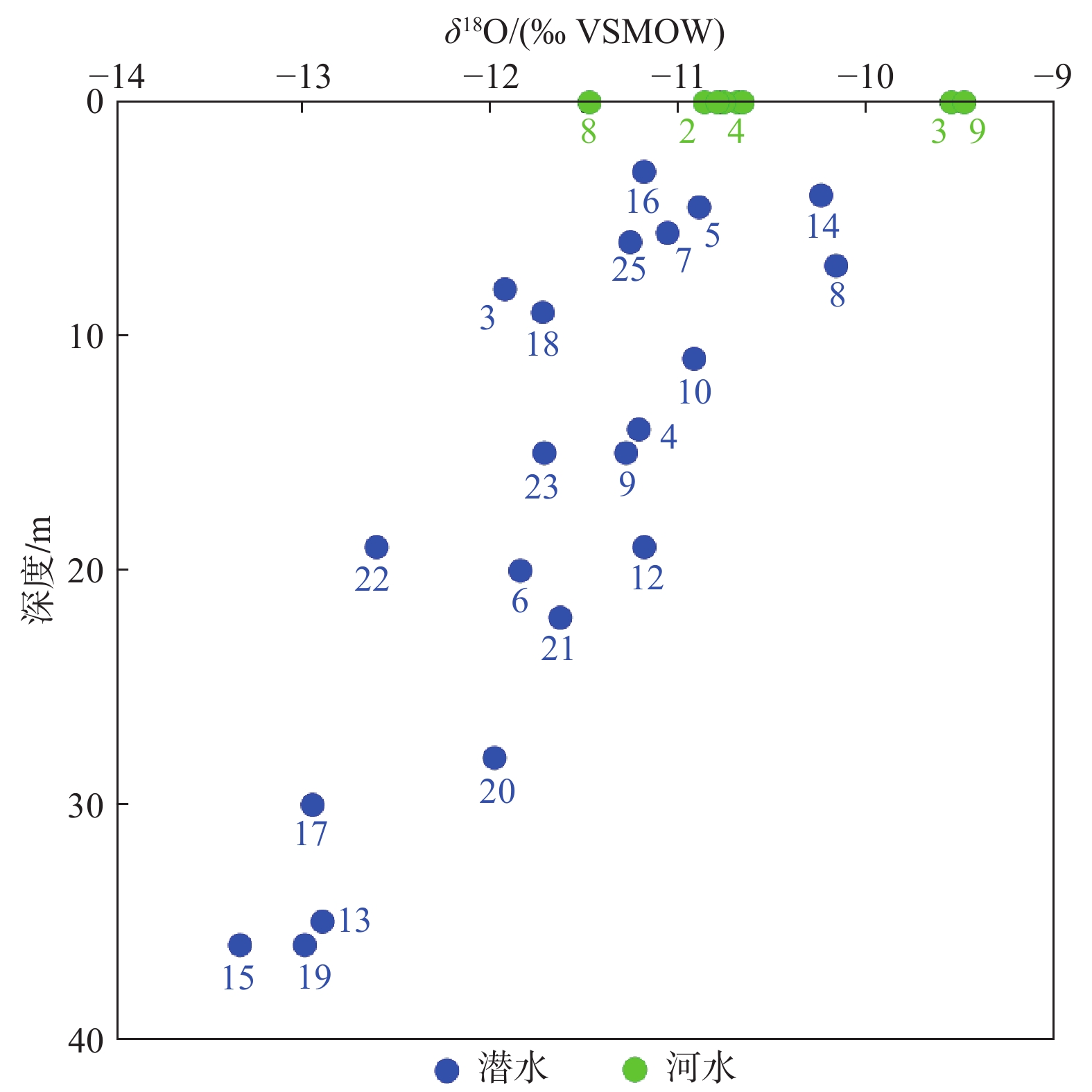
参数 潜 水 河 水 最小值 最大值 均值 最小值 最大值 均值 井深/ m 3 36 16.5 − − − 水温/ ℃ 5.7 10.1 7.3 16.9 20.8 19.4 pH 6.8 8 7.5 7.68 8.78 8.35 ORP/ mV −98 95.7 −15.1 25.4 81.1 53.2 TDS/(mg·L−1) 207 459 320 72.0 195 165 Na+/(mg·L−1) 5.7 36.2 12 5.31 13.6 10.4 Ca2+/(mg·L−1) 45.1 182 106 31.6 49.8 44.3 K+/(mg·L−1) 1.3 18.7 4.4 1.29 1.64 1.43 Mg2+/(mg·L−1) 7.8 27.2 14.0 4.69 13.9 11.21 Cl−/(mg·L−1) 4.0 15.2 8.0 2.83 10.2 7.83  /(mg·L−1)
/(mg·L−1)
3.5 90.6 18.5 5.05 19.2 14.8  /(mg·L−1)
/(mg·L−1)
0.0 10.1 3.5 0.00 4.63 2.33  /(mg·L−1)
/(mg·L−1)
258 601 382 136 199 175 Fe2+/(mg·L−1) 0.0 2.6 0.4 0.01 0.09 0.03  −N/(mg·L−1)
−N/(mg·L−1)
0.0 0.9 0.2 0.01 0.14 0.04 As/(μg·L−1) 0.46 17.7 4.40 1.07 3.05 1.65 FeTal/(μg·L−1) 11.3 3980 754 14.3 97.2 43.0 MnTal/(μg·L−1) 0.5 1080 323 3.56 201 31.2 TOC/(mg·L−1) 0.8 8.1 2.6 1.76 6.84 3.26 δ18O/‰ −13.3 −10.2 −11.8 −11.5 −9.48 −10.6 δD/‰ −102 −78.2 −88.0 −87.0 −74.1 −79.8 SI方解石 −0.3 0.8 0.2 −0.31 0.97 0.60 SI白云石 −1.5 0.8 −0.4 −1.15 1.48 0.86 表 2 研究区水化学成分相关矩阵
Table 2. Correlation coefficient matrix of groundwater chemical compositions in study area
TDS 
Cl− 
Ca2+ K+ Mg2+ Na+ TDS 1 0.94** 0.60** 0.80** 0.96** −0.12 0.81** −0.13 
1 0.44** 0.63** 0.95** −0.29 0.80** −0.27 Cl− 1 0.46** 0.50** −0.11 0.46** −0.04 
1 0.81** −0.06 0.71** −0.08 Ca2+ 1 −0.30 0.80** −0.33 * K+ 1 −0.36* 0.73** Mg2+ 1 −0.23 Na+ 1 注:**表示在 0.01 水平(双侧)上显著相关;*表示在 0.05 水平(双侧)上显著相关。 -
[1] 袁宏波, 王辉, 李晓兵, 等. 玛曲县天然草地沙化动态及现状分析[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报,2006,41(1):73 − 78. [YUAN Hongbo, WANG Hui, LI Xiaobing, et al. Analysis on desertification dynamics and present situation of the natural grassland in Maqu County[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University,2006,41(1):73 − 78. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4315.2006.01.018
[2] 王素萍, 宋连春, 韩永翔, 等. 玛曲气候变化对生态环境的影响[J]. 冰川冻土,2006,28(4):556 − 561. [WANG Suping, SONG Lianchun, HAN Yongxiang, et al. Impacts of climate change on ecological environment in Maqu grassland, Gansu[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2006,28(4):556 − 561. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2006.04.015
[3] 王建兵, 王振国, 吕虹. 黄河重要水源补给区草地退化的气候背景分析—以玛曲县为例[J]. 草业科学,2008,25(4):23 − 27. [WANG Jianbing, WANG Zhenguo, LU Hong. Climate background analysis of grassland degradation in the Yellow River important water source supply area—a case study of Maqu County[J]. Pratacultural Science,2008,25(4):23 − 27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 韩海涛, 祝小妮. 气候变化与人类活动对玛曲地区生态环境的影响[J]. 中国沙漠,2007,27(4):608 − 613. [HAN Haitao, ZHU Xiaoni. Climate change and human activities of Maqu area and its impact on eco-environment[J]. Journal of Desert Research,2007,27(4):608 − 613. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2007.04.014
[5] 李晋昌, 王文丽, 胡光印, 等. 玛曲县土地利用/覆盖变化对区域生态系统服务价值的影响[J]. 中国环境科学,2010,30(11):1579 − 1584. [LI Jinchang, WANG Wenli, HU Guangyin, et al. Impacts of land use and land cover change on ecosystem service values in Maqu County[J]. China Environmental Science,2010,30(11):1579 − 1584. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 李文龙, 薛中正, 郭述茂, 等. 基于3S技术的玛曲县草地植被覆盖度变化及其驱动力[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2010,46(1):85 − 90. [LI Wenlong, XUE Zhongzheng, GUO Shumao, et al. Vegetation coverage changes and analysis of the driving forces in Maqu county based on 3S technology[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University(Natural Sciences),2010,46(1):85 − 90. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 高建飞, 丁悌平, 罗续荣, 等. 黄河水氢、氧同位素组成的空间变化特征及其环境意义[J]. 地质学报,2011,85(4):596 − 602. [GAO Jianfei, DING Tiping, LUO Xurong, et al. δD and δ18O variations of water in the Yellow River and its environmental significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2011,85(4):596 − 602. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 戚登臣, 李广宇, 陈文业, 等. 黄河上游玛曲县天然草场退化现状、成因及治理对策[J]. 中国沙漠,2006,26(2):202 − 207. [QI Dengchen, LI Guangyu, CHEN Wenye, et al. Present status, causes and control countermeasures of natural grassland degeneration in Maqu County[J]. Journal of Desert Research,2006,26(2):202 − 207. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2006.02.008
[9] 盛海洋, 杨学俊, 白宪洲, 等. 甘南玛曲县草地沙化遥感监测研究[J]. 水土保持研究,2007,14(5):67 − 70. [SHENG Hhaiyang, YANG Xuejun, BAI Xianzhou, et al. The romote sensing interpreter study on grassland desertification in Maqu County in south Gansu Province[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2007,14(5):67 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 《玛曲县志》编纂委员会. 玛曲县志(1991-2004)[M]. 兰州: 甘肃人民出版社, 2005: 134−232.
"Maqu County Chronicles" Compilation Committee. Maqu County Annals (1991-2004) [M]. Lanzhou: Gansu People's Publishing House, 2005: 134−232. (in Chinese)
[11] 杨爱丽. 地化学元素揭示的中晚全新世以来玛曲高原的成壤环境演变[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2015.
YANG Aili. The pedogenetic environment changes since the middle-late Holocene in the Maqu plateau reflected by geochemical elements[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 郑淑蕙, 侯发高, 倪葆龄. 我国大气降水的氢氧稳定同位素研究[J]. 科学通报,1983,28(13):801 − 806. [ZHENG Shuhui, HOU Fagao, NI Baoling. A study on stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of atmospheric precipitation in China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,1983,28(13):801 − 806. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/csb1983-28-13-801
[13] PANG Z H, KONG Y L, LI J, et al. An isotopic geoindicator in the hydrological cycle[J]. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science,2017,17:534 − 537. doi: 10.1016/j.proeps.2016.12.135
[14] CRAIG H. Isotopic variations in meteoric water[J]. Science,1961,133(1461):1702 − 1703.
[15] MAZOR E. Chemical and isotopic groundwater hydrology[M]. Marcel Dekker, 2004, 1-453.
[16] BATLLE A J, BANKS E W, BATELAAN O, et al. Groundwater residence time and aquifer recharge in multilayered, semi-confined and faulted aquifer systems using environmental tracers[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2017,546:150 − 165. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.12.036
[17] 王雨山, 李戍, 李海学, 等. 海原盆地地下水咸化特征和控制因素[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(4):10 − 17. [WANG Yushan, LI Shu, LI Haixue, et al. Groundwater salinization characteristics and controlling factors in the Haiyuan Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(4):10 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] SMEDLEY P L. Sources and distribution of arsenic in groundwater and aquifers[J]. Earth Sciences,2008:1 − 34.
[19] GIBBS R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry[J]. Science,1970,170(3962):1088 − 1090. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1088
[20] GAILLARDET J, DUPRE B, LOUVAT P, et al. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers[J]. Chemical Geology,1999,159(1/4):3 − 30.
[21] MUKHERJEE A, SCANLON B R, FRYAR A E, et al. Solute chemistry and arsenic fate in aquifers between the Himalayan foothills and Indian craton (including central Gangetic plain): Influence of geology and geomorphology[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2012,90:283 − 302. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.05.015
[22] 胡梦珺, 杨爱丽, 张文丽. 常量元素氧化物含量及其比值揭示的中晚全新世以来玛曲高原的环境演变[J]. 中国沙漠,2007,35(2):313 − 321. [HU Mengjun, YANG Aili, ZHANG Wenli. Environmental evolution since the Middle-Late Holocene in the Maqu Plateau reflected by constant element oxides content and ratios[J]. Journal of Desert Research,2007,35(2):313 − 321. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 郭华明, 郭琦, 贾永锋, 等. 中国不同区域高砷地下水化学特征及形成过程[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2013,35(3):83 − 96. [GUO Huaming, GUO Qi, JIA Yongfeng, et al. Chemical characteristics and geochemical processes of high arsenic groundwater in different regions of China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,2013,35(3):83 − 96. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2013.03.008
[24] SMEDLEY P L and KINNIBURGH D G. A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2002,17(5):517 − 568. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00018-5
[25] ERBAN L E, GORELICK S M, FENDORF S. Arsenic in the multi-aquifer system of the Mekong Delta, Vietnam: analysis of large-scale spatial trends and controlling factors[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2014,48(11):6081 − 6088.
[26] FENDORF S, MICHAEL H A, VAN GEEN A. Spatial and temporal variations of groundwater arsenic in South and Southeast Asia[J]. Science,2010,328(5982):1123 − 1127. doi: 10.1126/science.1172974
[27] 高存荣, 李朝星, 周晓虹, 等. 河套平原临河区高砷地下水分布及水化学特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2008,35(6):22 − 28. [GAO Cunrong, LI Chaoxing, ZHOU Xiaohong, et al. Occurrence and hydrochemical characteristics of As-rich groundwater in the Linhe district of the Hetao Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2008,35(6):22 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2008.06.006
[28] 李晓青. 黄河源区玛曲极端气候变化及其生态环境影响研究[J]. 环境保护,2017,45(5):45 − 50. [LI Xiaoqing. Study on the extreme climate change and it's ecological environment impact in Maqu area of the Yellow River[J]. Environmental Protection,2017,45(5):45 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 沈萌萌, 郭华明, 李晓萌, 等. 高砷含水层沉积物含铁矿物特性及其对砷的水文地球化学作用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(2):1 − 7. [SHEN Mengmeng, GUO Huaming, LI Xiaomeng, et al. Characteristics of Fe oxide minerals and their roles in arsenic hydrogeochemistry in high arsenic aquifer sediments[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(2):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] WANG Z, GUO H M, XIU W, et al. High arsenic groundwater in the Guide basin, northwestern China: Distribution and genesis mechanisms[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,640/641:194 − 206. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.255
[31] MCARTHUR J M, BANERJEE D M, HUDSON-EDWARDS K A, et al. Natural organic matter in sedimentary basins and its relation to arsenic in anoxic ground water: the example of West Bengal and its worldwide implications[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2004,19(8):1255 − 1293. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.02.001
-



 下载:
下载: