Influence of hydrodynamic factors on the migration of arsenic in river sand: Column experiment and models
-
摘要:
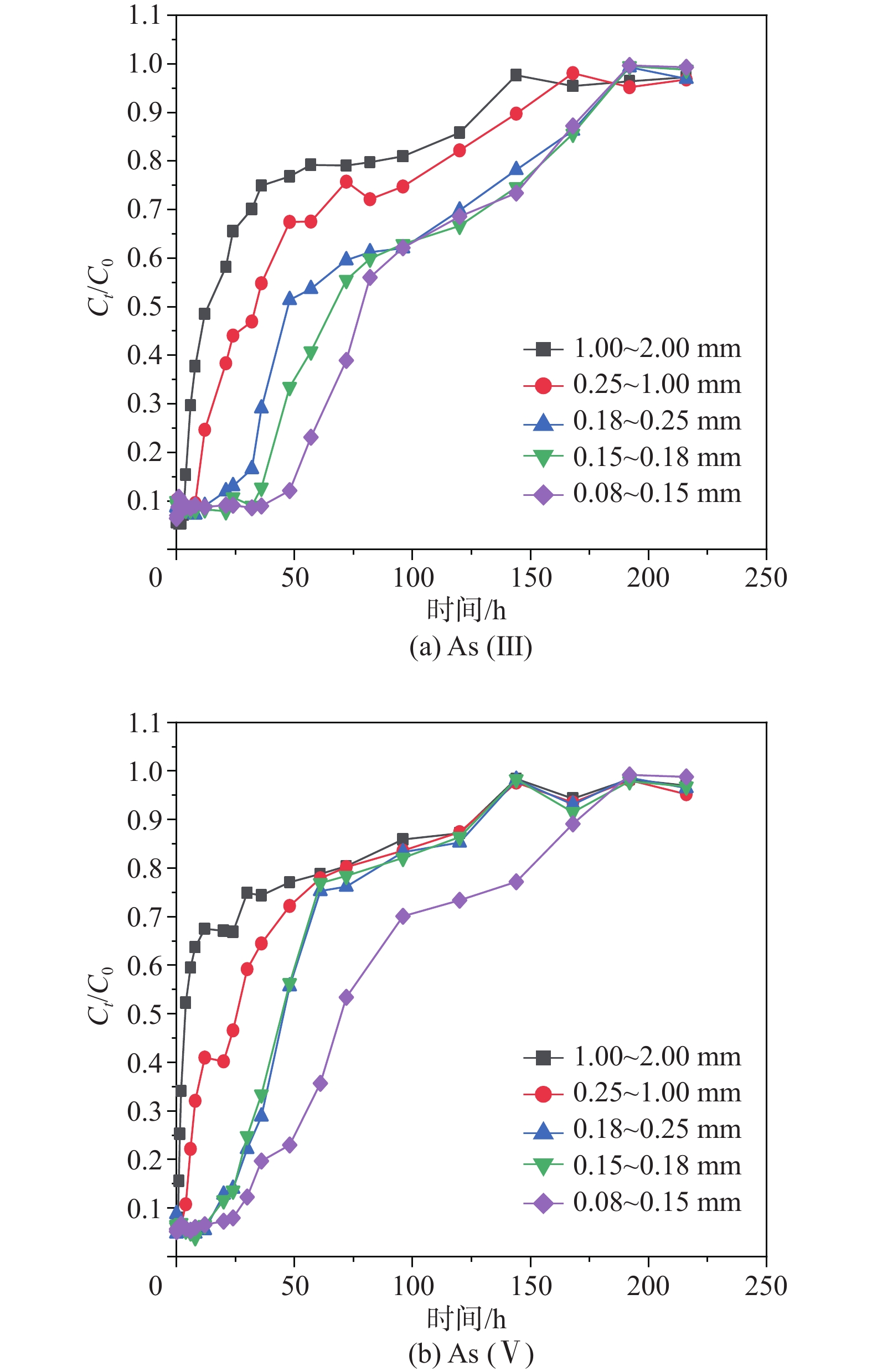
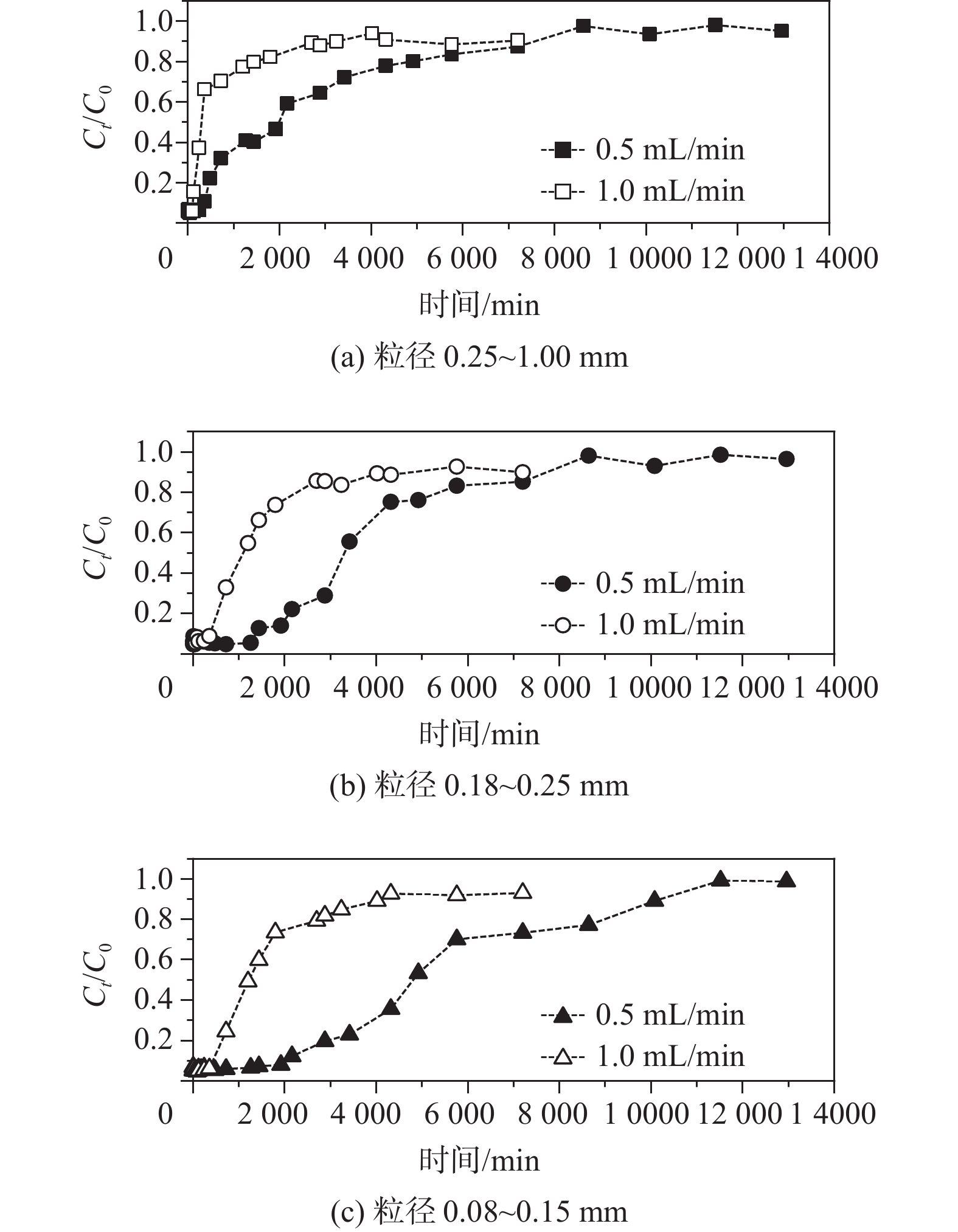
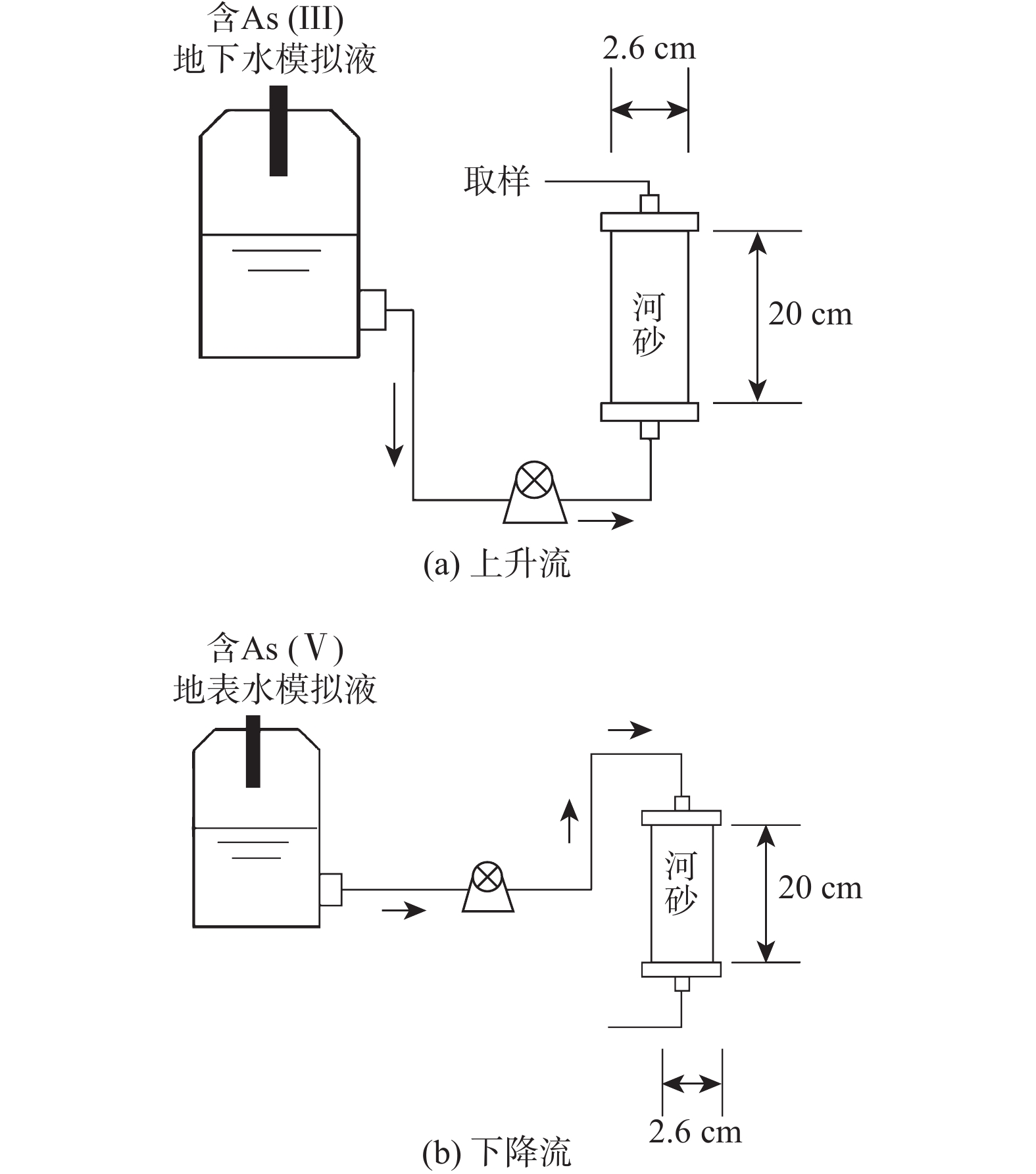
河岸带作为一种典型的地下水-地表水相互作用带,不同水动力学条件下砷在该作用带中的行为较少有研究报道。基于此,采集河岸带河砂开展室内柱试验,分析不同水动力因素(包括流速和粒径)对砷在河砂中迁移的影响并建立相关模型。结果表明:(1) 0.5 mL/min流速下,河砂对As(V)的吸附速度和达到平衡所需的时间均比As(III)快,且粒径越小,该现象越明显;1.0 mL/min流速下,不同粒径的河砂对As(V)的吸附速度随粒径的增大而增大,对As(III)的吸附则没有明显差异;(2) 相同粒径的填充柱中,河砂对As(III)和As(V)的吸附能力均随流速的增加而降低;(3)不同流速和粒径条件下,As(III)和As(V)在砂柱中的迁移过程均更符合Thomas模型,拟合R2高于相同条件下Yoon-Nelson和Adams-Bohart模型。其中,低流速下,Thomas模型对0.15~0.25 mm粒径中As(III)和As(V)迁移过程拟合的R2(≥0.94)显著优于1.00~2.00 mm的较大粒径;高流速下,该模型对不同粒径中砷迁移过程的拟合R2差异不大。研究有助于加深对地下水-地表水相互作用下水动力因素对砷迁移转化规律影响的认识,并丰富和完善高砷地下水形成的机制理论。
Abstract:The riparian zone is a typical groundwater-surface water interaction zone, and there are few research reports on the behavior of arsenic in this interaction zone under different hydrodynamic conditions. In this study, the river sand samples from the riparian zone are collected to carry out indoor column experiments, the influence of different hydrodynamic factors (including flow velocity and particle size) on the migration of arsenic in the river sand are analyzed, and related models are established. The results show that (1) at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min, the adsorption rate of the river sand on As(V) and the time required to reach an equilibrium state are both faster than those on As(III), and the smaller the particle size, the more obvious the phenomenon; at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min, the adsorption rate of the river sand with different particle sizes on As(V) increases with the increasinng particle size, but there is no significant difference in the adsorption of As(III). (2) In a packed column filled with sand of the same particle size, the adsorption capacity of the river sand for As(III) and As(V) decreases with the increasing flow velocity. (3) Under the conditions of different flow rates and particle sizes, the migration processes of As(III) and As(V) in the sand column are more in line with the Thomas model, and the fitting R2 are higher than those of the Yoon-Nelson and Adams-Bohart models under the same conditions. Among them, at low flow rates, the Thomas model fitting R2 (≥0.94) to the migration processes of As(III) and As(V) in the particle size of 0.15−0.25 mm are significantly better than that of the larger particle size of 1.00−2.00 mm. At high flow rates, the model has little difference in fitting R2 to the migration process of arsenic in different particle sizes.
-
Key words:
- arsenic /
- river sand /
- different particle sizes /
- different flow rates /
- column experiment
-

-
表 1 河砂化学组分
Table 1. Chemical composition of river sand
成分 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO K2O MgO MnO Na2O TiO2 含量/% 90.69 5.91 1.51 0.32 1.62 0.15 0.06 0.14 0.17 表 2 模拟液相关化学性质和组分
Table 2. Chemical composition of simulated solution
模拟液 化学性质 组分/(mg·L−1) pH Eh/
mVDO/(mg·L−1) EC/(μS·cm−1) K+ Ca2+ Na+ Mg2+ Cl− 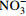


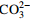
地下水 8.27 253.7 <2.00 254.0 0.312 59.53 4.18 7.61 9.52 3.54 15.66 179.7 - 地表水 7.72 293.5 7.44 221.5 1.414 50.45 1.16 7.36 10.16 10.83 17.36 125.2 10.97 表 3 Br-示踪柱试验参数和结果
Table 3. Experimental parameters and results of sand column using Br- as a tracer
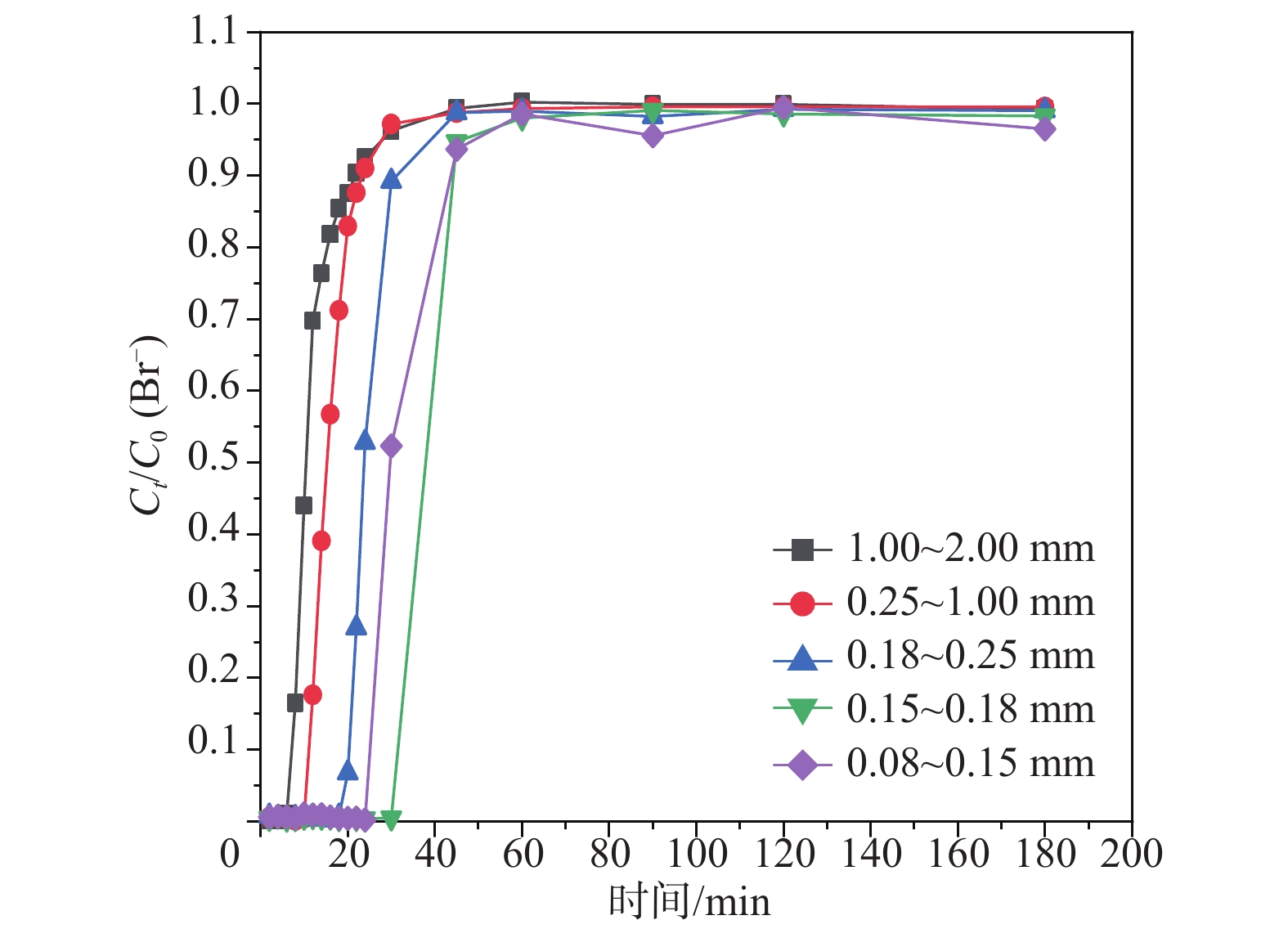
粒径/mm 流速/(mL·min−1) 河砂质量/g 床体积/cm3 穿透时间/min 孔隙体积/PV 回收率/% 1.00~2.00 0.5 131.2485 33.0 30 27.3 99.85±0.4 0.25~1.00 0.5 133.0719 29.0 30 31.0 99.54±0.1 0.18~0.25 0.5 128.4681 27.5 45 49.1 98.90±0.4 0.15~0.18 0.5 125.4052 25.0 45 54.0 98.52±0.5 0.08~0.15 0.5 123.7817 22.0 60 81.8 97.56±1.8 表 4 模型参数
Table 4. Model parameters
砷 粒径/
mm流速/
(mL·min−1)qeq(exp) /
(mg·g−1)Y /
%Thomas模型 Yoon−Nelson模型 Adams−Bohart模型 Kth/
(mL·min−1·mg−1)qcal/
(mg·g−1)R2 KYN τ0.5/min R2 U0/
(cm·min−1)KAB N0/
(mg·L−1)R2 As
(III)1.00~2.00 0.5 0.0245 74.5 4.7131×10−4 0.0118 0.73 4.713×10−4 3521.222 0.72 0.0942 −1.03×10−3 86.0445 0.30 0.25~1.00 0.5 0.0258 68.4 4.6750×10−4 0.0144 0.87 4.675×10−4 3852.043 0.86 0.0942 −8.58×10−4 90.5948 0.47 0.18~0.25 0.5 0.0262 58.7 4.6082×10−4 0.0196 0.94 4.081×10−4 5039.767 0.94 0.0942 −1.05×10−3 92.3181 0.66 0.15~0.18 0.5 0.0251 54.6 4.8527×10−4 0.0206 0.95 4.853×10−4 5153.398 0.95 0.0942 −1.04×10−3 96.5882 0.72 0.08~0.15 0.5 0.0238 51.1 5.0669×10−4 0.0215 0.94 5.007×10−4 5381.936 0.94 0.0942 −1.11×10−3 98.3468 0.77 As
(V)1.00~2.00 0.5 0.0259 79.1 4.7135×10−4 0.0118 0.73 4.394×10−4 2079.840 0.68 0.0942 −6.96×10−4 92.1270 0.17 0.25~1.00 0.5 0.0233 71.9 4.6750×10−4 0.0145 0.87 5.052×10−4 3449.247 0.80 0.0942 −1.05×10−3 88.4562 0.35 0.18~0.25 0.5 0.0205 61.0 4.6081×10−4 0.0196 0.94 5.870×10−4 4308.115 0.90 0.0942 −1.46×10−3 89.0529 0.56 0.15~0.18 0.5 0.0213 61.8 4.8527×10−4 0.0206 0.95 5.870×10−4 4308.115 0.90 0.0942 −1.48×10−3 89.1980 0.56 0.08~0.15 0.5 0.0260 55.8 5.0669×10−4 0.0215 0.94 5.730×10−4 5059.386 0.97 0.0942 −1.58×10−3 91.2719 0.71 As
(III)0.25~1.00 1.0 0.0261 76.5 1.0600×10−3 0.0065 0.82 9.108×10−4 437.807 0.91 0.1884 −1.22×10−3 85.3488 0.09 0.18~0.25 1.0 0.0253 75.4 1.4100×10−3 0.0082 0.90 1.460×10−3 1042.281 0.89 0.1884 −1.72×10−3 80.1356 0.12 0.08~0.15 1.0 0.0275 74.2 1.1300×10−3 0.0100 0.76 1.080×10−3 1504.046 0.75 0.1884 −2.50×10−3 77.1731 0.29 As
(V)0.25~1.00 1.0 0.0236 78.5 7.8834×10−4 0.0124 0.77 7.883×10−4 1655.333 0.57 0.1884 −2.09×10−3 91.0646 0.33 0.18~0.25 1.0 0.0200 63.7 9.0418×10−4 0.0179 0.76 9.042×10−4 2300.545 0.76 0.1884 −2.65×10−3 90.7246 0.53 0.08~0.15 1.0 0.0197 60.6 9.5807×10−4 0.0192 0.81 9.581×10−4 2370.398 0.81 0.1884 −2.95×10−3 90.5542 0.54 -
[1] 袁晓芳, 邓娅敏, 杜尧, 等. 江汉平原高砷地下水稳定碳同位素特征及其指示意义[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(5):156 − 163. [YUAN Xiaofang, DENG Yamin, DU Yao, et al. Characteristics of stable carbon isotopes and its implications on arsenic enrichment in shallow groundwater of the Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2020,39(5):156 − 163. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] GUO H M, LIU Z Y, DING S S, et al. Arsenate reduction and mobilization in the presence of indigenous aerobic bacteria obtained from high arsenic aquifers of the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Environmental Pollution,2015,203:50 − 59. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.03.034
[3] 严克涛, 郭清海. 地下水环境中的硫代砷研究进展[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(6):132 − 141. [YAN Ketao, GUO Qinghai. Advances in thioarsenic in groundwater systems[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(6):132 − 141. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 张真, 董俊秀, 刘晓雯, 等. 东平湖表层沉积物中砷赋存特征及风险评价[J]. 环境化学,2020,39(11):3190 − 3199. [ZHANG Zhen, DONG Junxiu, LIU Xiaowen, et al. Arsenic speciation characteristics and risk assessment of surface sediment in Dongping Lake[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2020,39(11):3190 − 3199. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019082002
[5] 高存荣, 冯翠娥, 刘文波, 等. 地壳表层砷的循环与污染地下水模式[J]. 地球学报,2014,35(6):741 − 750. [GAO Cunrong, FENG Cuie, LIU Wenbo, et al. Patterns of arsenic cycle and groundwater arsenic contamination on the earth's surface[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2014,35(6):741 − 750. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2014.06.10
[6] 邬建勋, 余倩, 蒋庆肯, 等. 江汉平原高砷地下水与含水层沉积物的地球化学特征[J]. 地质科技情报,2019,38(1):250 − 257. [WU Jianxun, YU Qian, JIANG Qingken, et al. Geochemical characteristics of groundwater and aquifer sediments in high arsenic groundwater in Jianghan plain[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2019,38(1):250 − 257. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 张皓月, 刘文波, 张绪教, 等. 河套平原地下水中砷的空间变异特征及影响因素分析[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(1):192 − 199. [ZHANG Haoyue, LIU Wenbo, ZHANG Xujiao, et al. Analysis of spatial variability and influencing factors of arsenic in groundwater of Hetao Plain, Inner Mongolia[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(1):192 − 199. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 张扬, 郭华明, 贾永峰, 等. 内蒙古河套平原典型高砷区地下水中砷的演化规律[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(2):15 − 22. [ZHANG Yang, GUO Huaming, JIA Yongfeng, et al. Geochemical evolution of high arsenic groundwater in a typical area of the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(2):15 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] ZHI C S, CHEN H H, LI P, et al. Spatial distribution of arsenic along groundwater flow path in Chaobai River alluvial-proluvial fan, North China Plain[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2019,78(8):1 − 11.
[10] 张迪, 郭华明, 倪萍, 等. 氧化还原条件对地下水中砷释放迁移的影响: 以通榆县高砷地下水为例[J]. 第四纪研究,2014,34(5):1072 − 1081. [ZHANG Di, GUO Huaming, NI Ping, et al. Effect of redox conditions on arsenic release and transport in groundwater systems: a case study in the Tongyu County[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2014,34(5):1072 − 1081. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2014.05.16
[11] 沈萌萌, 郭华明, 李晓萌, 等. 高砷含水层沉积物含铁矿物特性及其对砷的水文地球化学作用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(2):1 − 7. [SHEN Mengmeng, GUO Huaming, LI Xiaomeng, et al. Characteristics of Fe oxide minerals and their roles in arsenic hydrogeochemistry in high arsenic aquifer sediments[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(2):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] AMARATHUNGA U, DIYABALANAGE S, BANDARA U G C, et al. Environmental factors controlling arsenic mobilization from sandy shallow coastal aquifer sediments in the Mannar Island, Sri Lanka[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2019,100:152 − 159. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.11.011
[13] KHAN T A, CHAUDHRY S A, ALI I. Thermodynamic and kinetic studies of As(V) removal from water by zirconium oxide-coated marine sand[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2013,20(8):5425 − 5440. doi: 10.1007/s11356-013-1543-y
[14] KHAN S A, IMTEAZ M A. Batch experiments on arsenic removal efficiencies through adsorption using synthetic and natural sand samples[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology,2021,18(8):2357 − 2364. doi: 10.1007/s13762-020-02999-0
[15] KHAN S A, IMTEAZ M A. Experimental studies on arsenic removal efficiencies through adsorption using different natural adsorbents[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution,2021,232(1):1 − 10.
[16] 何剑汶, 李文旭, 谌书, 等. 湖南桃江锰矿对溶液中As(Ⅴ)和As(Ⅲ)的去除及迁移行为对比[J]. 环境化学,2019,38(8):1801 − 1810. [HE Jianwen, LI Wenxu, CHEN Shu, et al. Comparison of removal and migration behavior of As(Ⅴ) and As(Ⅲ) in solution on Taojiang manganese ore, Hunan Province[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2019,38(8):1801 − 1810. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018102304
[17] 宫志恒, 郭亚丹, 李泽兵, 等. 改性稻壳去除废水中砷(Ⅴ)的动态吸附试验[J]. 工业水处理,2019,39(4):33 − 37. [GONG Zhiheng, GUO Yadan, LI Zebing, et al. Experiments on the dynamic adsorption of arsenic(Ⅴ) from wastewater by modified rice husks[J]. Industrial Water Treatment,2019,39(4):33 − 37. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11894/1005-829x.2019.39(4).033
[18] 段艳华, 甘义群, 郭欣欣, 等. 江汉平原高砷地下水监测场水化学特征及砷富集影响因素分析[J]. 地质科技情报,2014,33(2):140 − 147. [DUAN Yanhua, GAN Yiqun, GUO Xinxin, et al. Hydrogeochemistry and arsenic contamination of groundwater in the monitoring field, Jianghan plain[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2014,33(2):140 − 147. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 严怡君. 灌溉活动影响下非饱和带砷迁移转化规律研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2018
YAN Yijun. Study on arsenic migration and transformation in the unsaturated zone under the influence of irrigation[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] CAO H L, HE J R, XIE X J, et al. The effect of groundwater velocities on sulfidation of arsenic-bearing ferrihydrite: insight from column experiments[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2020,586:124827. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124827
[21] 李付兰, 倪萍, 郭华明, 等. 松嫩平原含水层沉积物特征及其对砷赋存态分布的影响[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2015,37(1):101 − 110. [LI Fulan, NI Ping, GUO Huaming, et al. Characteristics of aquifer sediments in Songnen plain and their influences on distribution of arsenic occurrence modes[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,2015,37(1):101 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2015.01.011
[22] 胡晓明, 冀泽华, 裴元生. 复合污染对Pb2+在固定床系统中的动态吸附过程影响及机制[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(2):446 − 454. [HU Xiaoming, JI Zehua, PEI Yuansheng. Effect of complex contaminants on dynamic adsorption behaviors of Pb2+ in fixed-bed system: breakthrough curve characteristics and parameters[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2020,33(2):446 − 454. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 安强, 朱胜, 缪乐, 等. 碱改柚子皮生物炭对水体中Mn(Ⅱ)的动态吸附研究[J]. 重庆大学学报,2021,44(6):96 − 108. [AN Qiang, ZHU Sheng, MIAO Yue, et al. The dynamic adsorption of Mn(Ⅱ) in water by alkali modified pomelo peel biochar[J]. Journal of Chongqing University,2021,44(6):96 − 108. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2020.291
[24] 袁林, 陈滢, 刘敏, 等. 改性纳米纤维素对磷的动态吸附及再生[J]. 化工进展,2020,39(7):2907 − 2914. [YUAN Lin, CHEN Ying, LIU Min, et al. Dynamic adsorption of phosphorus by modified nano cellulose and its regeneration[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2020,39(7):2907 − 2914. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] WANG Y H, HU H P, QIU X J. Fixed-bed column study for deep removal of copper(Ⅱ) from simulated cobalt electrolyte using polystyrene-supported 2-aminomethylpyridine chelating resin[J]. Journal of Central South University,2019,26(5):1374 − 1384. doi: 10.1007/s11771-019-4093-8
[26] 李琪, 李红艳, 张峰, 等. 废菌渣活性炭对Cr(Ⅵ)动态吸附及再生性能的研究[J]. 应用化工,2021,50(4):1000 − 1005. [LI Qi, LI Hongyan, ZHANG Feng, et al. Study on the dynamic adsorption and regeneration of Cr(Ⅵ) by mushroom residue activated carbon[J]. Applied Chemical Industry,2021,50(4):1000 − 1005. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2021.04.032
[27] AKSU Z, GÖNEN F. Biosorption of phenol by immobilized activated sludge in a continuous packed bed: prediction of breakthrough curves[J]. Process Biochemistry,2004,39(5):599 − 613. doi: 10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00132-8
[28] XU Zhe, CAI Jianguo, PAN Bingcai. Mathematically modeling fixed-bed adsorption in aqueous systems[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE A,2013,14(3):155 − 176. doi: 10.1631/jzus.A1300029
[29] YOON Y H, NELSON J H. Application of gas adsorption kinetics I. A theoretical model for respirator cartridge service life[J]. American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal,1984,45(8):509 − 516. doi: 10.1080/15298668491400197
[30] HAMDAOUI O. Dynamic sorption of methylene blue by cedar sawdust and crushed brick in fixed bed columns[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2006,138(2):293 − 303. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.04.061
[31] 梁美娜, 王敦球, 朱义年, 等. 纳米氧化铁/蔗渣活性炭对水中As(Ⅴ)的动态吸附研究[J]. 环境科学与技术,2017,40(7):97 − 102. [LIANG Meina, WANG Dunqiu, ZHU Yinian, et al. Dynamic adsorption characteristics of as(Ⅴ) to nanometer iron oxide/bagasse activated carbon composite adsorbent[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2017,40(7):97 − 102. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] WICKRAMASINGHE A D L, SHUKLA S P. Performance evaluation of a pellet based column bed for removal of a potentially carcinogenic Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon (PAH) from water[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2018,6(5):6012 − 6020. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2018.09.009
[33] 张强. 河水位波动下潜流带非均质性对氮的迁移转化过程影响研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019
ZHANG Qiang. The effects of heterogeneity of hyporheic zone on nitrogen migration and transformation under fluctuation of river level[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 王佳琪, 马瑞, 孙自永. 地表水与地下水相互作用带中氮素污染物的反应迁移机理及模型研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报,2019,38(4):270 − 280. [WANG Jiaqi, MA Rui, SUN Ziyong. Reactive transport and model of nitrogen pollutants in the surface water-ground water interaction zones: a review[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2019,38(4):270 − 280. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] 邓国鸿, 罗学刚, 杨嘉怡, 等. 改性废弃皮革对U(Ⅵ)的动态吸附[J]. 环境工程学报,2018,12(9):2602 − 2608. [DENG Guohong, LUO Xuegang, YANG Jiayi, et al. Dynamic adsorption of U(Ⅵ) by modified leather waste[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2018,12(9):2602 − 2608. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201803124
[36] 陈海儿, 朱宗强, 朱义年, 等. 桉树遗态Fe/C复合材料对水中Cr(Ⅵ)的动态吸附探讨[J]. 环境科学研究,2018,31(7):1303 − 1309. [CHEN Haier, ZHU Zongqiang, ZHU Yinian, et al. Column adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ) from aqueous solution by the porous BiomorphGenetic Fe/C composite with eucalyptus wood microstructure[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2018,31(7):1303 − 1309. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: