A simulation study of the activity characteristics and genetic mechanism of coupled ground fissures: Exemplified by the Songzhuang ground fissure in Beijing
-
摘要:
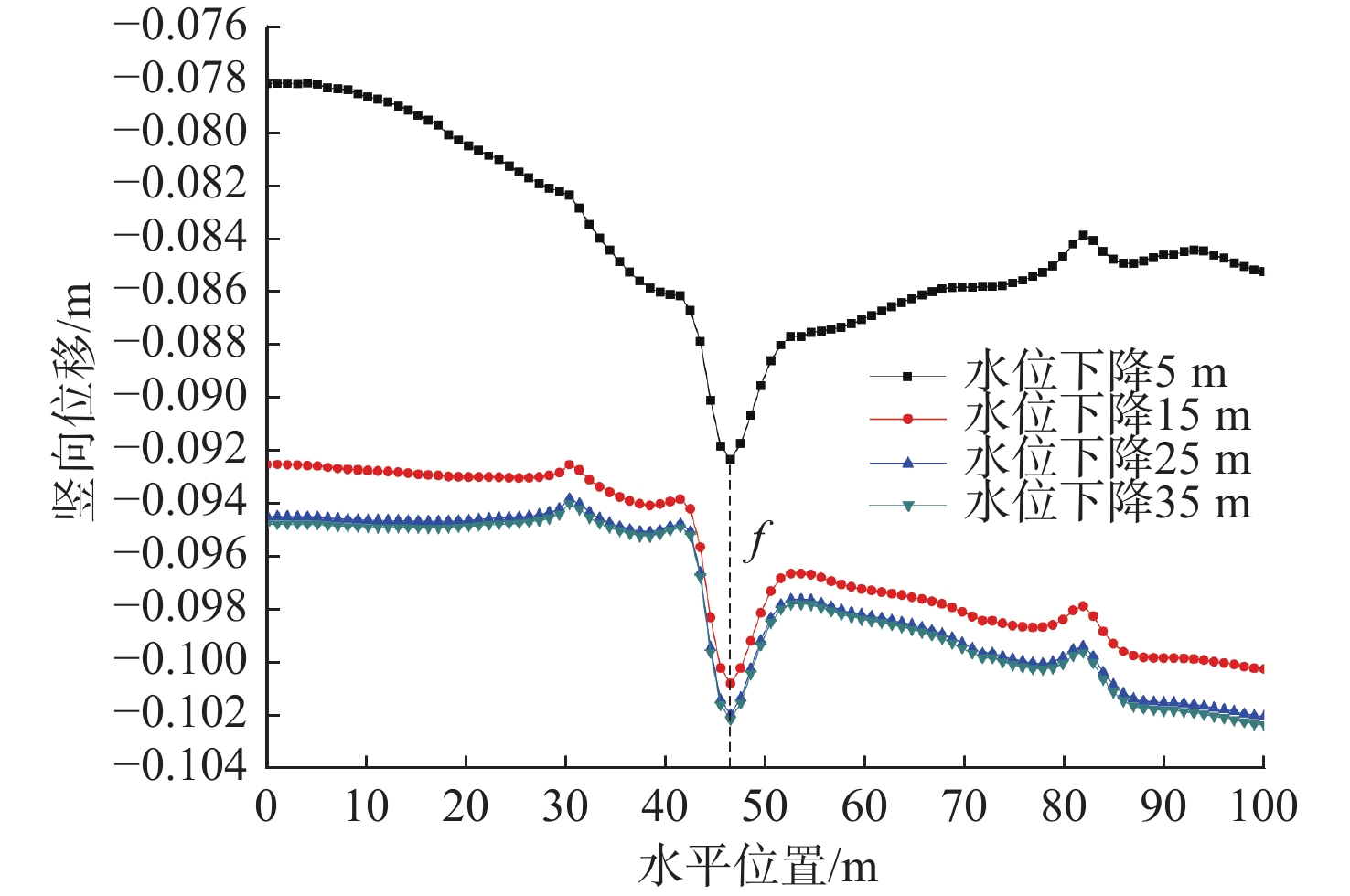
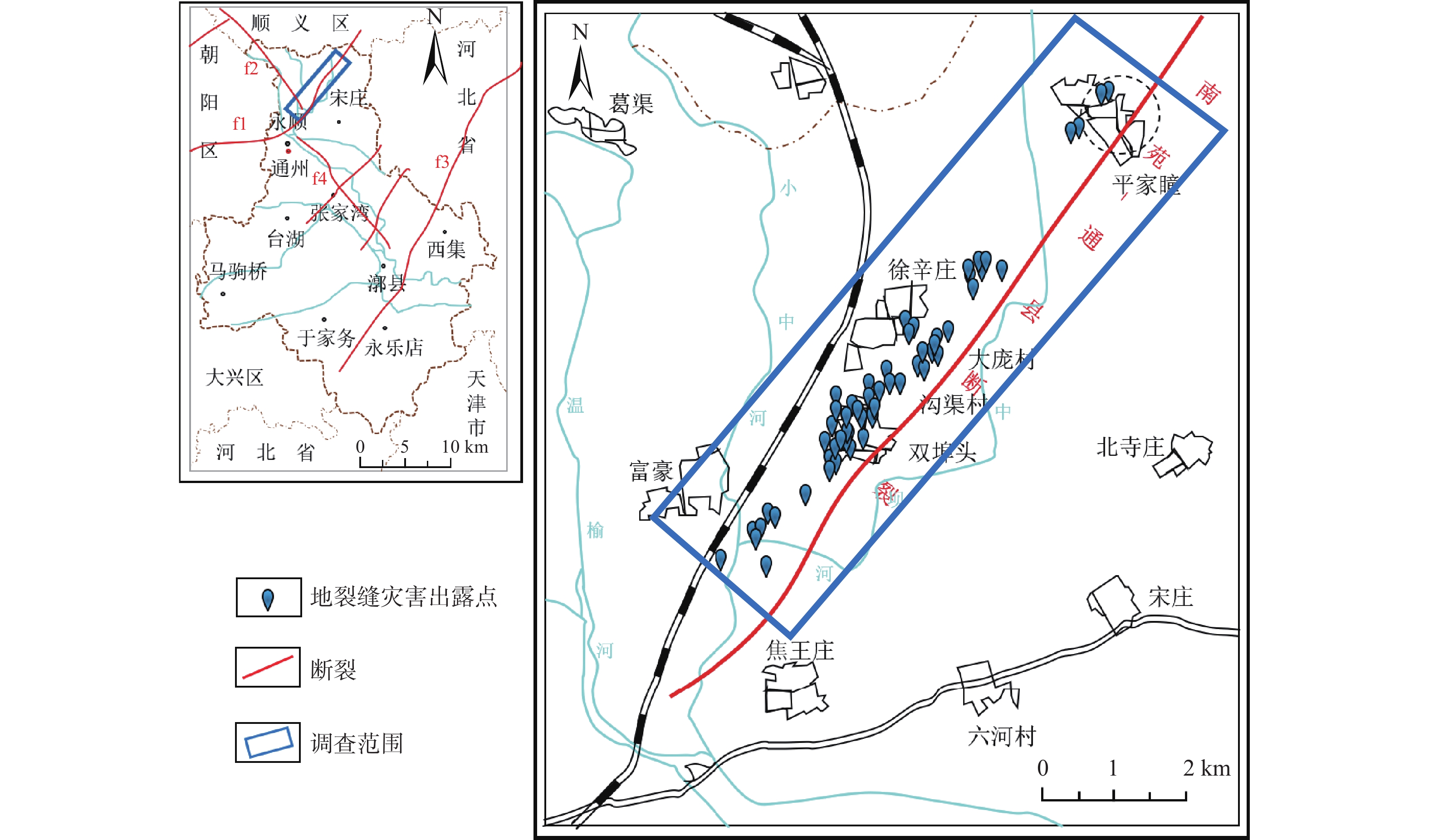
以北京通州区宋庄地裂缝为原型,研究以断裂活动和抽水为主要诱因的耦合型地裂缝的发育活动特征和成因机制,揭示了不同位错量和水位下降量引发的地层位移场和应力场的变化特征。通过实地踏勘,阐明了地裂缝造成的地表平面及地层剖面的破坏现象;运用有限差分法模拟研究了断层错动和抽水2种工况下的模型地层的变化响应过程,最后讨论了该类型地裂缝与各诱因之间的关系。结果表明:(1)该类型地裂缝具有三维活动等特点,一般造成浅表地层及墙体的水平张开量为0.3~1.2 cm,深部地层的垂直位错量随埋深而逐渐增大;(2)断裂活动引起的应力变化在裂缝发育区集中,并造成上盘地层出现明显的竖向位移,裂缝区地层出现较大的剪切牵引变形,且其两侧的竖向位移差异量最大;断层位错量的增加造成隐伏裂缝向上逐渐延伸扩展,并在上盘浅表层引发次级裂缝,致使地裂缝整体呈具有一定宽度的带状展布;(3)地下水位下降对地裂缝的竖向延伸和水平扩张均有加剧作用,裂缝两侧地表产生持续的沉降响应,并导致沉降漏斗中心成为地裂缝集中发育区,且该处的模型地层沉降量也最大,为10.2 cm,上盘地层的沉降范围宽度约38 m,下盘约16 m;(4)该类型地裂缝受断裂控制明显,但现阶段活动加剧主要为超采地下水所致。研究将对深入理解地裂缝成因机理、建立地层响应和断裂位错与地下水变化的定量联系,以及防灾减灾具有重要理论意义和实际应用价值。
Abstract:The active characteristics and genetic mechanism of coupled ground fissures mainly induced by fault activities and pumping are studied, and the Songzhuang Town in Tongzhou District of Beijing is taken as the research archetype. The damage of surface planes and stratigraphic profiles caused by ground fissure activities are clarified through field investigation, and the variation characteristics of the displacement field and stress field of the strata caused by different dislocation amounts and groundwater level drop are revealed. The response processes of the model stratum under the two conditions of fault misalignment and groundwater extraction are simulated and studied respectively by using the finite difference method. Finally, the relationship between this type of ground fissure and the main inducing factors is discussed. The results show that (1) the ground fissure is characterized by three-dimensional activities, which causes the vertical tension of the shallow stratum and wall to be 0.3−1.2 cm, and the vertical dislocation of the deep stratum gradually increases with the burial depth. (2) Stress changes caused by fracture activities are concentrated in the ground fissure development area and lead to significant vertical displacements in the hanging wall, the stratum located in the ground fissure area has large shear and traction deformation, and the vertical displacement difference between the two sides is the largest. The gradual increase of fault dislocations causes the hidden fractures to extend upward, and cause secondary cracks on the shallow surface of the hanging wall, resulting in the overall distribution of ground fissures with a certain width. (3) The vertical extension and horizontal expansion of ground fissures are aggravated by the lowering of groundwater levels, and the surface on both sides of the crack produces continuous settlement response, making the center of the subsidence funnel become a concentrated development area of ground fissures, with the maximum settlement of 10.2 cm in the model stratum at the fissure in its central area, and the settlement range of about 38 m in the hanging wall and about 16 m in the foot wall. (4) This type of ground fissures is obviously controlled by faults, but the increased activity in this period is mainly due to groundwater over-exploitation. This work will be of great theoretical and practical significance to understand ground fissure mechanism, establish quantitative relationship between formation and fault with groundwater, and prevent and reduce disasters.
-
Key words:
- ground fissure /
- fault /
- groundwater /
- displacement /
- stress /
- genetic mechanism
-

-
表 1 模型地层计算参数
Table 1. Calculation parameters of the model stratum
序号 模型
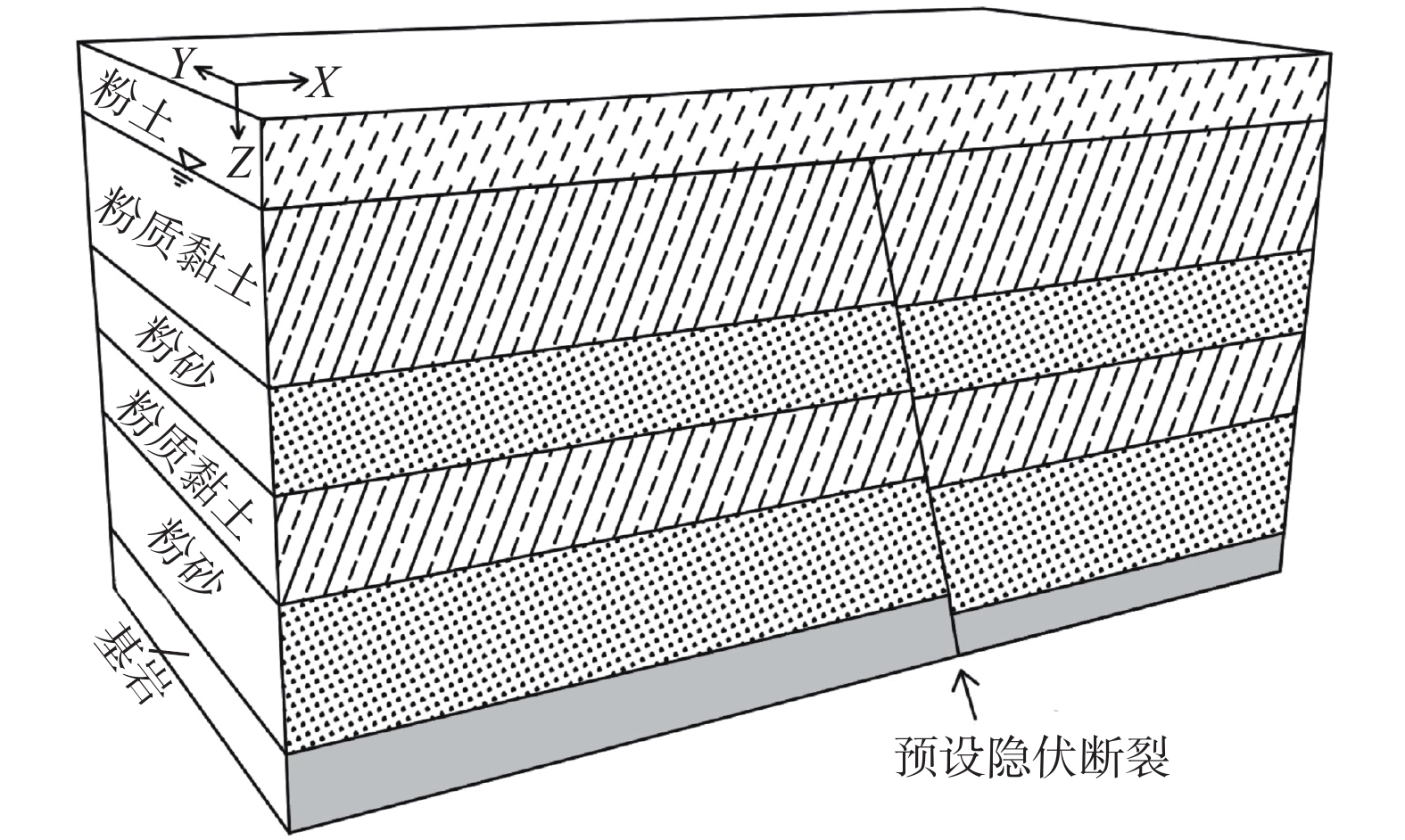
地层重度/(kN·m−3) 弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 渗透系数/(m·s−1) 1 粉土 17.0 4.0 0.28 10 15 1.0×10−9 2 粉质黏土 17.5 8.5 0.35 40 20 1.0×10−11 3 粉砂 18.0 9.0 0.30 0 30 1.0×10−7 4 粉质黏土 18.5 10.5 0.33 50 15 5.0×10−12 5 粉砂 19.5 12 0.30 0 30 5.0×10−8 6 基岩 25.0 10000 0.25 2000 40 1 -
[1] AYALEW L,YAMAGISHI H,REIK G. Ground cracks in Ethiopian Rift Valley facts and uncertainties[J]. Engineering Geology,2004,75(3/4):309 − 324.
[2] HOLZER T L. Ground failure induced by ground-water withdrawal from unconsolidated sediment[C]// HOLZER T L. Man-induced land subsidence. Boulder: Geological Society of America, 1984: 67-106.
[3] 邵长庆,杨强,李浩,等. 活动断层作用下地裂缝开裂机理研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(4):34 − 41. [SHAO Changqing,YANG Qiang,LI Hao,et al. A study of the cracking mechanism of ground fissures under the action of active faults[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(4):34 − 41. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2019.04.05
[4] 李志明,杨旭东,兰剑梅,等. 河北邢台柏乡地裂缝成因分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2010,37(2):135 − 138. [LI Zhiming,YANG Xudong,LAN Jianmei,et al. An analysis of earth fissure at Baixiang County,Xingtai City[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2010,37(2):135 − 138. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.02.029
[5] 贾润幸,方维萱,张建国,等. 山西清徐—太谷地区地裂缝形成机理[J]. 地质通报,2022,41(7):1282 − 1290. [JIA Runxing,FANG Weixuan,ZHANG Jianguo,et al. The formation mechanism of ground fissures in Qingxu-Taigu area,Shanxi Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2022,41(7):1282 − 1290. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2022.07.014
[6] 汪丽,李新生,李同录. 隐伏地裂缝扩展的大型原位浸水试验研究[J]. 地质力学学报,2019,25(3):412 − 420. [WANG Li,LI Xinsheng,LI Tonglu. Large-scale in-situ submerging experiment on buried ground-fissures expansion[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2019,25(3):412 − 420. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.03.038
[7] 谭鹏,刘阳,蒋富强,等. 肯尼亚裂谷区地裂缝特征及成因分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(6):53 − 62. [TAN Peng,LIU Yang,JIANG Fuqiang,et al. Analysis of the characteristics and causes of ground fissures in Kenya rift region[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(6):53 − 62. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.06-07
[8] 乔建伟. 基于地球关键带理论的渭北台塬地裂缝成因机理研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2018
QIAO Jianwei. Study on the formation mechanism of ground fissures in Weibei Terrace based on earth’s critical zone theory[D]. Xi’an: Changan University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] PENG Jianbing,HUANG Qiangbing,HU Zhiping. A proposed solution to the ground fissure encountered in urban metro construction in Xi’an,China[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2017,61:12 − 25. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2016.09.002
[10] 彭建兵,范文,李喜安,等. 汾渭盆地地裂缝成因研究中的若干关键问题[J]. 工程地质学报,2007,15(4):433 − 440. [PENG Jianbing,FAN Wen,LI Xi’an,et al. Some key questions in the formation of ground fissures in the Fen-Wei Basin[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2007,15(4):433 − 440. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2007.04.001
[11] 武强,陈佩佩,张宇,等. 我国城市地裂缝灾害问题与对策[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2002,13(2):70 − 72. [WU Qiang,CHEN Peipei,ZHANG Yu,et al. The problem and countermeasure of ground fracture in city[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2002,13(2):70 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2002.02.015
[12] 赵忠海. 北京地区地裂缝灾害的分布特征及其成因探讨[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,2006,17(3):75 − 78. [ZHAO Zhonghai. Discussion on the distribution characteristics and genetic type of the land crack in Beijing[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,2006,17(3):75 − 78. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2006.03.018
[13] 贾三满,刘明坤,田芳,等. 北京地区地裂缝分类及防治措施[J]. 城市地质,2011,6(2):4 − 7. [JIA Sanman,LIU Mingkun,TIAN Fang,et al. The classification of ground fissures and their prevention measures in Beijing area[J]. Urban Geology,2011,6(2):4 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2011.02.002
[14] 田苗壮,王荣,赵龙,等. 高密度电法在北京宋庄地裂缝中的应用[J]. 上海国土资源,2017,38(3):90 − 93. [TIAN Miaozhuang,WANG Rong,ZHAO Long,et al. High-density electrical method application in the Beijing Songzhuang ground fissure[J]. Shanghai Land & Resources,2017,38(3):90 − 93. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2017.03.020
[15] 刘德成,靳小平,周自梁. 灰色关联度分析法在北京通州区地裂缝灾害危险性评价中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2010,21(3):73 − 76. [LIU Decheng,JIN Xiaoping,ZHOU Ziliang. Application of grey degree of association evaluation method in ground fissures in Tongzhou District of Beijing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2010,21(3):73 − 76. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2010.03.015
[16] 刘方翠,祁生文,彭建兵,等. 北京市地裂缝分布与发育规律[J]. 工程地质学报,2016,24(6):1269 − 1277. [LIU Fangcui,QI Shengwen,PENG Jianbing,et al. Characters of the ground fissures developing in Beijing[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2016,24(6):1269 − 1277. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2016.06.029
[17] 赵龙,李玉梅,崔文君,等. 北京宋庄地裂缝灾害特征及影响因素分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(6):1600 − 1610. [ZHAO Long,LI Yumei,CUI Wenjun,et al. Disaster characteristics and influence factors for ground fissures at songzhuang village in Beijing[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(6):1600 − 1610. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017-426
[18] 赵龙,罗勇,李玉梅,等. 北京平原区地裂缝受灾体形态特征及影响因素[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(6):156 − 164. [ZHAO Long,LUO Yong,LI Yumei,et al. Characteristics of disaster-affected bodies and influence factors for earth fissure in Beijing Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(6):156 − 164. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2019.06.21
[19] HERNANDEZ-MARIN M,BURBEY T J. Controls on initiation and propagation of pumping-induced earth fissures:Insights from numerical simulations[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2010,18(8):1773 − 1785. doi: 10.1007/s10040-010-0642-9
[20] LOUKIDIS D,BOUCKOVALAS G D,PAPADIMITRIOU A G. Analysis of fault rupture propagation through uniform soil cover[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,2009,29(11-12):1389 − 1404. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2009.04.003
[21] ANASTASOPOULOS I,GAZETAS G,BRANSBY M F,et al. Fault rupture propagation through sand:finite-element analysis and validation through centrifuge experiments[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2007,133(8):943 − 958. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2007)133:8(943)
[22] 王海刚,刘明坤,贾三满,等. 基于FLAC3D的北京高丽营地裂缝模拟[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2013,11(5):86 − 90. [WANG Haigang,LIU Mingkun,JIA Sanman,et al. Simulation of gaoliying ground fissure based on FLAC3D[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2013,11(5):86 − 90. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 王启耀,蒋臻蔚,彭建兵. 抽水作用下先存断裂活化滑移机制研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2013,40(2):108 − 112. [WANG Qiyao,JIANG Zhenwei,PENG Jianbing. Mechanism of reactivation and slip of the preexisting fault under pumping[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2013,40(2):108 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2013.02.025
[24] 赵龙,刘久荣,王荣,等. 北京宋庄地裂缝分布特征及成因分析[J]. 上海国土资源,2017,38(2):35 − 38. [ZHAO Long,LIU Jiurong,WANG Rong,et al. Distribution characteristics and cause analysis of Songzhuang ground fissures in Beijing[J]. Shanghai Land & Resources,2017,38(2):35 − 38. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2017.02.009
[25] 蒋臻蔚,彭建兵,王启耀. 抽水作用下先期断裂对地裂缝的影响研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2010,18(5):651 − 656. [JIANG Zhenwei,PENG Jianbing,WANG Qiyao. Influence of pre-existing fault on ground fissures during pumping action[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2010,18(5):651 − 656. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.05.007
[26] 李宁,李明,赵法锁,等. 基于FLAC2D的西安地面沉降数值模拟分析[J]. 灾害学,2013,28(3):210 − 214. [LI Ning,LI Ming,ZHAO Fasuo,et al. Numerical simulation analysis of xi’an land subsidence by FLAC2D[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2013,28(3):210 − 214. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2013.03.039
[27] 戴文彬. 抽水地面沉降对地铁隧道变形的影响研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2013
DAI Wenbin. Study on the effect of land subsidence on subway tunnel structure[D]. Xi’an: Changan University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 陈育民, 徐鼎平. FLAC/FLAC3D基础与工程实例[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2009
CHEN Yumin, XU Dingping. FLAC/FLAC3D foundation and engineering example[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2009. (in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载: