Experimental study on slope collapse characteristics of granite residual soil slope under heavy rainfall
-
摘要:
以东南沿海地区花岗岩残积土为代表性土样,以土体斜坡坡度、降雨强度为控制变量,设计了降雨滑坡模拟试验方案,在大雨、暴雨、大暴雨、特大暴雨等四种不同降雨等级条件下对四种不同坡度的斜坡模型进行了强降雨模拟试验,研究降雨强度和斜坡坡度对其滑塌破坏的影响特征。结果表明:降雨强度越大,发生深层破坏或浅层整体破坏的趋势越明显,其变形跨塌滑块尺寸越大,破坏范围越集中,破坏程度增强;同时土体裂纹出现的时间越早,斜坡滑塌破坏所需的降雨时长逐渐减少。随斜坡坡度的增大,破坏形式由滑落滑坡逐步转化散落崩塌破坏,其相应斜坡滑塌破坏所需的降雨时长减少。研究结论对揭示降雨引发残积土滑坡等地质灾害发生规律具有重要的理论和现实意义。
Abstract:The granite residual soil in southeast coast area is selected as the representative soil sample and the simulation test schemes of rainfall triggered landslide are designed with the slope gradient and the rainfall intensity as their control variables. Then the heavy rainfall simulation experiment of slope models with four different gradients are performed under four kinds of different conditions, i.e. heavy rain, rainstorm, heavy rainstorm, extreme rainstorm, and the influence characteristics of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on slope slumping destruction are studied. The results show that the greater rainfall intensity is, the larger the slide block size of collapse is and the more concentrated the scope of damage is, while more obvious the trend of deep or shallow overall damage of slope. In addition, the extent of slope damage is enhanced and the less time needed for soil cracks appear and slope slumping destruction at the same time. With the slope gradient increases, the failure modes of slope gradually become scattered collapse from landslide sliding and the rainfall duration of slope sliding damage is reduced. The research results have important theoretical and practical significance for disclosing the rule of residual soil landslides and other geological disasters triggered by heavy rainfall.
-
Key words:
- granite residual soil /
- simulation experiment /
- slope model /
- rainfall intensity /
- slope gradient
-

-
表 1 不同条件下16种模拟试验方案及编号
Table 1. 16 kinds of schemes and numbers of simulation experiment under different conditions
坡度/(°) 1档(大雨) 2档(暴雨) 3档(大暴雨) 4档(特大暴雨) 30(Ⅰ) Ⅰ1 Ⅰ2 Ⅰ3 Ⅰ4 40(Ⅱ) Ⅱ1 Ⅱ2 Ⅱ3 Ⅱ4 50(Ⅲ) Ⅲ1 Ⅲ2 Ⅲ3 Ⅲ4 55(Ⅳ) Ⅳ1 Ⅳ2 Ⅳ3 Ⅳ4 表 2 残积土初始土性参数
Table 2. Initial soil parameters of residual soil
项目 密度/(g·cm−3) 含水率/% 颗粒粒径/cm 取值 <1.6 15.25~19.25 <2 表 3 模拟试验过程动态监测方案
Table 3. Dynamic monitoring schemes of the simulation test
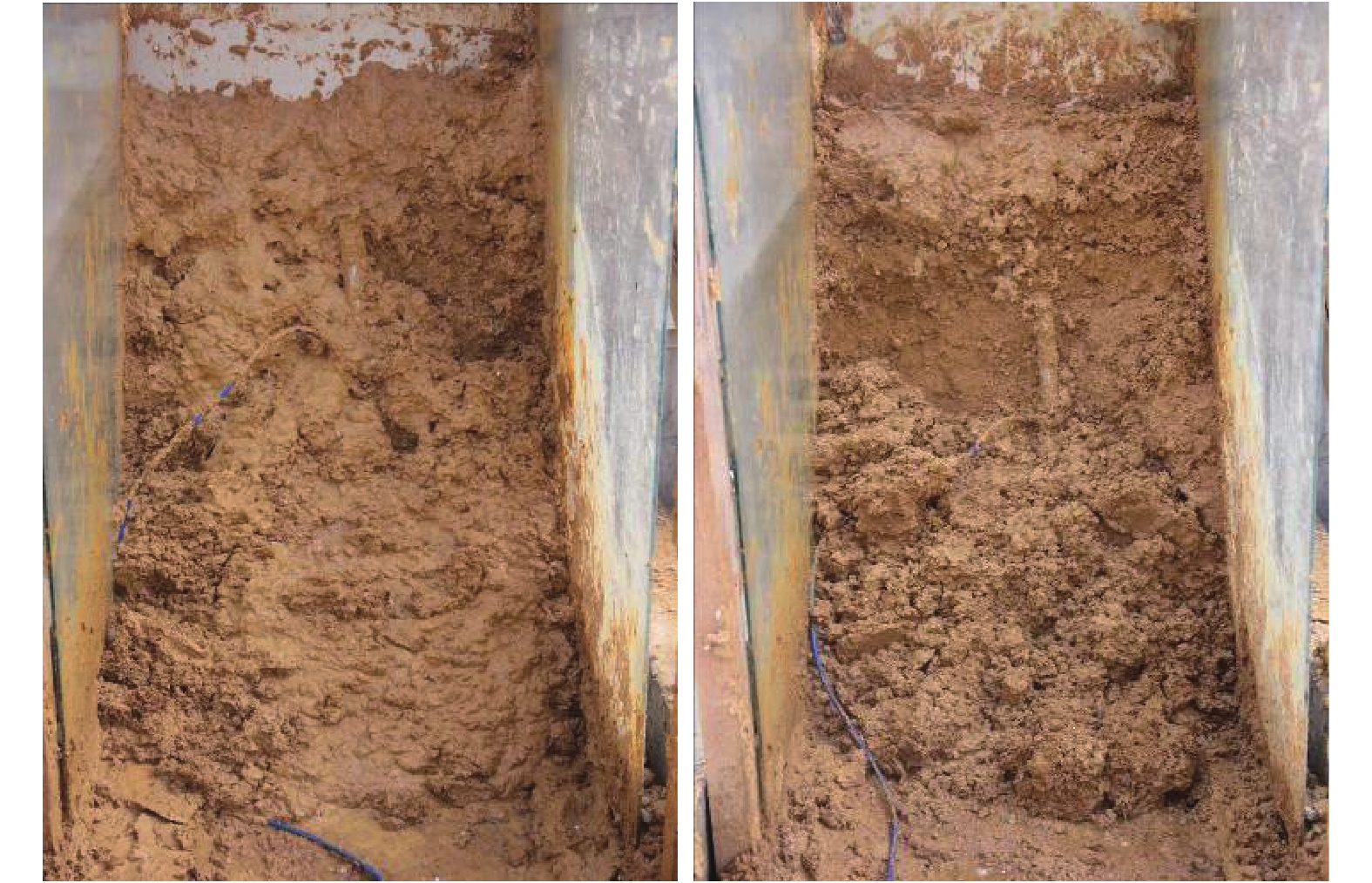
项目 起始 滑塌出现前 滑塌出现后 正面图像 1~2张 间隔5 min 间隔2 min 侧面观测框图像 各拍1张 间隔10 min 间隔5 min 侧面观测框卧式显微镜
细观演变观测1~2张 间隔5 min 间隔2 min 正面滑塌破坏的时间段
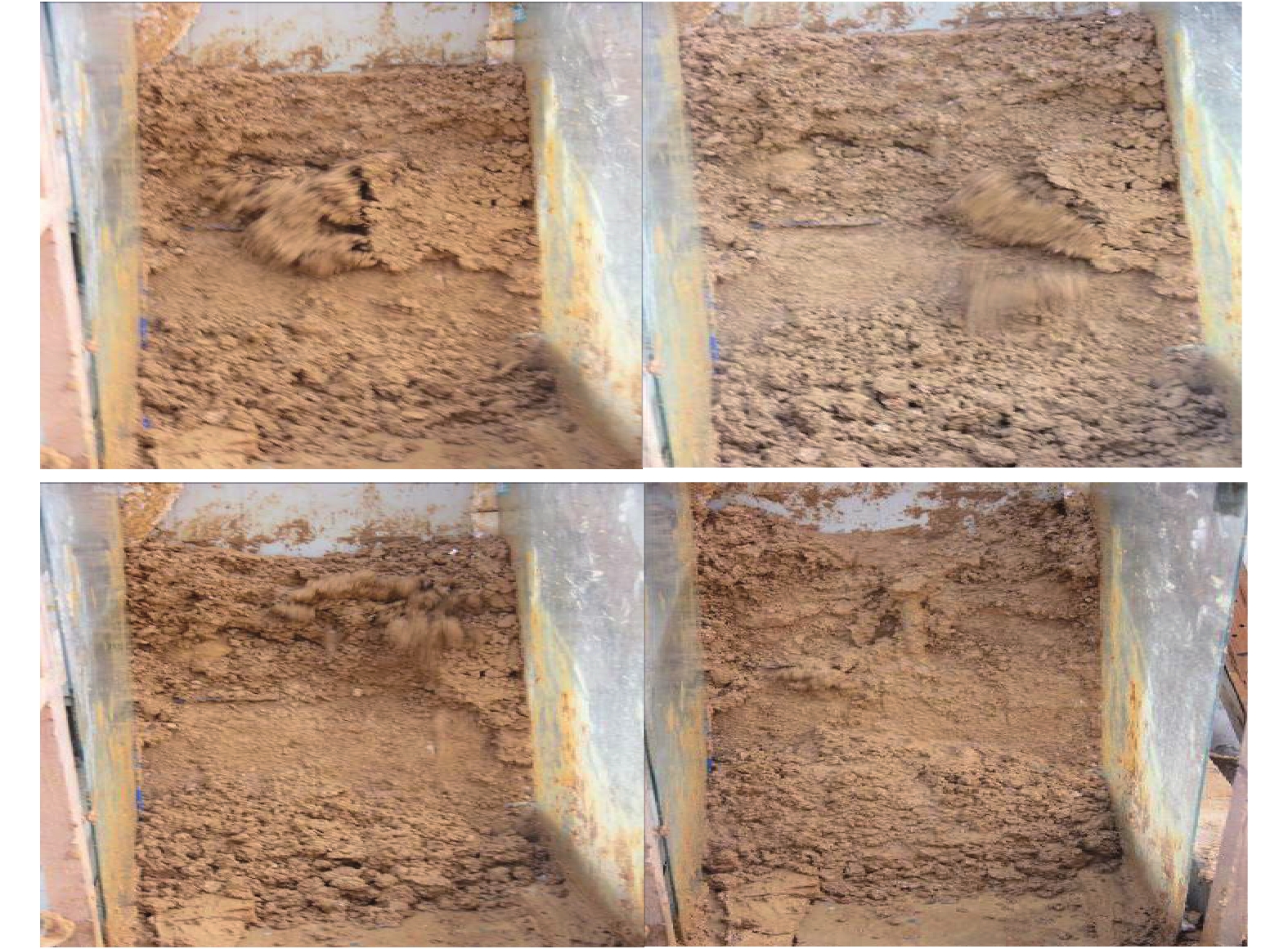
宏观观测高清晰录像机跟拍关键滑塌破坏过程 各种传感器读数 记录初始读数 间隔5 min 间隔2 min 表 4 斜坡模型滑塌破坏模式分类统计表
Table 4. Classification statistics of sliding mode of model slope
变形破坏模式 深层
整体失稳深层
局部失稳浅层
整体失稳浅层
局部失稳模拟试验
方案编号55°1档;
50°4档;
50°3档40°4档 30°4档;
30°3档30°2档;30°1档;
40°3档;50°2档;
40°1档;40°2档;
50°1档;55°4档;
55°3档;55°2档数量/个 3 1 2 10 表 5 降雨强度对斜坡模型滑塌破坏过程的影响分类统计表
Table 5. Classification statistics of the effect of model slope gradient on slope sliding process
坡度/(°) 1档(大雨) 2档(暴雨) 3档(大暴雨) 4档(特大暴雨) 30 裂缝出现时间晚,
滑块尺寸小且分散裂缝出现时间较晚,
滑块尺寸较小且分散裂缝出现时间较早,滑块尺寸较大
且集中,破坏程度大裂缝出现时间早,滑块尺寸大
且集中,破坏程度大40 滑块出现时间晚,
范围大,破坏程度小滑块出现时间较晚,
范围较小滑块出现时间较快,范围小,
但破坏程度大深层局部失稳破坏,破坏程度大 50 滑块出现时间晚,滑块尺寸小
且位置分散,破坏程度小裂缝出现时间较早,滑块尺寸
较大且位置较集中深层整体失稳破坏,破坏程度大 裂缝出现时间早,滑块尺寸大
且破坏程度大55 深层整体失稳破坏 滑块出现时间较均匀,滑块
尺寸小,次数多,位置分散滑块出现时间较早但滑块尺寸小
且均匀,大滑块出现时间晚滑块出现时间早,但滑块尺寸小
且均匀,大滑块出现时间较晚表 6 斜坡模型开始滑塌失稳破坏时间统计表
Table 6. The time(minutes)of instability and failure of model slope
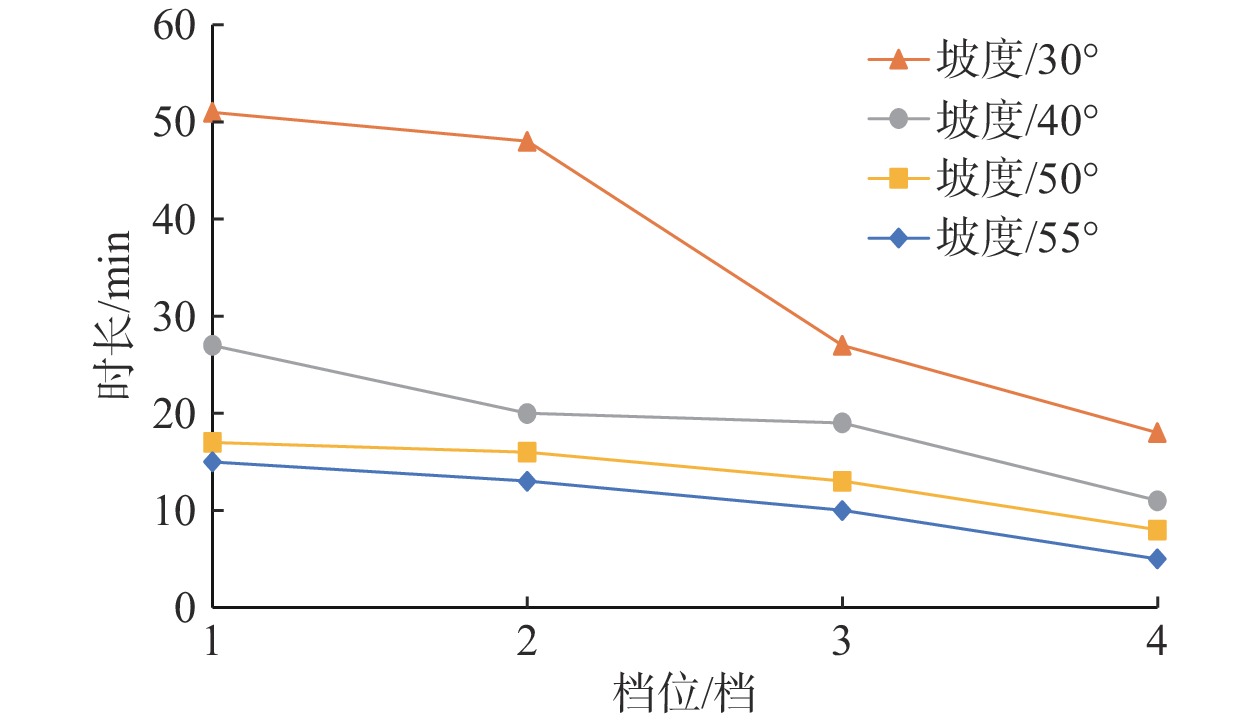
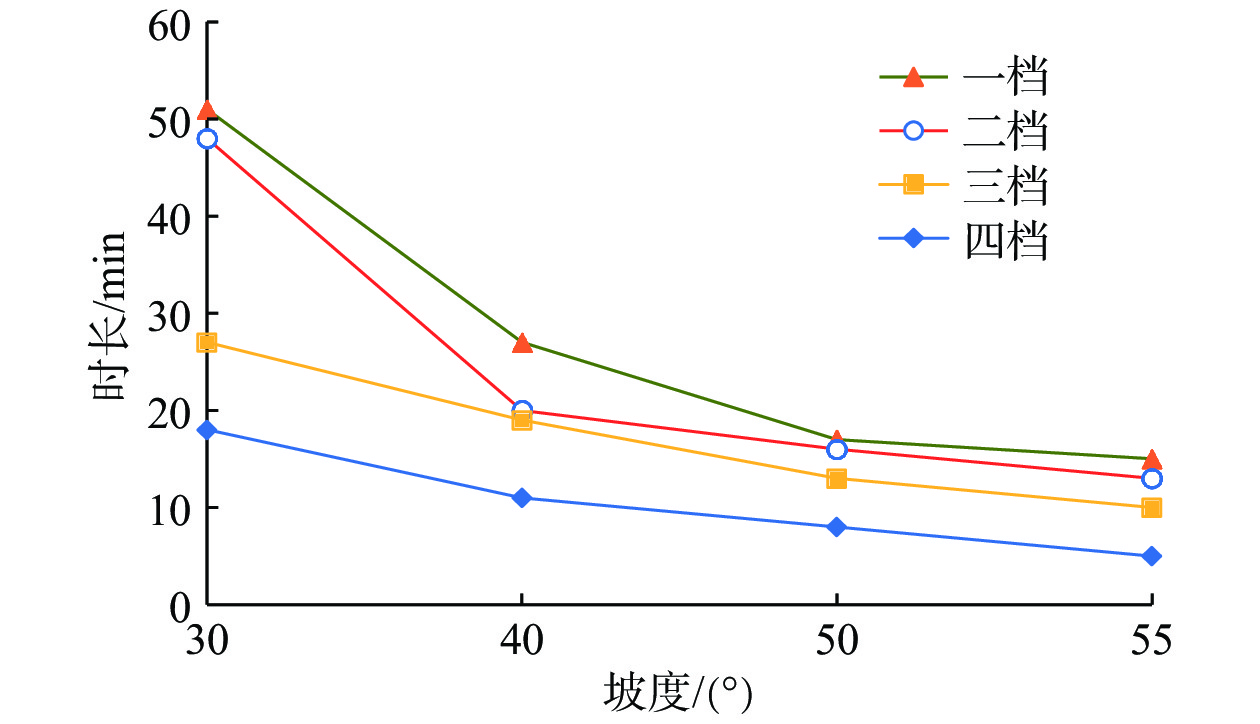
/min 坡度/(°) 1(大雨) 2(暴雨) 3(大暴雨) 4(特大暴雨) 30 51 48 27 18 40 27 20 19 11 50 17 16 13 8 55 15 13 10 5 表 7 斜坡模型坡度对坡体滑塌破坏形式的影响分类统计表
Table 7. Classification statistics of the effect of model slope gradient on slope sliding mode
坡度/
(°)滑塌破坏形式描述 破坏
(散落)
数量/个破坏
(滑落)
数量/个30 都有裂缝的优先发展而将土体分割为大
或小的滑块,之后这些滑块才在不同的降雨
强度条件下出现不同的破坏形式0 4 40 除4档雨强的突破外,其余土坡均由坡上部
开始有滑块形成并下滑,且较其他坡度的
土坡,其最终的破坏程度最小2 2 50 都有裂缝的优先发展而将土体分割为大或小的
滑块,之后这些滑块又都以散落的形式破坏4 0 55 都未出现裂缝,土体均在受雨一段时间后形成大
或小的滑块,后直接从土体上散落破坏4 0 -
[1] 胡华, 蔡亮, 梁建业. 花岗岩残积土冲击损伤与损伤演化特性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(3):872 − 880. [HU Hua, CAI liang, LIANG Jianye. Experimental research on impact damage and damage evolution characteristics of granite residual soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2012,33(3):872 − 880. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 胡华, 梁建业. 花岗岩残积土含水率对动态流变损伤力学特性与损伤度影响试验研究[J]. 水利学报,2015,46(7):54 − 58. [HU Hua, LIANG Jianye. Experiment and research on dynamic rheological damage mechanics characteristics and damage degree influence with different moisture content of granite residual soil[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2015,46(7):54 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 胡华, 蔡亮. 残积土含水率对其动力特性影响试验研究[J]. 地震工程学报,2015,37(3):754 − 758. [HU Hua, CAI Liang. Test study of the influence of moisture content on dynamic characteristics of residual soil[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2015,37(3):754 − 758. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2015.03.0754
[4] 胡华, 谢金华. 改进的不等时距灰色马尔科夫模型在斜坡位移预测中的应用[J]. 水利与建筑工程学报,2016(6):1 − 6. [HU Hua, XIE Jinhua. Application of improved unequal time interval gray markov model in roadbed sloped displacement prediction[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering,2016(6):1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1144.2016.06.001
[5] 阙云, 胡昌斌, 姚晓琴. 降雨入渗对裂隙性粘土边坡稳定性作用机理的分析[J]. 福州大学学报(自然科学版),2009,37(3):423 − 429. [QUE Yun, HU Changbin, YAO Xiaoqin. Mechanism analysis on the influence of the rainfall infiltration on the stability of fissured clay slope[J]. Journal of Fuzhou University (Natural Science Edition),2009,37(3):423 − 429. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 詹良通, 李鹤, 陈云敏, 等. 东南沿海残积土地区降雨诱发型滑坡预报雨强-历时曲线的影响因素分析[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(3):872 − 880. [ZHAN Liangtong, LI He, CHEN Yunmin, et al. Parametric analyses of intensity-duration curve for predicting rainfall-induced landslides in residual soil slope in Southeastern coastal areas of China[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2012,33(3):872 − 880. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 张友谊, 胡卸文, 朱海勇. 滑坡与降雨关系研究展望[J]. 自然灾害学报,2007,16(1):104 − 108. [ZHANG Youyi, HU Xiewen, ZHU Haiyong. Prospect of research on relationship between landslide and rainfall[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2007,16(1):104 − 108. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2007.01.020
[8] 陈天健, 蔡和伦, 黄彦荣, 等. 人工降雨模型试验研究降雨入渗对滑坡类型之影响[J]. 水土保持研究,2012,19(1):254 − 257. [CHEN Tianjian, CAI Helun, HUANG Yanrong, et al. Slope failure mode related to soil infiltration-laboratory rainfall model test[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2012,19(1):254 − 257. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 李长江, 麻土华, 李炜, 等. 滑坡频度-降雨量的分形关系[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2010,21(1):87 − 93. [LI Changjiang, MA Tuhua, LI Wei, et al. Fractal relation of landslide frequency and rainfall[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2010,21(1):87 − 93. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2010.01.018
[10] 左自波. 降雨诱发堆积体滑坡室内模型试验研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2013.
ZUO Zibo. Investigation on rainfall-induced colluvium landslides using laboratory model tests[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 李鹤. 东南沿海残积土地区降雨型滑坡预警预报体系的研究与应用[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2011.
LI He. Study on early warning system for rain-induced slope failure in residual soils in southeast coastal region of China[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 常晓军, 王德伟, 唐业旗. 中国滑坡降雨试验的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,2010,30(1):98 − 102. [CHANG Xiaojun, WANG Dewei, TANG Yeqi. Simulation experiments of the rainfall-induced landslides in China: insights and foresights[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,2010,30(1):98 − 102. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2010.01.017
-




 下载:
下载: