Influence of control point number on UAV low-altitude photogrammetry and its application: A case study in subsidence monitoring of a tailing dam area in northwestern China
-
摘要:
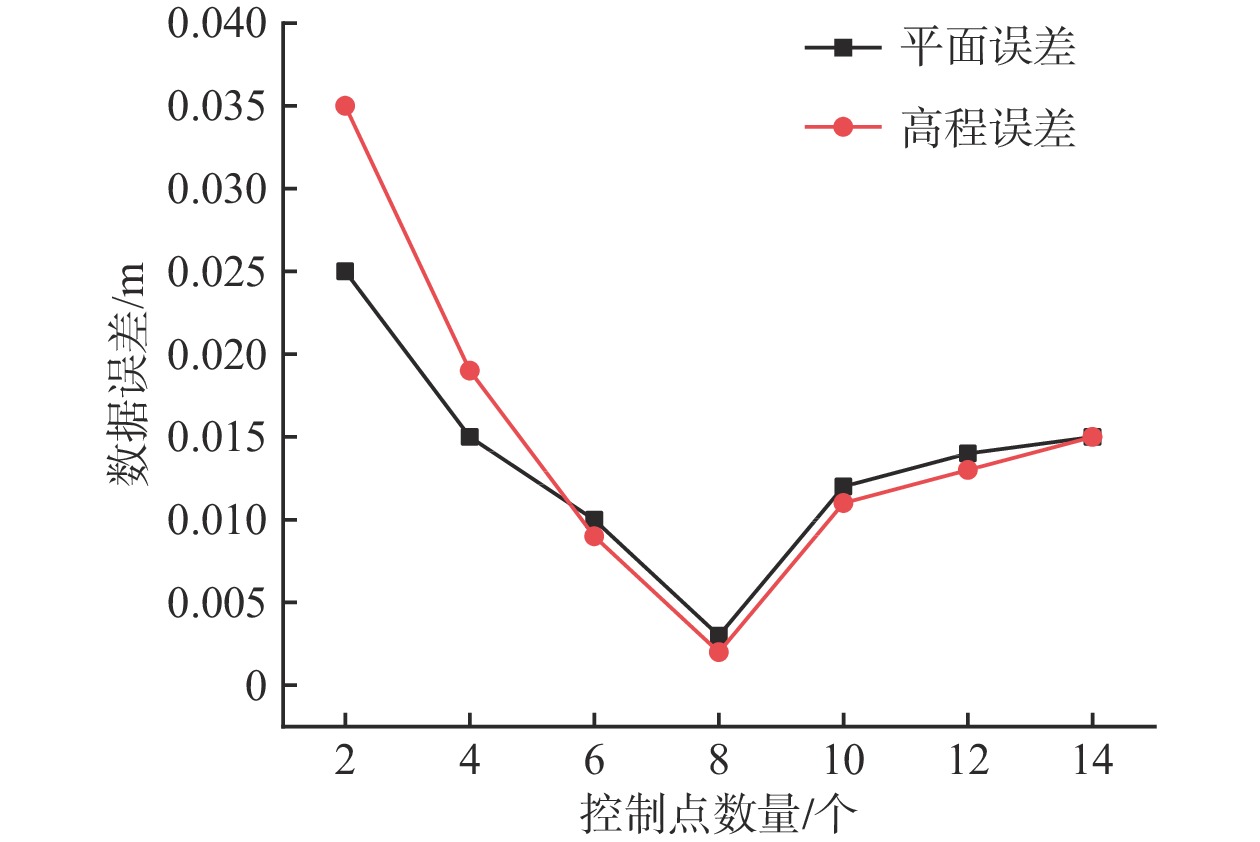
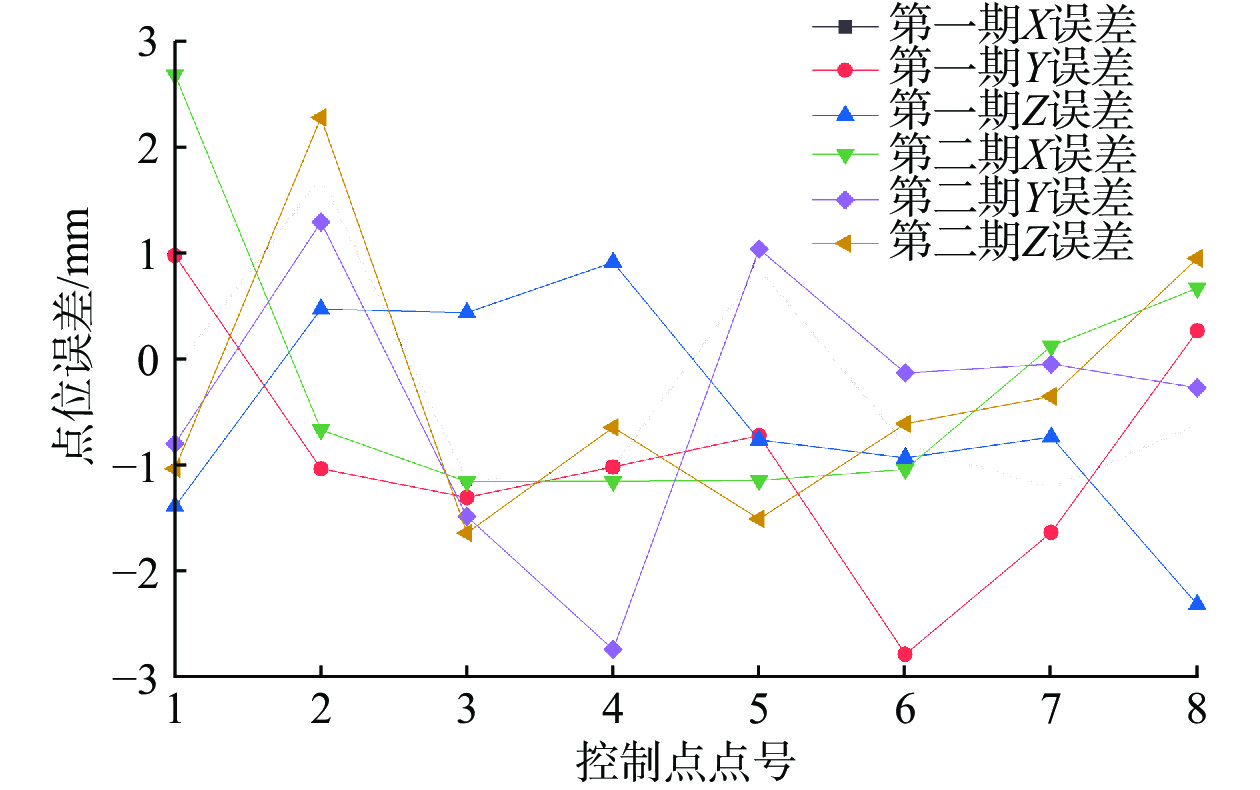
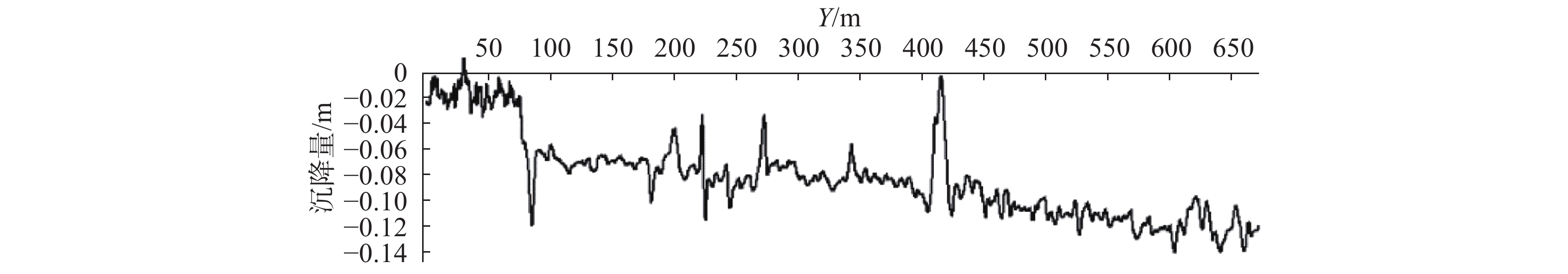
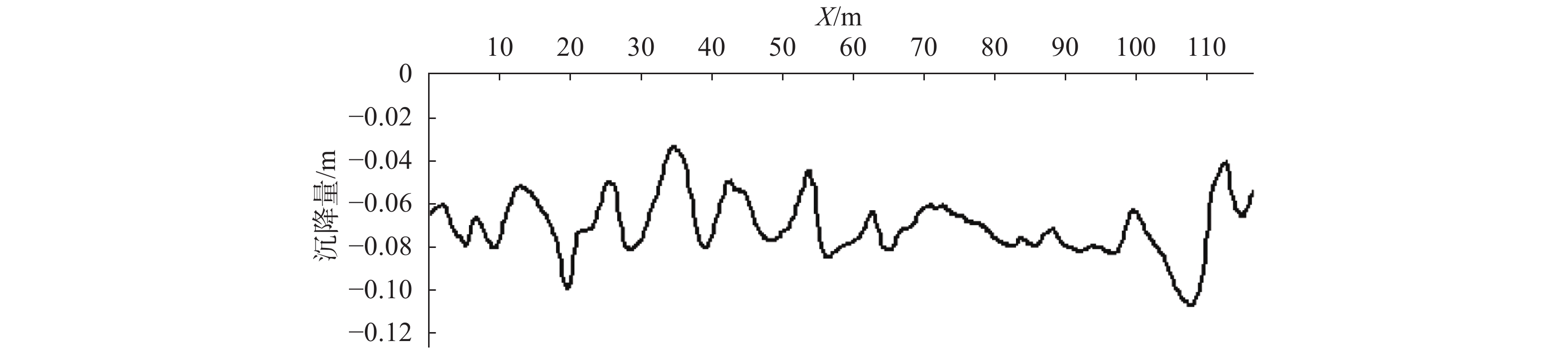
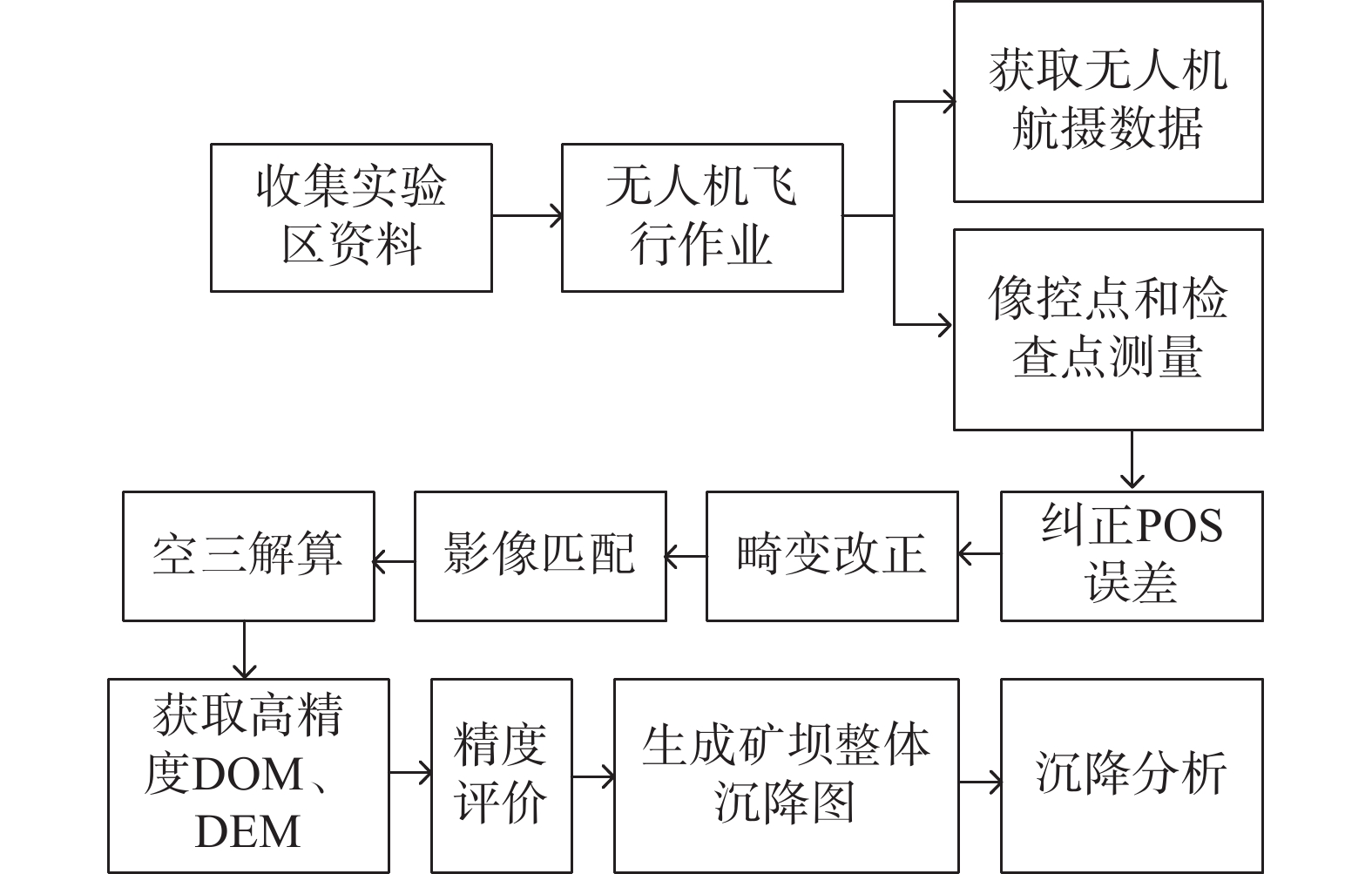
近年来矿区地质灾害愈发严重。为准确监测尾矿坝地表沉陷变形,以地形地貌复杂的尾矿坝为研究实例,开展无人机低空摄影的形式进行监测数据收集。无人机原始POS数据存在系统误差的问题,文章利用误差改正模型纠正原始POS数据,并设计7种像控点布设方案,并对获取的尾矿坝高分辨率正射影像及DEM进行了精度评价。结果显示,当布设像控点数量为8个时,数据误差可以控制在3 mm以内;用两期DEM数据差值覆于地面模型,生成尾矿坝沉降图, 沿Y=350 m、Y=100 m和X=60 m剖面线做剖面图。基于测量结果发现,尾矿坝已出现整体沉降,其中南部尾矿坝下坡沉降范围最大,沉降范围在0.16 m之内。这次应用验证了在尾矿坝地表监测中无人机低空摄影测量的精度是可靠的。利用无人机的高精度成图方法对尾矿坝变形进行监测,对应急响应溃坝可能导致的绿洲地区及周边河湖生态灾难地形和矿区安全生产起到一定的预警作用。
Abstract:Geological disasters in mining areas have become more and more serious in recent years. For accurate monitoring of surface subsidence with complex topography of tailings dam, based on the monitoring data of UAV(Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) low-altitude photogrammetry, the UAV original POS(Position and Orientation System) data error were improved, data from the error correction model was used to correct the original POS model and 7 kinds of control point layout were designed, high resolution evaluation was conducted on the orthogonal projection as well as the DEM(Digital Elevation Model) accuracy. The results show that when the number of image control points is 8, the data error can be controlled within 3 mm. The settlement map of the mining dam is generated by overlaying the ground model with the difference values of the two DEM data, and the profiles with Y=350 m, Y=100 m and X=60 m were made respectively. The measurement results indicated that the tailing dam has been subsided as a whole, and the southern mining dam has the largest subsidence area, which is within 0.16 m. This application verifies that the accuracy of UAV low altitude photogrammetry in mining dam surface monitoring is reliable. The high-precision mapping method of UAV is used to monitor the deformation of tailing dam, which plays a certain early warning role in the ecological disaster terrain of the oasis area and the surrounding rivers and lakes which may be caused by the emergency response of dam break and the safe production of mining area.
-
Key words:
- UAV photogrammetry /
- mine dam surface subsidence /
- error correction /
- deformation analys
-

-
表 1 外方位元素的改正值和误差来源
Table 1. Correction values and error sources of elements with external orientation
外方位元素 改正值 改正误差 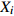
奇数行带 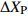
相反性误差
偏移误差偶数行带 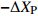
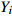
奇数行带 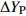
相反性误差
偏移误差偶数行带 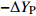
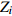
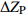
偏移误差 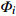
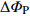
视准轴误差 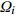

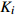
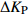
表 2 原始POS数据与纠正后POS数据对比
Table 2. Comparison of original POS data and corrected POS data
ID 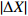
/m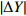
/m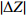 /m
/m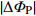
/(°)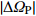 /(°)
/(°)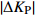 /(°)
/(°)D35 0.013 0.046 0.093 0.18 0.13 0.87 D36 0.056 0.099 0.034 0.20 0.43 0.50 D42 0.074 0.060 0.089 0.47 0.59 0.61 D43 0.025 0.054 0.051 0.78 0.78 0.84 D92 0.076 0.012 0.060 0.14 0.11 0.26 D93 0.047 0.083 0.081 0.28 0.25 0.55 -
[1] 国家安全生产监督管理总局. 尾矿库安全技术规程 : AQ 2006—2005[S]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 2006.
State Administration of Quality and Technical Supervision of the People's Republic of China. Safety technical regulations for the tailings pond: AQ 2006—2005[S]. Beijing: China Coal Industry Publishing House, 2006. (in Chinese)
[2] 李超越. 马家田尾矿库环境风险评价及危险范围预测[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2019.
LI Chaoyue. Environmental risk assessment of Majiatian tailing pond and hazardous range forecast[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 张凯翔. 基于“3S”技术的地质灾害监测预警系统在我国应用现状[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(6):1 − 11. [ZHANG Kaixiang. Review on geological disaster monitoring and early warning system based on “3S” technology in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(6):1 − 11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 侯燕军, 周小龙, 石鹏卿, 等. “空-天-地”一体化技术在滑坡隐患早期识别中的应用: 以兰州普兰太公司滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(6):12 − 20. [HOU Yanjun, ZHOU Xiaolong, SHI Pengqing, et al. Application of “Air-Space-Ground” integrated technology in early identification of landslide hidden danger: Taking Lanzhou Pulantai company landslide as an example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(6):12 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 张鸣之, 湛兵, 赵文祎, 等. 基于虚拟参考站技术的滑坡高精度位移监测系统设计与实践[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(6):54 − 59. [ZHANG Mingzhi, ZHAN Bing, ZHAO Wenyi, et al. Design and practice of high precision landslide displacement monitoring system based on VRS[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(6):54 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 李德仁, 李明. 无人机遥感系统的研究进展与应用前景[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2014,39(5):505 − 513. [LI Deren, LI Ming. Research advance and application prospect of unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing system[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2014,39(5):505 − 513. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 李文鹏. 地质灾害隐患和水文地质环境地质调查计划进展[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(2):1 − 4. [LI Wenpeng. Achievements of the program of geological investigation on geo-hazards and hydrogeology and environmental geology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(2):1 − 4. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 李学刚, 韩术合, 燕鸣. 矿山地质环境治理保证金制度发展历程及现实意义: 以内蒙古赤峰地区为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(3):104 − 109. [LI Xuegang, HAN Shuhe, YAN Ming. Development process and practical significance of the deposit system of mine geological environment management: Take Chifeng area of Inner Mongolia as an example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(3):104 − 109. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 曹伟, 盛煜. 煤矿开采过程中的冻土环境问题与对策[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2013,40(5):91 − 96. [CAO Wei, SHENG Yu. Permafrost environment problems and countermeasures in the process of coal mining[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2013,40(5):91 − 96. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 马瑞升, 孙涵, 林宗桂, 等. 微型无人机遥感影像的纠偏与定位[J]. 南京气象学院学报,2005,28(5):632 − 639. [MA Ruisheng, SUN Han, LIN Zonggui, et al. Geometric correction and registration of optical remote sensing image from miniature unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology,2005,28(5):632 − 639. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 邴媛媛. 无人机遥感在某铁矿矿区资源监测中的应用[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2008.
BING Yuanyuan. UAV remote sensing in a mine iron resources monitoring[D]. Fuxin: Liaoning Technical University, 2008. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 张慧超. 基于无人机摄影测量技术的地表塌陷变形监测及应用研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2018.
ZHANG Huichao. Application of photogrammetry based on UAV in surface collapse deformation monitoring[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 喜文飞. 滇东北山区无人机遥感影像预处理方法及滑坡特征识别研究[J]. 测绘学报,2020,49(8):1071. [XI Wenfei. Study on remote sensing image preprocessing method and landslide feature identification of UAV in northeast Yunnan mountain area[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica,2020,49(8):1071. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2020.20200081
[14] 黄海宁, 黄健, 周春宏, 等. 无人机影像在高陡边坡危岩体调查中的应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(6):149 − 155. [HUANG Haining, HUANG Jian, ZHOU Chunhong, et al. Application of UAV images to rockfall investigation at the high and steep slope[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(6):149 − 155. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 金伟, 葛宏立, 杜华强, 等. 无人机遥感发展与应用概况[J]. 遥感信息,2009,24(1):88 − 92. [JIN Wei, GE Hongli, DU Huaqiang, et al. A review on unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing and its application[J]. Remote Sensing Information,2009,24(1):88 − 92. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2009.01.017
[16] 迟臣鑫, 陈伟强, 朱鹏程, 等. 采煤塌陷积水区面积无人机采集方法[J]. 金属矿山,2020(8):136 − 141. [CHI Chenxin, CHEN Weiqiang, ZHU Pengcheng, et al. Acquisition method of accumulated water area in mining subsidence area by unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Metal Mine,2020(8):136 − 141. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 林元茂, 李建, 韩立. 灾后复杂地形区域的测量测绘模型设计[J]. 灾害学,2019,34(4):35 − 40. [LIN Yuanmao, LI Jian, HAN Li. Design of survey and mapping model for complex topographic areas after disaster[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2019,34(4):35 − 40. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2019.04.007
[18] 赵星涛, 胡奎, 卢晓攀, 等. 无人机低空航摄的矿山地质灾害精细探测方法[J]. 测绘科学,2014,39(6):49 − 52. [ZHAO Xingtao, HU Kui, LU Xiaopan, et al. Precise detection method for mine geological disasters using low-altitude photogrammetry based on unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping,2014,39(6):49 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 鲁恒, 李永树, 江禹. 一种基于POS数据的无人机影像自动展绘控制点方法[J]. 光电工程,2011,38(9):25 − 29. [LU Heng, LI Yongshu, JIANG Yu. A method of automatic extraction of image control points for UAV image based on POS data[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering,2011,38(9):25 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 贾鑫, 杨树文, 张志华, 等. 搭载POS数据的无人机影像提高定位精度的方法[J]. 遥感信息,2019,34(4):92 − 96. [JIA Xin, YANG Shuwen, ZHANG Zhihua, et al. A method to improve positioning accuracy of UAV image based on POS data[J]. Remote Sensing Information,2019,34(4):92 − 96. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2019.04.015
[21] 鲍先凯, 杨东伟, 段东明, 等. 施工工法对浅埋软岩小净距隧道地表沉降和围岩稳定的影响研究[J]. 公路工程,2019,44(4):22 − 29. [BAO Xiankai, YANG Dongwei, DUAN Dongming, et al. Influence of construction methods on surface subsidence and surrounding rock stability of shallow buried soft rock with smalldistance tunnel[J]. Highway Engineering,2019,44(4):22 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 杜娟, 景恒青, 何仁志. 隧道施工中地表沉降致险因素识别机制研究[J]. 公路工程,2019,44(6):38 − 45. [DU Juan, JING Hengqing, HE Renzhi. Identification mechanism research of ground subsidence risk factors in tunnel construction based on hierarchical clustering[J]. Highway Engineering,2019,44(6):38 − 45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 鲁恒, 李永树, 何敬, 等. 无人机低空遥感影像数据的获取与处理[J]. 测绘工程,2011,20(1):51 − 54. [LU Heng, LI Yongshu, HE Jing, et al. Capture and processing of low altitude remote sensing images by UAV[J]. Engineering of Surveying and Mapping,2011,20(1):51 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7949.2011.01.014
[24] 段平, 李佳, 李海昆, 等. 无人机影像点云与地面激光点云配准的三维建模方法[J]. 测绘工程,2020,29(4):44 − 47. [DUAN Ping, LI Jia, LI Haikun, et al. 3D modeling method of UAV image point cloud and ground laser point cloud registration[J]. Engineering of Surveying and Mapping,2020,29(4):44 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 赵魁. 基于ArcGIS平台的广东云浮云安区地质灾害危害程度分区评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(3):89 − 95. [ZHAO Kui. The assessment on hazard degree division of geology disaster in Yun'an District based on ArcGIS[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(3):89 − 95. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: