A study of dispersion experiment and simulation of the cohesive layered soil in the transition zone of the Jianghan Plain
-
摘要:
为研究江汉平原—大别山区过渡带黏性层状土中溶质迁移的规律,以保守性阴离子Br−为示踪剂,通过等温吸附试验、一维弥散试验、HYDRUS-1D软件模拟反演手段,研究了Br−在黏性层状土中的吸附参数、迁移规律,模拟反演其弥散参数。结果表明:(1)Freundlich模型和Langmuir模型均能较好的拟合吸附试验结果,随着土壤中黏粒比例的增大,土壤对Br−的饱和吸附量有所增加;(2)层状土中土壤质地与结构均会影响穿透曲线的形状,但一维饱和土柱中的弥散过程主要取决于含水介质系统中黏性颗粒的占比,黏粒的增加会对溶质运移产生阻碍作用;(3)通过HYDRUS-1D软件构建模型反演弥散参数,R2均大于0.991,拟合效果较好,分析发现层状土中无论土壤组成类型还是层厚及排序的影响,其本质都是改变了土壤的平均孔隙流速从而影响弥散作用,平均孔隙流速越小其弥散系数越小;(4)试验中粉质黏土弥散系数约为0.005~0.048 cm2/d,远远小于下部砂土弥散系数0.524~7.477 cm2/d,差值达到了至少两个数量级,表明研究区内厚层黏土为控制地层,会较大程度阻碍地下水中溶质运移,上部含水层中的污染物或有机质很难穿透该层向下迁移,具有良好的截污性能。研究结果对江汉平原过渡带地下水环境保护、水质治理具有重要应用价值。
Abstract:In order to study the law of solute migration in the cohesive stratified soil in the transitional zone of the Jianghan Plain-Dabie Mountain area, the conservative anion Br− is taken as a tracer agent in the isothermal adsorption experiment. One-dimensional dispersion experiment and HYDRUS-1D software simulation inversion method are used, and the adsorption parameter, migration law and migration inversion dispersion parameter of Br− in the cohesive stratified soil are examined. The results indicate that (1) both the Freundlich model and Langmuir model can well fit the adsorption experiment results, along with the increase of proportion of clay particle in the soil, and the saturation adsorption amount of the soil to Br- increases. (2) Both the soil texture and structure in the stratified soil can influence the shape of the breakthrough curve, but the dispersion process in one-dimensional saturation earth pillar mainly depends on the proportion of clay particles in the water-bearing media system, and the increase of clay particles will produce resistance for solute transport. (3) The invert dispersion parameter through the HYDRUS-1D software construction model, R2 is always larger than 0.991, and the fitting effect is good. The analysis results show that no matter soil component type or layer thickness and ordering in the stratified soil, the essence to influence dispersion function is by changing the average hole flow velocity of the soil, and the dispersion coefficient becomes smaller as the average hole flow velocity is smaller. (4) The silty clay dispersion coefficient in the experiment ranges from 0.005 to 0.048 cm2/d, far less than the sand dispersion coefficient 0.524 to 7.477 cm2/d in the under part, the difference value reaches two order of magnitudes, indicating that the thick layer clay soil is a control layer and will greatly resist solute transport of groundwater. The pollutant or organic matter in the upside water-bearing stratum is very hard to penetrate this layer and migrate downward, and this layer has very good sewage removal performance. The results are of great application value for groundwater environmental protection and water quality control in the transition zone of the Jianghan Plain.
-

-
表 1 研究区土壤颗粒分级数据
Table 1. Soil particle classification data in the study area
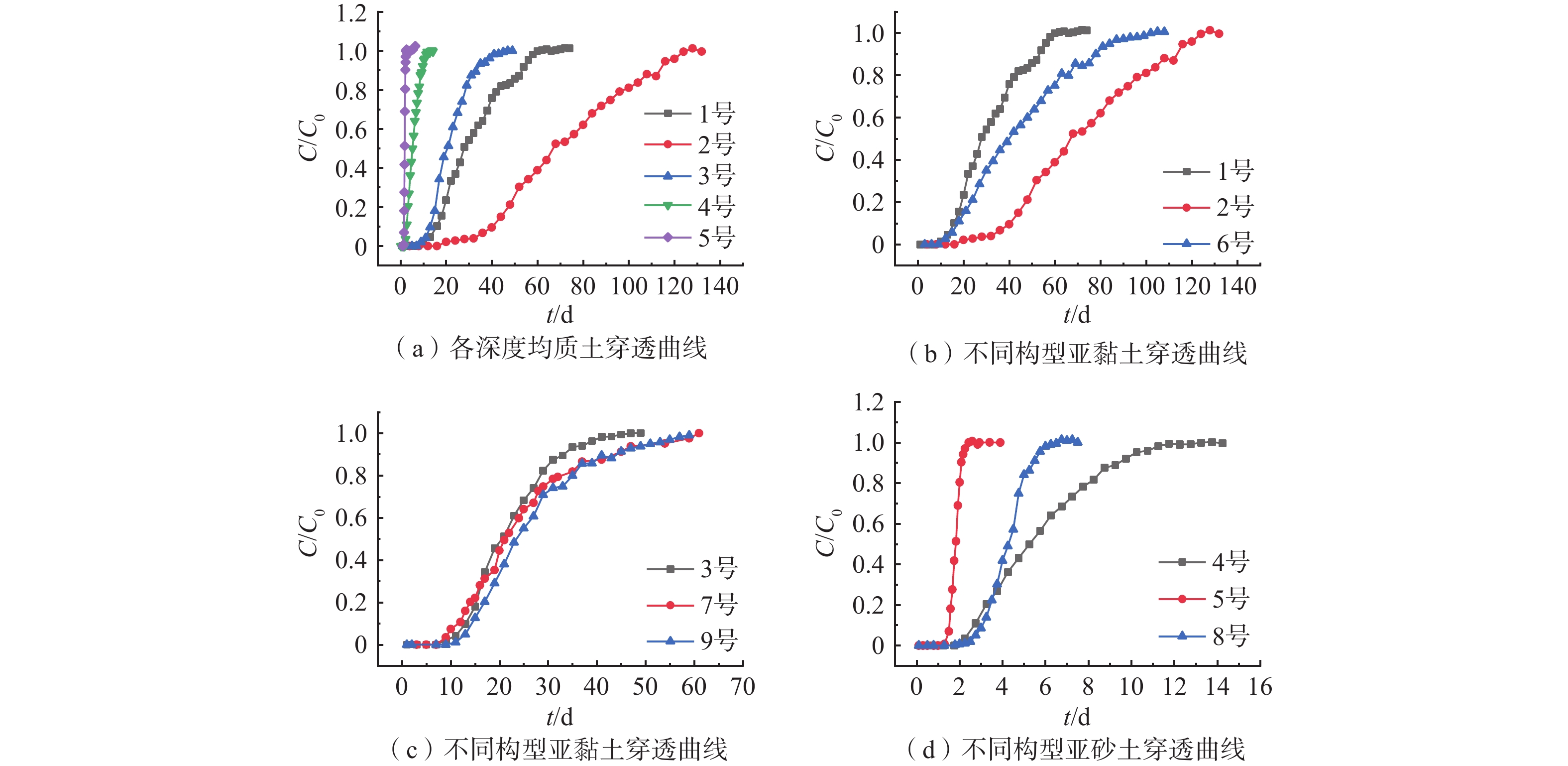
编号 深度/m 砂粒/% 粉粒/% 黏粒/% 土壤质地类型 1号 2.0 1.17 75.07 23.76 粉质亚黏土 2号 5.0 1.20 62.15 36.65 粉质黏土 3号 6.5 3.00 79.42 17.58 粉质亚黏土 4号 13.5 45.10 41.54 13.36 砂质亚黏土 5号 14.2 66.17 26.43 7.40 砂质亚砂土 表 2 试验各土柱具体构型
Table 2. Specific configurations of soil columns in the experiment
编号 总长度/ cm 土柱构型及厚度(由上至下) 1号 10 粉质亚黏土(10 cm) 2号 粉质黏土(10 cm) 3号 粉质亚黏土(10 cm) 4号 砂质亚黏土(10 cm) 5号 砂质亚砂土(10 cm) 6号 粉质亚黏土(7.6 cm)+粉质黏土(2.4 cm) 7号 粉质黏土(1.6 cm)+粉质亚黏土(8.4 cm) 8号 砂质亚黏土(5 cm)+砂质亚砂土(5 cm) 9号 粉质亚黏土(3.5 cm)+粉质黏土(1 cm)+
粉质亚黏土(5.5 cm)表 3 Freundlich方程和Langmuir方程拟合参数结果
Table 3. Fitting parameter results of Freundlich equation and Langmuir equation
样品 Langmuir模型拟合 Freundlich模型拟合 qm /(mg·g−1) KL R2 Kf /(L·mg−1) n/(L·mg−1) R2 1号 粉质亚黏土 5.988±0.433 0.065 0.970 0.836 2.488 0.921 2号 粉质黏土 10.169±1.995 0.023 0.957 0.557 1.809 0.927 3号 粉质亚黏土 3.831±0.373 0.052 0.960 0.451 2.324 0.924 4号 砂质亚黏土 3.522±0.230 0.039 0.987 0.324 2.113 0.986 5号 砂质亚砂土 2.651±0.254 0.087 0.926 0.429 2.624 0.922 表 4 均质土柱HYDRUS模型反演弥散参数
Table 4. Dispersion parameters inversed by Hydrus model of homogeneous soil column
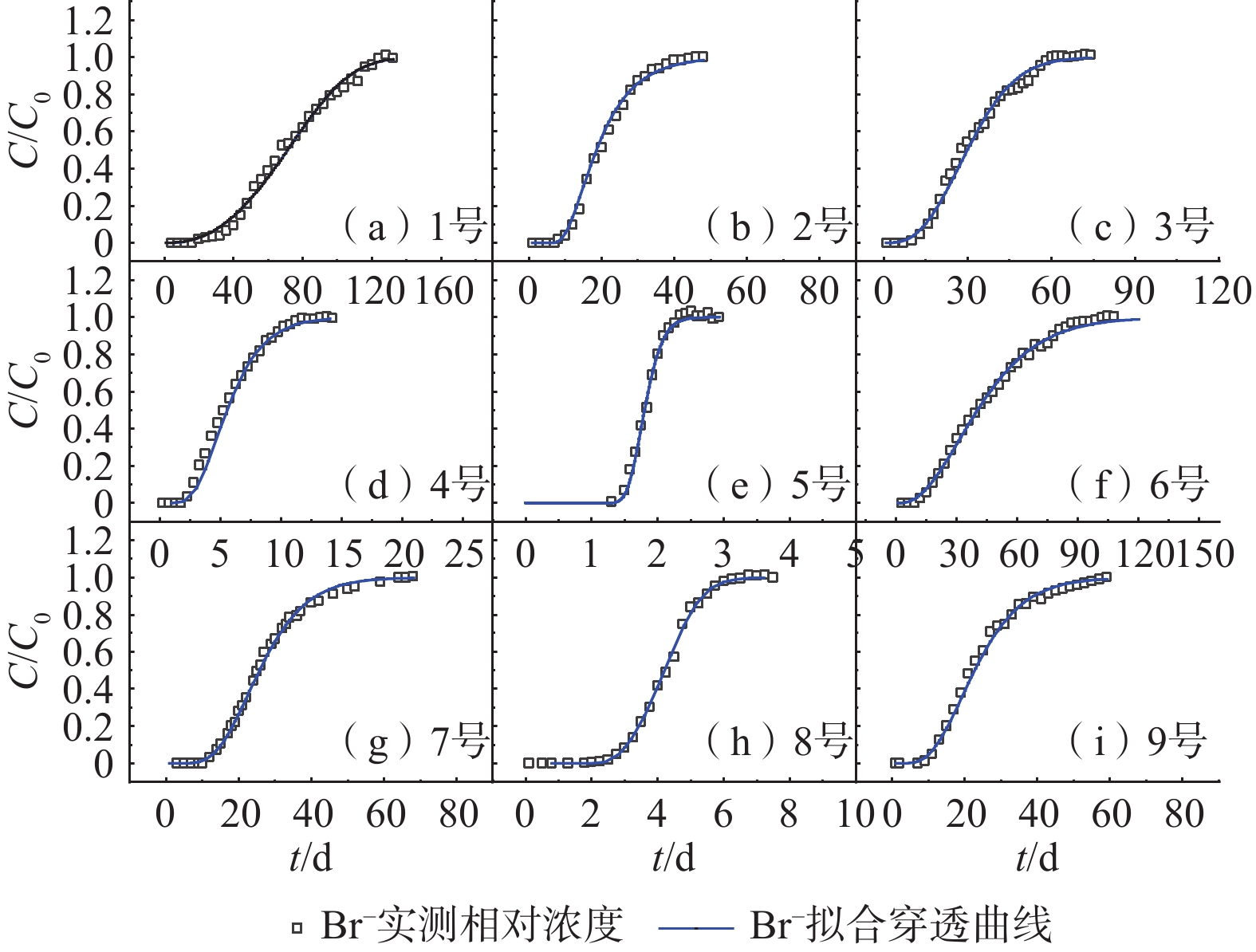
土柱编号 V /(cm·d−1) Br−质量浓度/(g·L−1) α/cm D/(cm2·d−1) R2 1号 粉质亚黏土 0.15 3.883 0.327 0.048 0.992 2号 粉质黏土 0.04 3.883 0.118 0.005 0.991 3号 粉质亚黏土 0.24 3.883 0.481 0.118 0.997 4号 砂质亚黏土 0.44 3.883 1.200 0.524 0.997 5号 砂质亚砂土 2.92 3.883 2.561 7.477 0.993 表 5 层状土柱HYDRUS模型反演弥散参数
Table 5. Dispersion parameters inversed by Hydrus model of layered soil column
土柱编号 V
/(cm·d−1)Br−质量浓度
/(g·L−1)α
/cmD
/(cm2·d−1)R2 6号 粉质亚黏土(上) 0.08 3.883 0.382 0.031 0.997 粉质黏土(下) 0.129 0.010 7号 粉质黏土(上) 0.23 3.883 0.125 0.029 0.997 粉质亚黏土(下) 0.513 0.118 8号 砂质亚黏土(上) 1.23 3.883 1.385 1.704 0.998 砂质亚砂土(下) 2.455 3.020 9号 粉质亚黏土(上) 0.24 3.883 0.313 0.075 0.994 粉质黏土(中) 0.133 0.032 粉质亚黏土(下) 0.490 0.118 -
[1] 魏山忠. 贯彻实施《地下水管理条例》 切实履行地下水保护治理法定职责[J]. 水利发展研究,2021,21(11):1 − 3. [WEI Shanzhong. Implement the regulations on the administration of groundwater and earnestly perform the legal responsibilities of groundwater protection and governance[J]. Water Resources Development Research,2021,21(11):1 − 3. (in Chinese)
[2] KUMAR G S. Effect of sorption intensities on dispersivity and macro-dispersion coefficient in a single fracture with matrix diffusion[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2008,16(2):235 − 249. doi: 10.1007/s10040-007-0234-5
[3] WANG Chaozi,WANG Ruoyu,HUO Zailin,et al. Colloid transport through soil and other porous media under transient flow conditions:A review[J]. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews:Water,2020,7(4):e1439.
[4] WANG Tieliang,ZHANG Kan,FENG Xue. The concentration and dispersion coefficient of the advection dispersion equation[J]. Journal of Modern Mathematics Frontier Volume,2013,2(3):.85 − 91.
[5] 孙启明,高茂生,党显璋. 垃圾填埋场渗滤液变密度的地下水溶质运移模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2022,52(4):1265 − 1274. [Sun Qiming,Gao Maosheng,Dang Xianzhang. Simulation of solute transport in variable-density groundwater for landfill leachate[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2022,52(4):1265 − 1274. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] BOURAZANIS G,PSYCHOGIOU M,NIKOLAOU N. Chloride transport parameters prediction for a clay-loam soil column[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology,2017,98(3):378 − 384. doi: 10.1007/s00128-016-1867-7
[7] GUPTA P,ALAM J,MUZZAMMIL M. Influence of thickness and position of the individual layer on the permeability of the stratified soil[J]. Perspectives in Science,2016,8:757 − 759. doi: 10.1016/j.pisc.2016.06.080
[8] 郝瑞,施斌,曹鼎峰,等. 层状土毛细水上升过程中Lucas-Washburn模型评价及修正[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(6):84 − 92. [HAO Rui,SHI Bin,CAO Dingfeng,et al. Evaluation and modification of the Lucas-Washburn model during capillary water rising in the layered soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(6):84 − 92. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2018.06.13
[9] 孙芳强,尹立河,王晓勇,等. 新疆三工河流域厚层包气带区地下水垂向补给量的厘定[J]. 中国地质,2017,44(5):913 − 923. [SUN Fangqiang,YIN Lihe,WANG Xiaoyong,et al. Determination of vertical infiltration recharge of groundwater in the thick unsaturated zone of Sangong River Basin,Xinjiang[J]. Geology in China,2017,44(5):913 − 923. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 赵小二,常勇,吴吉春,等. 穿透曲线随流量升高的变化特征及预测[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(4):21 − 30. [ZHAO Xiaoer,CHANG Yong,WU Jichun,et al. Change characteristics of breakthrough curves with increasing flow rate and prediction[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(4):21 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2018.04.04
[11] 郭蕾蕾,许模,王璐,等. 定流量条件下壤土夹层对苯和Br−穿透包气带的影响[J]. 环境工程学报,2017,11(12):6524 − 6531. [GUO Leilei,XU Mo,WANG Lu,et al. Effect of loam interlayer on benzene and Br− breakthrough vadose zone under constant flow[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2017,11(12):6524 − 6531. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201703126
[12] SELIM H M,DAVIDSON J M,RAO P S C. Transport of reactive solutes through multilayered soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal,1977,41(1):3 − 10. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1977.03615995004100010007x
[13] SHARMA P K,SAWANT V A,SHUKLA S K,et al. Experimental and numerical simulation of contaminant transport through layered soil[J]. International Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2014,8(4):345 − 351. doi: 10.1179/1939787913Y.0000000014
[14] 卜新峰,万伟锋. 豫西丘陵地带黄土介质水动力弥散特性试验研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2021(12):27 − 31. [BU Xinfeng,WAN Weifeng. Experimental research on the hydrodynamic dispersion characteristics of loess medium in hilly area of western Henan Province[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower,2021(12):27 − 31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 邰托娅,郑跃军,王金生. 应用HYDRUS-1D模型模拟分析PFCs在土壤中的迁移特征[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2018,37(10):2175 − 2182. [TAI Tuoya,ZHENG Yuejun,WANG Jinsheng. Simulation and analysis of PFCs migration in the soil column using the Hydrus-1D model[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2018,37(10):2175 − 2182. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 葛建,黄德文,高旭,等. 分层土壤的持水性能研究[J]. 西南农业学报,2019,32(9):2126 − 2132. [GE Jian,HUANG Dewen,GAO Xu,et al. Water retention capacity of drained soil columns with grained layers[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2019,32(9):2126 − 2132. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 马蒙蒙,林青,徐绍辉. 不同因素影响下层状土壤水分入渗特征及水力学参数估计[J]. 土壤学报,2020,57(2):347 − 358. [MA Mengmeng,LIN Qing,XU Shaohui. Water infiltration characteristics of layered soil under influences of different factors and estimation of hydraulic parameters[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica,2020,57(2):347 − 358. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] BECH T B,ROSENBOM A E,SORENSEN S R,et al. Conservative tracer bromide inhibits pesticide mineralisation in soil[J]. Environmental Pollution,2017,222:404 − 411. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.016
[19] LIU Tianwen,HU Cheng,WANG Qing,et al. Conversion relationship of rainfall-soil moisture-groundwater in Quaternary thick cohesive soil in Jianghan Plain,Hubei Province,China[J]. China Geology,2020,3(3):462 − 472.
[20] 刘添文,潘越,胡成,等. 应用D、18O同位素示踪孝感市厚层黏性土中土壤水入渗补给及其生态环境效应[J]. 中国地质,2021,48(5):1429 − 1440. [LIU Tianwen,PAN Yue,HU Cheng,et al. Tracing infiltration and recharge of thick silt by using D and 18O isotopes of soil moisture in Xiaogan,Hubei and its ecological efffects[J]. Geology in China,2021,48(5):1429 − 1440. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 蔡玲,胡成,陈植华,等. 江汉平原东北部地区高铁锰地下水成因与分布规律[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(4):18 − 25. [CAI Ling,HU Cheng,CHEN Zhihua,et al. Distribution and genesis of high Fe and Mn groundwater in the northeast of the Jianghan Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(4):18 − 25. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 常威,黄琨,胡成,等. 云应盆地东北部含水层结构特征及地下水转化模式[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(5):9 − 15. [CHANG Wei,HUANG Kun,HU Cheng,et al. Characteristics of the aquifer structure and groundwater conversion model in the northeastern Yunying Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(5):9 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2019.05.02
[23] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部.建筑地基基础设计规范: GB50007—2011[S].北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2012.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Code for design of building foundation: GB50007—2011[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2012.(in Chinese)
[24] 魏亮,郭华明,谢振华,等. 北京平原包气带典型沉积物对
$ {\rm{NH}}_4^+ $ [25] 张效先. 饱和条件下田间土壤纵向及横向弥散系数的试验和计算[J]. 水利学报,1989,20(1):1 − 8. [ZHANG Xiaoxian. A method for determining the longitudinal and lateral dispersion parameters of field soils under saturated condition[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,1989,20(1):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.1989.01.001
[26] MOHAMMED E,ALANI E,ABID M. Modeling infiltration and water distribution process of layered soils using HYDRUS-1D[J]. Indian Journal of Ecology,2021,48(1):66 − 71.
[27] 刘勇,郑军芳,贾海红. 西北某黏土矿水动力弥散系数的室内测定[J]. 环境科学与技术,2012,35(增刊 2):319 − 321. [LIU Yong,ZHENG Junfang,JIA Haihong. In-lab determination of northwest clay mine hydrodynamic dispersion coefficient[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2012,35(Sup 2):319 − 321. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 孙庆超,王旭东,乔建晨,等. 不同质地土壤对镉的吸附特性及影响因子研究[J]. 土壤,2020,52(3):545 − 551. [SUN Qingchao,WANG Xudong,QIAO Jianchen,et al. Study on Cd adsorption characteristics and influencing factors of soils with different textures[J]. Soils,2020,52(3):545 − 551. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2020.03.018
[29] GOLDBERG S,J KABENGI N. Bromide adsorption by reference minerals and soils[J]. Vadose Zone Journal,2010,9(3):780 − 786. doi: 10.2136/vzj2010.0028
[30] KOROM S F,SEAMAN J C. When “conservative” anionic tracers aren’t[J]. Groundwater,2012,50(6):820 − 824. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2012.00950.x
[31] 杨晨,向本富,董高峰,等. 加热卷烟不同类型专用基片水吸附特性研究[J]. 中国造纸,2021,40(8):56 − 63. [YANG Chen,XIANG Benfu,DONG Gaofeng,et al. Study on vapor adsorption characteristics of heated substrate with different types[J]. China Pulp & Paper,2021,40(8):56 − 63. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 陈孜涵,汪丙国,赵建芳. 江汉平原旱地和水田土壤镉的吸附与解吸特征及影响因素[J]. 地球科学,2022,47(2):544 − 555. [CHEN Zihan,WANG Bingguo,ZHAO Jianfang. Adsorption and desorption characteristics of Cd in upland and paddy soil of Jianghan plain[J]. Earth Science,2022,47(2):544 − 555. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.2.dqkx202202012
[33] 虎胆·吐马尔白,穆丽德尔·托伙加,朱珠. 北疆典型土壤纵向弥散系数试验[J]. 新疆农业科学,2021,58(1):151 − 158. [HUDAN Tumaerbai,MULIDEER Tuohuojia,ZHU Zhu. Experimental study on longitudinal dispersion coefficient of typical soil in northern Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences,2021,58(1):151 − 158. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 涂安国. 层状土壤水分入渗与溶质运移研究进展[J]. 江西农业大学学报,2017,39(4):818 − 825. [TU Anguo. Advances in water infiltration and solute transport in layered soil[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis,2017,39(4):818 − 825. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] 甯娜,许模,段永祥,等. 保守性离子在包气带层状土中运移规律研究[J]. 环境工程,2015,33(5):70 − 74. [NING Na,XU Mo,DUAN Yongxiang,et al. Research on the migration law of conservative ion in layered soil under unsaturated zone[J]. Environmental Engineering,2015,33(5):70 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[36] 苑绍东, 张文杰, 袁姗姗. 溶质迁移的弥散度取值试验研究[J/OL]. 岩土力学. (2020-10-13)[2021-10-21]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=YTLX20201012003&DbName=DKFX2020.
YUAN Shaodong, ZHANG Wenjie, YUAN Shanshan. Dispersion values in solute migration tests[J]. Rock and soil mechanics. (2020-10-13)[2021-10-21]. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[37] 李培月,钱会,吴健华,等. 银川地区饱和细砂含水介质弥散实验研究[J]. 水资源与水工程学报,2012,23(4):69 − 74. [LI Peiyue,QIAN Hui,WU Jianhua,et al. Experiment on the mass dispersion in porous media of saturated fine sand in Yinchuan area[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering,2012,23(4):69 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[38] 司高华,于静,王青海,等. 钚在黏土中的迁移试验[J]. 核化学与放射化学,2013,35(1):29 − 33. [SI Gaohua,YU Jing,WANG Qinghai,et al. Migration experiment of plutonium in clay[J]. Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemistry,2013,35(1):29 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[39] 城市建设研究院. 生活垃圾卫生填埋场防渗系统工程技术规范: CJJ 113—2007[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2007
Technical code for liner system of municipal solid waste landfill: CJJ 113—2007[S]. Beijing: China Architecture Publishing & Media Co., Ltd, 2007. (in Chinese)
[40] 黎艺明,李才. 垃圾污染质在粉质黏土包气带中运移情况的调查[J]. 环境化学,2013,32(1):166 − 167. [LI Yiming,LI Cai. Investigation on the transport of waste pollutants in the aerated zone of silty clay[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2013,32(1):166 − 167. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.01.027
-



 下载:
下载: