Research progress on the impact of antibiotics in groundwater systems on denitrification
-
摘要:
微生物反硝化过程是地下水中硝酸盐最重要的脱氮形式。再生水利用和养殖业引起的抗生素污染常与硝酸盐共存。因此,需深入研究抗生素及其存在形式对地下水中硝酸盐反硝化过程及抗生素抗性基因(ARGs)产生、富集和传播的影响,以综合解析地下水硝酸盐浓度升高的原因。近年来的研究识别了地下水系统中抗生素的解离/络合形态、吸附形式(层间吸附/表面吸附)、水解与微生物降解产物等存在形式,并从反硝化微生物群落、功能酶的种类与活性、功能基因丰度以及ARGs产生与传播途径阐释了抗生素对反硝化过程的抑制机制。主要结论为:(1)地下水系统中,抗生素以多种形式存在,而不同形式的抗生素对微生物的毒性有显著差异;(2)在每升纳克至微克水平的抗生素存在下,地下水反硝化过程受到抑制,抗生素改变了微生物群落结构,抑制了功能酶活性,增加了ARGs的丰度,在这些作用的协同影响下,硝酸盐降解动力学由零级向一级转变;(3)在抗生素抑制反硝化过程中,还增加了温室气体N2O的释放量,抗生素影响了功能基因nosZ表达,N2O浓度与nosZ丰度呈负指数关系。在综述相关文献的基础上,对未来研究提出了展望:(1)定量识别典型抗生素进入地下水系统后的存在形式;(2)厘清不同存在形式的抗生素对反硝化微生物群落、功能酶种类与活性、功能基因丰度和多样性的影响;(3)探索反硝化功能基因在抗生素不同存在形式和不同输入方式下的变化过程,并建立ARGs产生、富集与传播模式;(4)结合野外观测和室内实验从分子生物学、环境化学和水文地质学多尺度研究复合污染下地下水系统的反硝化过程,可为日益复杂的地下水污染防治和饮用水安全保障提供理论依据。
Abstract:The microbial denitrification process is the most important form of nitrate-nitrogen removal in groundwater. The reclaimed water reuse and livestock breeding caused antibiotic pollution usually co-occurs with nitrate. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct in-depth research on the effects of denitrification and the generation, accumulation, and dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) by antibiotics and their forms to comprehensively analyze the reasons for the increased concentration of nitrate in groundwater. Many studies in recent years have identified the dissociation/complexation, adsorption forms (interlayer adsorption/surface adsorption), and the products of hydrolysis and microbial degradation of antibiotics in groundwater systems; and have elucidated the inhibitory mechanism of antibiotics on the denitrification process from the perspectives of denitrifying microbial communities, the types and activities of functional enzymes, abundance of functional genes, as well as the production and transmission pathways of ARGs. The main conclusions are as follows: (1) In groundwater systems, antibiotics exist in various forms, and different forms of antibiotics exhibit significant differences in toxicity to microorganisms. (2) In the presence of antibiotics at levels ranging from nanograms to micrograms per liter, the denitrification process in groundwater is inhibited. Antibiotics alter the microbial community structure, suppress enzymatic activity, and increase the abundance of ARGs. Under the synergistic effects of these actions, the kinetics of nitrate degradation shift from zero-order to first-order. (3) During the antibiotic-induced inhibition of denitrification, there is also an increase in the emission of the greenhouse gas N2O. Antibiotics primarily affect the expression of the functional gene nosZ, and the concentration of N2O shows a negative exponential relationship with nosZ abundance. Based on the review of relevant literature, the prospects for future research are put forward: (1) quantitatively identifying the existence forms of typical antibiotics after entering groundwater systems; (2) elucidating the impact of antibiotics in different existence forms on denitrifying microbial communities, the types and activities of functional enzymes, and the abundance and diversity of functional genes; (3) exploring the dynamic process of denitrification functional genes under different existence forms and input modes of antibiotics, and establishing models for the production, enrichment, and transmission of ARGs; (4) combining field observations and laboratory experiments to study the denitrification process in groundwater systems under complex pollution from molecular biology, environmental chemistry, and hydrogeology perspectives. This research can provide a theoretical basis for addressing the increasingly complex groundwater pollution prevention and drinking water safety assurance.
-
Key words:
- aquifer /
- co-contamination /
- nitrate /
- denitrification /
- antibiotics /
- antibiotic resistance genes
-

-
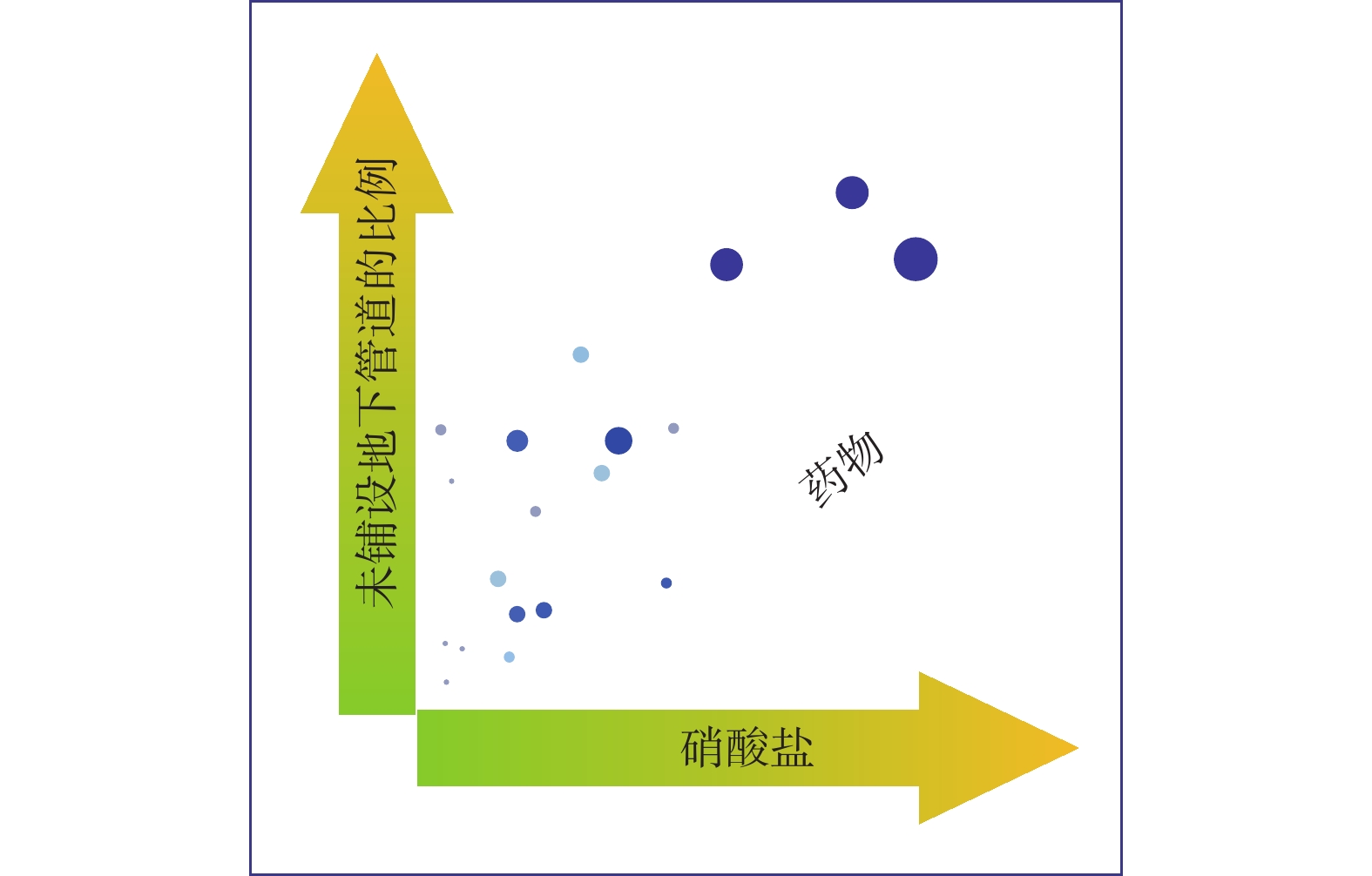
图 1 地下水中硝酸盐和药物检出的关系[12]
Figure 1.
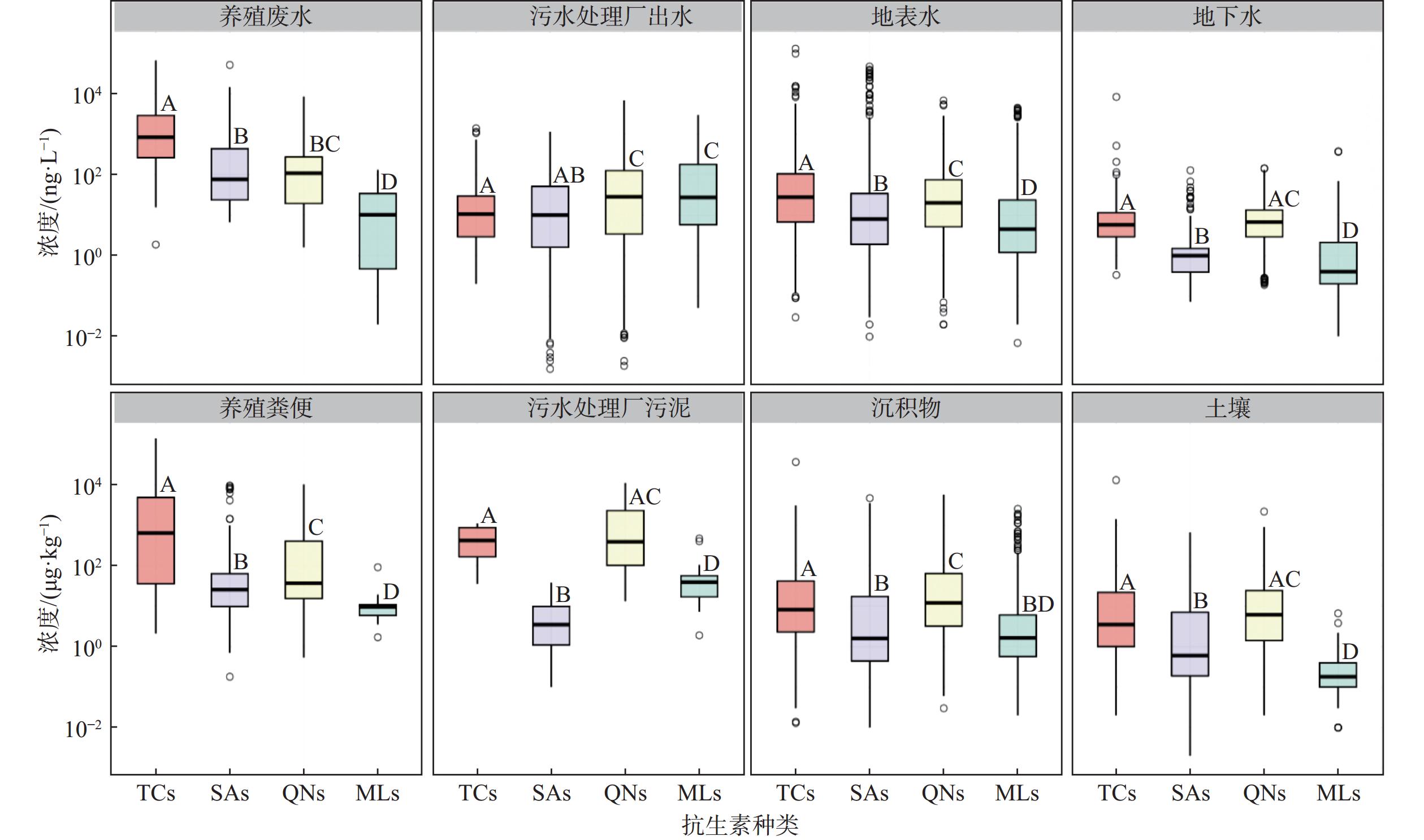
图 2 我国不同环境介质中抗生素浓度的箱线图[16]
Figure 2.
-
[1] JIANG Longwei,ZHAI Wanying,WANG Jun,et al. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in the water sources of the Wuhan stretch of the Yangtze River:Occurrence,distribution,and ecological risks[J]. Environmental Research,2023,239(P1):117295.
[2] ZHANG Mingzhi,HOU Jun,XIA Jun,et al. Antibiotics can alter the bacterial extracellular polymeric substances and surface properties affecting the cotransport of bacteria and antibiotics in porous media[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2023,461:132569.
[3] QADEER A,GUO Rui,LIU Yaqing,et al. A mega study of antibiotics contamination in Eastern aquatic ecosystems of China:Occurrence,interphase transfer processes,ecotoxicological risks,and source modeling[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2023,458:131980. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131980
[4] WANG Xuerong,ZHANG Xu,LI Na,et al. Prioritized regional management for antibiotics and heavy metals in animal manure across China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2023,461:132706.
[5] LV Yinzhi,LUO Xiaojun,ZHAO Jianliang,et al. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in sediments from black-odor ditches in urban areas from China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,787:147554. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147554
[6] ZENG Huiping,LI Jianxue,ZHAO Weihua,et al. The current status and prevention of antibiotic pollution in groundwater in China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2022,19(18):11256. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191811256
[7] 高立红,史亚利,厉文辉,等. 抗生素环境行为及其环境效应研究进展[J]. 环境化学,2013,32(9):1619 − 1633. [GAO Lihong,SHI Yali,LI Wenhui,et al. Environmental behavior and impacts of antibiotics[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2013,32(9):1619 − 1633. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.09.004
GAO Lihong, SHI Yali, LI Wenhui, et al . Environmental behavior and impacts of antibiotics[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2013 ,32 (9 ):1619 −1633 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[8] HAN Maozhen,ZHANG Lu,ZHANG Na,et al. Antibiotic resistome in a large urban-lake drinking water source in middle China:Dissemination mechanisms and risk assessment[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2022,424:127745. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127745
[9] YANG Chao,ZHAO Yanhua,CAO Wei,et al. Metagenomic analysis reveals antibiotic resistance genes and virulence factors in the saline-alkali soils from the Yellow River Delta,China[J]. Environmental Research,2022,214:113823. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.113823
[10] MADISON R J,BRUNETT J O. Overview of the occurrence of nitrate in ground water of the United States[J]. US Geological Survey Water Supply Paper,1985,2275:93 − 105.
[11] HAN Dongmei,MATTHEW J C,CAO Guoliang. Deep challenges for China’s war on water pollution[J]. Environmental Pollution,2016,218:1222 − 1233. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.078
[12] SCHAIDER L A,RUDEL R A,ACKERMAN J M,et al. Pharmaceuticals,perfluorosurfactants,and other organic wastewater compounds in public drinking water wells in a shallow sand and gravel aquifer[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2014,468-469:384 − 393. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.067
[13] MENG Ting,CHENG Wen,WAN Tian,et al. Occurrence of antibiotics in rural drinking water and related human health risk assessment[J]. Environmental Technology,2021,42(5):671 − 681. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2019.1642390
[14] LI Feifei,CHEN Lyujun,BAO Yingyu,et al. Identification of the priority antibiotics based on their detection frequency,concentration,and ecological risk in urbanized coastal water[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,747:141275. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141275
[15] WANG Yingying,DONG Xiaolian,ZANG Jinxin,et al. Antibiotic residues of drinking-water and its human exposure risk assessment in rural Eastern China[J]. Water Research,2023,236:119940 doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2023.119940
[16] LIU Zhong,ZOU Huiyun,LAN Zouran,et al. Prioritized antibiotics screening based on comprehensive risk assessments and related management strategy in various animal farms[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2022,319:115702. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115702
[17] HU Jingrun,LI Si,ZHANG Wei,et al. Animal production predominantly contributes to antibiotic profiles in the Yangtze River[J]. Water Research,2023,242:120214. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2023.120214
[18] ZHI Suli,SHEN Shizhou,ZHOU Jing,et al. Systematic analysis of occurrence,density and ecological risks of 45 veterinary antibiotics:Focused on family livestock farms in Erhai Lake basin,Yunnan,China[J]. Environmental Pollution,2020,267:115539. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115539
[19] LI Xiaohua,LIU Chong,CHEN Yongxing,et al. Antibiotic residues in liquid manure from swine feedlot and their effects on nearby groundwater in regions of North China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2018,25(12):11565. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1339-1
[20] 黄福杨. 中国不同环境介质中典型抗生素识别及优先控制清单研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学,2021. [HUANG Fuyang. Research on the identification of typical antibiotics and listof priority controlled antibiotics in various environmental compartments in China[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HUANG Fuyang. Research on the identification of typical antibiotics and listof priority controlled antibiotics in various environmental compartments in China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) [21] ZHANG Yingjie,BOYD S A,TEPPEN B J,et al. Role of tetracycline speciation in the bioavailability to Escherichia coli for uptake and expression of antibiotic resistance[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2014,48(9):4893 − 4900.
[22] MUSTAPHA Z,MOHAMED B,RAMDHANE D. Experimental study of degradation and biodegradability of oxytetracycline antibiotic in aqueous solution using Fenton process[J]. Environmental Engineering Research,2020,25(3):316 − 323.
[23] HAN Dongya,HOU Qinxuan,SONG Jiangmin,et al. Groundwater antibiotics contamination in an alluvial-pluvial fan,North China Plain:Occurrence,sources,and risk assessment[J]. Environmental Research,2023,235:116653. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.116653
[24] KIM Y,LIM S,HAN M,et al. Sorption characteristics of oxytetracycline,amoxicillin,and sulfathiazole in two different soil types[J]. Geoderma,2012,185/186:97 − 101. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2012.03.016
[25] 秦晓鹏. 左氧氟沙星在针铁矿上的吸附:磷酸盐和腐殖酸的影响[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2014. [QIN Xiaopeng. Adsorption of levofloxacin to goethite:Effects of phosphate and humic acid[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences,2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
QIN Xiaopeng. Adsorption of levofloxacin to goethite: Effects of phosphate and humic acid[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26] 王阳. 不同吸附态的左氧氟沙星对大肠杆菌的毒理学研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2014. [WANG Yang. The toxicological study of different adsorbed levofloxacin on Escherichia coli[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences,2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Yang. The toxicological study of different adsorbed levofloxacin on Escherichia coli[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] LI Jiping,LI Wei,LIU Kai,et al. Global review of macrolide antibiotics in the aquatic environment:Sources,occurrence,fate,ecotoxicity,and risk assessment[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2022,439:129628. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129628
[28] CHENG Yan,LI Wenxuan,ZHANG Dan,et al. Hydrolysis of sulfamethoxazole in the hyporheic zone:Kinetics,factors and pathways[J]. Environmental Technology,2023,1 − 14.
[29] MAKI T,HASEGAWA H,KITAMI H,et al. Bacterial degradation of antibiotic residues in marine fish farm sediments of Uranouchi Bay and phylogenetic analysis of antibiotic-degrading bacteria using 16S rDNA sequences[J]. Fisheries Science,2006,72(4):811 − 820. doi: 10.1111/j.1444-2906.2006.01222.x
[30] GIRARDI C,GREVE J,LAMSHÖFT M,et al. Biodegradation of ciprofloxacin in water and soil and its effects on the microbial communities[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2011,198:22 − 30. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.004
[31] ZAREI-BAYGI A,SMITH A L. Intracellular versus extracellular antibiotic resistance genes in the environment:Prevalence,horizontal transfer,and mitigation strategies[J]. Bioresource Technology,2021,319:124181. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124181
[32] AMINOV R I. The role of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in nature[J]. Environmental Microbiology,2009,11(12):2970 − 2988. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.01972.x
[33] JOAKIM LARSSON D G,FLACH C F. Antibiotic resistance in the environment[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology,2022,20:257 − 269. doi: 10.1038/s41579-021-00649-x
[34] ZHU Yongguan,JOHNSON T A,SU Jianqiang,et al. Diverse and abundant antibiotic resistance genes in Chinese swine farms[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2013,110(9):3435 − 3440.
[35] ZAINAB S M,JUNAID M,XU N,et al. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistant genes (ARGs) in groundwater:A global review on dissemination,sources,interactions,environmental and human health risks[J]. Water Research,2020,187:116455. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116455
[36] FETH J H. Nitrogen compounds in natural water—A review[J]. Water Resources Research,1966,2(1):41 − 58. doi: 10.1029/WR002i001p00041
[37] BRUCE D,MICHAEL G. Methods for evaluating temporal groundwater quality data and results of decadal-scale changes in chloride,dissolved solids,and nitrate concentrations in groundwater in the United States,1988-2010[M]. Reston:U. S. Department of the Interior,2012.
[38] 张维理,田哲旭,张宁,等. 我国北方农用氮肥造成地下水硝酸盐污染的调查[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报,1995,1(2):82 − 89. [ZHANG Weili,TIAN Zhexu,ZHANG Ning,et al. Investigation of nitrate pollution in ground water due to nitrogen fertilization in agriculture in North China[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizing Science,1995,1(2):82 − 89. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Weili, TIAN Zhexu, ZHANG Ning, et al . Investigation of nitrate pollution in ground water due to nitrogen fertilization in agriculture in North China[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizing Science,1995 ,1 (2 ):82 −89 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[39] 刘宏斌,李志宏,张云贵,等. 北京平原农区地下水硝态氮污染状况及其影响因素研究[J]. 土壤学报,2006,43(3):405 − 413. [LIU Hongbin,LI Zhihong,ZHANG Yungui,et al. Nitrate contamination of groundwater and its affecting factors in rural areas of Beijing Plain[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica,2006,43(3):405 − 413. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Hongbin, LI Zhihong, ZHANG Yungui, et al . Nitrate contamination of groundwater and its affecting factors in rural areas of Beijing Plain[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica,2006 ,43 (3 ):405 −413 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[40] 赵同科,张成军,杜连凤,等. 环渤海七省(市)地下水硝酸盐含量调查[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2007,26(2):779 − 783. [ZHAO Tongke,ZHANG Chengjun,DU Lianfeng,et al. Investigation on nitrate concentration in groundwater in seven provinces (city) surrounding the Bo-Hai Sea[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2007,26(2):779 − 783. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2007.02.072
ZHAO Tongke, ZHANG Chengjun, DU Lianfeng, et al . Investigation on nitrate concentration in groundwater in seven provinces (city) surrounding the Bo-Hai Sea[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2007 ,26 (2 ):779 −783 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[41] 文冬光,何江涛,孙继朝,等. DZ/T0290—2015《地下水水质标准》解读[M]. 北京:地质出版社,2016. [WEN Dongguang,HE Jiangtao,SUN Jizhao,et al. DZ/T0290—2015 groundwater quality standards interpretation[M]. Beijing:Geology Press,2016. (in Chinese)]
WEN Dongguang, HE Jiangtao, SUN Jizhao, et al. DZ/T0290—2015 groundwater quality standards interpretation[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 2016. (in Chinese) [42] GAN Lin,HUANG Guanxing,PEI Lixin,et al. Distributions,origins,and health-risk assessment of nitrate in groundwater in typical alluvial-pluvial fans,North China Plain[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2022,29(12):17031 − 17048. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-17067-4
[43] ZHANG Yanchun,PROMMER H,BROERS H P,et al. Model-based integration and analysis of biogeochemical and isotopic dynamics in a nitrate-polluted pyritic aquifer[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2013,47(18):10415 − 10422.
[44] GÓMEZ-ALDAY J J,CARREY R,VALIENTE N,et al. Denitrification in a hypersaline lake–aquifer system (Pétrola Basin,Central Spain):The role of recent organic matter and Cretaceous organic rich sediments[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2014,497/498:594 − 606. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.07.129
[45] WONG W W,GRACE M R,CARTWRIGHT I,et al. Unravelling the origin and fate of nitrate in an agricultural–urban coastal aquifer[J]. Biogeochemistry,2015,122(2):343 − 360.
[46] MURGULET D,TICK G R. Understanding the sources and fate of nitrate in a highly developed aquifer system[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2013,155:69 − 81. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2013.09.004
[47] ZHU Aiping,CHEN Jianyao,GAO Lei,et al. Combined microbial and isotopic signature approach to identify nitrate sources and transformation processes in groundwater[J]. Chemosphere,2019,228:721 − 734. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.163
[48] BROOKS M H,SMITH R L,MACALADY D L. Inhibition of existing denitrification enzyme activity by chloramphenicol[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,1992,58(5):1746 − 1753. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.5.1746-1753.1992
[49] SCHAUSS K,FOCKS A,LEININGER S,et al. Dynamics and functional relevance of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea in two agricultural soils[J]. Environmental Microbiology,2009,11(2):446 − 456. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01783.x
[50] COSTANZO S D,MURBY J,BATES J. Ecosystem response to antibiotics entering the aquatic environment[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2005,51(1/2/3/4):218 − 223.
[51] CHEN Yuan,CHEN Yunzeng,DING Cheng,et al. Effects of tetracycline on simultaneous biological wastewater nitrogen and phosphorus removal[J]. RSC Advances,2015,5:59326 − 59334. doi: 10.1039/C5RA08434B
[52] NAVA A,DANESHIAN L,SARMA H. Antibiotic resistant genes in the environment-exploring surveillance methods and sustainable remediation strategies of antibiotics and ARGs[J]. Environmental Research,2022,215:114212. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.114212
[53] SINGH R, SINGH A P, KUMAR S, et al. Antibiotic resistance in major rivers in the world: a systematic review on occurrence, emergence, and management strategies[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2019,234:1484 − 1505.
[54] 周启星,罗义,王美娥. 抗生素的环境残留、生态毒性及抗性基因污染[J]. 生态毒理学报,2007,2(3):243 − 251. [ZHOU Qixing,LUO Yi,WANG Meie. Environmental residues and ecotoxicity of antibiotics and their resistance gene pollution:A review[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology,2007,2(3):243 − 251. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5897.2007.03.001
ZHOU Qixing, LUO Yi, WANG Meie . Environmental residues and ecotoxicity of antibiotics and their resistance gene pollution: A review[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology,2007 ,2 (3 ):243 −251 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[55] 王丽平,章明奎,郑顺安. 土壤中恩诺沙星的吸附-解吸特性和生物学效应[J]. 土壤通报,2008(2):393 − 397. [WANG Liping,ZHANG Mingkui,ZHENG Shun’an. Adsorption-desorption char acteristics and biological effects of enrofloxacin in agricultur al soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science,2008(2):393 − 397. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Liping, ZHANG Mingkui, ZHENG Shun’an . Adsorption-desorption char acteristics and biological effects of enrofloxacin in agricultur al soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science,2008 (2 ):393 −397 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[56] 王加龙,刘坚真,陈杖榴,等. 恩诺沙星残留对土壤微生物功能的影响[J]. 生态学报,2005,25(2):279 − 282. [WANG Jialong,LIU Jianzhen,CHEN Zhangliu,et al. Effects of enrofloxacin residues on the functions of soil microbes[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2005,25(2):279 − 282. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Jialong, LIU Jianzhen, CHEN Zhangliu, et al . Effects of enrofloxacin residues on the functions of soil microbes[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2005 ,25 (2 ):279 −282 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[57] YANG Qingxiang,ZHANG Jing,ZHU Kongfang,et al. Influence of oxytetracycline on the structure and activity of microbial community in wheat rhizosphere soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences,2009,21(7):954 − 959. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62367-0
[58] GUAN Aomei,QI Weixiao,PENG Qiang,et al. Environmental heterogeneity determines the response patterns of microbially mediated N-reduction processes to sulfamethoxazole in river sediments[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2022,421:126730. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126730
[59] GUI M Y,CHEN Q,NI J R. Effect of sulfamethoxazole on aerobic denitrification by strain Pseudomonas stutzeri PCN-1[J]. Bioresource Technology,2017,235:325-331.
[60] SHAN J,YANG P P,RAHMAN M M,et al. Tetracycline and sulfamethazine alter dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes and increase N2O release in rice fields[J]. Environmental Pollution,2018,242:788 − 796. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.061
[61] HOU L,YIN G,LIU M,et al. Effects of sulfamethazine on denitrification and the associated N2O release in estuarine and coastal sediments[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2015,49(1):326 − 333.
[62] CHEN Cheng,YIN Guoyu,HOU Lijun,et al. Effects of sulfamethoxazole on coupling of nitrogen removal with nitrification in Yangtze Estuary sediments[J]. Environmental Pollution,2021,271(2):116382
[63] YIN Guoyu,HOU Lijun,LIU Min,et al. Effects of multiple antibiotics exposure on denitrification process in the Yangtze Estuary sediments[J]. Chemosphere,2017,171:118 − 125. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.12.068
[64] ZOU Hua,HE Jiangtao,GUAN Xiangyu,et al. Microbial responses underlying the denitrification kinetic shifting exposed to ng/L- and μg/L-level lomefloxacin in groundwater[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,417(7):126093.
[65] 杨美萍,何江涛,邹华,等. 盐酸洛美沙星输入方式对水中反硝化过程的影响[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2022,44(1):78 − 90. [YANG Meiping,HE Jiangtao,ZOU Hua,et al. Effects of lomefloxacin hydrochloride input modes on denitrification process in water[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,2022,44(1):78 − 90. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YANG Meiping, HE Jiangtao, ZOU Hua, et al . Effects of lomefloxacin hydrochloride input modes on denitrification process in water[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,2022 ,44 (1 ):78 −90 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[66] WU Dong,CHEN Guanzhou,ZHANG Xiaojun,et al. Change in microbial community in landfill refuse contaminated with antibiotics facilitates denitrification more than the increase in ARG over long-term[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):41230. doi: 10.1038/srep41230
[67] AMANN R I,BINDER B J,OLSON R J,et al. Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analyzing mixed microbial populations[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,1990,56(6):1919 − 1925. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1919-1925.1990
[68] SCHOLZ M B,LO C C,CHAIN P S. Next generation sequencing and bioinformatic bottlenecks:The current state of metagenomic data analysis[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology,2012,23(1):9 − 15.
[69] MICAH H,JEFFREY J W,KIRK H J,et al. Error-correcting barcoded primers for pyrosequencing hundreds of samples in multiplex[J]. Nature Methods,2008,5(3):235 − 237. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1184
[70] LI Bo,YAN Tao. Next generation sequencing reveals limitation of qPCR methods in quantifying emerging antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in the environment[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2021,105(7):2925 − 2936. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11202-4
[71] FANG Linfa,CHEN Chengyu,LI Shiyang,et al. A comprehensive and global evaluation of residual antibiotics in agricultural soils:Accumulation,potential ecological risks,and attenuation strategies[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2023,262:115175. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115175
[72] YANG Han,XU Mu,WANG Liqing,et al. Metagenomic analysis to determine the characteristics of antibiotic resistance genes in typical antibiotic-contaminated sediments[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences,2023,128:12 − 25. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2022.08.014
[73] JI Bingzhen,QIN Junjun,MA Yijia,et al. Metagenomic analysis reveals patterns and hosts of antibiotic resistance in different pig farms[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2023,30(18):52087 − 52106. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-25962-1
[74] LAPIDUS A L,KOROBEYNIKOV A I. Metagenomic data assembly:The way of decoding unknown microorganisms[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2021,12:613791. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.613791
[75] JAY M,JAMIE W,DANIEL J,et al. Microbial community transcriptomes reveal microbes and metabolic pathways associated with dissolved organic matter turnover in the sea[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,2010,107(38):16420 − 16427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010732107
-



 下载:
下载: