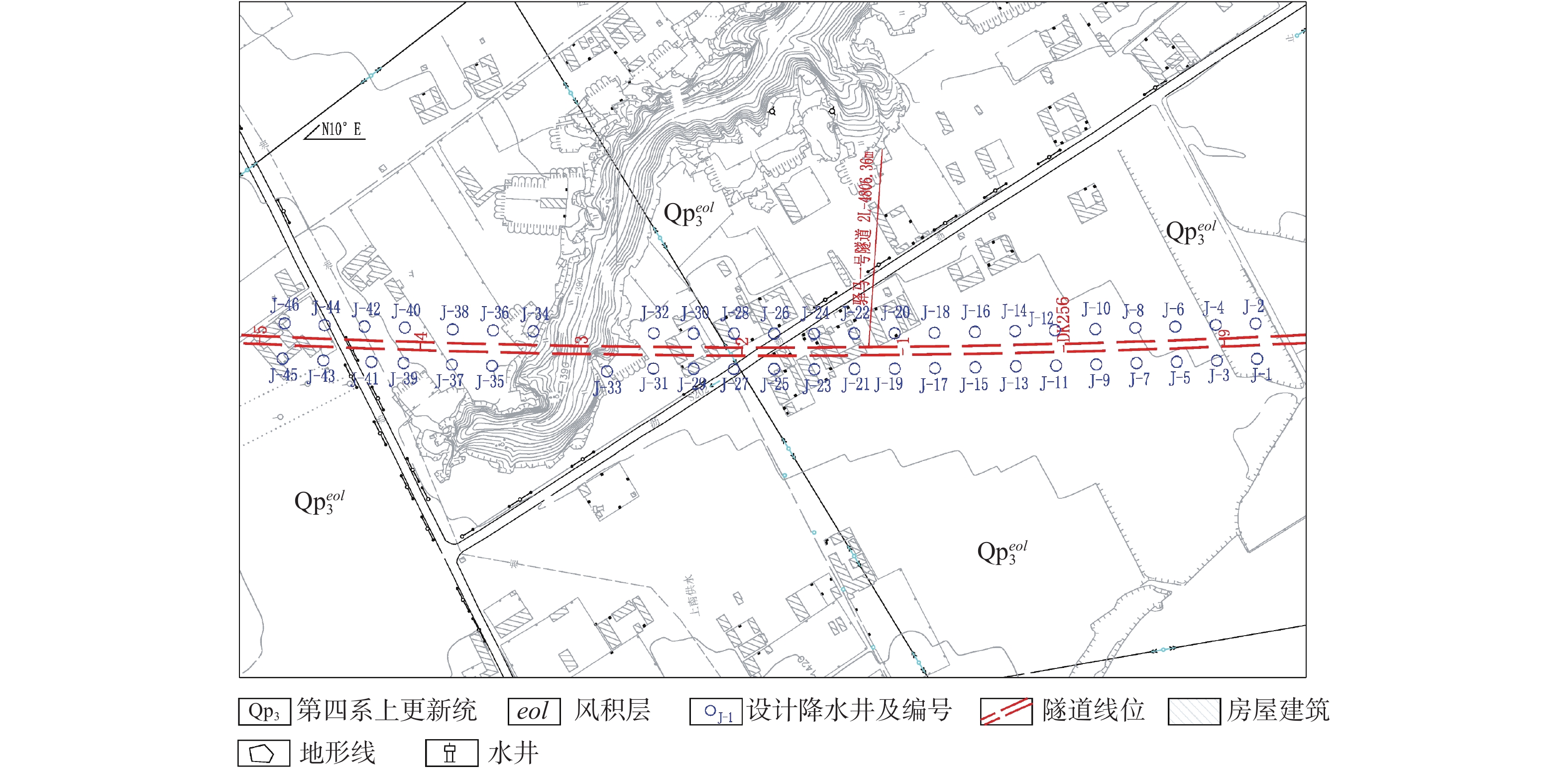
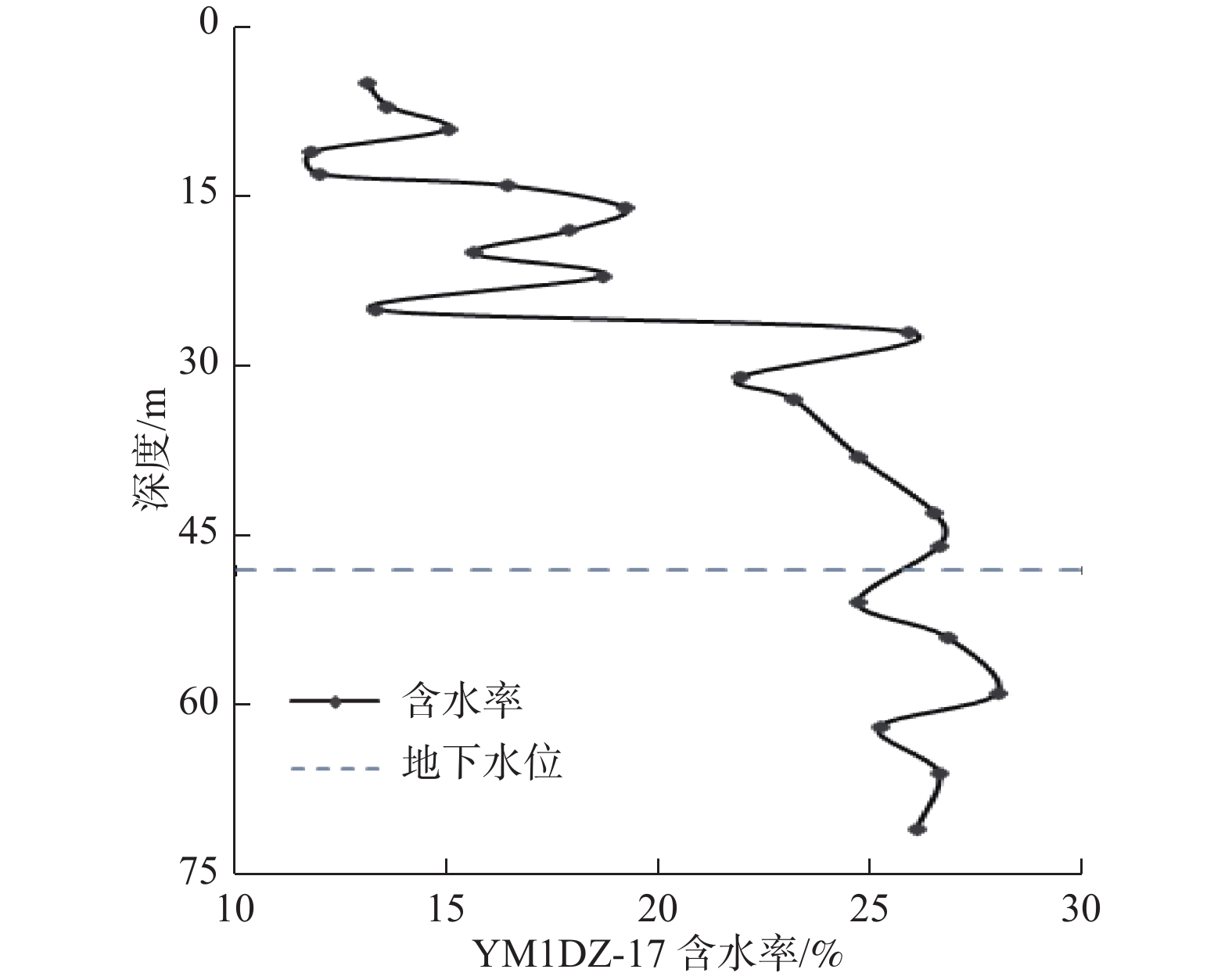
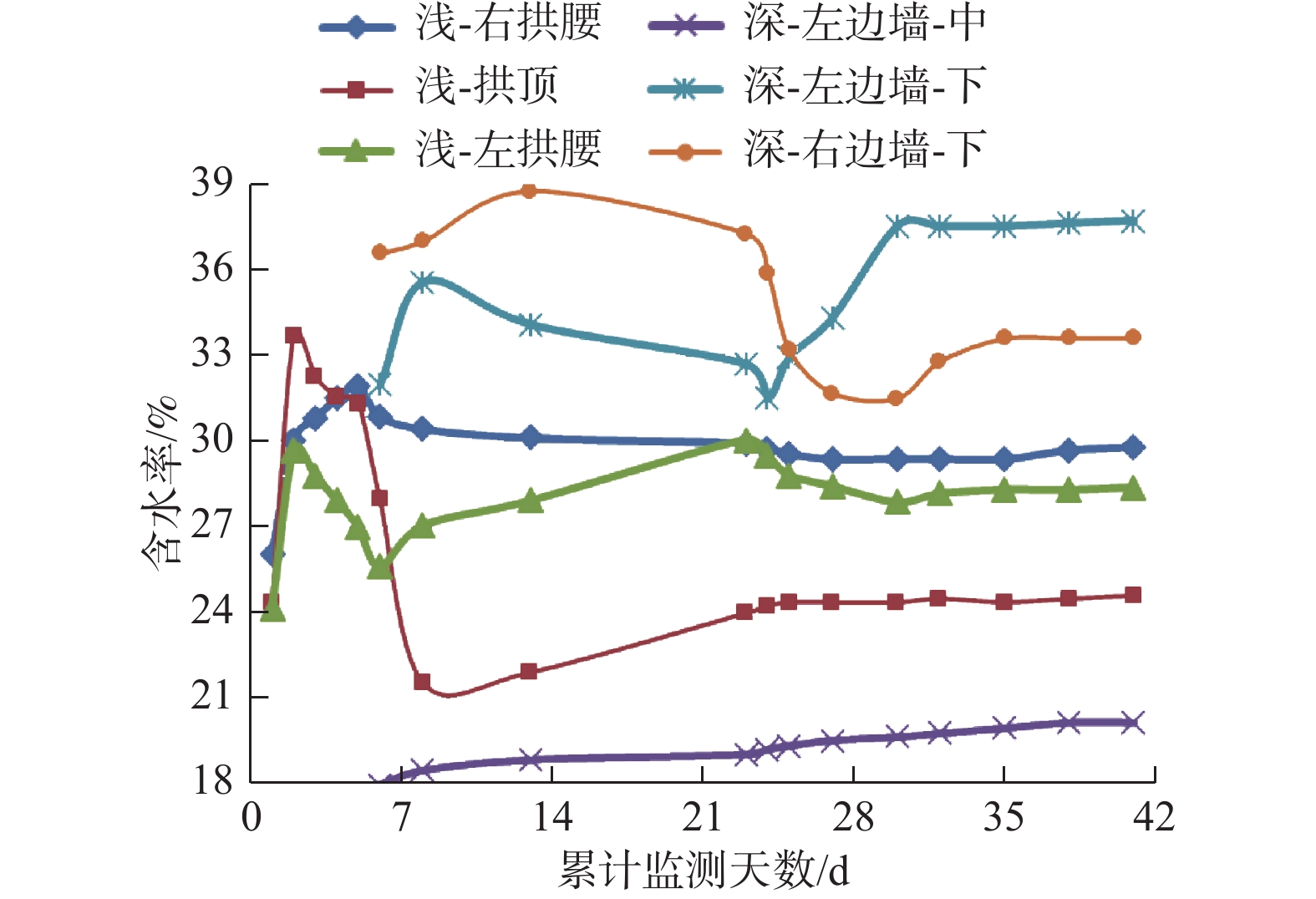
Characteristics of moisture content variation of loess under seepage and its influence on tunnel engineering
-
摘要:
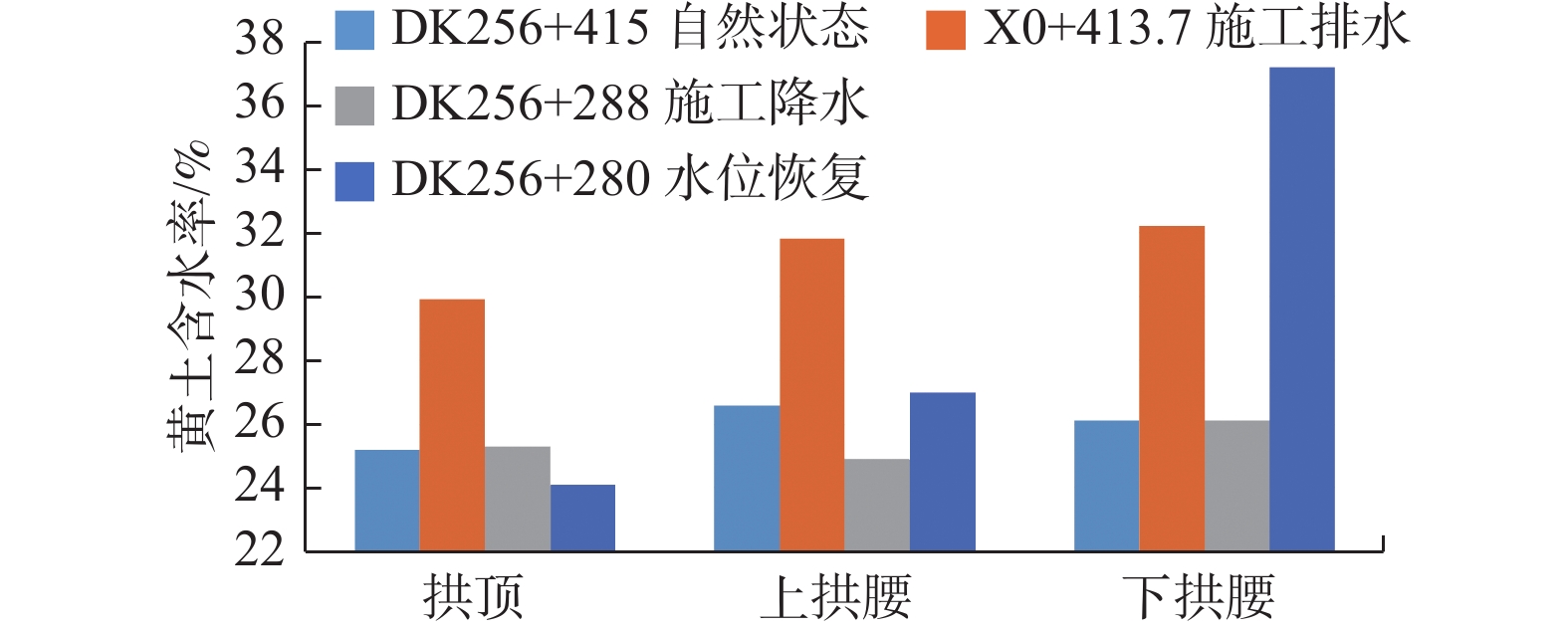
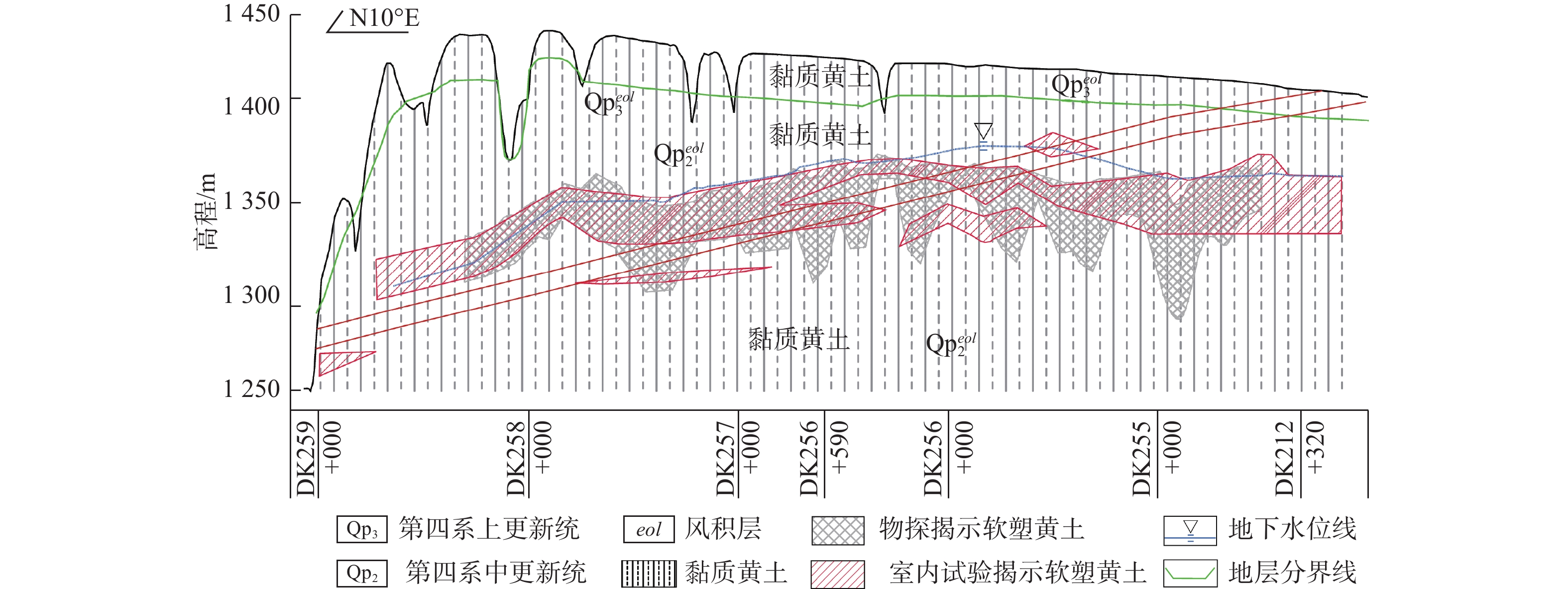
富水黄土隧道施工开挖后含水率增加对隧道工程施工影响较大,前人建立了多种以黄土含水率为指标的工程措施判别标准,但对于黄土含水率的变化原因及时空变化特征缺乏系统研究。银西高铁驿马一号隧道不同工况下含水率的变化特征表明,自然渗流状态下隧道洞身黄土含水率平均为25.9%,局部为软塑;施工排水阶段受渗涌水影响,黄土含水率平均上升到31.3%,下拱腰上升到32.2%,引起了隧底软化、掌子面滑塌失稳、围岩稳定性变差等问题;采取地表降水后,黄土含水率下降为25.4%,改善了黄土的物理性质,确保了隧道施工安全与进度;水位恢复后,黄土含水率平均上升到29.4%,拱顶与上拱腰变化较小,下拱腰达到了37.2%。研究认为地下水渗流变化将使得隧道洞身黄土含水率变幅达15%~33%,通过控制地下水渗流作用可以达到隧道安全施工的目的。
Abstract:The increase of moisture content after excavation of water-rich loess tunnel has a great influence on the construction of tunnel. Many discriminant standards of engineering measures based on loess moisture content were established by predecessors, but there is a lack of systematic researches on the causes and temporal and spatial characteristics of the change in loess moisture content. The variation characteristics of moisture content under different working conditions of the Yima No.1 Tunnel along the Xi'an-Yinchuan High-Speed Railway show that the average moisture content of loess in the tunnel body under the state of natural seepage is 25.9%, with some part being soft plastic. Under the influence of seepage and water gusher, the loess moisture content rises to 31.3% on the average, and the moisture content in the lower arch waist rises to 32.2%, which causes problems such as tunnel bottom softening, slide and instability of the tunnel face, and poor stability of surrounding rock. After the adoption of surface precipitation, the moisture content of loess decreases to 25.4%, which improves the physical properties of loess and ensures the safety and progress of tunnel construction. After the groundwater level is restored, the loess moisture content rises to 29.4% on the average. The loess moisture content of the arch roof and upper arch waist changes little, and that of the lower arch waist reaches 37.2%. It is believed that the variation of groundwater seepage will make the moisture content of loess range from 15% to 33%, and the safe construction of tunnel can be achieved by controlling groundwater seepage.
-
Key words:
- tunnel engineering /
- soft Loess /
- seepage /
- moisture content /
- groundwater /
- surface precipitation /
- temporal and spatial variation
-

-
表 1 洞内排水黄土含水率监测结果
Table 1. Monitoring results of moisture contentof the drained loess in the hole
/% 序号 断面里程 拱顶 上拱腰 下拱腰 平均值 1 X0+408.9 29.1 29.3 29.7 29.4 2 X0+413.7 29.9 31.8 32.2 31.3 3 X0+426.9 29.8 30.1 30.2 30.0 表 2 降水期间掌子面黄土含水率监测结果
Table 2. Monitoring results of loess moisture content in the tunnel face during extraction of water
/% 序号 断面里程 拱顶 上拱腰 下拱腰 平均值 1 DK256+288 25.3 24.9 26.1 25.4 2 DK256+587 26.8 27.4 28.1 27.4 3 DK256+978 23.8 26.2 27.9 26.0 表 3 驿马一号隧道不同时空黄土含水率
Table 3. Test results of loess moisture content in different time and space of the Yima No.1 tunnel
时间 里程位置 工况 测试方式 埋深/m 与隧道关系 黄土含水率
/%黄土含水率
平均值/%不同位置最大
变化值/%与上一阶段
对比2015年7月 DK256+415 自然渗流 钻孔取样 58 拱顶 25.2 25.9 1.4 − 62 上拱腰 26.6 66 下拱腰 26.1 2017年9月 X0+413.7 排水施工 掌子面取样 65 拱顶 29.9 31.3 2.3 上升20.8% 68 上拱腰 31.8 71 下拱腰 32.2 2019年3月 DK256+288 降水施工 掌子面取样 60 拱顶 25.3 25.4 3.0 下降18.8% 64 上拱腰 24.9 68 下拱腰 26.1 2019年5月 DK256+280 水位恢复 断面监测 60 拱顶 24.1 29.4 13.1 上升15.7% 64 上拱腰 27.0 68 下拱腰 37.2 -
[1] 张宏刚. 含水率变化对西安地区深基坑土钉支护稳定性的可靠度影响研究[J]. 水利与建筑工程学报,2019,17(4):32 − 38. [ZHANG Honggang. Impacts of moisture content on the reliability of soil nail support stability of deep foundation pit in Xi’an area[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering,2019,17(4):32 − 38. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1144.2019.04.006
[2] 郭安邦, 张吾渝, 刘凌霄, 等. 含水率对青海地区原状黄土力学性能的影响[J]. 水利水电技术,2019,50(1):10 − 17. [GUO Anbang, ZHANG Wuyu, LIU Lingxiao, et al. Influence of moisture content on mechanical properties of intact loess in Region Qinghai[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,2019,50(1):10 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 邢鲜丽, 李同录, 李萍, 等. 黄土抗剪强度与含水率的变化规律[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2014,41(3):53 − 59. [XING Xianli, LI Tonglu, LI Ping, et al. Variation regularities of loess shear strength with the moisture content[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2014,41(3):53 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 谢超. 泾阳南塬黄土渗透特性及黄土滑坡研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2016.
XIE Chao. Study on the permeability and landslide of loess in south Jingyang Plateau[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 赵景波, 王长燕, 刘护军, 等. 陕西洛川黄土剖面上部土层水分入渗规律与含水条件研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2010,37(1):124 − 129. [ZHAO Jingbo, WANG Changyan, LIU Hujun, et al. A study of water infiltration and water-bearing condition of the L1—S4 layers in Luochuan, Shaanxi[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2010,37(1):124 − 129. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.01.025
[6] 习羽, 李同录, 江睿君, 等. 陇东黄土工程地质分层及其物理特性[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(4):67 − 72. [XI Yu, LI Tonglu, JIANG Ruijun, et al. Engineering geological stratigraphy and physical properties of the loess in eastern Gansu[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(4):67 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 李寿福. 黄土隧道渗漏水病害治理方法研究[J]. 甘肃科技,2008,24(8):107 − 109. [LI Shoufu. Study on the control method of seepage leakage disease in Loess tunnel[J]. Gansu Science and Technology,2008,24(8):107 − 109. (in Chinese)
[8] 王新东. 高含水率黄土大断面隧道变形特性及施工方法[J]. 铁道建筑,2018,58(5):59 − 61. [WANG Xindong. Deformation characteristics and construction method for large section loess tunnel with high water content[J]. Railway Engineering,2018,58(5):59 − 61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 陈福江. 黄土隧道围岩含水量变化对隧道形态影响的研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2008: 1−2.
CHEN Fujiang. Study on the tunnel's modality impact of changes of surrounding rock water content at loess tunnel[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2008: 1−2. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 赵永虎, 罗浩洋, 苗学云, 等. 黄土隧道围岩含水率变化及拱架受力特征研究[J]. 铁道标准设计,2019,63(4):128 − 131. [ZHAO Yonghu, LUO Haoyang, MIAO Xueyun, et al. Research on the characteristics of steel arch stress and variation of water content of loess tunnel surrounding rock[J]. Railway Standard Design,2019,63(4):128 − 131. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 张晓宇. 银西高铁软塑黄土隧道地表降水试验研究[J]. 现代隧道技术,2019,56(3):154 − 160. [ZHANG Xiaoyu. Experimental study on ground dewatering of the soft plastic loess tunnel on the Yinchuan-Xi’an railway[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology,2019,56(3):154 − 160. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 陈鹤, 管振祥, 乔春生. 富水黄土隧道的开挖监控及变形判别[J]. 岩土工程界,2002(10):44 − 46. [CHEN He, GUAN Zhenxiang, QIAO Chunsheng. Excavation controlling and deformation identifying of water-rich loess tunnels[J]. Geotechnical Engineering World,2002(10):44 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 刘平贵, 李雪菊. 黄土高原缺水的地质环境及找水途径[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2001,28(3):18 − 22. [LIU Pinggui, LI Xueju. Geological environment deficient in water and way to seek water in the loess plateau[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2001,28(3):18 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2001.03.005
[14] 刘彤. 黄土地区公路隧道渗漏水分析[J]. 路基工程,2007(3):16 − 17. [LIU Tong. Analyze the leakage water of highway tunnel in loess zone[J]. Subgrade Engineering,2007(3):16 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8825.2007.03.008
[15] 杨晓华, 王航, 张小荣. 黄土软岩隧道渗水病害成因与防治对策研究[J]. 公路交通科技(应用技术版),2007,3(5):5 − 7. [YANG Xiaohua, WANG Hang, ZHANG Xiaorong. Study on the causes and prevention of seepage disease of soft rock tunnel in Loess[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development (Application technical edition),2007,3(5):5 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 张志勇, 杨晓华, 李宁军. 甘肃黄土公路隧道渗涌水类型划分[J]. 公路交通科技 (应用技术版),2006,2(5):40 − 43. [ZHANG Zhiyong, YANG Xiaohua, LI Ningjun. Classification of infiltration and water gusher in loess highway tunnel in Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development (Application technical edition),2006,2(5):40 − 43. (in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载: