Remote sensing estimation on regional continuous daily evapotranspiration based on Richards equation
-
摘要:
蒸散发作为自然界水循环的重要组成部分,时空尺度上的蒸散量估算一直是研究热点。遥感手段可以实现区域尺度蒸散量的估算,但是受到卫星过境时间的限制,难以获取连续时间序列的蒸散量。土壤水分作为蒸散发的重要控制因素,结合土壤水分数据改进遥感蒸散发模型,在提高遥感蒸散量估算精度方面也具有重要意义,但是目前大多数遥感方法对土壤水分胁迫性的考虑仍有不足。针对目前蒸散发研究在土壤水分胁迫和连续性方面的不足,以涡度相关法计算的蒸散量作为实际蒸散量,结合联合国粮农组织推荐的单作物系数法,将土壤含水量信息引入Penman-Monteith(P-M)公式计算实际蒸散量,并用Richards方程进行蒸发条件下一维垂向土壤水分运动过程的数值模拟,实现土壤水分胁迫下的连续日蒸散量的估算,并结合遥感数据实现区域尺度的扩展。结果表明:涡度相关法计算的实际日蒸散量与P-M公式计算的潜在日蒸散量具有很强的相关性,相关系数达到0.918;引入土壤含水量信息后的P-M公式,日蒸散量的估算精度显著提升,均方根误差达到0.133 mm/d;基于Richards方程的土壤水分胁迫下连续日蒸散量的估算结果与实测值较为接近,均方根误差为0.288 mm/d;受研究区南北高中间低的地势影响,日蒸散量的高值集中在研究区中部的水域和耕地区域,不同土地利用类型下的平均日蒸散量水域>耕地>林地>草地>未利用土地,且区域扩展的结果与站点的实测结果在时间序列上表现出一致的变化规律。文章可为土壤水分对蒸散发的影响机理研究以及区域蒸散量的估算提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 蒸散发遥感反演 /
- 涡度相关法 /
- 土壤水分胁迫 /
- Richards方程 /
- P-M公式
Abstract:Evapotranspiration (ET) is an important part of water cycle in nature, and the estimation of evapotranspiration on spatio-temporal scale has always been a hot issue. Remote sensing can estimate evapotranspiration on regional scale, but it is difficult to obtain evapotranspiration in continuous time series due to the limitation of satellite transit time. Soil moisture is an important controlling factor of evapotranspiration. Improving the remote sensing evapotranspiration model by combining soil moisture data is of great significance in improving the accuracy of remote sensing evapotranspiration estimation. However, most remote sensing methods give limited consideration to the characterization of soil moisture stress. This study used the evapotranspiration calculated by the vorticity correlation method as the actual evapotranspiration. combining with the single crop coefficient method recommended by FAO, the soil water content information was introduced into the Penman-Monteith formula to calculate the actual evapotranspiration. Based on Richards equation, the one-dimensional vertical soil water movement process under evaporation conditions was simulated to estimate the continuous daily evapotranspiration under soil water stress. Combining with remote sensing data, the regional scale evapotranspiration was estimated. The results show that the actual daily evapotranspiration calculated by the vorticity correlation method has a strong correlation with the potential daily evapotranspiration calculated by P-M formula, with the correlation coefficient of 0.918. With the introduction of soil water content information, the P-M formula improves the estimation accuracy of daily evapotranspiration significantly, and the RMSE reaches 0.133 mm/d. The estimated daily evapotranspiration under soil water stress based on Richards equation is close to the measured value, with the RMSE of 0.288 mm/d. The high value of daily evapotranspiration affected by the topography of the study area is concentrated in the water area and cultivated land area in the middle of the study area. The average daily evapotranspiration under different soil use types is water area > cultivated land > woodland > grassland > unused land, and the results on the regional scale show similar change with that measured in the the station in time series. This study provides basic information for understanding the influence mechanism of soil moisture on evapotranspiration and estimating regional evapotranspiration.
-

-
表 1 潜在/实际日蒸散量计算结果
Table 1. Calculationresults of potential/actual daily evapotranspiration
日期 潜在日蒸散量/mm 实际日蒸散量/mm 4月27日 5.597 4.211 4月28日 5.020 3.040 4月29日 5.175 3.336 4月30日 5.226 3.454 5月1日 5.385 3.462 5月2日 4.522 2.260 5月3日 3.055 1.775 表 2 不同土壤水分胁迫函数构建的蒸散量估算模型精度对比
Table 2. Accuracy comparison of evapotranspiration estimation models constructed by different soil water stress functions
埋深/cm 均方根误差/(mm·d−1) 线性函数 指数函数 对数函数 Sigmoid函数 2 0.496 0.433 0.437 0.393 4 0.413 0.329 0.332 0.232 10 0.416 0.331 0.337 0.223 0~4 0.428 0.347 0.350 0.133 2~4 0.424 0.310 0.311 0.157 4~10 0.414 0.330 0.335 0.226 2~10 0.409 0.324 0.327 0.217 0~10 0.407 0.314 0.316 0.195 表 3 日蒸散量模拟值与实测值的误差分析
Table 3. Error analysis of simulated and measured evapotranspiration
日期 实测值/mm 模拟值/mm 绝对误差/mm 4月28日 3.040 3.191 0.151 4月29日 3.336 3.037 −0.299 4月30日 3.454 3.684 0.231 5月1日 3.462 3.917 0.455 5月2日 2.260 2.185 −0.074 5月3日 1.775 1.428 −0.346 表 4 三个站点日蒸散量遥感反演结果的精度评价
Table 4. Accuracy evaluation of remote sensing inversion results of daily evapotranspiration at three stations
站点 实测平均蒸
散量/(mm·d−1)遥感反演平均蒸
散量/(mm·d−1)平均绝对误
差/(mm·d−1)均方根误差
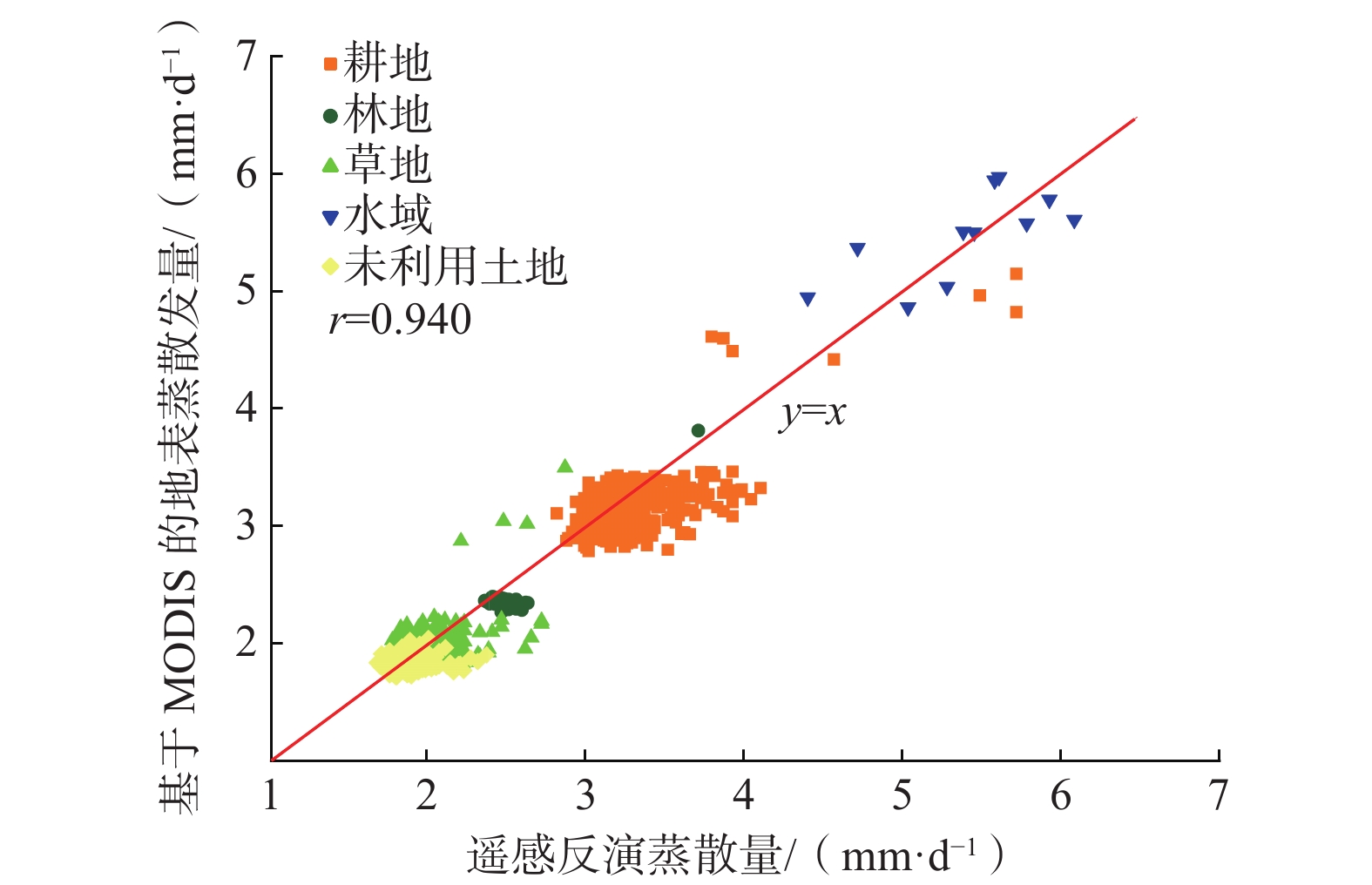
/(mm·d−1)大满站 2.787 2.907 0.283 0.287 花寨子站 1.732 1.599 0.334 0.308 张掖湿地站 4.881 5.070 0.307 0.343 表 5 不同土地利用类型下遥感反演日蒸散量与基于MODIS的逐日地表蒸散发数据的精度评价
Table 5. Accuracy evaluation of daily evapotranspiration retrieved by remote sensing and daily surface evapotranspiration data based on MODIS under different land use types
土地利用
类型基于MODIS的平均
蒸散量/(mm·d−1)遥感反演平均蒸
散量/(mm·d−1)平均绝对误
差/(mm·d−1)均方根误
差/(mm·d−1)耕地 3.152 3.233 0.157 0.173 林地 2.281 2.426 0.127 0.143 草地 1.971 1.980 0.103 0.153 水域 5.771 5.571 0.114 0.165 未利用土地 1.571 1.620 0.133 0.225 -
[1] WANG Kaicun,DICKINSON R E. A review of global terrestrial evapotranspiration:Observation,modeling,climatology,and climatic variability[J]. Reviews of Geophysics,2012,50(2):RG2005.
[2] 周剑,程国栋,李新,等. 应用遥感技术反演流域尺度的蒸散发[J]. 水利学报,2009,40(6):679 − 687. [ZHOU Jian,CHENG Guodong,LI Xin,et al. Application of remote sensing technology to estimate river basin evapotranspiration[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2009,40(6):679 − 687. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2009.06.006
ZHOU Jian, CHENG Guodong, LI Xin, et al. Application of remote sensing technology to estimate river basin evapotranspiration[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2009, 40(6): 679 − 687. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2009.06.006
[3] 冯景泽,王忠静. 遥感蒸散发模型研究进展综述[J]. 水利学报,2012,43(8):914 − 925. [FENG Jingze,WANG Zhongjing. A review on evapotranspiration estimation models using remotely sensed data[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2012,43(8):914 − 925. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
FENG Jingze, WANG Zhongjing. A review on evapotranspiration estimation models using remotely sensed data[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2012, 43(8): 914 − 925. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] HASSAN A,ISMAIL S S,ELMOUSTAFA A,et al. Evaluating evaporation rate from high Aswan Dam Reservoir using RS and GIS techniques[J]. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science,2018,21(3):285 − 293. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrs.2017.10.001
[5] 王卓月,孔金玲,李英,等. 基于MOD16的银川平原地表蒸散量时空特征及影响因素分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(3):53 − 61. [WANG Zhuoyue,KONG Jinling,LI Ying,et al. An analysis of spatio-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of surface evapotranspiration in the Yinchuan Plain based on MOD16 data[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(3):53 − 61. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Zhuoyue, KONG Jinling, LI Ying, et al. An analysis of spatio-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of surface evapotranspiration in the Yinchuan Plain based on MOD16 data[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(3): 53 − 61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 范丽. 基于微波遥感土壤水分驱动下的陆面蒸散发估算研究[D]. 鞍山:辽宁科技大学,2021. [FAN Li. Study on estimation of land surface evapotranspiration driven by microwave soil moisture[D]. Anshan:University of Science and Technology Liaoning,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
FAN Li. Study on estimation of land surface evapotranspiration driven by microwave soil moisture[D]. Anshan: University of Science and Technology Liaoning, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 问晓梅. 半干旱地区降露水和蒸发特征研究[D]. 北京:中国气象科学研究院,2009. [WEN Xiaomei. Research of dew and evaporation characteristics of semi-arid area[D]. Beijing:Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences,2009. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WEN Xiaomei. Research of dew and evaporation characteristics of semi-arid area[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] AKURAJU V R,RYU D,GEORGE B,et al. Seasonal and inter-annual variability of soil moisture stress function in dryland wheat field,Australia[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2017,232:489 − 499. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2016.10.007
[9] 周剑,吴雪娇,李红星,等. 改进SEBS模型评价黑河中游灌溉水资源利用效率[J]. 水利学报,2014,45(12):1387 − 1398. [ZHOU Jian,WU Xuejiao,LI Hongxing,et al. Improved SEBS model for evaluating irrigation water use efficiency in the middle reaches of the Heihe River[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2014,45(12):1387 − 1398. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHOU Jian, WU Xuejiao, LI Hongxing, et al. Improved SEBS model for evaluating irrigation water use efficiency in the middle reaches of the Heihe River[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2014, 45(12): 1387 − 1398. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] FU Jianyu,WANG Weiguang,SHAO Quanxi,et al. Improved global evapotranspiration estimates using proportionality hypothesis-based water balance constraints[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2022,279:113140. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2022.113140
[11] ALLEN R G,PEREIRA L S,RAES D,et al. Crop evapotranspiration :Guidelines for computing crop water requirements,F[M]. Finland:Agricultural and Food Sciences,Environmental Science,1998.
[12] 李毅,付亚亚,唐德秀,等. 砂石覆盖条件下冬小麦蒸散量的单、双作物系数法估算[J]. 农业机械学报,2018,49(3):261 − 270. [LI Yi,FU Yaya,TANG De xiu,et al. Estimation of evapotranspiration of winter wheat based on single and dual crop coefficient approaches under sand gravel mulching conditions[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2018,49(3):261 − 270. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Yi, FU Yaya, TANG De xiu, et al. Estimation of evapotranspiration of winter wheat based on single and dual crop coefficient approaches under sand gravel mulching conditions[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(3): 261 − 270. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 余昭君,胡笑涛,冉辉,等. 基于波文比-能量平衡法的半湿润地区葡萄园蒸发蒸腾量估算[J]. 干旱地区农业研究,2020,38(4):175 − 183. [YU Zhaojun,HU Xiaotao,RAN Hui,et al. Estimation of grape evapotranspiration in semi-humid region based on Bowen ratio energy balance method[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas,2020,38(4):175 − 183. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YU Zhaojun, HU Xiaotao, RAN Hui, et al. Estimation of grape evapotranspiration in semi-humid region based on Bowen ratio energy balance method[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2020, 38(4): 175 − 183. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 张堂堂,文军,李振朝,等. 基于微波遥感参数估算区域蒸散发的方法研究[J]. 高原气象,2013,32(6):1651 − 1657. [ZHANG Tangtang,WEN Jun,LI Zhenchao,et al. A method for determing regional evaportranspiration based on microwave sensing technique[J]. Plateau Meteorology,2013,32(6):1651 − 1657. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2013.00152
ZHANG Tangtang, WEN Jun, LI Zhenchao, et al. A method for determing regional evaportranspiration based on microwave sensing technique[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2013, 32(6): 1651 − 1657. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2013.00152
[15] 王韦娜,张翔,张立锋,等. 蒸渗仪法和涡度相关法测定蒸散的比较[J]. 生态学杂志,2019,38(11):3551 − 3559. [WANG Weina,ZHANG Xiang,ZHANG Lifeng,et al. A comparison study of the evapotranspiration measured by lysimeter and eddy covariance[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology,2019,38(11):3551 − 3559. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Weina, ZHANG Xiang, ZHANG Lifeng, et al. A comparison study of the evapotranspiration measured by lysimeter and eddy covariance[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(11): 3551 − 3559. (in Chinese with English abstract)
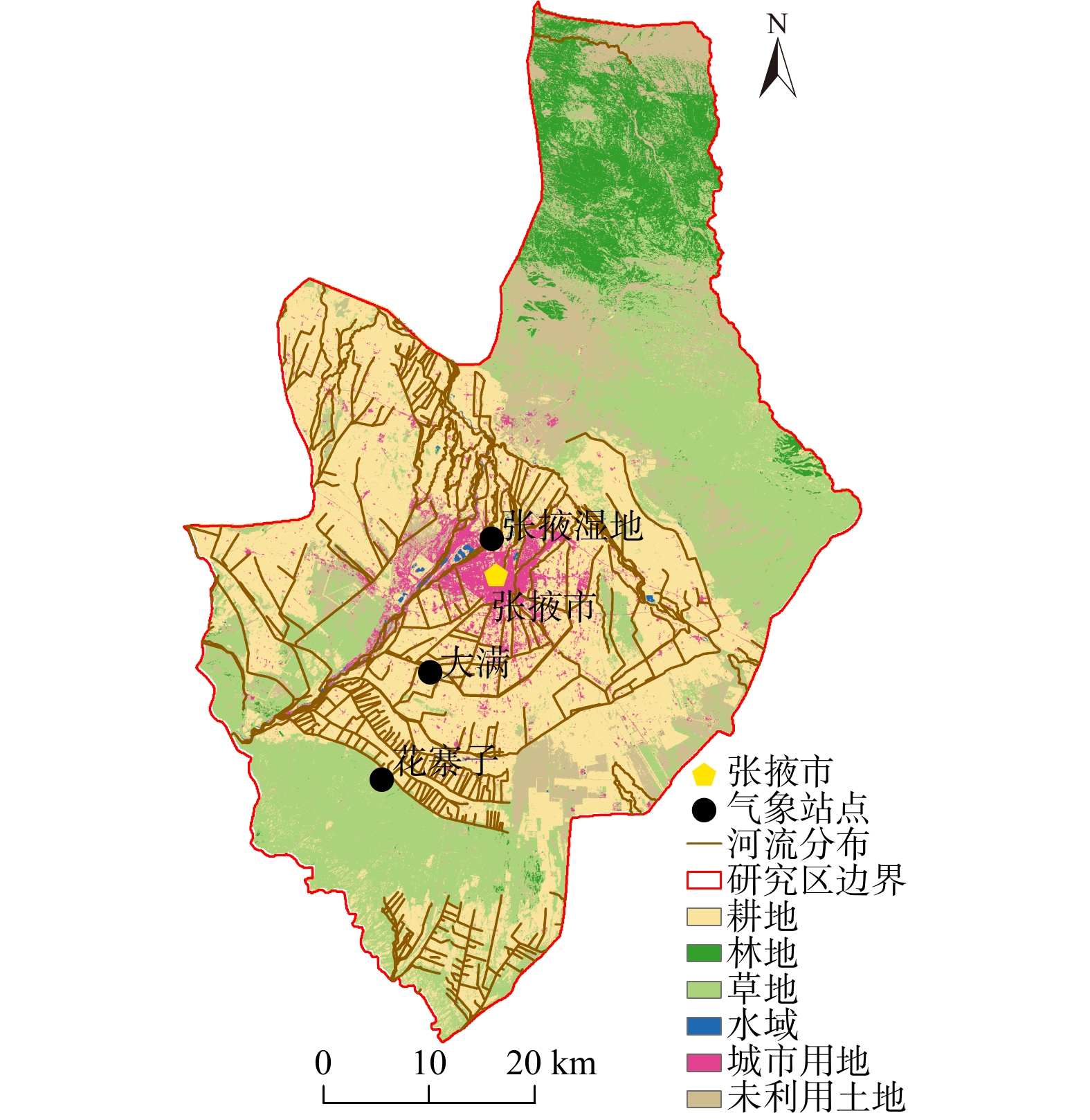
[16] 年雁云. 黑河流域河流分布数据集[Z]. 兰州:国家冰川冻土沙漠科学数据中心,2020. [NIAN Yanyun. River Distribution dataset of the Heihe river basin[Z]. Lanzhou:National glacier frozen soil desert science data center,2020. (in Chinese)]
NIAN Yanyun. River Distribution dataset of the Heihe river basin[Z]. Lanzhou: National glacier frozen soil desert science data center, 2020. (in Chinese)
[17] 刘良云,张肖. 2020年全球30米地表覆盖精细分类产品V1.0[Z]. 北京:中国科学院空天信息创新研究院,2021. [LIU Liangyun,ZHANG Xiao. Fine classification products V1.0 of global 30-meter surface coverage in 2020[Z]. Beijing:Aerospace Information Research Institute,Chinese Academy of Sciences,2021. (in Chinese)]
LIU Liangyun, ZHANG Xiao. Fine classification products V1.0 of global 30-meter surface coverage in 2020[Z]. Beijing: Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021. (in Chinese)
[18] 刘绍民,车涛,徐自为,等. 祁连山综合观测网:黑河流域地表过程综合观测网(大满超级站气象要素梯度观测系统-2020)[Z]. 北京:国家青藏高原科学数据中心,2021. [LIU Shaomin,CHE Tao,XU Ziwei,et al. Qilian Mountains integrated observatory network:Dataset of Heihe integrated observatory network (an observation system of Meteorological elements gradient of Daman Superstation,2020)[Z]. Beijing:National Tibetan Plateau / Third Pole Environment Data Center,2021. (in Chinese)]
LIU Shaomin, CHE Tao, XU Ziwei, et al. Qilian Mountains integrated observatory network: Dataset of Heihe integrated observatory network (an observation system of Meteorological elements gradient of Daman Superstation, 2020)[Z]. Beijing: National Tibetan Plateau / Third Pole Environment Data Center, 2021. (in Chinese)
[19] LIU S M,XU Z W,WANG W Z,et al. A comparison of eddy-covariance and large aperture scintillometer measurements with respect to the energy balance closure problem[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2011,15(4):1291 − 1306. doi: 10.5194/hess-15-1291-2011
[20] 刘绍民,车涛,徐自为,等. 祁连山综合观测网:黑河流域地表过程综合观测网(大满超级站涡动相关仪-2020)[Z]. 北京:国家青藏高原科学数据中心,2021. [LIU Shaomin,CHE Tao,XU Ziwei,et al. Qilian Mountains integrated observatory network:Dataset of Heihe integrated observatory network (eddy covariance system of Daman Superstation,2020)[Z]. Beijing:National Tibetan Plateau / Third Pole Environment Data Center,2021. (in Chinese)]
LIU Shaomin, CHE Tao, XU Ziwei, et al. Qilian Mountains integrated observatory network: Dataset of Heihe integrated observatory network (eddy covariance system of Daman Superstation, 2020)[Z]. Beijing: National Tibetan Plateau / Third Pole Environment Data Center, 2021. (in Chinese)
[21] 刘绍民,车涛,徐自为,等. 祁连山综合观测网:黑河流域地表过程综合观测网(花寨子站涡动相关仪-2020)[Z]. 北京:国家青藏高原科学数据中心,2021. [LIU Shaomin,CHE Tao,XU Ziwei,et al. Qilian Mountains integrated observatory network:Dataset of Heihe integrated observatory network (eddy covariance system of Huazhaizi station,2020)[Z]. Beijing:National Tibetan Plateau / Third Pole Environment Data Center,2021. (in Chinese)]
LIU Shaomin, CHE Tao, XU Ziwei, et al. Qilian Mountains integrated observatory network: Dataset of Heihe integrated observatory network (eddy covariance system of Huazhaizi station, 2020)[Z]. Beijing: National Tibetan Plateau / Third Pole Environment Data Center, 2021. (in Chinese)
[22] 刘绍民,车涛,徐自为,等. 祁连山综合观测网:黑河流域地表过程综合观测网(张掖湿地站涡动相关仪-2020)[Z]. 北京:国家青藏高原科学数据中心,2021. [LIU Shaomin,CHE Tao,XU Ziwei,et al. Qilian Mountains integrated observatory network:Dataset of Heihe integrated observatory network (eddy covariance system of Zhangye wetland station,2020)[Z]. Beijing:National Tibetan Plateau / Third Pole Environment Data Center,2021. (in Chinese)]
LIU Shaomin, CHE Tao, XU Ziwei, et al. Qilian Mountains integrated observatory network: Dataset of Heihe integrated observatory network (eddy covariance system of Zhangye wetland station, 2020)[Z]. Beijing: National Tibetan Plateau / Third Pole Environment Data Center, 2021. (in Chinese)
[23] 张甘霖,刘峰. 中国高分辨率国家土壤信息网格基本属性数据集(2010—2018)[Z]. 北京:国家青藏高原科学数据中心,2021. [ZHANG Ganlin,LIU Feng. Basic soil property dataset of high-resolution China Soil Information Grids (2010−2018)[Z]. Beijing:National Tibetan Plateau / Third Pole Environment Data Center,2021. (in Chinese)]
ZHANG Ganlin, LIU Feng. Basic soil property dataset of high-resolution China Soil Information Grids (2010−2018)[Z]. Beijing: National Tibetan Plateau / Third Pole Environment Data Center, 2021. (in Chinese)
[24] LIU Feng,ZHANG Ganlin,SONG Xiaodong,et al. High-resolution and three-dimensional mapping of soil texture of China[J]. Geoderma,2020,361:114061. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.114061
[25] 赵天杰,宋沛林,张永强,等. 中国1千米分辨率逐日全天候地表土壤水分数据集(2003-2022)[Z]. 北京:国家青藏高原科学数据中心,2021. [ZHAO Tianjie,SONG Peilin,ZHANG Yongqiang,et al. Daily all weather surface soil moisture data set with 1 km resolution in China (2003-2022)[Z]. Beijing:National Tibetan Plateau / Third Pole Environment Data Center,2021. (in Chinese)]
ZHAO Tianjie, SONG Peilin, ZHANG Yongqiang, et al. Daily all weather surface soil moisture data set with 1 km resolution in China (2003-2022)[Z]. Beijing: National Tibetan Plateau / Third Pole Environment Data Center, 2021. (in Chinese)
[26] 姚云军,刘绍民,尚珂. 祁连山地区基于MODIS的逐日地表蒸散发数据(2020)(ETHi-merge V1.0)[Z]. 北京:国家青藏高原科学数据中心,2021. [YAO Yunjun,LIU Shaomin,SHANG Ke. Daily MODIS-based land surface evapotranspiration dataset of 2020 in Qilian Mountain area (ETHi-merge V1.0)[Z]. Beijing:National Tibetan Plateau / Third Pole Environment Data Center,2021. (in Chinese)]
YAO Yunjun, LIU Shaomin, SHANG Ke. Daily MODIS-based land surface evapotranspiration dataset of 2020 in Qilian Mountain area (ETHi-merge V1.0)[Z]. Beijing: National Tibetan Plateau / Third Pole Environment Data Center, 2021. (in Chinese)
[27] 张颀. 灌区农田土壤水分运移模型研究与预测[D]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆农业大学,2005. [ZHANG Qi. Study and prediction of the soil water transport model in irrigation field[D]. Urumqi:Xinjiang Agricultural University,2005. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Qi. Study and prediction of the soil water transport model in irrigation field[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2005. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] BERG Alexis,SHEFFIELD Justin,MILLY P C D. Divergent surface and total soil moisture projections under global warming[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2017,44(1):236 − 244. doi: 10.1002/2016GL071921
-



 下载:
下载: