Monte Carlo simulation for variable-density groundwater flow through reduced-order model coupled with Gaussian process
-
摘要:
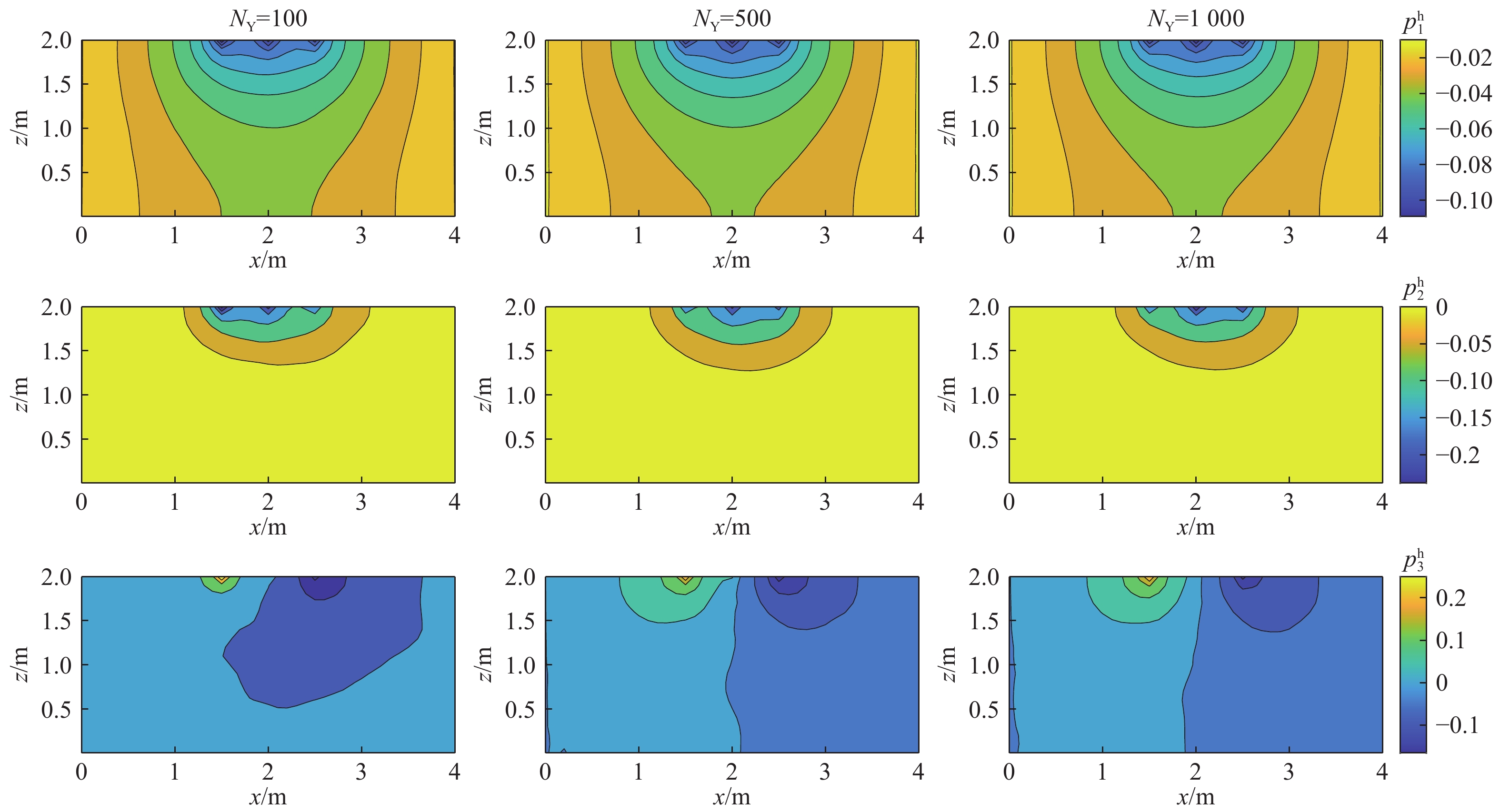
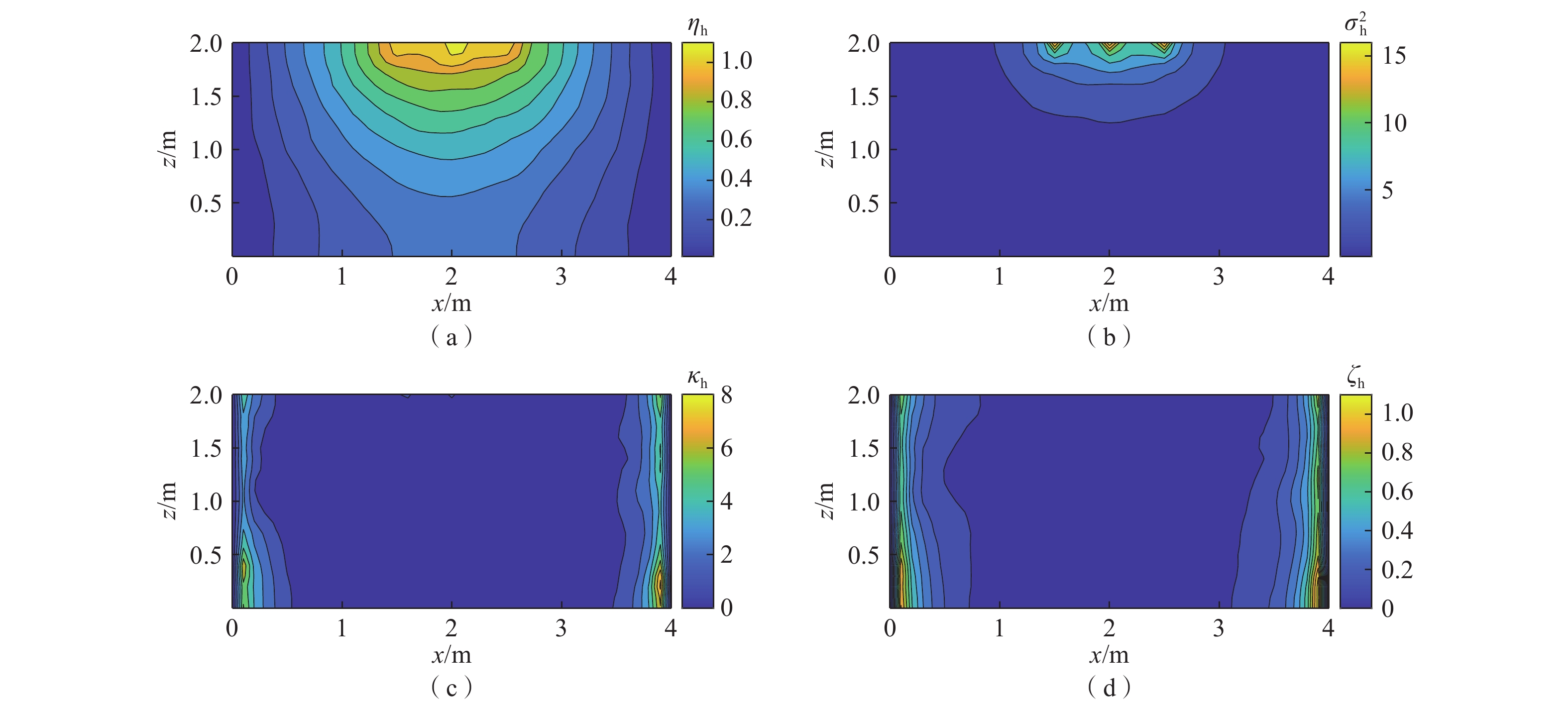
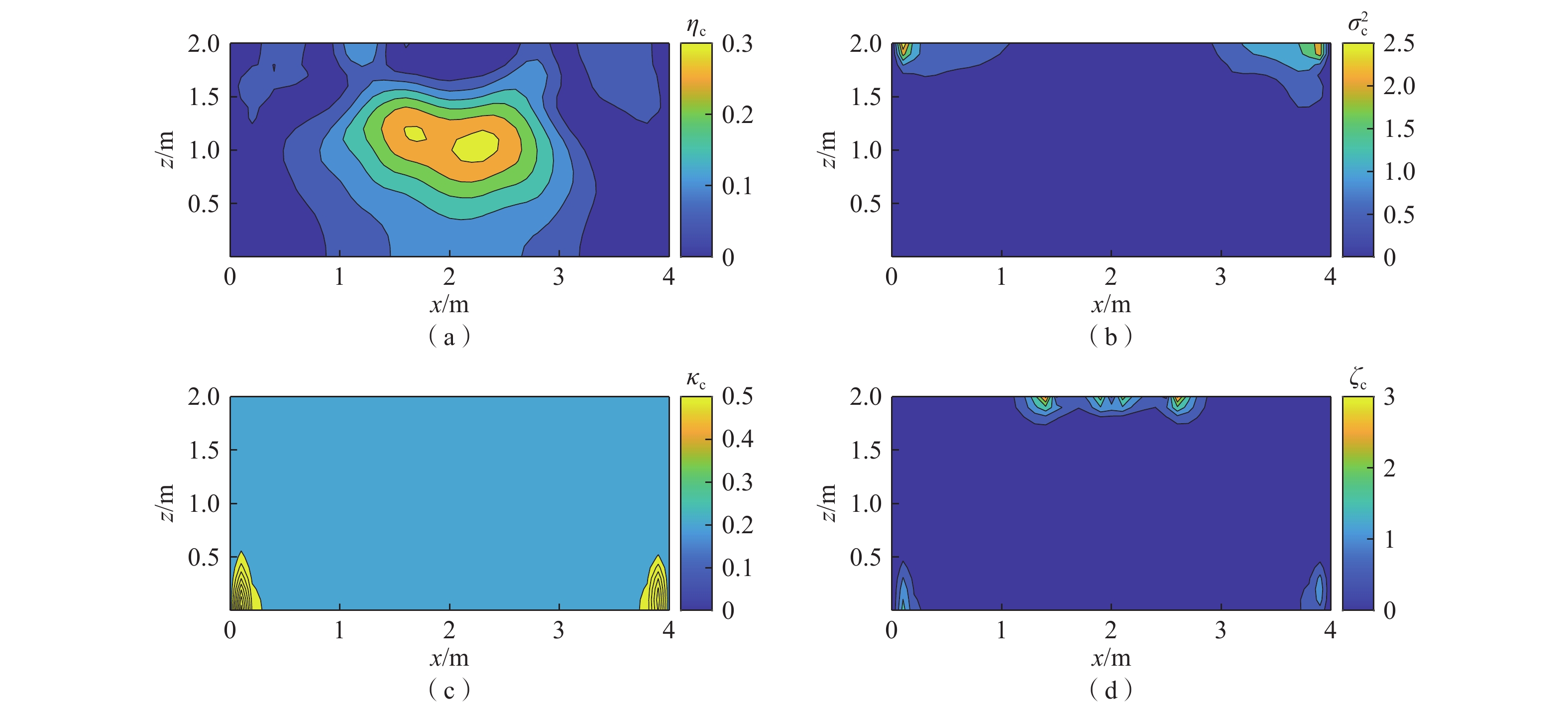
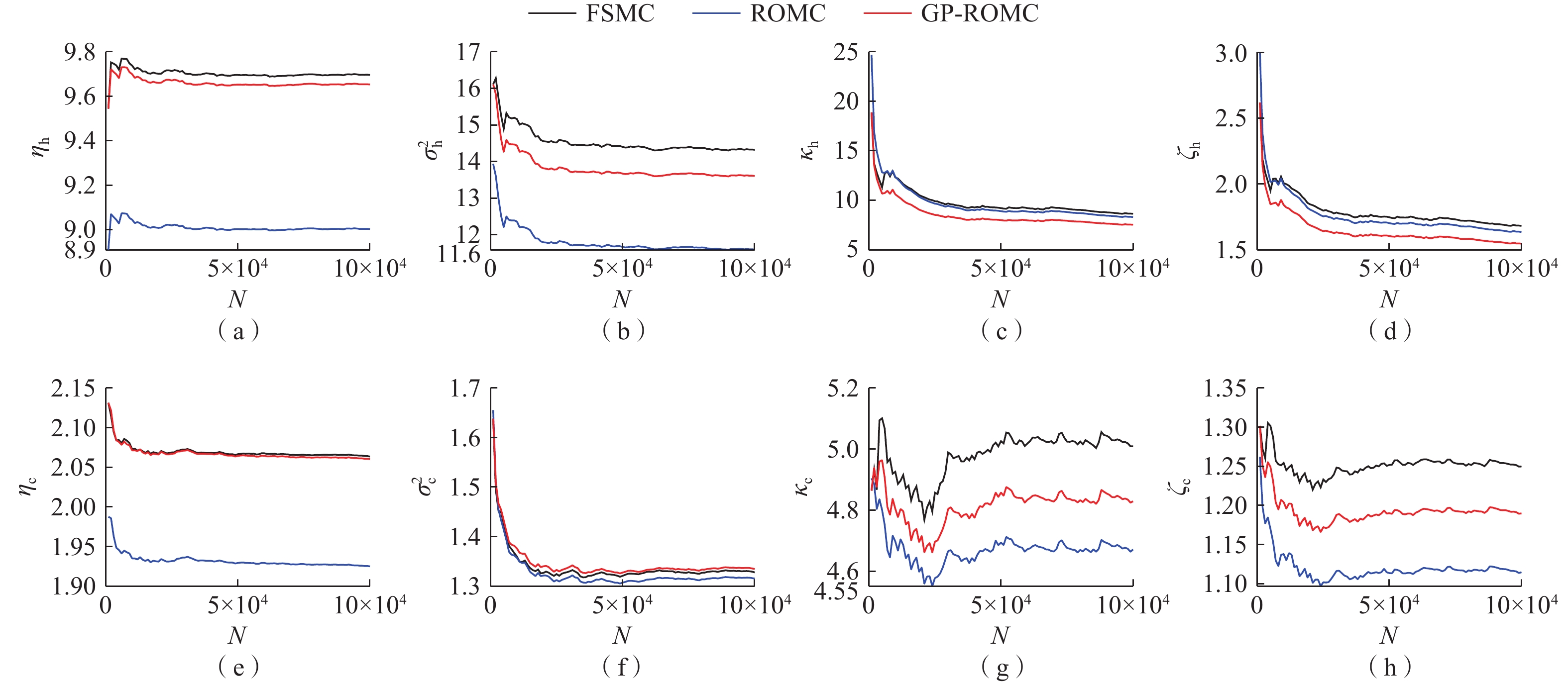
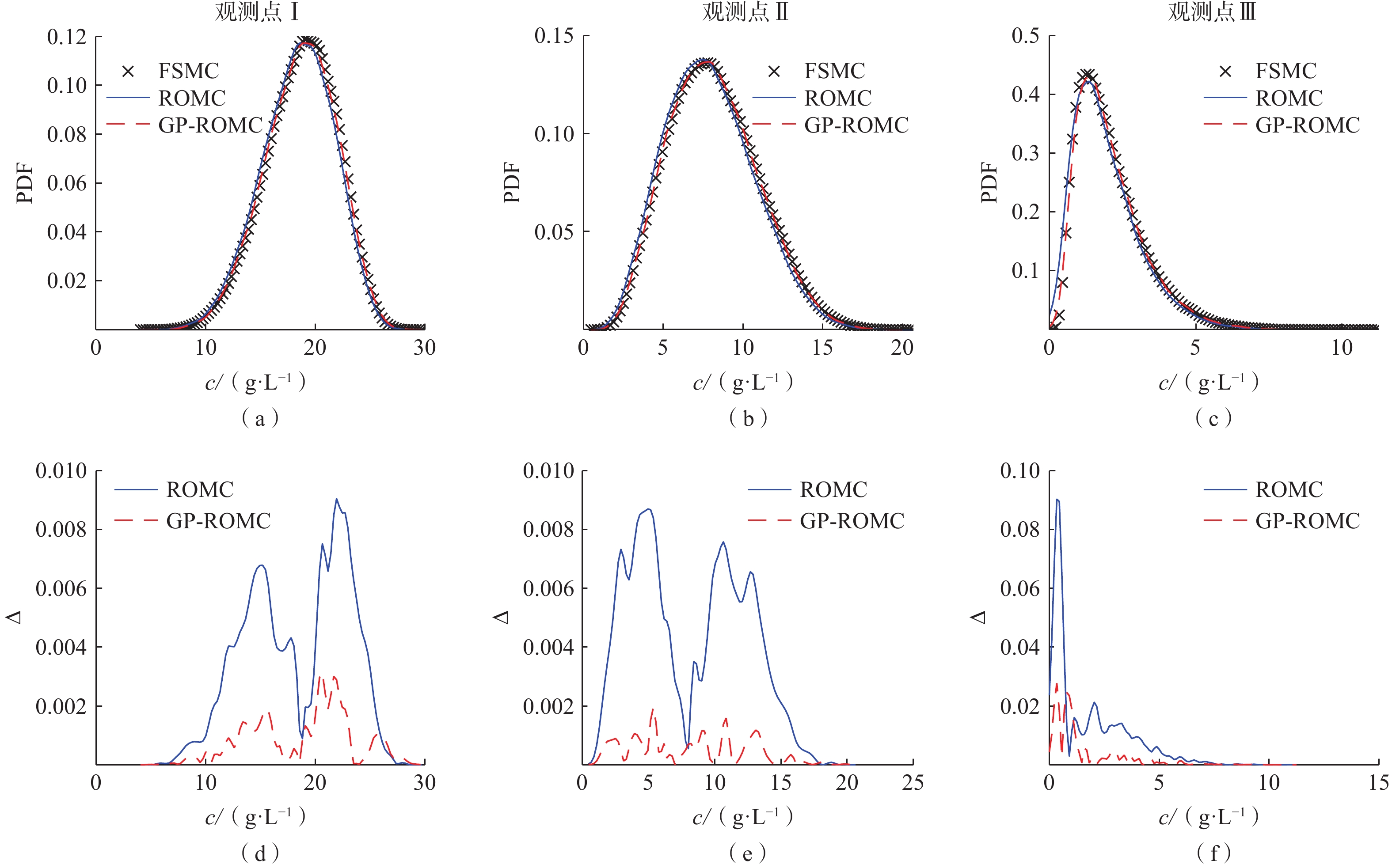
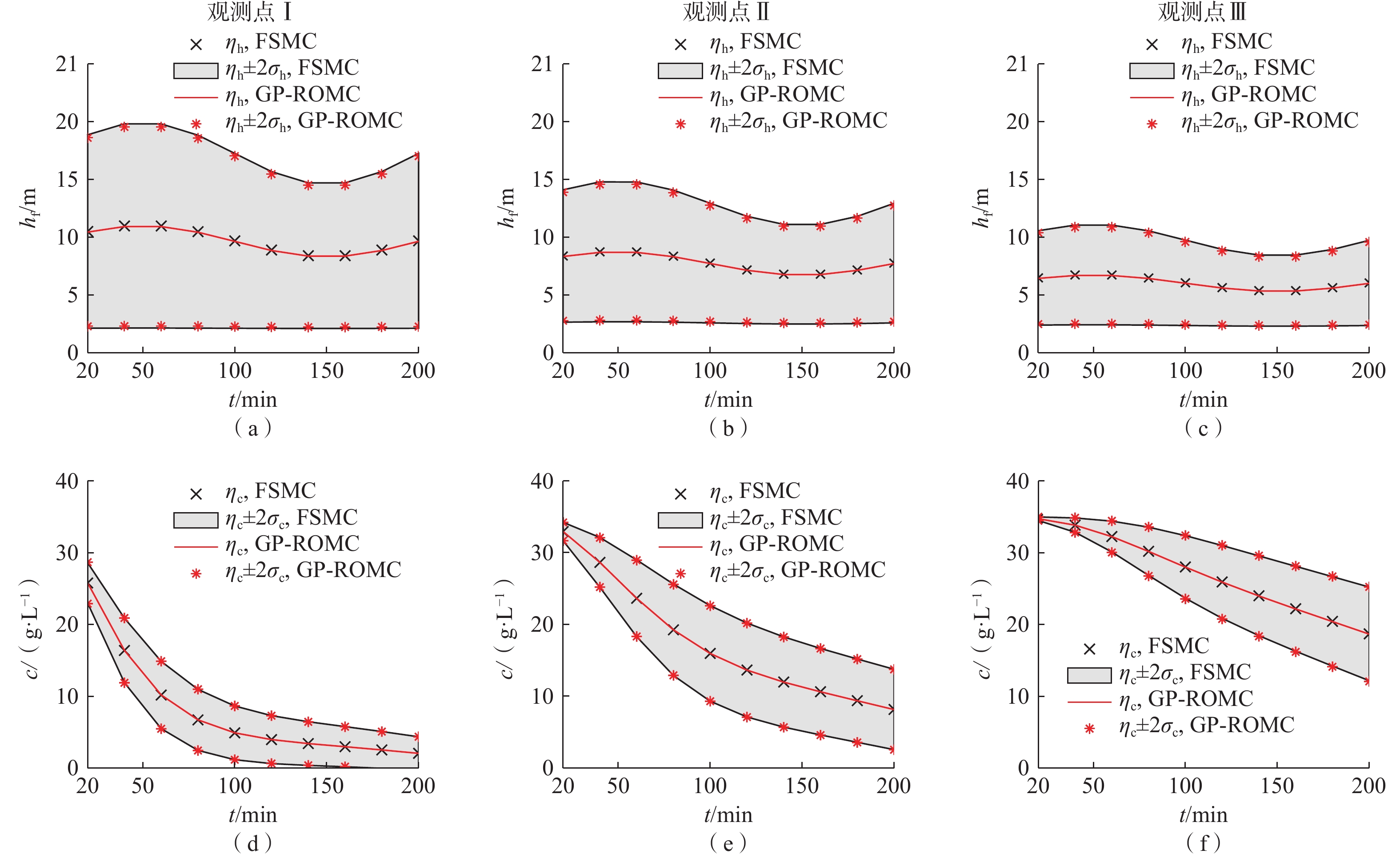
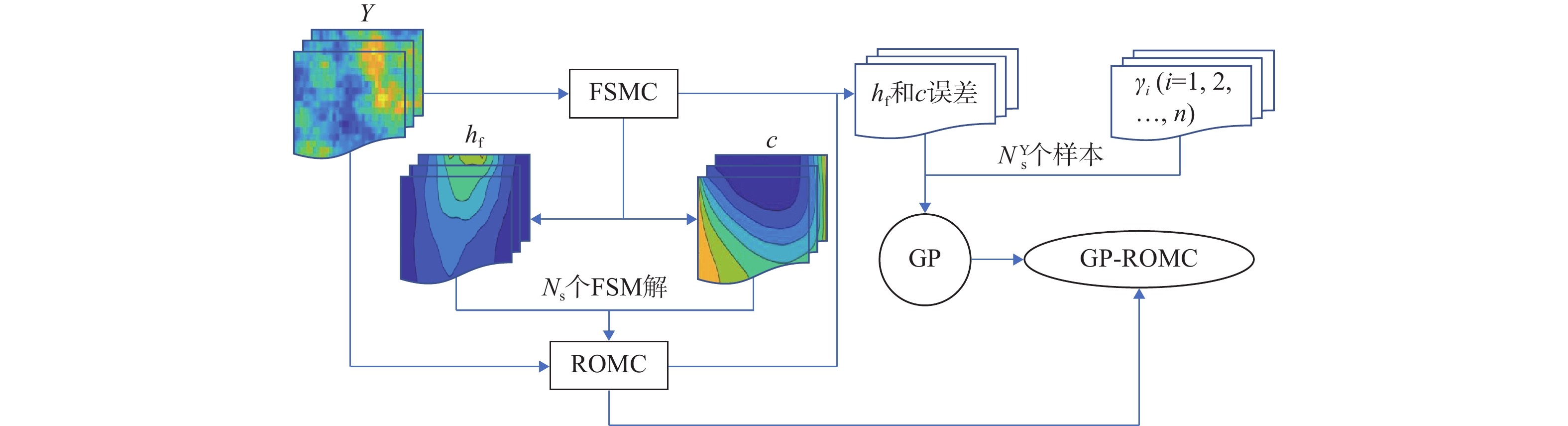
变密度地下水流系统受水力梯度和密度梯度共同驱动,非线性强,数值模型计算量大,尤其在开展不确定性分析时需要的计算成本很高。常规的数据驱动机器学习方法只能对点监测信息进行模拟分析,不能模拟整个地下水流系统。本研究发展了变密度地下水流降阶模型,利用高斯过程模型对降阶模型的数值误差进行修正组成耦合模型。耦合模型既能克服高斯过程只能模拟有限监测点信息的缺陷,又能提高降阶模型对监测点信息的模拟精度。考虑二维剖面变密度地下水流案例,将渗透系数场设定为空间随机变量,采用基于全阶模型(FSMC)、降阶模型(ROMC)和耦合模型(GP-ROMC)3种蒙特卡罗模拟方法进行不确定分析。研究结果表明:(1)ROMC能替代FSMC开展不确定性分析;(2)水头和盐度的平均相对二范误差与降阶模型维度的关系可用指数函数描述(决定性系数R2≥0.99);(3)GP-ROMC对监测点信息的模拟精度比ROMC高,GP-ROMC可有效修正降阶模型误差提高蒙特卡罗模拟的精度。研究成果可为地下水建模、不确定性分析、风险评估及参数反演等工作提供重要技术支撑。
Abstract:Variable-density groundwater flow (VDGF) is jointly driven by hydraulic and density gradient, leading to strong nonlinearity, large computational burden of numerical models, and therefore huge computational cost of Monte Carlo simulation for uncertainty analysis. This study developed the reduced-order model (ROM) for VDGF and built the Gaussian process (GP) for simulating the numerical error of the ROM. The coupled model can obtain solutions of head and salinity across the study domain while GP simulates observation information at limited locations. Moreover, the coupled model can provide higher solution accuracies of head and salinity at the observation locations than the ROM. A two-dimensional (cross-section) VDGF test case was considered, where hydraulic conductivity was taken as a spatially random field. MC simulations were performed using three models, including the full-system model, the ROM, and the coupled model, with corresponding MC strategies denoted as FSMC, ROMC, and GP-ROMC, respectively. The results show that ROMC can be an alternative to FSMC for conducting uncertainty quantification. The relationship between head (or salinity) and the dimensional of ROM can be characterized using power functions with determinate coefficients larger than 0.99. GP-ROMC has higher solution accuracy than ROMC, which indicates that GP is capable for simulating the numerical error of ROM. The results in this study are significant for performing simulation, uncertainty quantification, risk assessment, and parameter estimate in the context of groundwater.
-

-
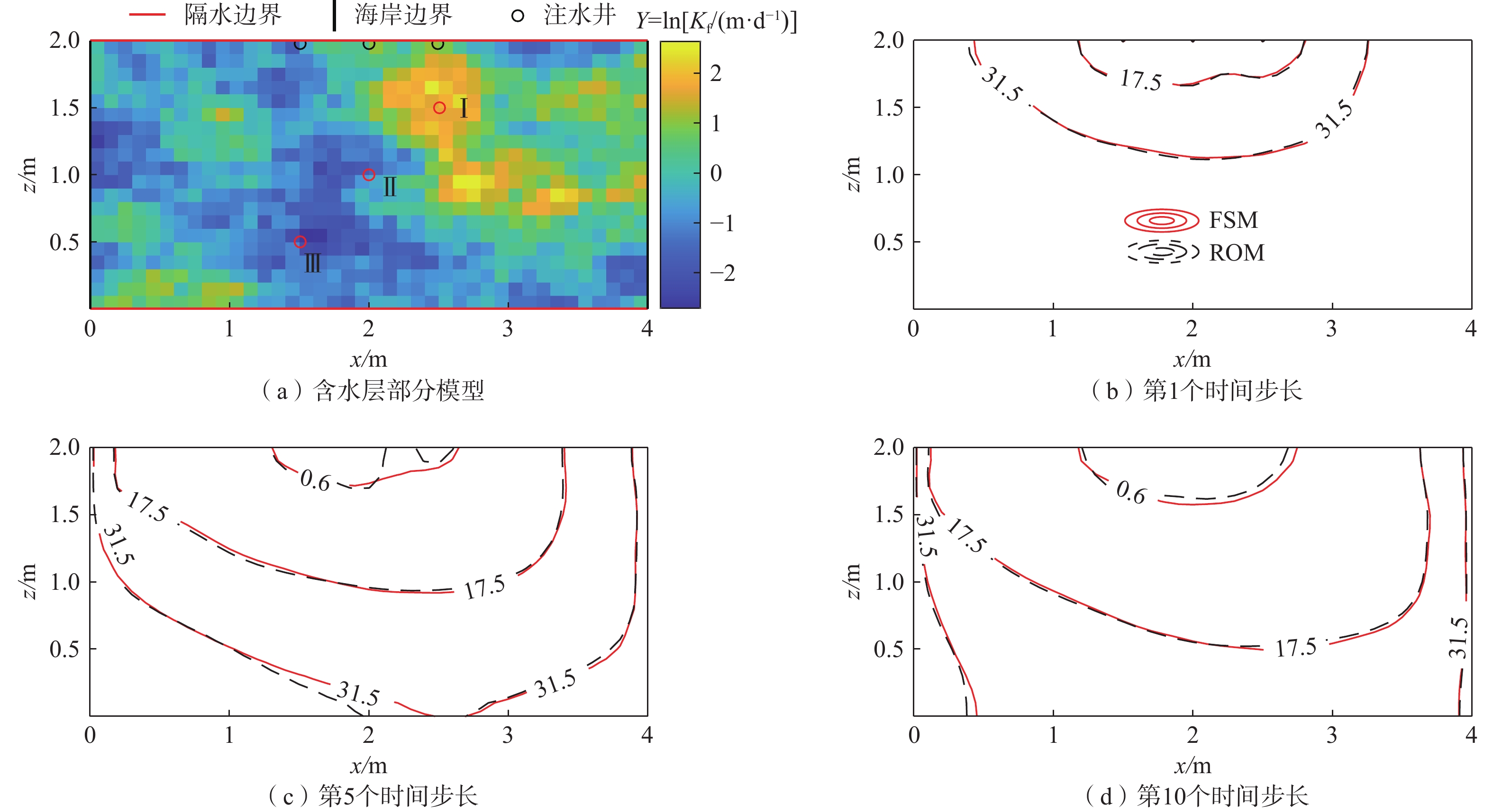
表 1 不同时刻
${{\boldsymbol{\mu}} _{\bf{h}}}$ 与${{\boldsymbol{\mu}} _{\bf{c}}}$ 关于m的指数函数回归结果Table 1. Regression results of power functions for characterizing the relationship between m and
${{\boldsymbol{\mu}} _{\bf{h}}}$ (or${{\boldsymbol{\mu}} _{\bf{c}}}$ ) obtained at each time stept/min y = αxβ hf c α β R2 α β R2 20 −0.92(−1.03,−0.81) −0.49(−0.53,−0.46) 0.995 −1.67(−1.88,−1.46) −0.93(−1.00,−0.86) 0.994 40 −0.89(−0.99,−0.80) −0.50(−0.53,−0.47) 0.996 −1.35(−1.63,−1.08) −0.96(−1.05,−0.87) 0.991 60 −0.90(−1.00,0.81) −0.50(−0.53,−0.47) 0.996 −1.06(−1.19,−0.93) −0.98(−1.02,−0.94) 0.998 80 −0.94(−1.04,−0.83) −0.49(−0.53,−0.46) 0.994 −0.92(−1.05,−0.79) −0.97(−1.01,−0.93) 0.998 100 −0.99(−1.12,−0.86) −0.48(−0.53,−0.44) 0.992 −0.80(−0.98,−0.62) −0.97(1.03,−0.91) 0.996 120 −1.04(−1.20,−0.89) −0.47(−0.53,−0.42) 0.989 −0.68(−0.88,−0.50) −0.98(−1.05,0.92) 0.996 140 −1.08(−1.25,−0.91) −0.47(−0.52,−0.41) 0.986 −0.59(−0.76,−0.41) −0.99(−1.05,−0.94) 0.997 160 −1.08(−1.25,−0.91) −0.47(−0.52,−0.41) 0.986 −0.47(−0.62,−0.32) −1.01(−1.05,−0.95) 0.998 180 −1.05(−1.20,−0.89) −0.47(−0.52,−0.42) 0.998 −0.33(−0.46,−0.20) −1.01(−1.06,0.97) 0.998 200 −1.00(−1.13,−0.86) −0.48(−0.53,−0.44) 0.991 −0.15(−0.26,−0.03) −1.03(−1.07,−0.99) 0.999 注:系数α和收敛指数β对应的单元数值为:回归值(95%置信区间下边界,95%置信区间上边界)。 -
[1] 石鸿蕾,郝奇琛,邵景力,等. 基于多源数据的弱透水层水文地质参数反演研究——以呼和浩特盆地某淤泥层为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(2):1 − 7. [SHI Honglei,HAO Qichen,SHAO Jingli,et al. Research on hydrogeological parameter inversion of an aquitard based on multi-source data:A case study of a silt layer in the Hohhot Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(2):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SHI Honglei, HAO Qichen, SHAO Jingli, et al. Research on hydrogeological parameter inversion of an aquitard based on multi-source data: A case study of a silt layer in the Hohhot Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(2): 1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 宗成元,康学远,施小清,等. 基于多点地质统计与集合平滑数据同化方法识别非高斯渗透系数场[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(2):1 − 8. [ZONG Chengyuan,KANG Xueyuan,SHI Xiaoqing,et al. Characterization of non-Gaussian hydraulic conductivity fields using multiple-point geostatistics and ensemble smoother with multiple data assimilation method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(2):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZONG Chengyuan, KANG Xueyuan, SHI Xiaoqing, et al. Characterization of non-Gaussian hydraulic conductivity fields using multiple-point geostatistics and ensemble smoother with multiple data assimilation method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(2): 1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 钟乐乐,曾献奎,吴吉春. 基于高斯过程回归的地下水模型结构不确定性分析与控制[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(1):1 − 10. [ZHONG Lele,ZENG Xiankui,WU Jichun. Quantification and reduction of groundwater model structural uncertainty based on Gaussian process regression[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(1):1 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHONG Lele, ZENG Xiankui, WU Jichun. Quantification and reduction of groundwater model structural uncertainty based on Gaussian process regression[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(1): 1 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 唐亚明,张茂省. 滑坡风险评价难点及方法综述[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2011,38(2):130 − 134. [TANG Yaming,ZHANG Maosheng. Landslide risk assessment difficulties and methods:An review[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2011,38(2):130 − 134. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2011.02.023
TANG Yaming, ZHANG Maosheng. Landslide risk assessment difficulties and methods: An review[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2011, 38(2): 130 − 134. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2011.02.023
[5] SHI H H,ZENG M,PENG H X,et al. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater of Hainan Island using the Monte Carlo simulation coupled with the APCS/MLR model[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2022,19(13):7827. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19137827
[6] 杨运,吴吉春,骆乾坤,等. 考虑预报偏差的迭代式集合卡尔曼滤波在地下水水流数据同化中的应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(6):13 − 23. [YANG Yun,WU Jichun,LUO Qiankun,et al. Application of the bias aware Ensemble Kalman Filter with Confirming Option (Bias-CEnKF) in groundwater flow data assimilation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(6):13 − 23. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YANG Yun, WU Jichun, LUO Qiankun, et al. Application of the bias aware Ensemble Kalman Filter with Confirming Option (Bias-CEnKF) in groundwater flow data assimilation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(6): 13 − 23. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 夏传安,王浩,简文彬. 基于相关性局域化迭代集合平滑反演渗透系数场[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2024,51(1):12 − 21. [XIA Chuan’an,WANG Hao,JIAN Wenbin. Estimation of conductivity fields by using a correlation-based localization scheme of iterative ensemble smoother[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2024,51(1):12 − 21. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XIA Chuan’an, WANG Hao, JIAN Wenbin. Estimation of conductivity fields by using a correlation-based localization scheme of iterative ensemble smoother[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2024, 51(1): 12 − 21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] XIA C A,LUO X D,HU B X,et al. Data assimilation with multiple types of observation boreholes via the ensemble Kalman filter embedded within stochastic moment equations[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2021,25(4):1689 − 1709. doi: 10.5194/hess-25-1689-2021
[9] BALLIO F,GUADAGNINI A. Convergence assessment of numerical Monte Carlo simulations in groundwater hydrology[J]. Water Resources Research,2004,40(4):e2003wr002876. doi: 10.1029/2003WR002876
[10] XIA C A,HU B X,TONG J X,et al. Data assimilation in density-dependent subsurface flows via localized iterative ensemble Kalman filter[J]. Water Resources Research,2018,54(9):6259 − 6281. doi: 10.1029/2017WR022369
[11] CHANG Y W,HU B X,XU Z X,et al. Numerical simulation of seawater intrusion to coastal aquifers and brine water/freshwater interaction in south coast of Laizhou Bay,China[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2018,215:1 − 10. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2018.06.002
[12] XIN P,WANG S S J,SHEN C J,et al. Predictability and quantification of complex groundwater table dynamics driven by irregular surface water fluctuations[J]. Water Resources Research,2018,54(3):2436 − 2451. doi: 10.1002/2017WR021761
[13] YANG H,SHIMADA J,SHIBATA T,et al. Freshwater lens oscillation induced by sea tides and variable rainfall at the uplifted atoll island of Minami-Daito, Japan [J]. Hydrogeology Journal:2020, 28(6):2105-2114.
[14] 李英豪,韩冬梅,曹天正,等. 边坡防渗增加灰沙岛地下淡水的试验与数值模拟研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(2):13 − 22. [LI Yinghao,HAN Dongmei,CAO Tianzheng,et al. A study of the increase in subsurface freshwater on coral islands by slope seepage control:Experiment and modeling[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(2):13 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Yinghao, HAN Dongmei, CAO Tianzheng, et al. A study of the increase in subsurface freshwater on coral islands by slope seepage control: Experiment and modeling[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(2): 13 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 马婧,鲁春辉,吴吉春,等. 一种可增加海岛地下淡水资源储量的方法研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):1 − 7. [MA Jing,LU Chunhui,WU Jichun,et al. A method for improving the fresh groundwater storage of oceanic islands[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
MA Jing, LU Chunhui, WU Jichun, et al. A method for improving the fresh groundwater storage of oceanic islands[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(3): 1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] BAUER P,HELD R J,ZIMMERMANN S,et al. Coupled flow and salinity transport modelling in semi-arid environments:The Shashe River Valley, Botswana[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2006,316(1/2/3/4):163 − 183.
[17] 蒙永辉,王集宁,张丽霞,等. 潍河下游典型卤水开采区海咸水入侵趋势研究[J]. 人民黄河,2018,40(1):66 − 70. [MENG Yonghui,WANG Jining,ZHANG Lixia,et al. Study on the sea salt water intrusion in typical brine exploration area of the lower Weihe River[J]. Yellow River,2018,40(1):66 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
MENG Yonghui, WANG Jining, ZHANG Lixia, et al. Study on the sea salt water intrusion in typical brine exploration area of the lower Weihe River[J]. Yellow River, 2018, 40(1): 66 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] JU L,ZHANG J J,MENG L,et al. An adaptive Gaussian process-based iterative ensemble smoother for data assimilation[J]. Advances in Water Resources,2018,115:125 − 135. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2018.03.010
[19] SREEKANTH J,DATTA B. Review:Simulation-optimization models for the management and monitoring of coastal aquifers[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2015,23(6):1155 − 1166. doi: 10.1007/s10040-015-1272-z
[20] LAL A,DATTA B. Genetic programming and Gaussian process regression models for groundwater salinity prediction:machine learning for sustainable water resources management[C]//2018 IEEE Conference on Technologies for Sustainability (SusTech). Long Beach: IEEE,2018:1 − 7.
[21] XIA C A,PASETTO D,HU B X,et al. Integration of moment equations in a reduced-order modeling strategy for Monte Carlo simulations of groundwater flow[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2020,590:125257. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125257
[22] PASETTO D,PUTTI M,YEH W W G. A reduced-order model for groundwater flow equation with random hydraulic conductivity:Application to Monte Carlo methods[J]. Water Resources Research,2013,49(6):3215 − 3228. doi: 10.1002/wrcr.20136
[23] LI X Y,CHEN X,HU B X,et al. Model reduction of a coupled numerical model using proper orthogonal decomposition[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2013,507:227 − 240. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.09.011
[24] LI X Y,HU B X. Proper orthogonal decomposition reduced model for mass transport in heterogenous media[J]. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment,2013,27(5):1181 − 1191. doi: 10.1007/s00477-012-0653-2
[25] PASETTO D,FERRONATO M,PUTTI M. A reduced order model-based preconditioner for the efficient solution of transient diffusion equations[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering,2017,109(8):1159 − 1179. doi: 10.1002/nme.5320
[26] PASETTO D,GUADAGNINI A,PUTTI M. A reduced-order model for Monte Carlo simulations of stochastic groundwater flow[J]. Computational Geosciences,2014,18(2):157 − 169. doi: 10.1007/s10596-013-9389-4
[27] MIAO T S,LU W X,LIN J,et al. Modeling and uncertainty analysis of seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers using a surrogate model:A case study in Longkou, China[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2018,12(1):1.
[28] AYED B,JMAL I,SAHAL S,et al. The seawater intrusion assessment in coastal aquifers using GALDIT method and groundwater quality index:The Djeffara of Medenine coastal aquifer (Southeastern Tunisia)[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2018,11(20):609. doi: 10.1007/s12517-018-3966-8
[29] BENNER P,GUGERCIN S,WILLCOX K. A survey of projection-based model reduction methods for parametric dynamical systems[J]. SIAM Review,2015,57(4):483 − 531. doi: 10.1137/130932715
[30] GUO W,LANGEVIN C D. User’s guide to SEAWAT: A computer program for simulation of three-dimensional variable-density ground-water flow [R]. Tallahassee:U. S. GeologicalSurvey, 2002.
[31] ZHENG C,WANG P. MT3DMS:A Modular three-dimensional multispecies transport model for simulation of advection, dispersion, and chemical reactions of contaminants in groundwater systems: Documentation and user's guide[R]. Tuscaloosa:Department of Geological Sciences University of Alabama, 1999.
-



 下载:
下载: