An analysis of cylindrical cavity expansion in sand based on a unified state parameter model
-
摘要:
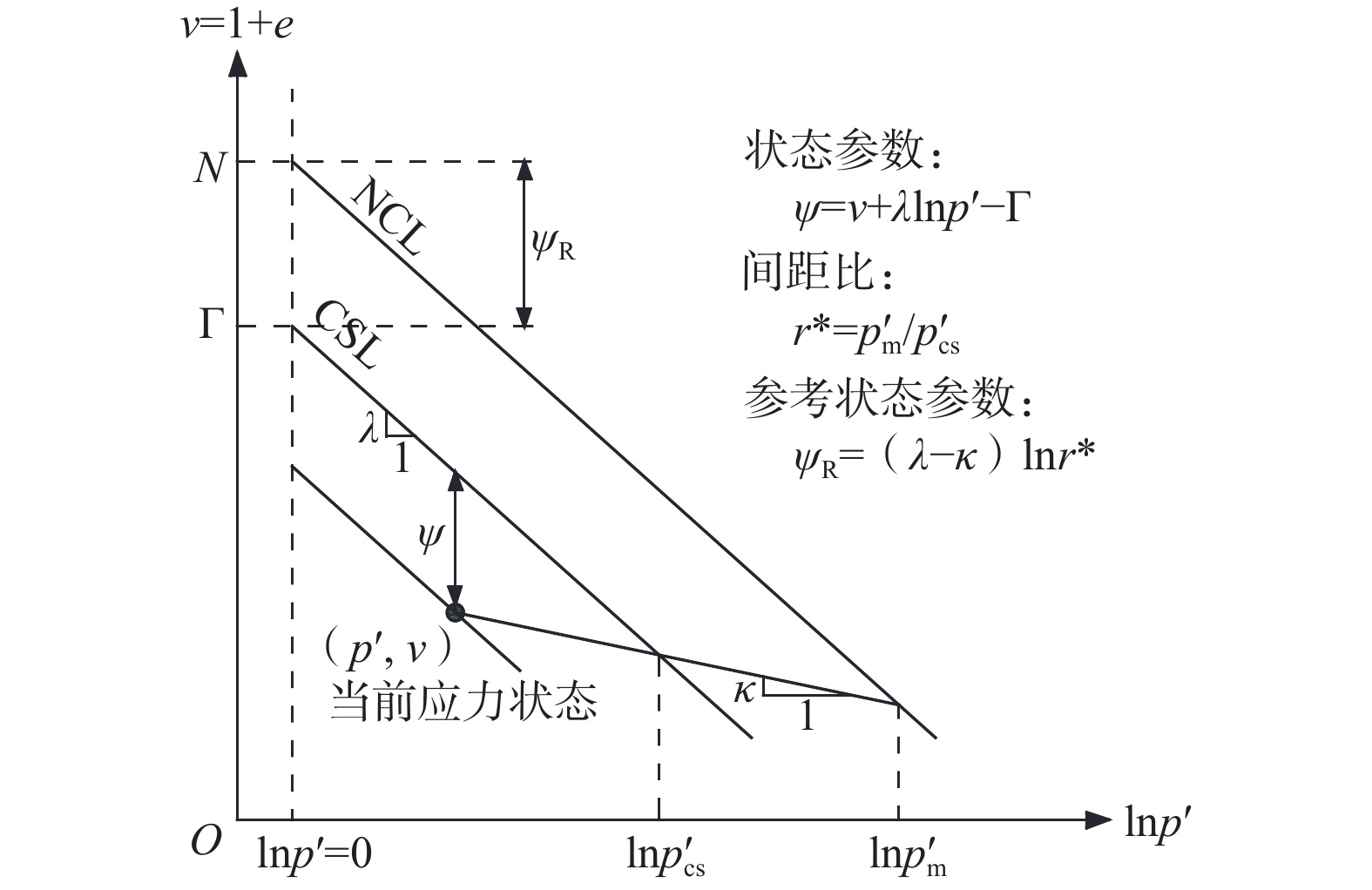
目前关于不同初始状态砂土砂中柱孔扩张的研究结果还缺乏更深层次的分析,并且由于没有考虑砂土屈服面形状因素的影响,造成许多研究成果难以在不同类型砂土中推广。采用统一状态参数模型(clay and sand model,CASM)和Rowe剪胀方程来描述砂的弹塑性变形特点,结合大变形理论并引入辅助变量,推导了基于拉格朗日描述的弹塑性区内砂土体积和有效应力的一阶偏微分方程组,在此基础上结合弹塑性区的边界条件和柱孔扩张弹性解,建立了饱和砂中的排水柱孔扩张半解析解。结果表明,CASM可以通过改变应力状态参数n和间距比r*的值使砂的屈服面形状发生改变,进而使文中解答能够用于不同类型饱和砂中的排水柱孔扩张计算,其中n、r*值越大,松砂初次屈服时的偏应力和后续砂中的扩孔压力越大,但中密、密实砂土中的情况与松砂完全相反。极限扩孔压力随砂土初始状态参数的减小而增大,相应的砂土体积也从一直剪缩变为先剪胀后剪缩,弹塑性区半径先减小后增大,硬化行为从一直硬化变为先软化后硬化。静止侧压力系数增大时,极限扩孔压力也增大,但对砂的体积变化规律影响不大。本研究可为相关岩土工程问题分析提供可靠理论支持。
Abstract:The current studies of the cylindrical cavity expansion in sand still lack a deeper analysis for the results obtained in sands with different initial states. In addition, most of previous studies have not considered the influence of the shape of yield surface of sand, which made their results difficult to be popularized in different types of sand. In order to obtain a general solution to expansion of cylindrical cavity in sand under the drained condition, a unified state parameter model - clay and sand model (CASM) with Rowe’s stress–dilatancy relation is used to describe the characteristics of elastic-plastic deformation of sand. By employing that large strain occurs in sand and introducing an auxiliary variable, several partial differential equations to calculate the effective stress and specific volume of sand in the elastoplastic zone are derived on the basis of the Lagrangian description.Under the elastic-plastic boundary conditions and the elastic solution of cylindrical cavity expansion, a semi-analytical solution for drained cylindrical cavity expansion in sand is obtained by solving the governing equations numerically. The results show that the solution of cylindrical cavity expansion established in this paper can be used in many types of sand by changing the values of stress-state parameter n and spacing ratio r* to select an appropriate shape of yield surface of sand, and the greater the values of n, r* are, the greater the initial yield deviatoric stress of loose sand and the subsequent expansion pressure, but these situations will reverse in medium dense and dense sand. The ultimate expansion pressure increases with the decreasing initial state parameter of the sand, and together with the volume variation rule of sand changes from always contraction into dilatation first and then contraction, the radius of the elastic-plastic zone decreases first and then increases, and the hardening response of sand changes from always hardening into softening first and then hardening. The ultimate expansion pressure increases with the increasing coefficient of earth pressure at rest of sand, but the volume change law of sand has little change. This study provides a reliable theoretical support for the analysis of related geotechnical engineering problem.
-

-
[1] BHARTIYA P,CHAKRABORTY T,BASU D. Nonlinear subgrade modulus of sandy soils for analysis of piled raft foundations[J]. Computers and Geotechnics,2020,118:103350. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2019.103350
[2] 赵明华,何玮茜,刘猛. 基于圆孔扩张理论的碎石桩承载力计算方法[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(3):55 − 60. [ZHAO Minghua,HE Weixi,LIU Meng. Calculation method for the bearing capacity of stone columns based on the cavity expansion theory[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(3):55 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2017.03.09
ZHAO Minghua, HE Weixi, LIU Meng . Calculation method for the bearing capacity of stone columns based on the cavity expansion theory[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017 ,44 (3 ):55 −60 . (in Chinese with English abstract).[3] 叶俊能,周晔,朱瑶宏,等. 竹节桩复合地基沉桩施工超孔隙水压力研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(1):103 − 110. [YE Junneng,ZHOU Ye,ZHU Yaohong,et al. A study of the excess pore water pressure during pile-sinking construction of nodular pile composite foundation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(1):103 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2019.01.14
YE Junneng, ZHOU Ye, ZHU Yaohong, et al . A study of the excess pore water pressure during pile-sinking construction of nodular pile composite foundation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019 ,46 (1 ):103 −110 . (in Chinese with English abstract).[4] MO P Q,YU H S. A state parameter-based cavity expansion analysis for interpretation of CPT data in sands[C]//HICKS M A,PISANO F,PEUCHEN J. Cone Penetration Testing 2018:Proceedings of the 4th international Symposium on Cone Penetration Testing. Bocaraton:CRC Press,2018:447 − 453.
[5] 肖先波,李波,王婷,等. 大应变静力触探数值模拟及锥形因子影响因素分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(2):70 − 76. [XIAO Xianbo,LI Bo,WANG Ting,et al. Large-strain numerical simulation for cone penetration and analysis of influence factors for the cone factor[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(2):70 − 76. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2018.02.11
XIAO Xianbo, LI Bo, WANG Ting, et al . Large-strain numerical simulation for cone penetration and analysis of influence factors for the cone factor[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018 ,45 (2 ):70 −76 . (in Chinese with English abstract).[6] 陈忠清,吴天宇,高彦斌,等. 扁铲探头贯入干砂的位移特征试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(3):119 − 125. [CHEN Zhongqing,WU Tianyu,GAO Yanbin,et al. An experimental study of the displacement characteristics of dry sand under dilatometer penetration[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(3):119 − 125. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202008046
CHEN Zhongqing, WU Tianyu, GAO Yanbin, et al . An experimental study of the displacement characteristics of dry sand under dilatometer penetration[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021 ,48 (3 ):119 −125 . (in Chinese with English abstract).[7] COLLINS I F,YU H S. Undrained cavity expansions in critical state soils[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics,1996,20(7):489 − 516. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9853(199607)20:7<489::AID-NAG829>3.0.CO;2-V
[8] CAO L F,TEH C I,CHANG M F. Undrained cavity expansion in modified Cam clay I:Theoretical analysis[J]. Géotechnique,2001,51(4):323 − 334.
[9] CHEN S L,ABOUSLEIMAN Y N. Exact drained solution for cylindrical cavity expansion in modified Cam Clay soil[J]. Géotechnique,2013,63(6):510 − 517.
[10] 李镜培,唐剑华,李林,等. 饱和黏土中柱孔三维弹塑性扩张机制研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(2):378 − 386. [LI Jingpei,TANG Jianhua,LI Lin,et al. Mechanism of three dimensional elastic-plastic expansion of cylindrical cavity in saturated clay[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(2):378 − 386. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2014.1645
LI Jingpei, TANG Jianhua, LI Lin, et al . Mechanism of three dimensional elastic-plastic expansion of cylindrical cavity in saturated clay[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016 ,35 (2 ):378 −386 . (in Chinese with English abstract).[11] LIU K,CHEN S L. Analysis of cylindrical cavity expansion in anisotropic critical state soils under drained conditions[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2019,56(5):675 − 686. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2018-0025
[12] CASTRO J,SIVASITHAMPARAM N. Theoretical solution for drained cylindrical cavity expansion in clays with fabric anisotropy and structure[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2022,17(5):1917 − 1933. doi: 10.1007/s11440-021-01311-9
[13] ROSCOE K,SCHOFIELD A,WROTH C. On the yielding of soils[J]. Géotechnique,1958,8:22 − 53. doi: 10.1680/geot.1958.8.1.22
[14] ROSCOE K H,BURLAND J B. On the generalised stress- strain behaviour of wet clay[C]//Engineering Plasticity 1968. Cambridge:Cambridge University Press,1968:535 − 609.
[15] YU H S. CASM:A unified state parameter model for clay and sand[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics,1998,22(8):621 − 653. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9853(199808)22:8<621::AID-NAG937>3.0.CO;2-8
[16] 姚仰平,侯伟,周安楠. 基于Hvorslev面的超固结土本构模型[J]. 中国科学(E辑:技术科学),2007,37(11):1417 − 1429. [YAO Yangping,HOU Wei,ZHOU Annan. Constitutive model of overconsolidated soil based on Hvorslev surface[J]. Scientia Sinica (Technologica),2007,37(11):1417 − 1429. (in Chinese)
YAO Yangping, HOU Wei, ZHOU Annan . Constitutive model of overconsolidated soil based on Hvorslev surface[J]. Scientia Sinica (Technologica),2007 ,37 (11 ):1417 −1429 . (in Chinese).[17] 李林,李镜培,孙德安,等. 剪胀性砂土中球孔扩张弹塑性解[J]. 岩土工程学报,2017,39(8):1453 − 1460. [LI Lin,LI Jingpei,SUN Dean,et al. Elasto-plastic solution to expansion of a spherical cavity in dilatant sand[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2017,39(8):1453 − 1460. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201708012
LI Lin, LI Jingpei, SUN Dean, et al . Elasto-plastic solution to expansion of a spherical cavity in dilatant sand[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2017 ,39 (8 ):1453 −1460 . (in Chinese with English abstract).[18] Yao Y P,Sun D A,Matsuoka H. A unified constitutive model for both clay and sand with hardening parameter independent on stress path[J]. Computers and Geotechnics,2008,35(2):210 − 222. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2007.04.003
[19] SU D,YANG Z X. Drained analyses of cylindrical cavity expansion in sand incorporating a bounding-surface model with state-dependent dilatancy[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling,2019,68:1 − 20. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2018.11.017
[20] 武孝天,徐永福. 基于CSUH模型的砂/黏土不排水柱孔扩张统一解[J]. 岩土工程学报,2021,43(6):1019 − 1028. [WU Xiaotian,XU Yongfu. Undrained unified solutions to cylindrical cavity expansion in soils and sands based on CSUH model[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2021,43(6):1019 − 1028. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE202106005
WU Xiaotian, XU Yongfu . Undrained unified solutions to cylindrical cavity expansion in soils and sands based on CSUH model[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2021 ,43 (6 ):1019 −1028 . (in Chinese with English abstract).[21] 姚仰平,张民生,万征,等. 基于临界状态的砂土本构模型研究[J]. 力学学报,2018,50(3):589 − 598. [YAO Yangping,ZHANG Minsheng,WAN Zheng,et al. Constitutive model for sand based on the critical state[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics,2018,50(3):589 − 598. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-17-334
YAO Yangping, ZHANG Minsheng, WAN Zheng, et al . Constitutive model for sand based on the critical state[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics,2018 ,50 (3 ):589 −598 . (in Chinese with English abstract).[22] 李海潮,童晨曦,马博,等. 基于双参数屈服函数的黏土和砂土非正交单屈服面模型[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(11):2319 − 2327. [LI Haichao,TONG Chenxi,MA Bo,et al. A non-orthogonal single yield surface model for clays and sands based on a two-parameter yield function[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(11):2319 − 2327. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2020.0096
LI Haichao, TONG Chenxi, MA Bo, et al . A non-orthogonal single yield surface model for clays and sands based on a two-parameter yield function[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020 ,39 (11 ):2319 −2327 . (in Chinese with English abstract).[23] Rowe P W. Theoretical meaning and observed values of deformation parameters for soil[C]//Proceedings of Roscoe Memorial Symposium. Cambridge University,1971:170 − 192.
[24] BEEN K,JEFFERIES M G. A state parameter for sands[J]. Géotechnique,1985,35(2):99 − 112.
[25] CHARLES M,YU H S,SHENG D. Finite element analysis of pressuremeter tests using critical state soil models[M]//PANDE G N,PIETRUSZCZAK S,SCHWEIGER H F. Numerical Models in Geomechanics. London:CRC Press,2020:645 − 650.
[26] MO Pinqiang,YU Haisui. Drained cavity expansion analysis with a unified state parameter model for clay and sand[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2018,55(7):1029 − 1040. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2016-0695
[27] XU Guangquan. Wellbore stability in geomechanics[D]. Nottingham,East Midlands,UK:University of Nottingham,2007.
[28] GHAFGHAZI M,SHUTTLE D. Interpretation of sand state from cone penetration resistance[J]. Géotechnique,2008,58(8):623 − 634.
[29] SLADEN J A,D’HOLLANDER R D,KRAHN J,et al. Back analysis of the Nerlerk berm liquefaction slides[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1985,22(4):579 − 588. doi: 10.1139/t85-077
[30] SLADEN J A,D'HOLLANDER R D,KRAHN J. The liquefaction of sands,a collapse surface approach[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1985,22(4):564 − 578. doi: 10.1139/t85-076
[31] YU H S,SCHNAID F,COLLINS I F. Analysis of cone pressuremeter tests in sands[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1996,122(8):623 − 632. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1996)122:8(623)
-




 下载:
下载: