Basic characteristics and stability evaluation of dangerous rockmasses in Yanqi Town, Beijing
-
摘要:
本文以北京市怀柔区雁栖镇研究区崩塌体为研究对象,通过现场调查和岩块试验检测,查明了崩塌体的基本特征。采用赤平投影分析法,对崩塌危岩带整体稳定性进行定性分析;运用极限平衡法,针对不同工况条件,对单体危岩崩塌进行定量评价。在此基础上,提出了具有针对性的治理措施。研究结果表明:(1)研究区内崩塌隐患点所在斜坡危岩带基本处于不稳定状态;(2)单体危岩W1、W2、W3在自重+裂隙水压力(天然状态)工况条件下,稳定系数1.02~1.17,均处于欠稳定状态;在自重+裂隙水压力(暴雨期间)工况条件下,稳定系数0.82~0.98,均处于不稳定状态;在自重+裂隙水压力(天然状态)+地震力工况条件下,稳定系数0.72~0.83,均处于不稳定状态。(3)提出的以清理危岩为基础,“主动+被动防护网”的综合工程治理措施在北京地区是可行的。研究成果可以作为北京地区开展崩塌灾害工程治理的参考。
Abstract:In this paper, taking Yanqi Town, Huairou District, Beijing as the research object, through the field investigation and rock block test and detection, the basic characteristics of the collapse are found out. By using the method of stereographic projection analysis, the overall stability of the collapse dangerous rock zone is qualitatively analyzed; by using the method of limit equilibrium, the single dangerous rock collapse is quantitatively evaluated according to different working conditions. On this basis, the targeted governance measures are put forward. The results show that: (1) the dangerous rock zone on the slope where the hidden danger point of collapse disaster is located is basically in an unstable state; (2) under the condition of self weight + fracture water pressure (natural state), the stability coefficient of single dangerous rock W1, W2 and W3 is 1.02~1.17, which are all in an unstable state; under the condition of self weight+ fracture water pressure (rainstorm), the stability coefficient is 0.82~0.98, both in an unstable state; under the condition of self weight + fissure water pressure (natural state) + seismic force, the stability coefficient is 0.72~0.83, both in an unstable state. (3) The comprehensive engineering control measures of “active + passive protection network” are feasible in Beijing area. The research results can be used as a reference for engineering control of collapse disaster in Beijing.
-
Key words:
- rock fall /
- dangerous rock /
- stability evaluation /
- prevention and control measures
-

-
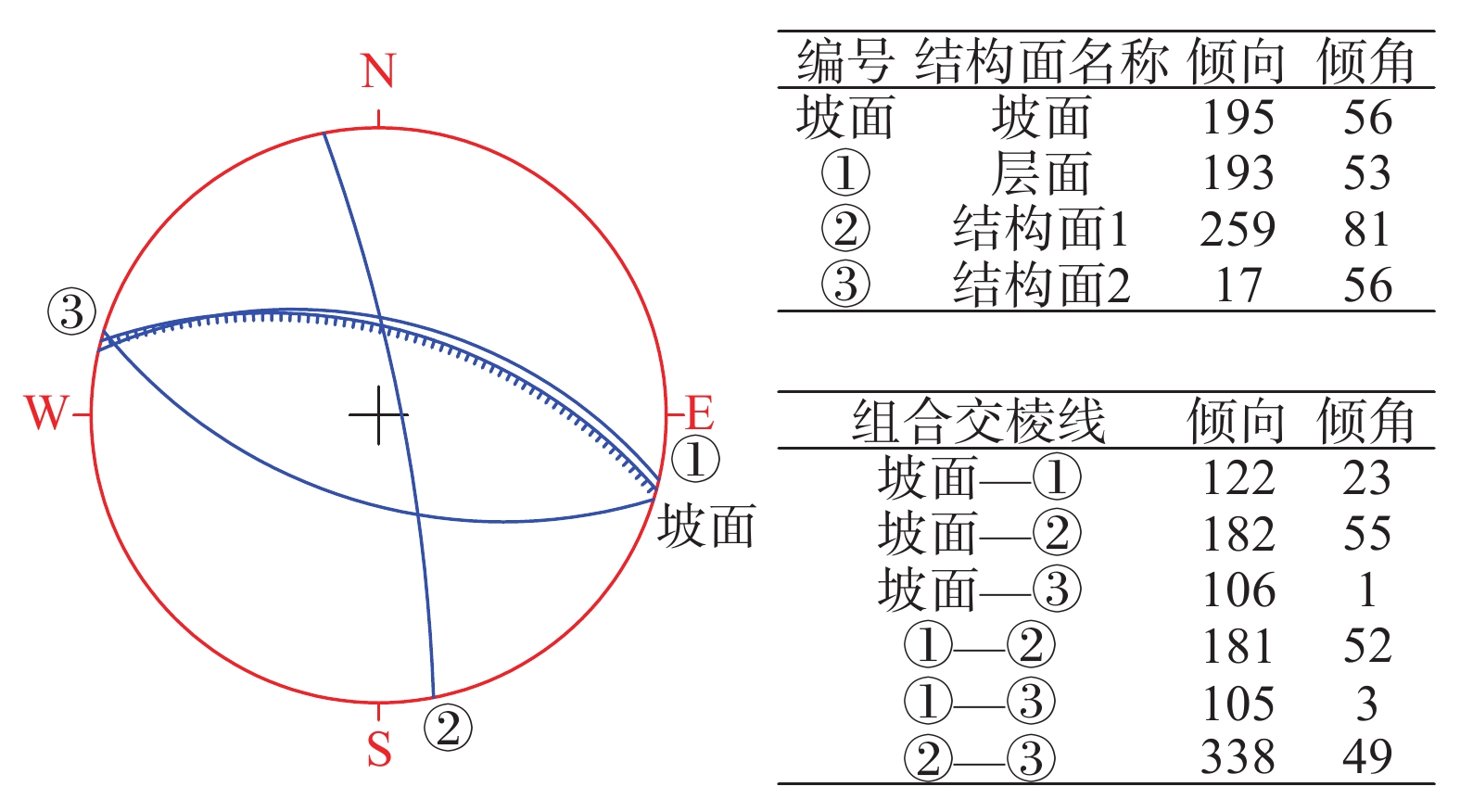
表 1 崩塌危岩体特征调查统计表
Table 1. Survey statistics of characteristics of collapse dangerous rock mass
序号 危岩体编号 所在位置 规模/m3 可能运动方式 可能运动最大距离/m 稳定性分析 危害对象 1 W1 坡顶下方20 m处靠东 10 倾倒式 80~90 欠稳定 人员、房屋、道路 2 W2 坡顶下方21 m处中部 4.5 倾倒式 80~90 欠稳定 人员、房屋 3 W3 坡顶下方22 m处靠西 4.5 倾倒式 80~90 欠稳定 人员、房屋 表 2 岩块试验检测数据
Table 2. Rock block test and detection data
岩性 试样编号 抗压强度/
MPa弹性模量/
104MPa内聚力/
MPa内摩擦角/
(°)白云岩 岩样1 96.41 7.27 2.80 45.57 岩样2 45.83 4.74 4.50 43.42 表 3 稳定性计算参数一览表
Table 3. Stability calculation parameters
重度/(KN·m−3) 天然 25 饱和 26 黏聚力/kPa 天然 37 饱和 35 内摩擦角/(°) 天然 44.5 饱和 43 表 4 稳定状态分级
Table 4. Stability classification
稳定性系数(Fs ) Fs <1.00 1.00≤Fs <1.3 1.3≤Fs <1.5 Fs≥1.5 稳定状态 不稳定 欠稳定 基本稳定 稳定 表 5 稳定性计算结果统计表
Table 5. Statistical table of stability calculation results
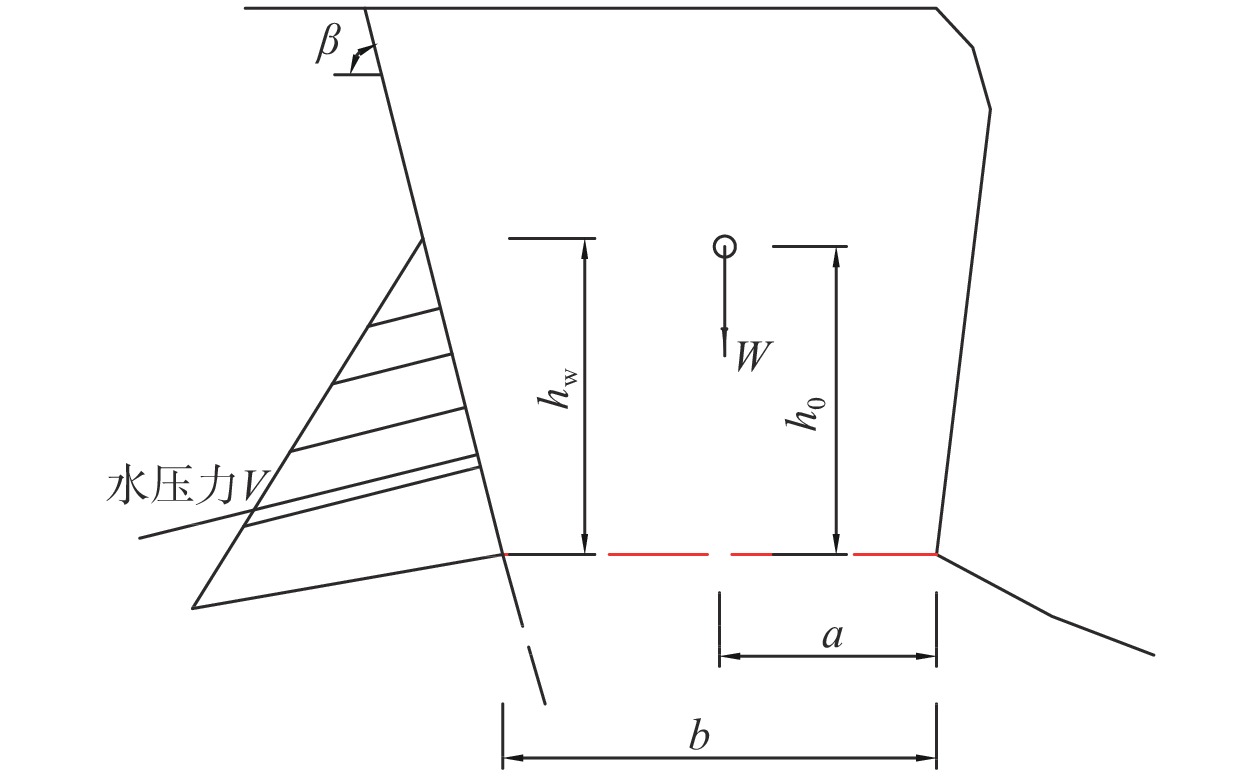
危岩体编号 工况1(天然状态) 工况2(持续暴雨) 工况3(地震) 破坏模式 稳定系数 状态 稳定系数 状态 稳定系数 状态 W1 1.17 欠稳定 0.98 不稳定 0.83 不稳定 倾倒式 W2 1.02 欠稳定 0.82 不稳定 0.72 不稳定 倾倒式 W3 1.10 欠稳定 0.87 不稳定 0.86 不稳定 倾倒式 -
[1] 刘德成. 北京市朝阳区地质灾害危险性区划研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015.
LIU Decheng. Study on geological hazard zoning of Chaoyang District, Beijing [D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] POWELL J W. Exploration of the Colorado River of the west and its tributaries[M]. Washington: Government Printing Office, 1875.
[3] POISELR, EPPENSTEINER W. A contribution to the systematics of rock mass movements [C]//The 5th International Symposium on Landslides, 1988: 1353 − 1357.
[4] POISEL R, ANGERER H, PÖLLINGER M, et al. Mechanics and velocity of the Lärchberg–Galgenwald landslide (Austria)[J]. Engineering Geology,2009,109(1/2):57 − 66.
[5] RAINER POISEL, ALEXANDERPREH. Rock fall detachment mechanisms [C]//Interdisciplinary Rockfall Workshop, 2011: 1 − 2.
[6] TERZAGHI K. Mechanism of landslides [M]. Berkey: The Geological Society of America, Engineering Geology, 1950.
[7] DUSSAUGEPEISSER C, HELMSTETTER A, GRASSO J, et al. Probabilistic approach to rock fall hazard assessment: potential of historical data analysis[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences,2002,2:15 − 26. doi: 10.5194/nhess-2-15-2002
[8] NICHOL S L, HUNGR O, EVANS S G. Large-scale brittle and ductile toppling of rock slopes[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2002,39(4):773 − 788. doi: 10.1139/t02-027
[9] GLASTONBURY J, FELLR. Report on the analysis of“Rapid”Natural Rock Slope Failures [M]. Sydney Australia: The University of New South Wales, 2000.
[10] 曾芮, 姜明顺, 孙琳馗, 等. 强降雨条件下岩质边坡倾倒崩塌破坏机理—以鄂西赵家岩崩塌为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(3):12 − 17. [ZENG Rui, JIANG Mingshun, SUN Linkui, et al. Toppling failure mechanism of rock slope induced by heavy rainfall: a case study of the Zhaojiayan Rockfall in Western Hubei[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(3):12 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 肖锐铧, 陈红旗, 冷洋洋, 等. 贵州纳雍“8•28”崩塌破坏过程与变形破坏机理初探[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(1):3 − 9. [XIAO Ruihua, CHEN Hongqi, LENG Yangyang, et al. Preliminary study on the collapse process and deformation failure mechanism of "8.28" in Nayong, Guizhou[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(1):3 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 王章琼, 晏鄂川, 刘骏, 等. 湖北鹤峰红莲池铁矿反倾岩坡崩塌破坏特征及形成机理分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2016,27(3):7 − 13. [WANG Zhangqiong, YAN E chuan, LIU Jun, et al. Characteristics and mechanism of the rockfall at Honglianchi iron mine in Hefeng, Hubei Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2016,27(3):7 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 董秀军, 裴向军, 黄润秋. 贵州凯里龙场镇山体崩塌基本特征与成因分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2015,26(3):3 − 9. [DONG Xiujun, PEI Xiangjun, HUANG Runqiu. The Longchangzhen collapse in Kaili, Guizhou: characteristics and failure causes[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015,26(3):3 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 贺凯, 陈春利, 冯振, 等. 塔柱状岩体崩塌灾害研究现状[J]. 地质力学学报,2016,22(3):714 − 724. [HE Kai, CHEN Chunli, FENG Zhen, et al. A review on the collapse hazards of tower-shaped rock[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2016,22(3):714 − 724. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.03.025
[15] 岳发政, 郭金城, 汪娟, 等. GB-InSAR技术在山体崩塌残余危岩体监测中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(5):78 − 80. [YUE Fazheng, GUO Jincheng, WANG Juan, et al. Application of GB-InSAR technology in monitoring of residual dangerous rock mass in mountain collapse[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(5):78 − 80. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 袁志辉, 陈志新, 倪万魁, 等. 倾倒式岩质崩塌运动过程数值模拟分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2014,25(2):26 − 31. [YUAN Zhihui, CHEN Zhixin, NI Wankui, et al. Numerical analysis of the movement process of toppling fall[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2014,25(2):26 − 31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 黄刚, 郑达. 贵州开阳磷矿山体崩塌形成机理与数值模拟[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2013,24(1):46 − 50. [HUANG Gang, ZHENG Da. Research on formation mechanism and numerical simulation of rockfall in Kaiyang phosphorite, Guizhou Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2013,24(1):46 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 马保成, 范丽晓, 田伟平. 黄土地区公路崩塌危险性简易快速评价方法探讨马保成, 范丽晓, 田伟平[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2014,25(2):19 − 25. [MA Baocheng, FAN Lixiao, TIAN Weiping. Study on quick and easy hazard evaluation method for highway slope collapse in loess area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2014,25(2):19 − 25. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 工程岩体分级标准: GB/T 50218—2014[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2015.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Standard for engineering classification of rock mass: GB/T 50218—2014[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2015. (in Chinese)
[20] 武中鹏, 刘宏, 董秀群, 等. 单体危岩崩塌灾害危险性评价—以贵州威宁县新发乡樊家岩为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(2):30 − 34. [WU Zhongpeng, LIU Hong, DONG Xiuqun, et al. Risk assessment of single dangerous rock collapse disaster:Taking fanjiayan, Xinfa Township, Weining County, Guizhou Province as an example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(2):30 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 彭宁波, 孙博, 王逢睿, 等. 危岩体在地震作用过程中的失稳模式及稳定性评价[J]. 地震工程学报,2016,38(6):916 − 921. [PENG Ningbo, SUN Bo, WANG Fengrui, et al. Failure mode and stability evaluation of unstable rock during earthquakes[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal,2016,38(6):916 − 921. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 中华人民共和国国土资源部. 滑坡防治工程勘查规范: DZ/T 0218—2006[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006.
Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China. Specification of geological investigation for landslide stabilization: DZ/T 0218—2006[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2006. (in Chinese)]
-




 下载:
下载: