Influencing factors of landslides and rockfalls along the Jinchuan-Xiaojin highway in Sichuan
-
摘要:
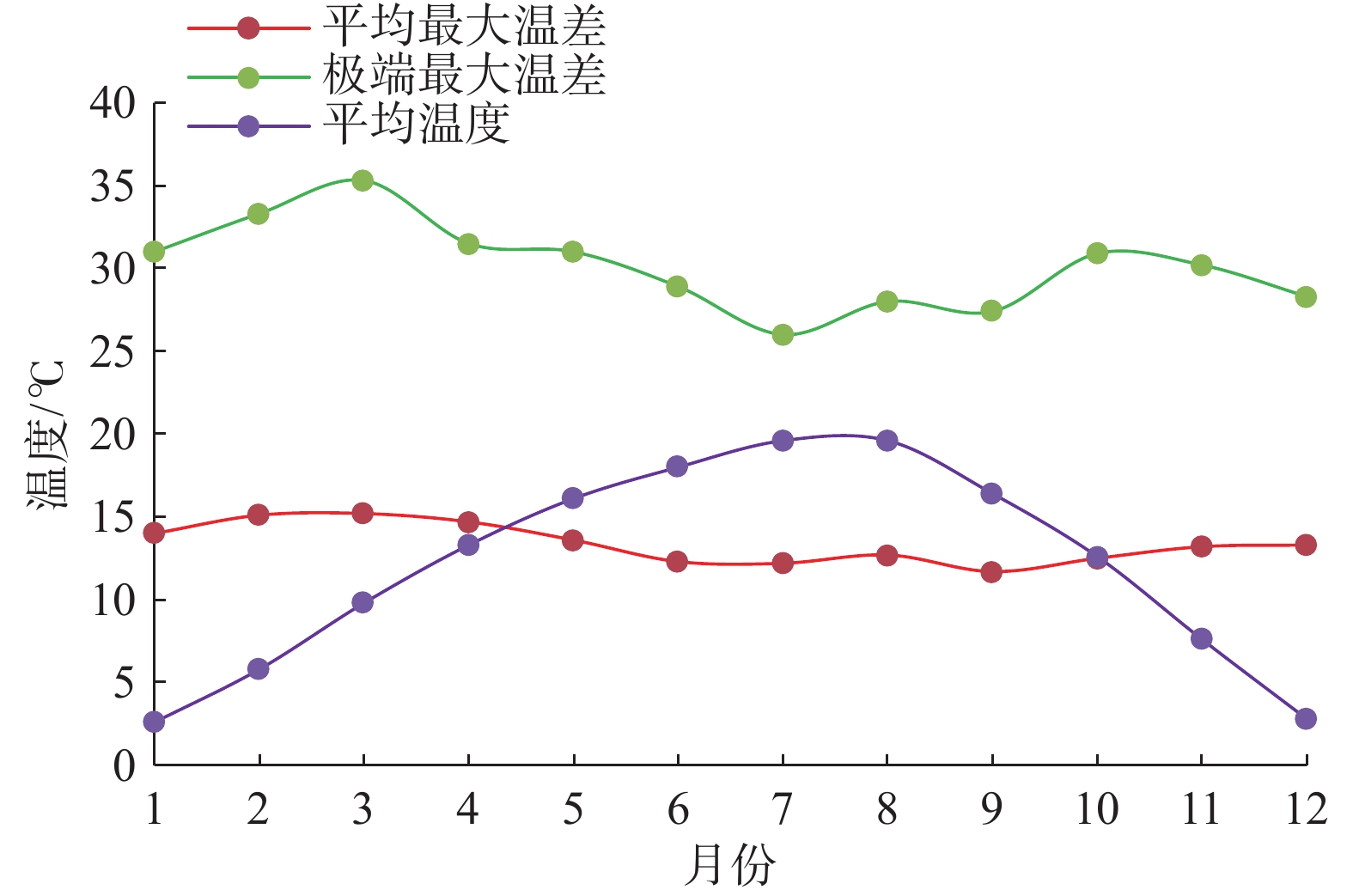
高原山区地质灾害是交通线路最大的危害,而有效避险的关键是掌握沿途地质灾害发生的工程地质条件内因及诱导因素。本文以川西阿坝州高原山区金小公路沿线带状区域内的滑坡、崩塌为研究对象,以地理、地质、气象、遥感资料和实地调查为基础,运用空间分析和数理统计方法,对其形成的影响因素进行了系统研究。结果表明:(1)金汤弧形褶皱形成的同时,区内软硬互层的炭质泥岩、粉砂质泥岩、粉砂岩的地层发生劈理化,喜山期构造运动及频繁的地震活动,加剧了岩石的破碎程度,为区内滑坡、崩塌提供了物源,并为高山峡谷地形地貌的塑造创造了有利条件;(2)区内6–9月份的集中降雨是诱发滑坡、崩塌的主要因素;(3)高山、峡谷、高角度斜坡等地形地貌以及公路建设中坡脚开挖为崩塌、滑坡等埋下了隐患;(4)季节性冻融作用加速了基岩风化破坏,对滑坡、崩塌的形成具有促进作用。
Abstract:Geological hazards in plateau mountainous areas are the greatest hazards to traffic lines, and the key to effectively avoid risks is to grasp the engineering geological factors and inducing factors of geological hazards along the high way. Based on the geographical, geological, meteorological, remote sensing and field investigation, the paper systematically studies the influencing factors of the landslide and collapse in the belt area along the Jinxiao Highway in the plateau of Aba Prefecture in western Sichuan. The results indicate that: (1)the cleavage transformation of the carbonaceous mudstone, silty mudstone and siltstone in the zone, as well as The Himalayan period tectonic movement and frequent seismic activity intensified the fracture of rock mass, provided the material source for the landslide and collapse in the area and created favorable conditions for shaping the topography of the alpine valley; (2)concentrated rainfall in the region from June to September is the main factor triggering landslides and collapses; (3)high mountains, valleys, high-angle slopes and other terrain and geomorphology background and slope foot excavation are also an important factor that triggeringcollapse, landslides;(4)seasonal freezing-thawing accelerates the bedrock weathering failure and promotes the formation of landslides and rockfalls.
-
Key words:
- landslides /
- rockfalls /
- Jinxiao highway /
- influencing factors
-

-
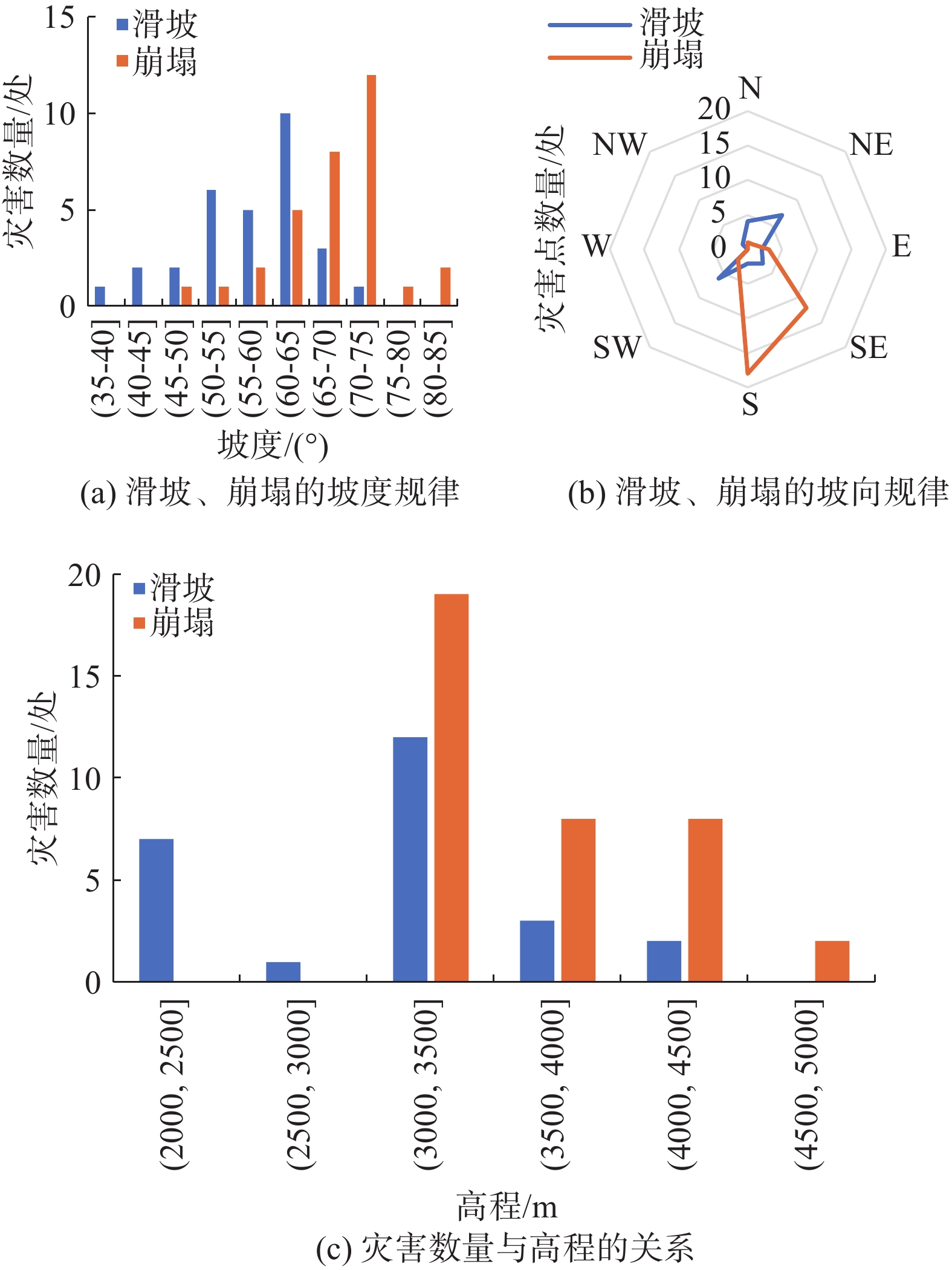
表 1 各地层中滑坡、崩塌发育频率
Table 1. Frequency of landslides and collapses developed in different strata
地层 主要岩性 发育密度/(处·km−2) 滑坡 崩塌 T3x 炭质板岩、粉砂质板岩及绢云母板岩 0.241 0.096 T3zh 变质砂岩、变质粉砂岩、含炭绢云母板岩、粉砂质板岩 0.043 0.249 表 2 小金县内历史上发生的5级以上的地震
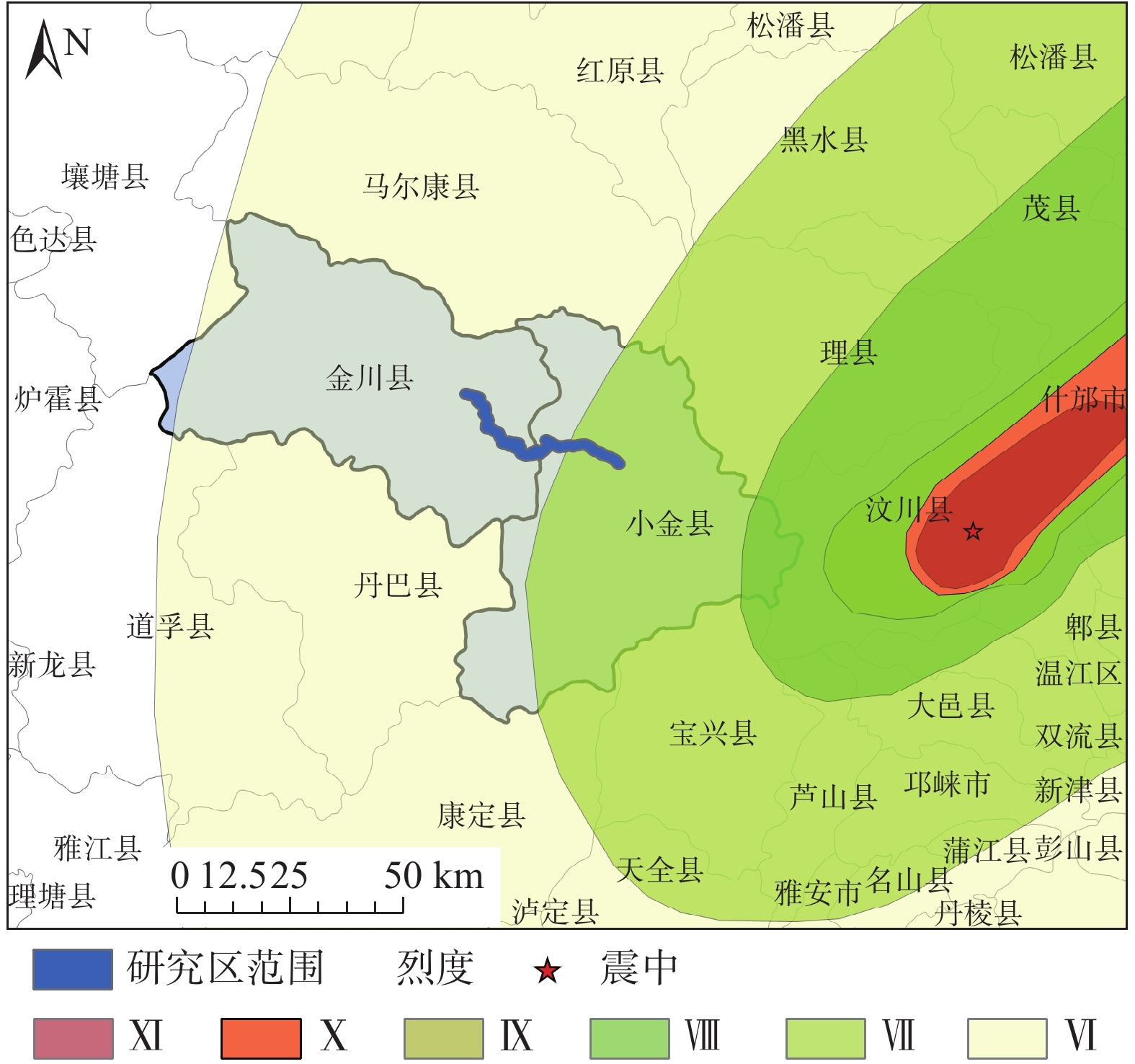
Table 2. The occurred earthquake with the magnitude more than 5 in Xiaojin County in history
宏观震中 发生日期 震级 黄草坪—黑虎碉之间 1989年3月1日 5.0 梭罗寨附近 1989年9月22日 6.6 白果坪 1991年2月18日 5.2 -
[1] 黄润秋. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2007,26(3):433 − 454. [HUANG Runqiu. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2007,26(3):433 − 454. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001
[2] 王珂, 郭长宝, 马施民, 等. 基于证据权模型的川西鲜水河断裂带滑坡易发性评价[J]. 现代地质,2016,30(3):705 − 715. [WANG Ke, GUO Changbao, MA Shimin, et al. Landslide susceptibility evaluation based on weight-of-evidence modeling in the Xianshuihe fault zone, east Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geoscience,2016,30(3):705 − 715. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.03.022
[3] 梁瑞锋, 王运生, 马保罡, 等. 杂谷脑河流域薛城段地质灾害分布特征与影响因素[J]. 科学技术与工程,2016,16(21):27 − 33. [LIANG Ruifeng, WANG Yunsheng, MA Baogang, et al. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of geohazards in Xuecheng section along the zagunao river[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2016,16(21):27 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2016.21.004
[4] 罗菲, 任光明, 李惠民, 等. 四川省道S216沿线滑坡、崩塌发育规律[J]. 长江科学院院报,2019,36(6):37 − 41. [LUO Fei, REN Guangming, LI Huimin, et al. Development rules of landslides and collapses along provincial highway S216 in Sichuan[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2019,36(6):37 − 41. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20171285
[5] 巴仁基, 王丽, 郑万模, 等. 大渡河流域地质灾害特征与分布规律[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 38(5):529−537.
BA Renji, WANG Li, ZHENG Wanmo, et al. Characteristics and distribution of the geology disasters of the Dadu River in Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Sci & Technol Ed), 2011, 38(5):529−537.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 李毅, 潘倩, 张洪. 小金县地质灾害的发育类型、分布特征及控制因素[J]. 四川地质学报,2018,38(2):299 − 303. [LI Yi, PAN Qian, ZHANG Hong. Type, distribution and control factors of geohazards in Xiaojin County[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan,2018,38(2):299 − 303. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2018.02.025
[7] 蔡长发, 陈廷方, 成华雄, 等. 九环公路(平武段)崩塌地质灾害特征与成因分析[J]. 西南科技大学学报,2012,27(4):58 − 64. [CAI Changfa, CHEN Tingfang, CHENG Huaxiong, et al. The characteristic and cause hazards of jiuhuan analysis of collapse geological road (Pingwu area)[J]. Journal of Southwest University of Science and Technology,2012,27(4):58 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8755.2012.04.012
[8] 刘传正. 中国崩塌滑坡泥石流灾害成因类型[J]. 地质论评,2014,60(4):858 − 868. [LIU Chuanzheng. Genetic types of landslide and debris flow disasters in China[J]. Geological Review,2014,60(4):858 − 868. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 邵铁全. 滑坡地质灾害超前地质预判技术研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2006.
SHAO Tiequan. Research on the technique for pre-estimating geological hazard of landslide[D]. Xi'an: Changan University, 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 朱煦, 蒋礼. 四川金川县城临江路斜坡稳定性分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2013,24(4):29 − 33. [ZHU Xi, JIANG Li. Formation mechanism and stability of the Jinchuan landslide, Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2013,24(4):29 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 段丽萍, 郑万模, 李明辉, 等. 川西高原主要地质灾害特征及其影响因素浅析[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,2005,25(4):95 − 98. [DUAN Liping, ZHENG Wanmo, LI Minghui, et al. Geologic hazards on the western Sichuan plateau and their controls[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,2005,25(4):95 − 98. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2005.04.016
[12] 孟晖, 张岳桥, 杨农. 青藏高原东缘中段地质灾害空间分布特征分析[J]. 中国地质,2004,31(2):218 − 224. [MENG Hui, ZHANG Yueqiao, YANG Nong. Analysis of the spatial distribution of geohazards along the middle segment of the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Chinese Geology,2004,31(2):218 − 224. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2004.02.016
[13] 杨振法.大渡河金川水电站外围抚边河断层的活动性研究[D].成都: 成都理工大学, 2006.
YANG Zhenfa. Activity analysis of the Fubianhe fault near Jinchuan hydroelectric power station on Dadu River[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 廖丽萍, 于淼, 文海涛, 等. 广西东南部容县崩塌滑坡的易发性评价[J]. 地球与环境,2019,47(4):518 − 526. [LIAO Liping, YU Miao, WEN Haitao, et al. Evaluation on the susceptibility of collapse and landslide in Rongxian County, southeastern Guangxi[J]. Earth and Environment,2019,47(4):518 − 526. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 胡芹龙, 王运生. 基于GIS的川西地貌过渡带滑坡灾害易发性评价[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 45(6):746−753.
HU Qinlong, WANG Yunsheng. The susceptibility assessment of geological disasters in geomorphic transition zone based on GIS, western Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Sci & Technol Ed), 2018, 45(6):746−753.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 周剑, 邓茂林, 李卓骏, 等.三峡库区浮托减重型滑坡对库水升降的响应规律[J].水文地质工程地质, 2019, 46(5):136−143.
ZHOU Jian,DENG Maolin,LI Zhuojun,et al. Response patterns of buoyancy weight loss landslides under reservoirwater level fluctuation in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J].Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(5):136−143. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 李彩侠, 马煜. 四川东俄洛至炉霍段公路沿线地质灾害类型及其成因[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2013,24(3):105 − 110. [LI Caixia, MA Yu. Types and causes of the geologic hazards along the highways along Dongeluo—Luhuo[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2013,24(3):105 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 铁永波, 白永健, 宋志. 川西高原的岩土体的冻融破坏类型及其灾害效应[J]. 水土保持通报, 2015, 35(2):241−245.
TIE Yongbo, BAI Yongjian, SONG Zhi. Damage types and hazards effects from freezing mThawing process in plateau of western Sichuan Province[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 35(2):241−245.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 吴玮江. 季节性冻融作用与斜坡整体变形破坏[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 1996, 7(4):59−64.
WU Weijiang. Seasonal freeze-thaw action and the entire deformation, failure of slope[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1996, 7(4):59−64.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 胡高社. 巨厚松散层高陡斜坡的形成机理及其防治工程效应研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2006.
HU Gaoshe. Research on the formation mechanism and control engineering effect of giant and thickness layer high-steep slope[D]. Xi'an: Changan University, 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 乔建平, 王萌, 吴彩燕, 等. 汶川地震扰动区小流域滑坡泥石流风险评估—以都江堰白沙河流域为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2018, 29(4):1−9.
QIAO Jianping, WANG Meng, WU Caiyan, et al. Landslide and debris flow risk assessment for small water sheels in the Wenchuan earthquake disturbance area: Taking the Baishahe River Basin in Dujiangyan as an example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2018, 29(4):1−9.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 孟国杰, 任金卫, 甘卫军, 等. 川西地区地壳形变特征及其对汶川8.0级地震成因的启示[J]. 国际地震动态,2008(11):114. [MENG Guojie, REN Jinwei, GAN Weijun, et al. Crustal Deformation in Western Sichuan and Its Enlightenment to the Origin of Wenchuan Ms8.0 Earthquake[J]. Recent Developments in World Seismology,2008(11):114. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4975.2008.11.115
[23] 李娟. 小金县震后地质灾害危险性评价研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2012.
LI Juan. Risk assessment of geological hazard after earthquake in Xiaojin country[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 温铭生, 刘传正, 刘艳辉, 等. 汶川地震高烈度区崩滑流灾害区域预警[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2019, 30(1):10−19.
WEN Mingsheng, LIU Chuanzheng, LIU Yanhui, et al. Regional warning of geological hazards in high seismic intensity area of Wenchuan Earthquake[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(1):10−19.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 范利学. 崩滑流灾变的渗透推移及阶段跟踪[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2009.
FAN Lixue. Landslide mud-rock flow passage of time and stages of the penetration of the disaster track[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 高会会, 裴向军, 崔圣华, 等. 汶川震区震后地质灾害发育分布及演化特征统计分析[J]. 长江科学院院报,2019,36(8):73 − 80. [GAO Huihui, PEI Xiangjun, CUI Shenghua, et al. Geological hazards after earthquake in Wenchuan earthquake area: distribution and evolvement features[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2019,36(8):73 − 80. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20180109
[27] 郭长宝, 杜宇本, 张永双, 等. 川西鲜水河断裂带地质灾害发育特征与典型滑坡形成机理[J]. 地质通报,2015,34(1):121 − 134. [GUO C B, DU Y B, ZHANG Y S, et al. Geohazard effects of the Xianshuihe fault and characteris-tics of typical landslides in western Sichuan[J]. Geologcal Bulletin of China,2015,34(1):121 − 134. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.01.010
-




 下载:
下载: