Mechanism of chemical-biological composite clogging of aquifer caused by Al(III) and bacteria
-
摘要:
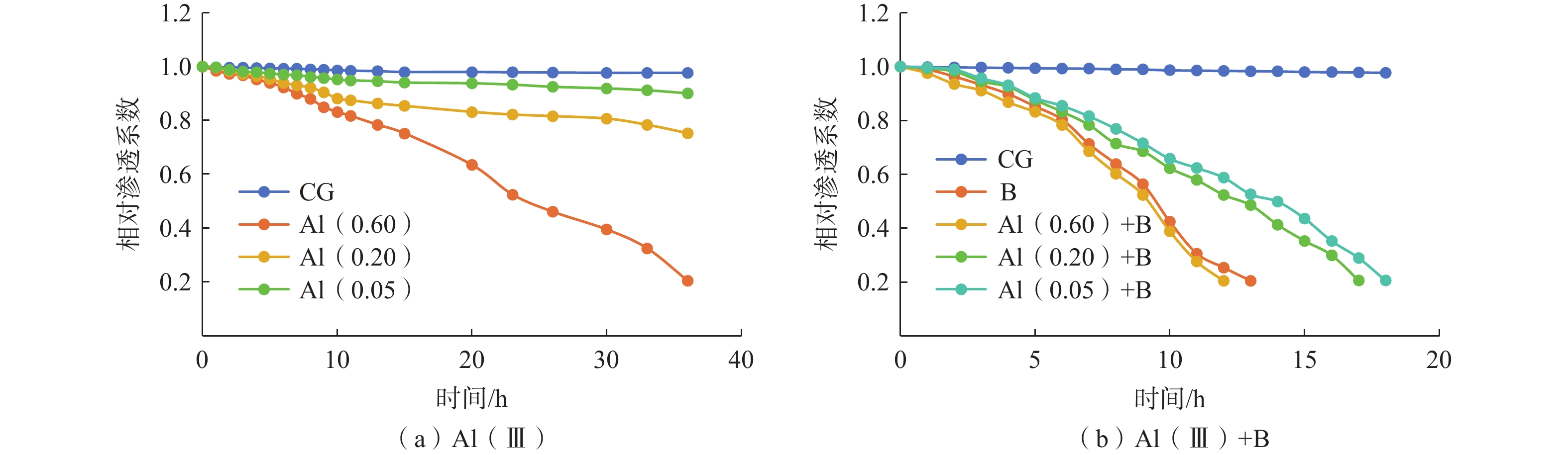
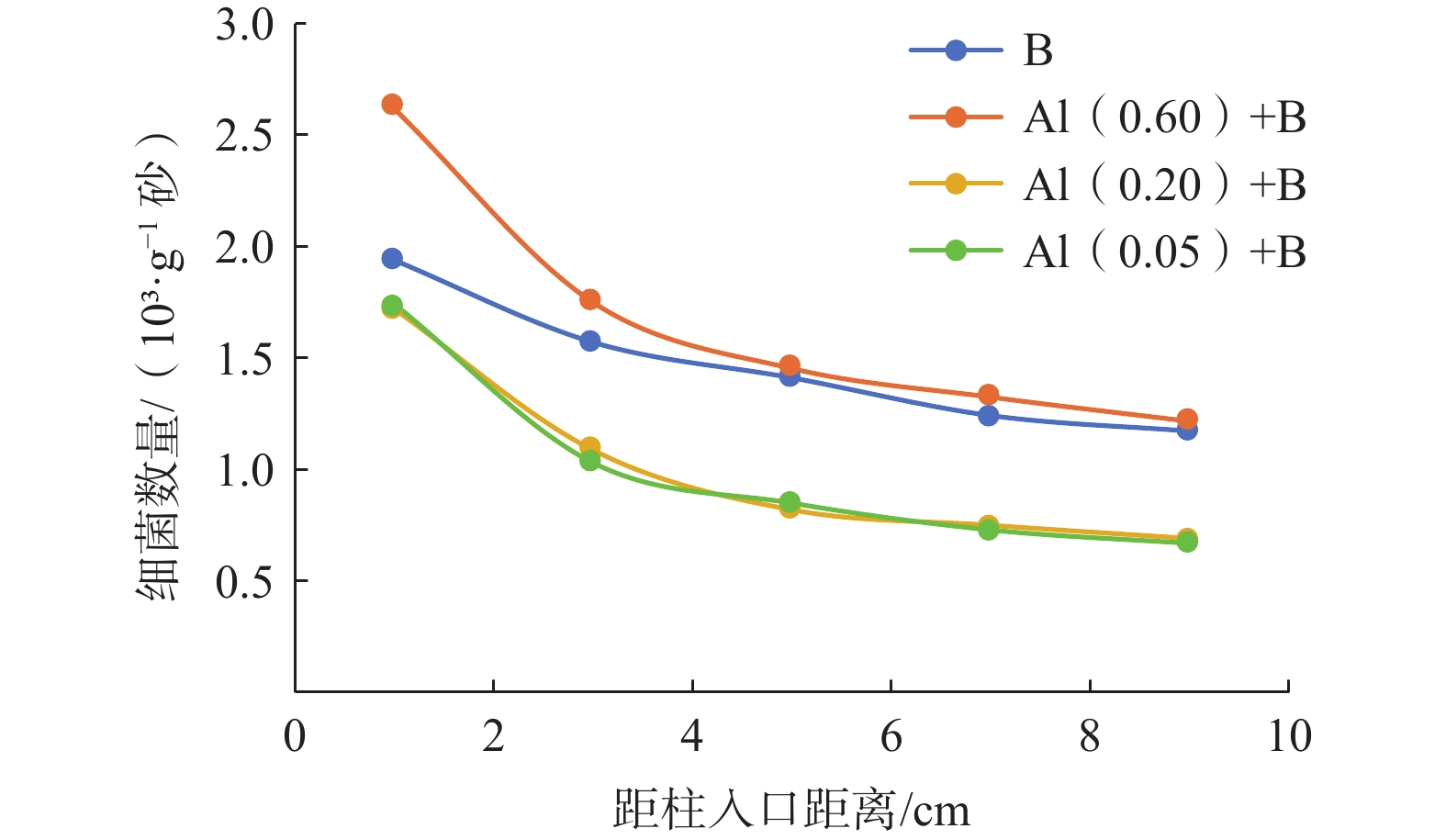
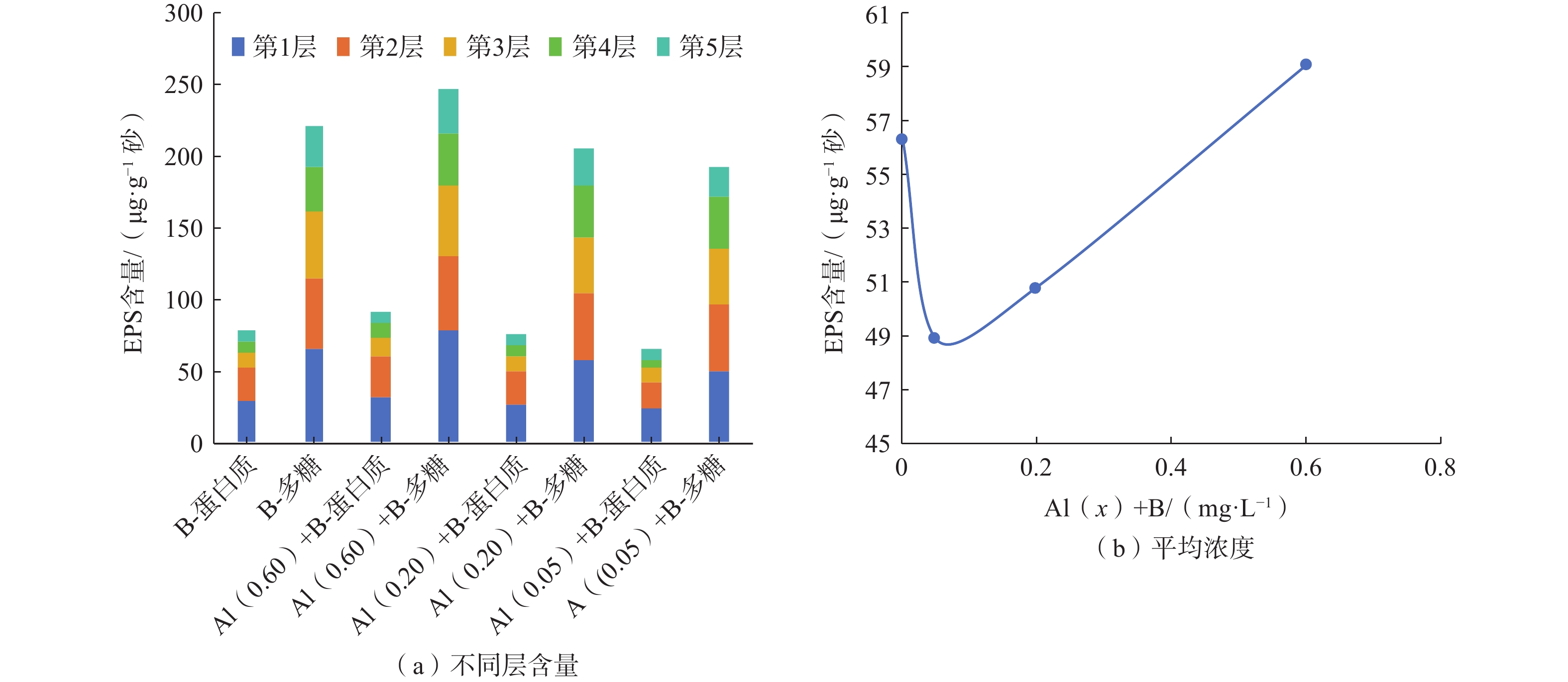
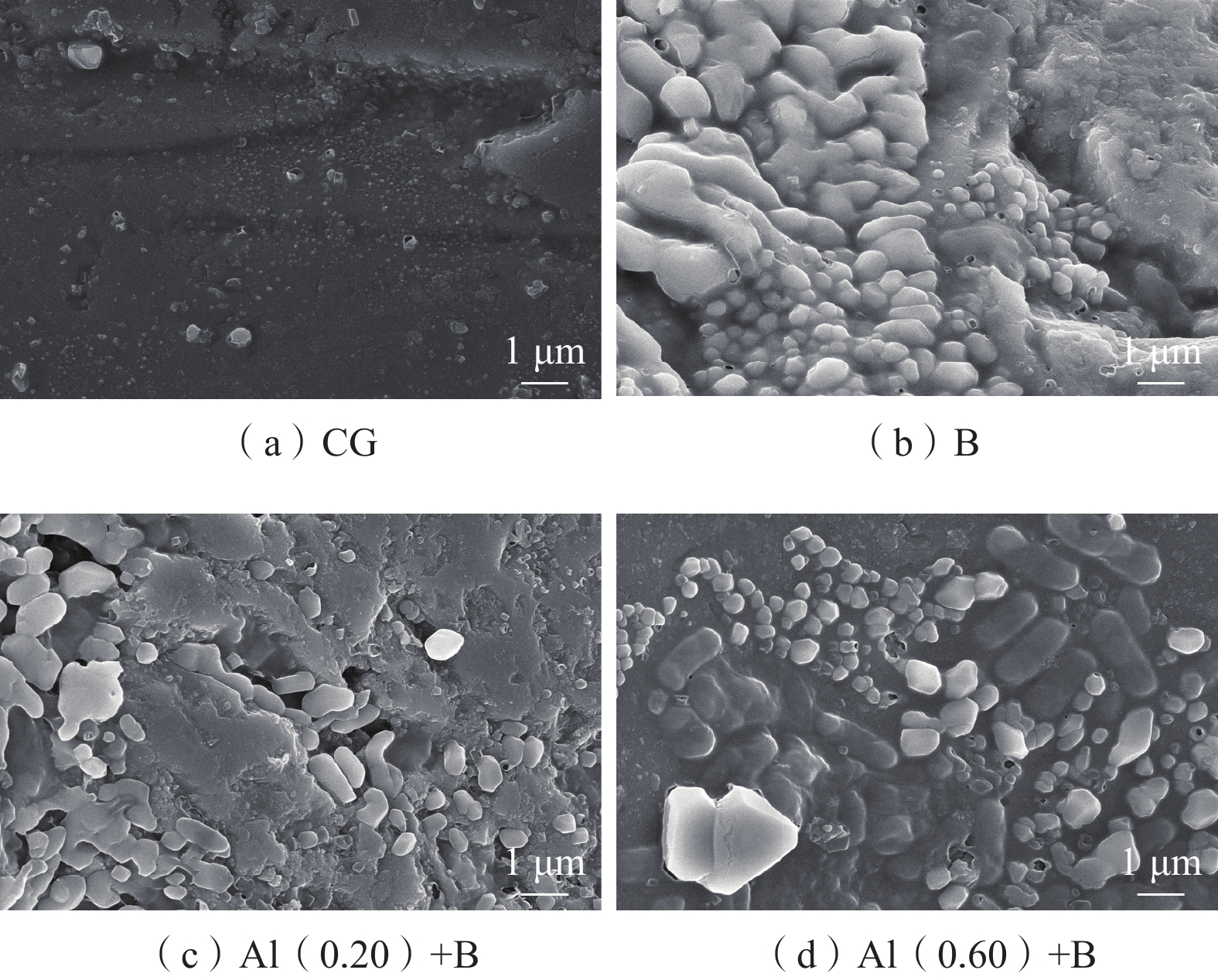
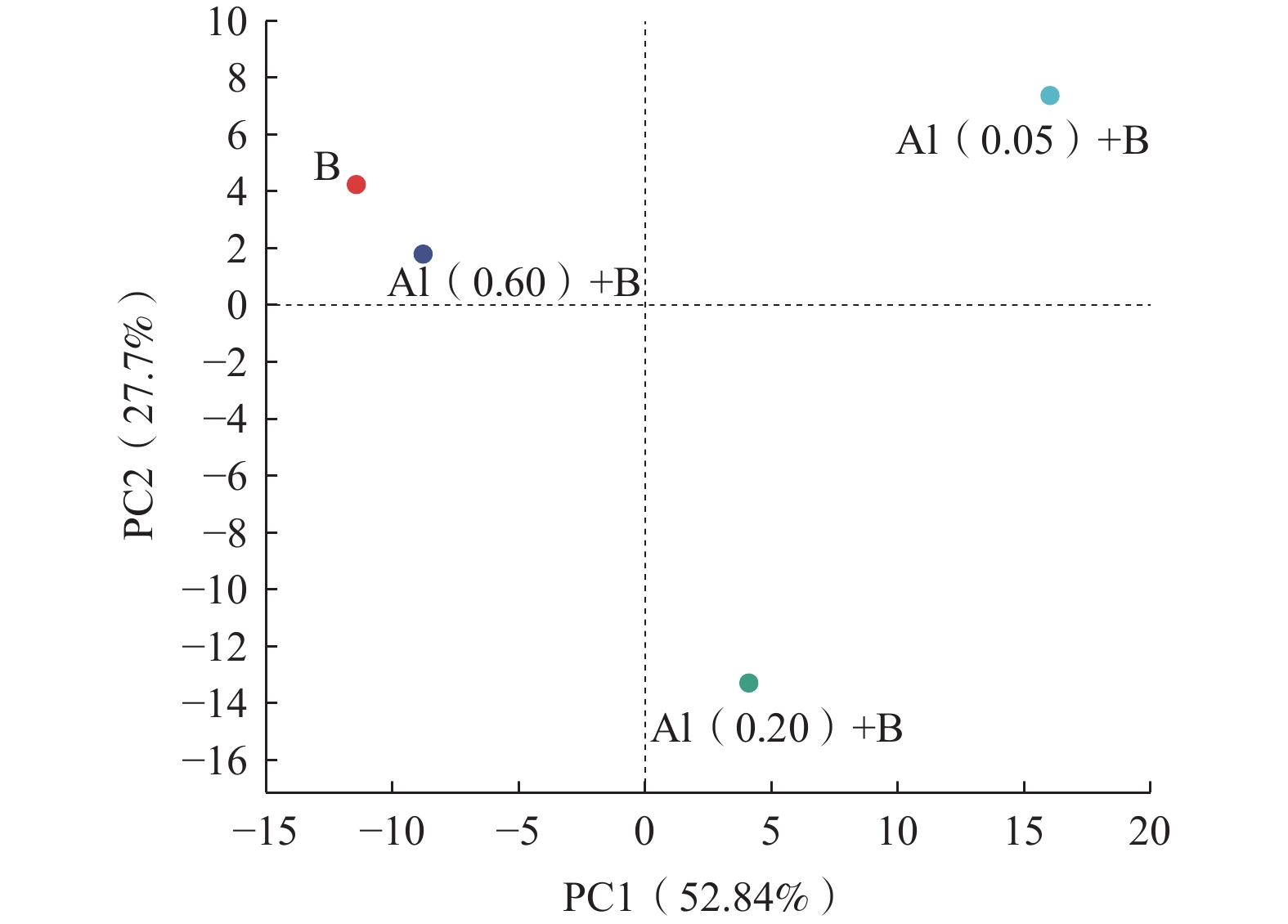
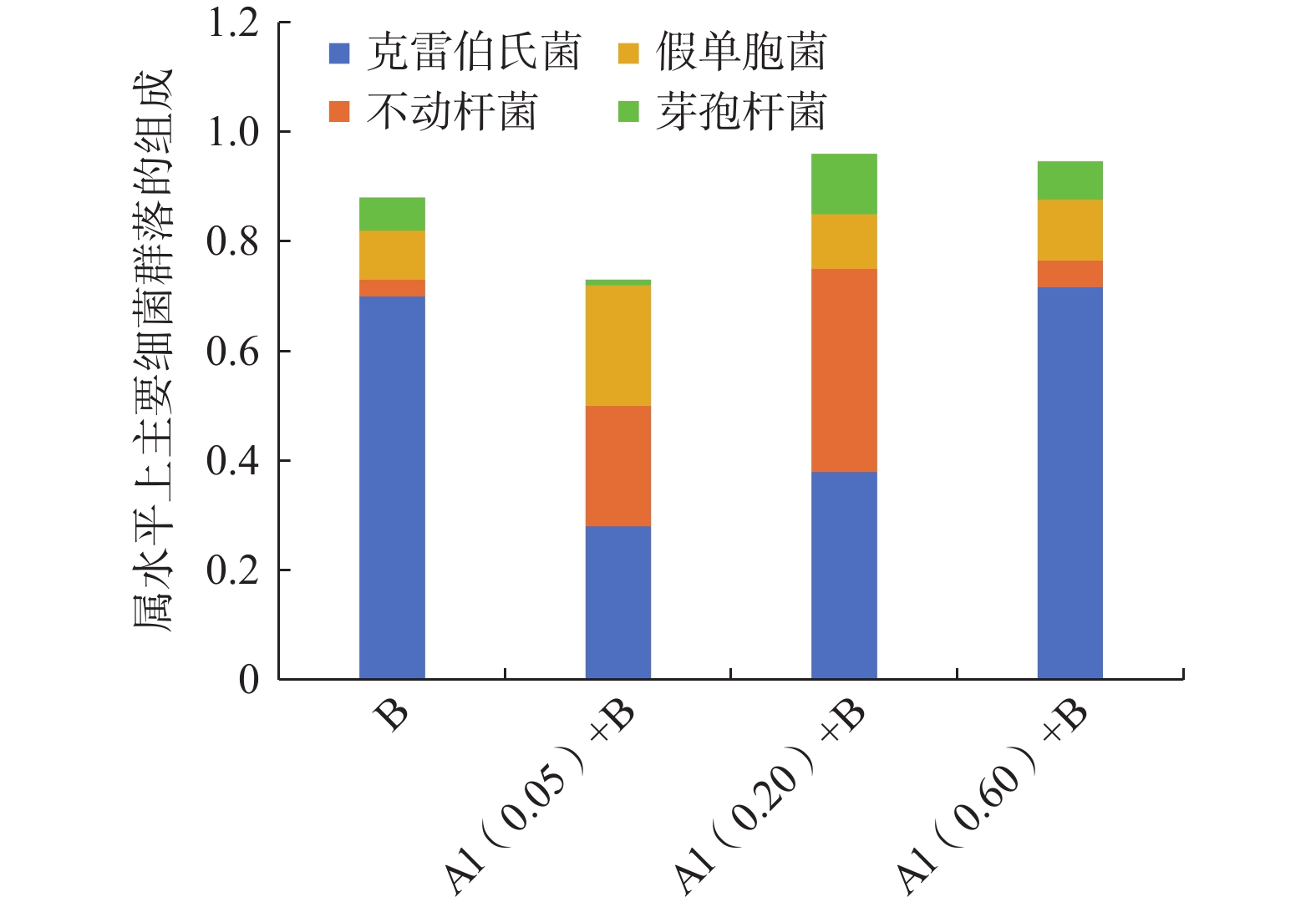
在采用人工回灌方法建设地下水库储存地下水的过程中,回灌水中三价铝[Al(Ⅲ)]和细菌共同作用下引发的化学-生物复合堵塞问题突出且复杂,然而目前对其研究较少。本研究通过渗流试验模拟人工回灌过程,探究了细菌与0.05,0.20,0.60 mg/L Al(Ⅲ)共存条件下含水层的复合堵塞机制。研究结果表明,回灌水中Al(Ⅲ)可以改变石英砂的表面形态,促使含铝化合物生成化学沉淀。Si—O—Al键的生成证明Al(Ⅲ)的加入可以引起含水层化学堵塞。回灌水中不同浓度Al(Ⅲ)对堵塞的影响机制不同。0.05,0.20 mg/L较低浓度Al(Ⅲ)对细菌活性有抑制作用,减少细菌团聚,整体上降低了对生物堵塞贡献大的菌属占比,缓解了生物堵塞。0.60 mg/L高浓度Al(Ⅲ)会刺激细菌产生胞外聚合物,将大部分分散的细菌桥联,加剧生物堵塞。石英砂表面含铝化合物片状沉积物与细菌形态明显,可见含水层发生了化学-生物复合堵塞。本研究通过深入探讨Al(Ⅲ)和细菌与堵塞效应之间的关系,可以为优化回灌过程的设计和管理提供理论基础,进而保障地下水可持续利用。
Abstract:This study investigated the chemical-biological clogging problem caused by the combined effect of aluminum trivalent [Al(Ⅲ)] and bacteria during artificial recharge processes. Laboratory-scale percolation experiments were conducted to explore the composite clogging mechanism of aquifers under the coexistence of bacteria and Al(Ⅲ) at the concentration of 0.05, 0.20, and 0.60 mg/L. The results indicate that Al(III) in the recharge water could modify the surface morphology of quartz sand and promote the chemical precipitation of aluminum-containing compounds. The formation of Si—O—Al bonds proves that the addition of Al(III) can cause chemical clogging of the aquifer. Different concentrations of Al(III) in the recharge water have different effects on clogging. Low Al(III) concentrations of 0.05 and 0.20 mg/L alleviate bioclogging by inhibiting effect on bacterial activity, reducing bacterial aggregation, and overall decreasing the proportion of bacterial genera that contribute significantly to bioclogging. In contrast, high Al(III) concentrations of 0.60 mg/L can stimulate bacteria to produce extracellular polymers (EPS), which bridge most dispersed bacteria and aggravate bioclogging. Flake deposits of aluminum-containing compounds and bacterial morphology were observed on quartz sand surface, further proving the role of Al(III) on chemical-biological complex clogging during the recharge processes. This study provides a theoretical basis for optimizing the design and management of the recharge process by improving our understanding of the relationship between Al(III), bacteria, and clogging effects, thus ensuring the sustainable utilization of groundwater.
-

-
表 1 试验组设计
Table 1. Design of the test group
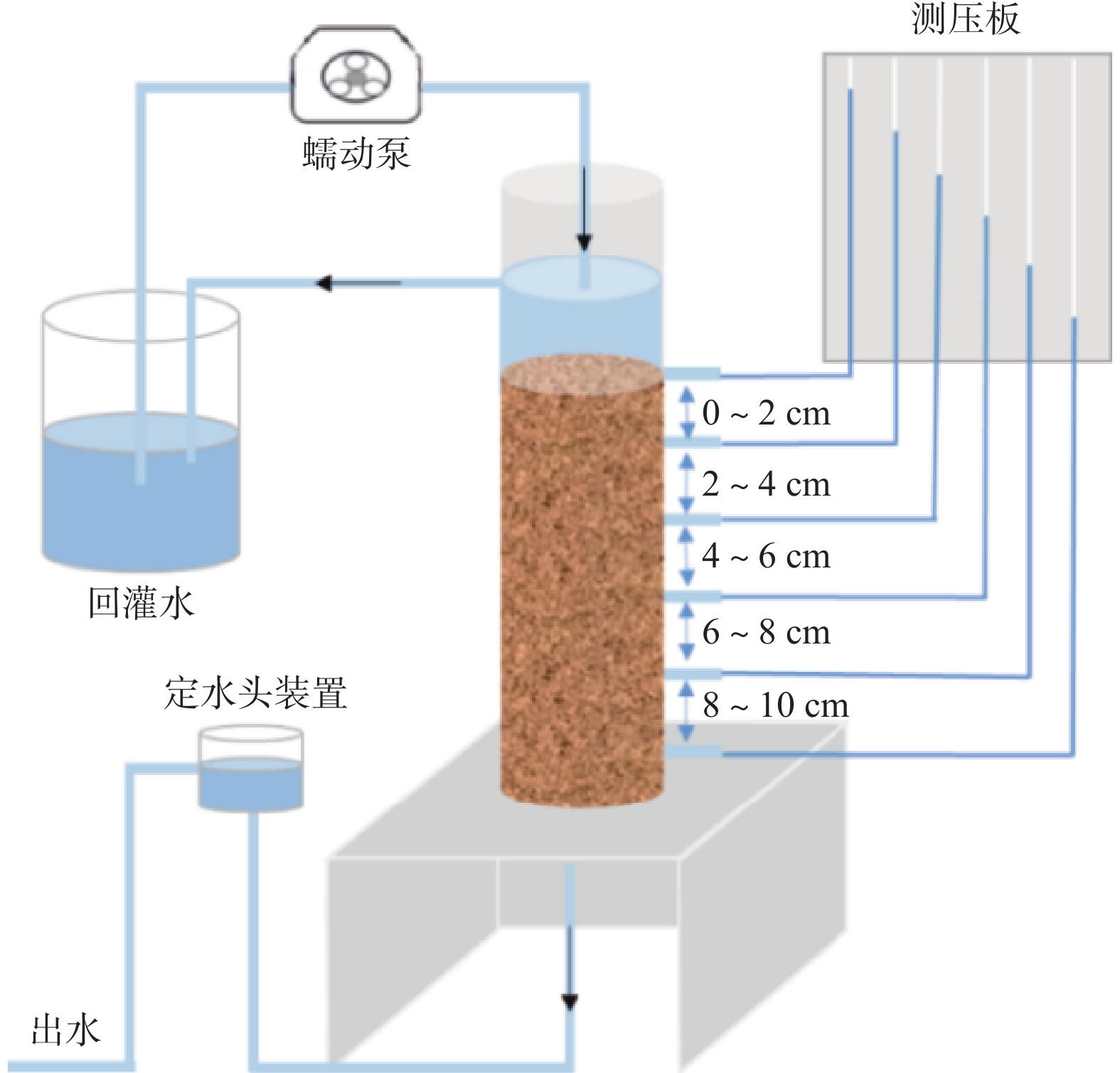
试验组 ρ(Al) /(mg·L−1) 细菌(Bacteria, B) 对照组(control groundwater,CG) 0 No Al(0.05) 0.05 No Al(0.20) 0.20 No Al(0.60) 0.60 No B 0 Yes Al(0.05)+B 0.05 Yes Al(0.20)+B 0.20 Yes Al(0.60)+B 0.60 Yes 注:ρ表示质量浓度;Yes表示试验组中添加细菌;No表示试验组中未添加细菌。 表 2 Alpha多样性指数
Table 2. Alpha diversity index
试验组 Chao Shannon Simpson B 170.45 1.37 0.51 Al(0.05)+B 200.78 2.49 0.15 Al(0.20)+B 171.34 1.95 0.26 Al(0.60)+B 167.00 1.21 0.53 注:Chao、Shannon和Simpson为不同的Alpha多样性指数。 -
[1] HAO A B,ZHANG Y L,ZHANG E Y,et al. Review:Groundwater resources and related environmental issues in China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2018,26(5):1325 − 1337. doi: 10.1007/s10040-018-1787-1
[2] 严琼. 我国地下水污染现状、治理技术及防治建议[J]. 山东化工,2021,50(22):225 − 227. [YAN Qiong. Pollution status,treatment technology and prevention suggestions of groundwater in China[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry,2021,50(22):225 − 227. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2021.22.075
YAN Qiong. Pollution status, treatment technology and prevention suggestions of groundwater in China[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2021, 50(22): 225 − 227. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2021.22.075
[3] 王从荣,尤爱菊,束龙仓. 地下水库研究的现状及展望[J]. 浙江水利科技,2018,46(5):68 − 71. [WANG Congrong,YOU Aiju,SHU Longcang. Current situation and prospect on groundwater reservoir research[J]. Zhejiang Hydrotechnics,2018,46(5):68 − 71. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Congrong, YOU Aiju, SHU Longcang. Current situation and prospect on groundwater reservoir research[J]. Zhejiang Hydrotechnics, 2018, 46(5): 68 − 71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] JIANG B B,GAO J,DU K,et al. Insight into the water–rock interaction process and purification mechanism of mine water in underground reservoir of Daliuta coal mine in China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2022,29(19):28538 − 28551. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-18161-3
[5] WANG H,XIN J,ZHENG X L,et al. Clogging evolution in porous media under the coexistence of suspended particles and bacteria:Insights into the mechanisms and implications for groundwater recharge[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2020,582:124554. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124554
[6] 王茜丹,路莹,杨悦锁,等. 微生物堵塞过程中生物膜生长特征对多孔介质渗流特征影响[J]. 中国环境科学,2022,42(6):2771 − 2778. [WANG Qiandan,LU Ying,YANG Yuesuo,et al. A study of microbial clogging on the variation of seepage characteristics with biofilm growth in porous medium[J]. China Environmental Science,2022,42(6):2771 − 2778. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.06.032
WANG Qiandan, LU Ying, YANG Yuesuo, et al. A study of microbial clogging on the variation of seepage characteristics with biofilm growth in porous medium[J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(6): 2771 − 2778. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.06.032
[7] OKWORI E,VIKLANDER M,HEDSTRÖM A. Spatial heterogeneity assessment of factors affecting sewer pipe blockages and predictions[J]. Water Research,2021,194:116934. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.116934
[8] 王诏楷,束龙仓,刘波,等. 孔隙结构对地下水回灌颗粒堵塞影响的试验研究[J]. 水利学报,2021,52(4):498 − 506. [WANG Zhaokai,SHU Longcang,LIU Bo,et al. Experimental research on the effects of pore structure on particle clogging of groundwater recharge[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2021,52(4):498 − 506. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Zhaokai, SHU Longcang, LIU Bo, et al. Experimental research on the effects of pore structure on particle clogging of groundwater recharge[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2021, 52(4): 498 − 506. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] YANG Y S,WU Y H,LU Y,et al. Microorganisms and their metabolic activities affect seepage through porous media in groundwater artificial recharge systems:A review[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2021,598:126256. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126256
[10] BREHM U,GORBUSHINA A,MOTTERSHEAD D. The role of microorganisms and biofilms in the breakdown and dissolution of quartz and glass[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2005,219(1/2):117 − 129.
[11] 崔瑞娟,杜新强,冶雪艳. 地下水人工回灌水化学因素对生物堵塞的影响[J]. 中国环境科学,2022,42(10):4658 − 4667. [CUI Ruijuan,DU Xinqiang,YE Xueyan. Effect of hydrochemical factors on bio-clogging during artificial recharge of groundwater[J]. China Environmental Science,2022,42(10):4658 − 4667. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.10.023
CUI Ruijuan, DU Xinqiang, YE Xueyan. Effect of hydrochemical factors on bio-clogging during artificial recharge of groundwater[J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(10): 4658 − 4667. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.10.023
[12] SAJIL KUMAR P J,KOKKAT A,KURIAN P K,et al. Correction to:Nutrient chemistry and seasonal variation in the groundwater quality of a Riverine Island on the west coast of Kerala,India[J]. Sustainable Water Resources Management,2021,7(6):105. doi: 10.1007/s40899-021-00586-w
[13] DUAN J M,GREGORY J. Coagulation by hydrolysing metal salts[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,2003,100:475 − 502.
[14] TORASKAR A D,MANOHAR C S,FERNANDES C L,et al. Seasonal variations in the water quality and antibiotic resistance of microbial pollution indicators in the Mandovi and Zuari estuaries,Goa,India[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,2022,194(2):71. doi: 10.1007/s10661-021-09679-7
[15] JIAN J,SONG W,LI H,et al. Influence of the stress of Zn (Ⅱ) and Cu (Ⅱ) on component changes and sorption behavior of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from bacillus vallismortis[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2017,37(6):2099 − 2106.
[16] CUI X C,CHEN C L,SUN S,et al. Acceleration of saturated porous media clogging and silicon dissolution due to low concentrations of Al(III) in the recharge of reclaimed water[J]. Water Research,2018,143:136 − 145. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.06.043
[17] RAMAZANPOUR ESFAHANI A,BATELAAN O,HUTSON J L,et al. Combined physical,chemical and biological clogging of managed aquifer recharge and the effect of biofilm on virus transport behavior:A column study[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering,2020,33:101115. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.101115
[18] JEONG H Y,JUN S C,CHEON J Y,et al. A review on clogging mechanisms and managements in aquifer storage and recovery (ASR) applications[J]. Geosciences Journal,2018,22(4):667 − 679. doi: 10.1007/s12303-017-0073-x
[19] CUI X C,ZHOU D D,FAN W,et al. The effectiveness of coagulation for water reclamation from a wastewater treatment plant that has a long hydraulic and sludge retention times:A case study[J]. Chemosphere,2016,157:224 − 231. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.05.009
[20] DUBOIS M,GILLES K A,HAMILTON J K,et al. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances[J]. Analytical Chemistry,1956,28(3):350 − 356. doi: 10.1021/ac60111a017
[21] ZAIDI M,AHFIR N D,ALEM A,et al. Assessment of clogging of managed aquifer recharge in a semi-arid region[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,730:139107. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139107
[22] LI X,YAN N,ZHENG X L,et al. Application of a novel process using biosurfactant rhamnolipid to reduce bioclogging in quartz sand during artificial recharge[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2021,595:126033. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126033
[23] LIU G S,ZHONG H,JIANG Y B,et al. Effect of low-concentration rhamnolipid biosurfactant on Pseudomonas aeruginosa transport in natural porous media[J]. Water Resources Research,2017,53(1):361 − 375. doi: 10.1002/2016WR019832
[24] CUI R J,PAGE D,DU X Q,et al. Effect of iron on biological clogging in porous media:Implications for managed aquifer recharge[J]. Hydrological Processes,2023,37(3):14839. doi: 10.1002/hyp.14839
[25] XIA L,ZHENG X L,SHAO H B,et al. Influences of environmental factors on bacterial extracellular polymeric substances production in porous media[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2014,519:3153 − 3162. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.10.045
[26] WU X H,GE X P,WANG D S,et al. Distinct coagulation mechanism and model between alum and high Al13-PACl[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2007,305(1/2/3):89 − 96.
[27] MOSER B,BEKNAZAROVA M,WHILEY H,et al. Investigation into the cause of iron-related clogging of groundwater bores used for viticulture in the limestone coast,South Australia[J]. Water,2021,13(5):683. doi: 10.3390/w13050683
[28] 高宗军,徐海龙,夏璐. 地下水人工回灌含水介质微生物堵塞试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):8 − 16. [GAO Zongjun,XU Hailong,XIA Lu. An experimental study of bioclogging of aquifer media during artificial reinjection of groundwater[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):8 − 16. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GAO Zongjun, XU Hailong, XIA Lu. An experimental study of bioclogging of aquifer media during artificial reinjection of groundwater[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(3): 8 − 16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] XIA L,YOU H C,LIU J H,et al. Characteristics and origin of clogging-functional bacteria during managed aquifer recharge:A laboratory study[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2022,312:114880. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114880
-



 下载:
下载: